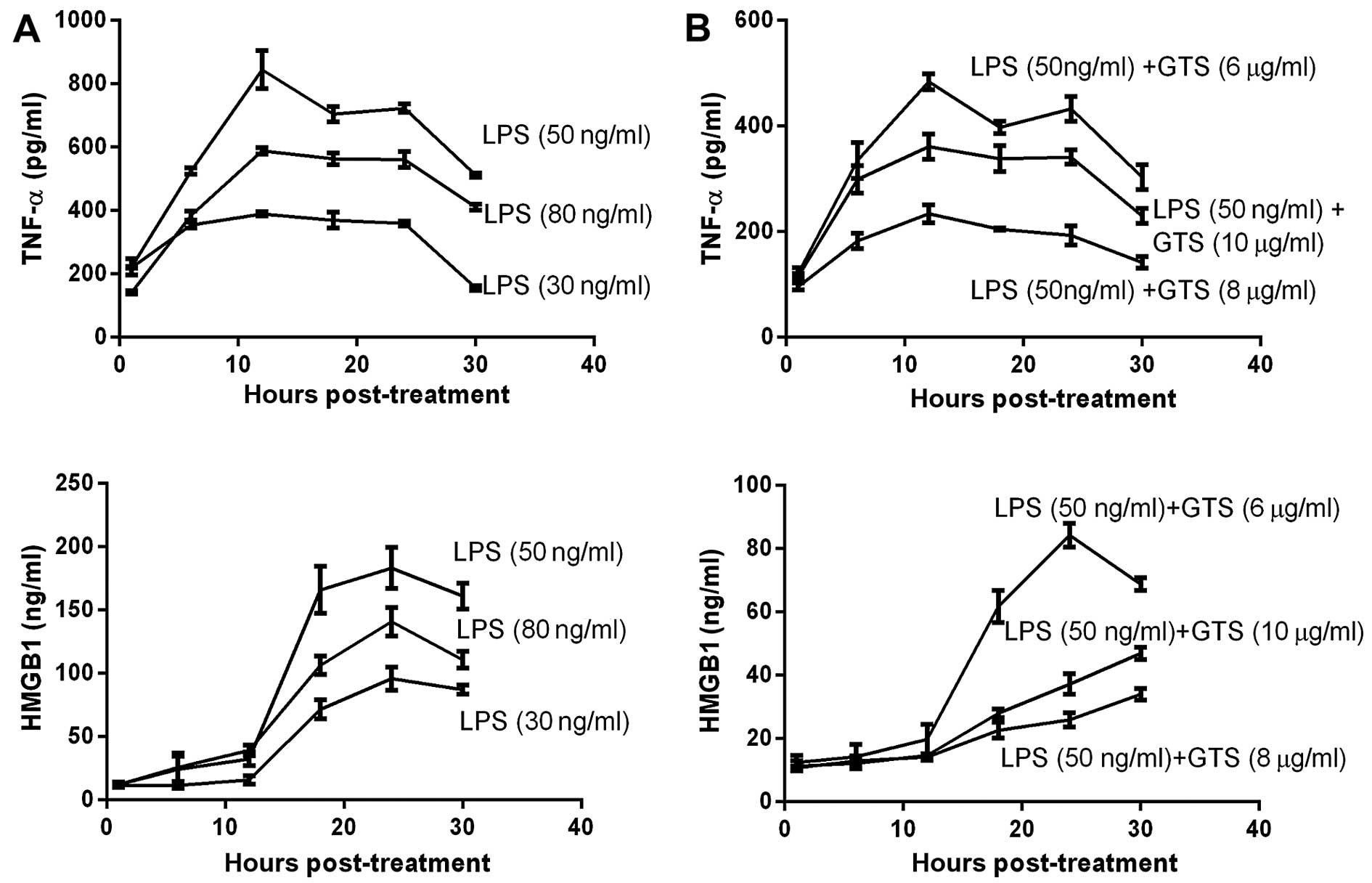
