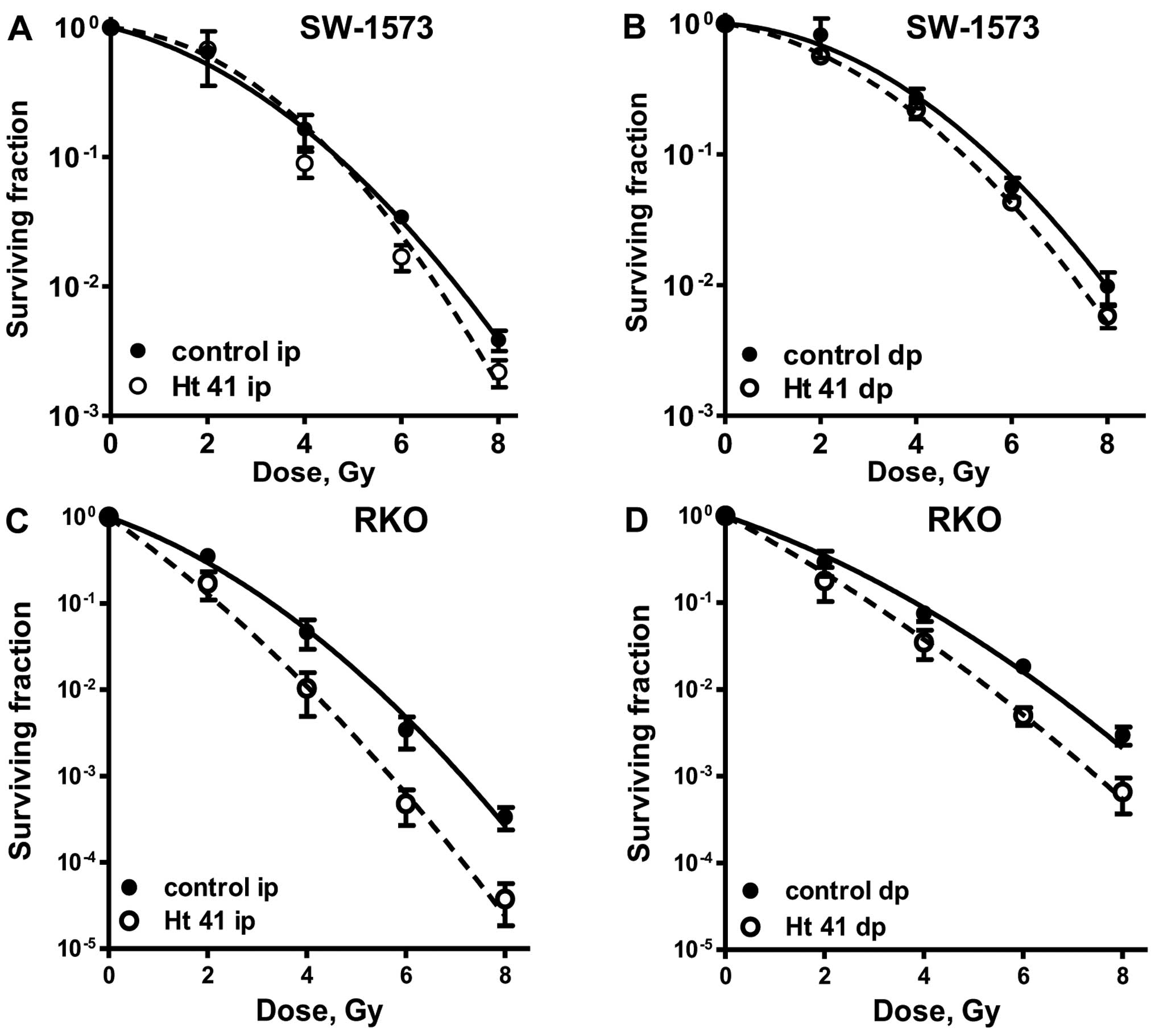
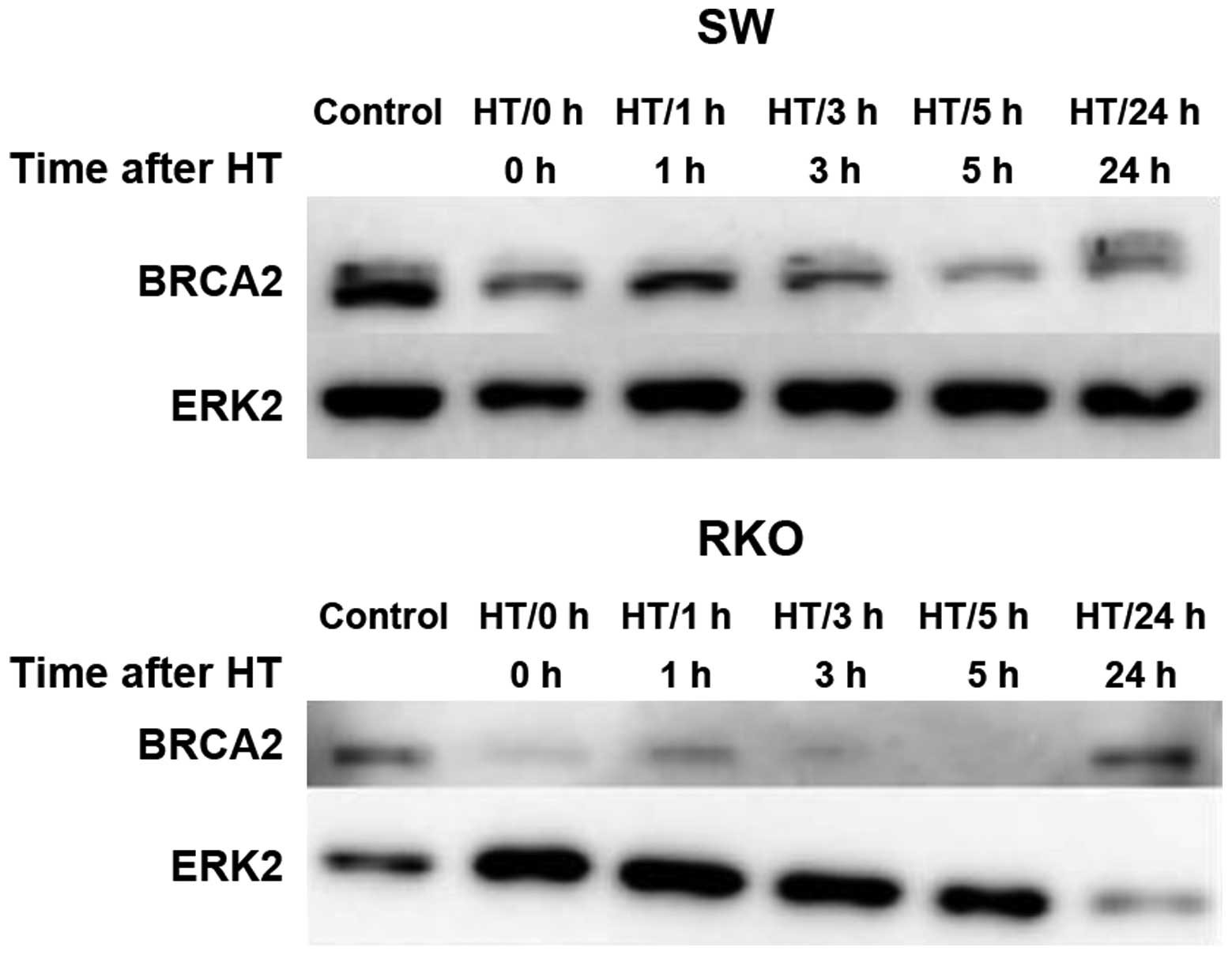