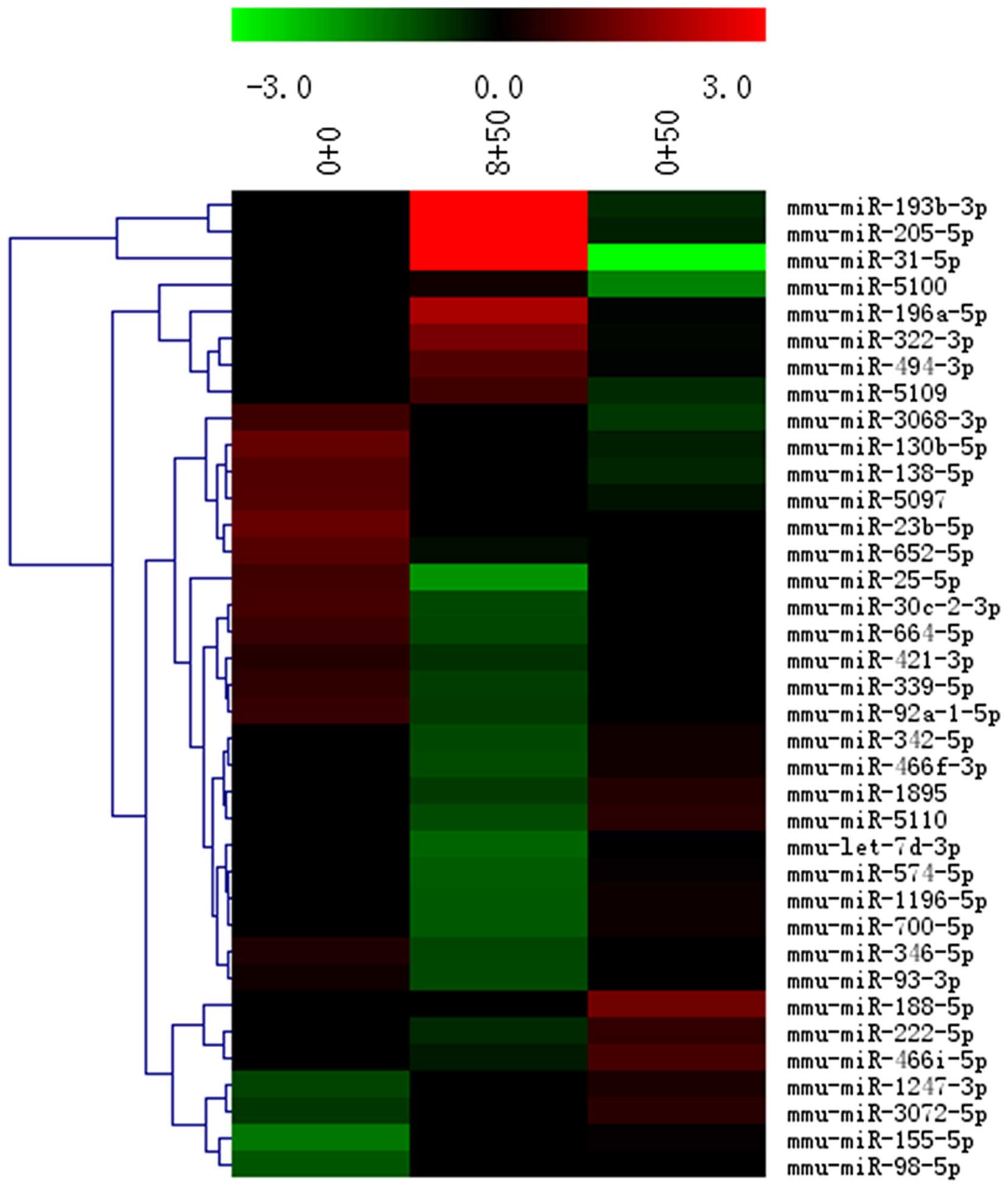