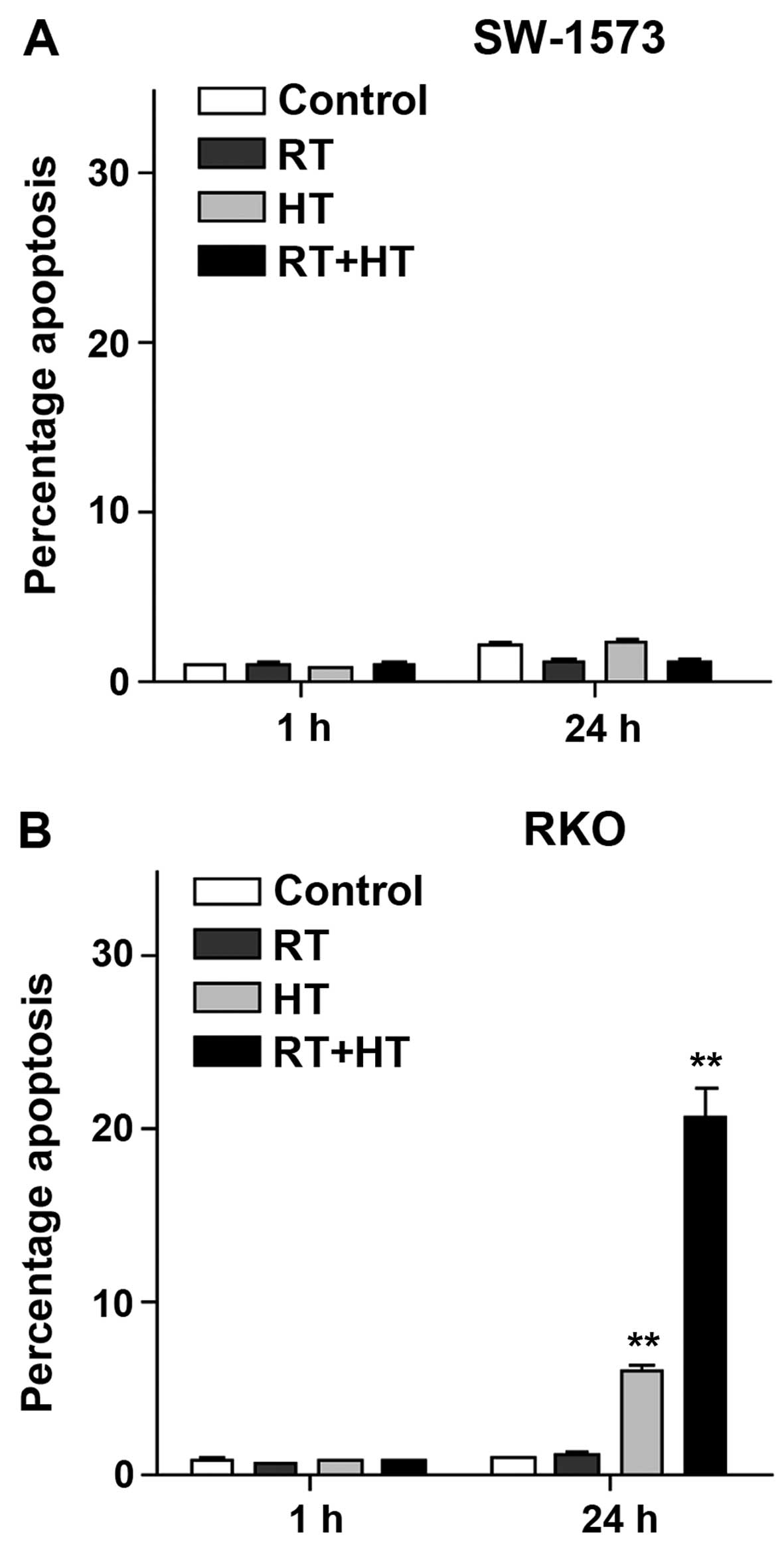
|
1
|
Oei AL, Vriend LEM, Crezee J, Franken NA
and Prawczyk PM: Effects of hyperthermia on DNA repair pathways:
one treatment to inhibit them all. Rad Onc. 10:652015.
|
|
2
|
Baeyens A, Thierens H, Claes K, Poppe B,
de Ridder L and Vral A: Chromosomal radiosensitivity in BRCA1 and
BRCA2 mutation carriers. Int J Radiat Biol. 80:745–756. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Krawczyk PM, Eppink B, Essers J, Stap J,
Rodermond H, Odijk H, Zelensky A, van Bree C, Stalpers LJ, Buist
MR, et al: Mild hyperthermia inhibits homologous recombination,
induces BRCA2 degradation, and sensitizes cancer cells to poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:9851–9856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Allen C, Halbrook J and Nickoloff JA:
Interactive competition between homologous recombination and
non-homologous end joining. Mol Cancer Res. 1:913–920.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kass EM and Jasin M: Collaboration and
competition between DNA double-strand break repair pathways. FEBS
Lett. 584:3703–3708. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Speit G and Schütz P: Hyperthermia-induced
genotoxic effects in human A549 cells. Mutat Res. 747–748:1–5.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bergs JW, Krawczyk PM, Borovski T, ten
Cate R, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Medema JP, Haveman J, Essers J, van
Bree C, et al: Inhibition of homologous recombination by
hyperthermia shunts early double strand break repair to
non-homologous end-joining. DNA Repair (Amst). 12:38–45. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tomita M: Involvement of DNA-PK and ATM in
radiation- and heat-induced DNA damage recognition and apoptotic
cell death. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 51:493–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kampinga HH, Dynlacht JR and Dikomey E:
Mechanism of radiosensitization by hyperthermia (> or = 43
degrees C) as derived from studies with DNA repair defective mutant
cell lines. Int J Hyperthermia. 20:131–139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Awady RA, Dikomey E and Dahm-Daphi J:
Heat effects on DNA repair after ionising radiation: Hyperthermia
commonly increases the number of non-repaired double-strand breaks
and structural rearrangements. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:1960–1966.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dahm-Daphi J, Brammer I and Dikomey E:
Heat effects on the repair of DNA double-strand breaks in CHO
cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 72:171–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bergs JW, ten Cate R, Haveman J, Medema
JP, Franken NA and van Bree C: Chromosome fragments have the
potential to predict hyperthermia-induced radio-sensitization in
two different human tumor cell lines. J Radiat Res (Tokyo).
49:465–472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dewey WC, Sapareto SA and Betten DA:
Hyperthermic radiosensitization of synchronous Chinese hamster
cells: Relationship between lethality and chromosomal aberrations.
Radiat Res. 76:48–59. 1978. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gotoh E, Asakawa I and Kosaka H:
Inhibition of protein serine/threonine phosphatases directly
induces premature chromosome condensation in mammalian somatic
cells. Biomed Res. 16:63–68. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Barendsen GW: Dose fractionation, dose
rate and iso-effect relationships for normal tissue responses. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 8:1981–1997. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barendsen GW, Van Bree C and Franken NA:
Importance of cell proliferative state and potentially lethal
damage repair on radiation effectiveness: Implications for combined
tumor treatments (Review). Int J Oncol. 19:247–256. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barendsen GW: The relationships between
RBE and LET for different types of lethal damage in mammalian
cells: Biophysical and molecular mechanisms. Radiat Res.
139:257–270. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franken NA, Van Bree C, Veltmaat MA,
Rodermond HM, Haveman J and Barendsen GW: Radiosensitization by
bromode-oxyuridine and hyperthermia: Analysis of linear and
quadratic parameters of radiation survival curves of two human
tumor cell lines. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 42:179–190. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Franken N, Vanbree C, Streefkerk J, Kuper
I, Rodermond H, Kipp J, Haveman J and Barendsen G:
Radiosensitization by iodo-deoxyuridine in cultured SW-1573 human
lung tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 4:1073–1076. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Franken NA, van Bree C, Veltmaat MA,
Ludwików G, Kipp JB and Barendsen GW: Increased chromosome exchange
frequencies in iodo-deoxyuridine-sensitized human SW-1573 cells
after γ-irradiation. Oncol Rep. 6:59–63. 1999.
|
|
21
|
Bergs JW, Franken NAP, ten Cate R, van
Bree C and Haveman J: Effects of cisplatin and gamma-irradiation on
cell survival, the induction of chromosomal aberrations and
apoptosis in SW-1573 cells. Mutat Res. 594:148–154. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Franken NA, van Bree C, ten Cate R, van
Oven CH and Haveman J: Importance of TP53 and RB in the repair of
potentially lethal damage and induction of color junctions after
exposure to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 158:707–714. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Castro Kreder N, Van Bree C, Franken NAP
and Haveman J: Colour junctions as predictors of radiosensitivity:
X-irradiation combined with gemcitabine in a lung carcinoma cell
line. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 129:597–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Franken NA, Ruurs P, Ludwików G, van Bree
C, Kipp JB, Darroudi F and Barendsen GW: Correlation between cell
reproductive death and chromosome aberrations assessed by FISH for
low and high doses of radiation and sensitization by
iodo-deoxyuridine in human SW-1573 cells. Int J Radiat Biol.