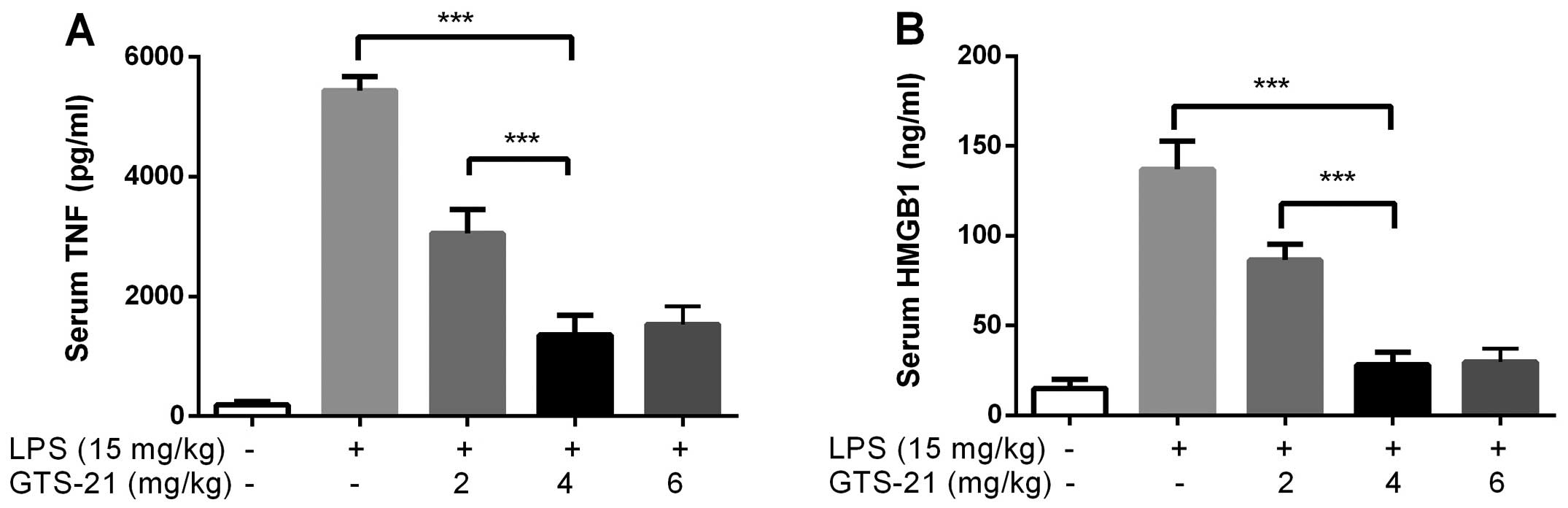
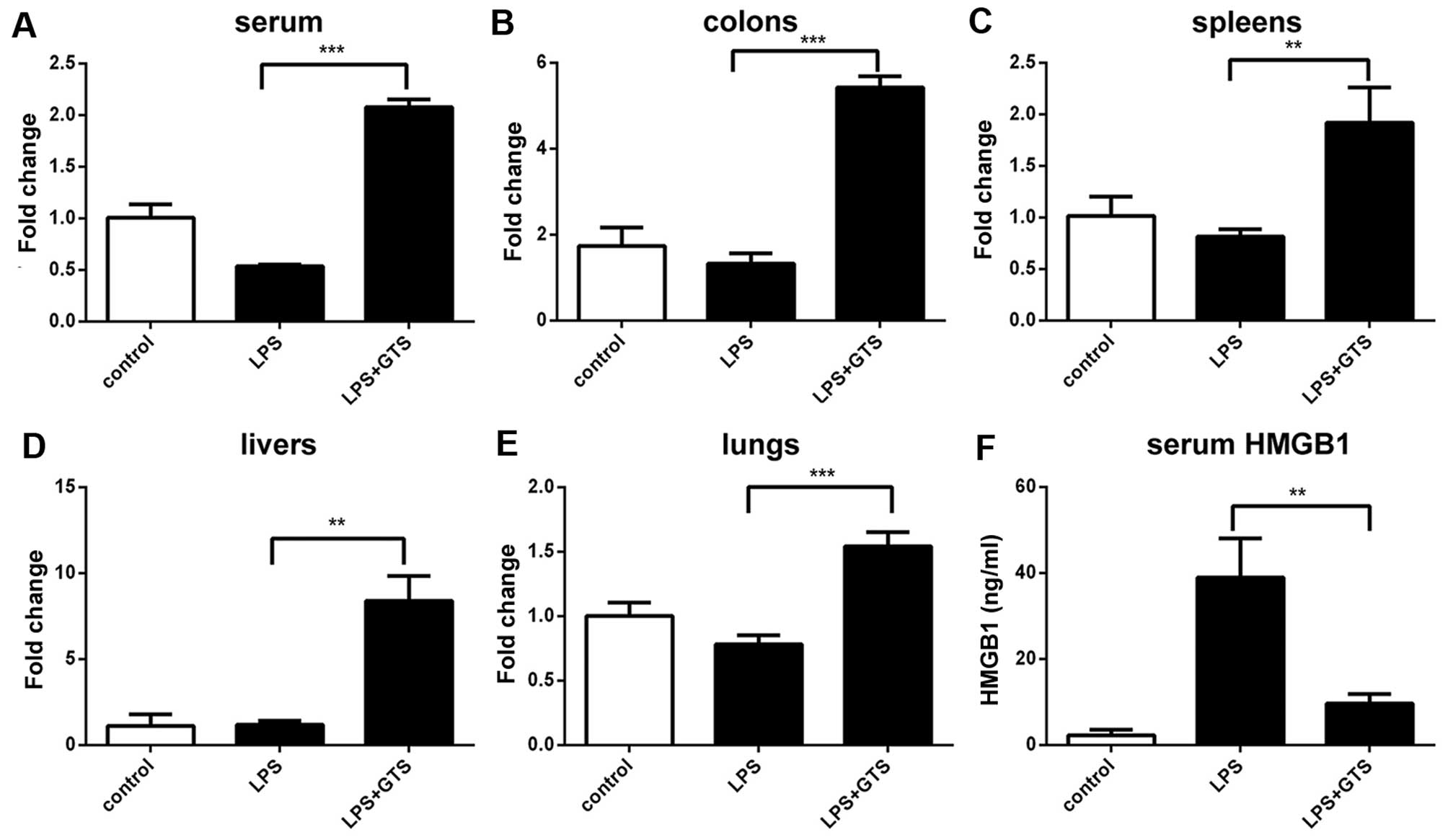