75:293–299. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Franken NA, ten Cate R, Krawczyk PM, Stap
J, Haveman J, Aten J and Barendsen GW: Comparison of RBE values of
high-LET α-particles for the induction of DNA-DSBs, chromosome
aberrations and cell reproductive death. Radiat Oncol. 6:642011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Franken NA, Hovingh S, Ten Cate R,
Krawczyk P, Stap J, Hoebe R, Aten J and Barendsen GW: Relative
biological effectiveness of high linear energy transfer α-particles
for the induction of DNA-double-strand breaks, chromosome
aberrations and reproductive cell death in SW-1573 lung tumour
cells. Oncol Rep. 27:769–774. 2012.
|
|
28
|
van Bree C, Franken NA, Rodermond HM,
Stalpers LJ and Haveman J: Repair of potentially lethal damage does
not depend on functional TP53 in human glioblastoma cells. Radiat
Res. 161:511–516. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Riccardi C and Nicoletti I: Analysis of
apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat
Protoc. 1:1458–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bergs JW, Franken NA, Haveman J, Geijsen
ED, Crezee J and van Bree C: Hyperthermia, cisplatin and radiation
trimodality treatment: A promising cancer treatment? A review from
preclinical studies to clinical application. Int J Hyperthermia.
23:329–341. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Franken NA and Barendsen GW: Enhancement
of radiation effectiveness by hyperthermia and incorporation of
halogenated pyrimidines at low radiation doses as compared with
high doses: Implications for mechanisms. Int J Radiat Biol.
90:313–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Franken NA, Oei AL, Kok HP, Rodermond HM,
Sminia P, Crezee J, Stalpers LJ and Barendsen GW: Cell survival and
radio-sensitisation: Modulation of the linear and quadratic
parameters of the LQ model (Review). Int J Oncol. 42:1501–1515.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu M, Myerson RJ, Straube WL, Moros EG,
Lagroye I, Wang LL, Lee JT and Roti Roti JL: Radiosensitization of
heat resistant human tumour cells by 1 hour at 41.1 degrees C and
its effect on DNA repair. Int J Hyperthermia. 18:385–403. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu M, Wright WD, Higashikubo R, Wang LL
and Roti Roti JL: Thermal radiosensitization of human tumour cell
lines with different sensitivities to 41.1 degrees C. Int J
Hyperthermia. 15:279–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu M, Myerson RJ, Xia Y, Whitehead T,
Moros EG, Straube WL and Roti JL: The effects of 41 degrees C
hyperthermia on the DNA repair protein, MRE11, correlate with
radiosensitization in four human tumor cell lines. Int J
Hyperthermia. 23:343–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kok HP, Crezee J, Franken NA, Stalpers LJ,
Barendsen GW and Bel A: Quantifying the combined effect of
radiation therapy and hyperthermia in terms of equivalent dose
distributions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88:739–745. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hunt CR, Pandita RK, Laszlo A, Higashikubo
R, Agarwal M, Kitamura T, Gupta A, Rief N, Horikoshi N, Baskaran R,
et al: Hyperthermia activates a subset of ataxia-telangiectasia
mutated effectors independent of DNA strand breaks and heat shock
protein 70 status. Cancer Res. 67:3010–3017. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coco-Martin JM and Begg AC: Detection of
radiation-induced chromosome aberrations using fluorescence in situ
hybridization in drug-induced premature chromosome condensations of
tumour cell lines with different radiosensitivities. Int J Radiat
Biol. 71:265–273. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Franken NA, Van Bree CV, Kipp JB and
Barendsen GW: Modification of potentially lethal damage in
irradiated Chinese hamster V79 cells after incorporation of
halogenated pyrimidines. Int J Radiat Biol. 72:101–109. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tucker JD, Cofield J, Matsumoto K, Ramsey
MJ and Freeman DC: Persistence of chromosome aberrations following
acute radiation: I, PAINT translocations, dicentrics, rings,
fragments, and insertions. Environ Mol Mutagen. 45:229–248. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|