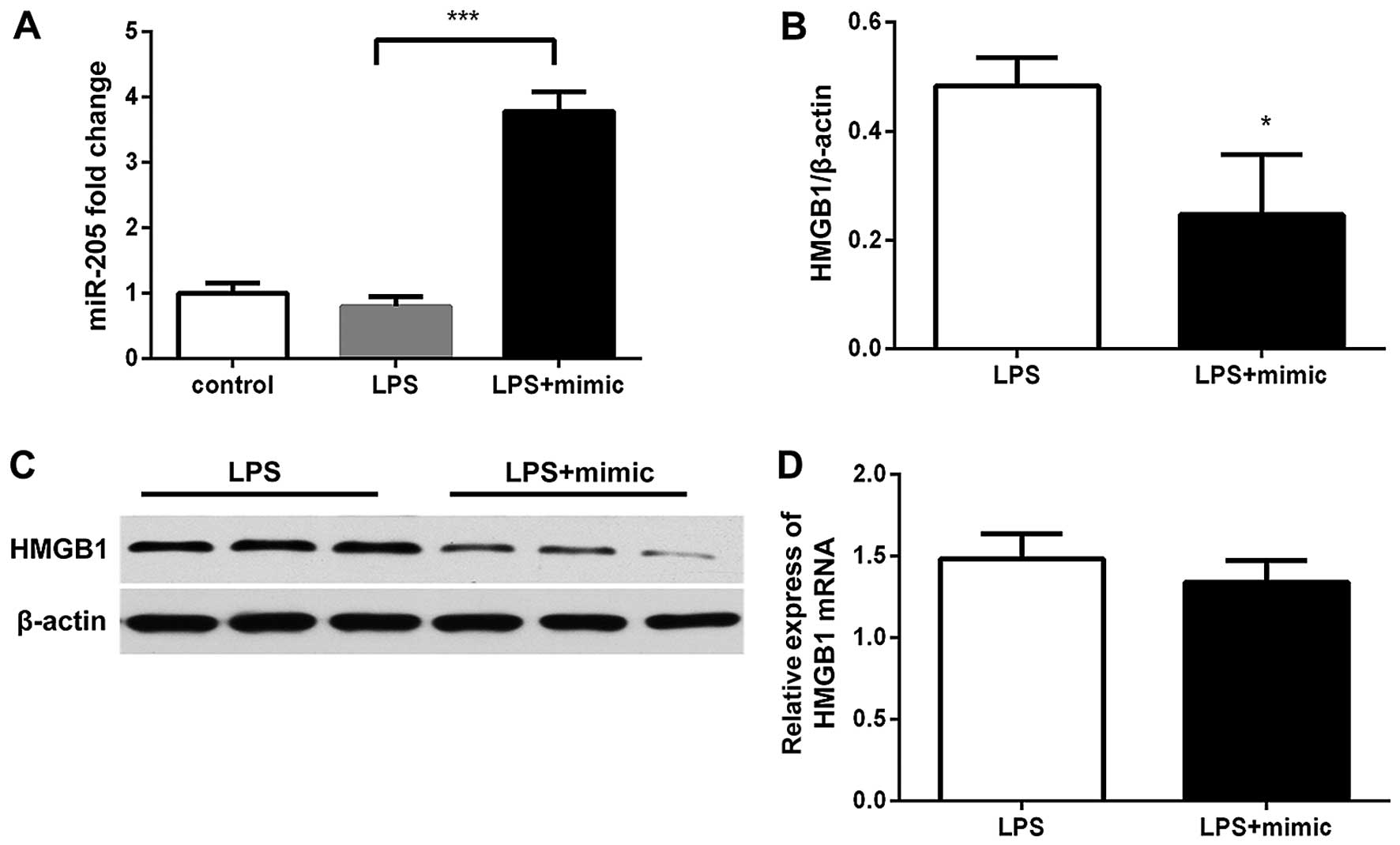
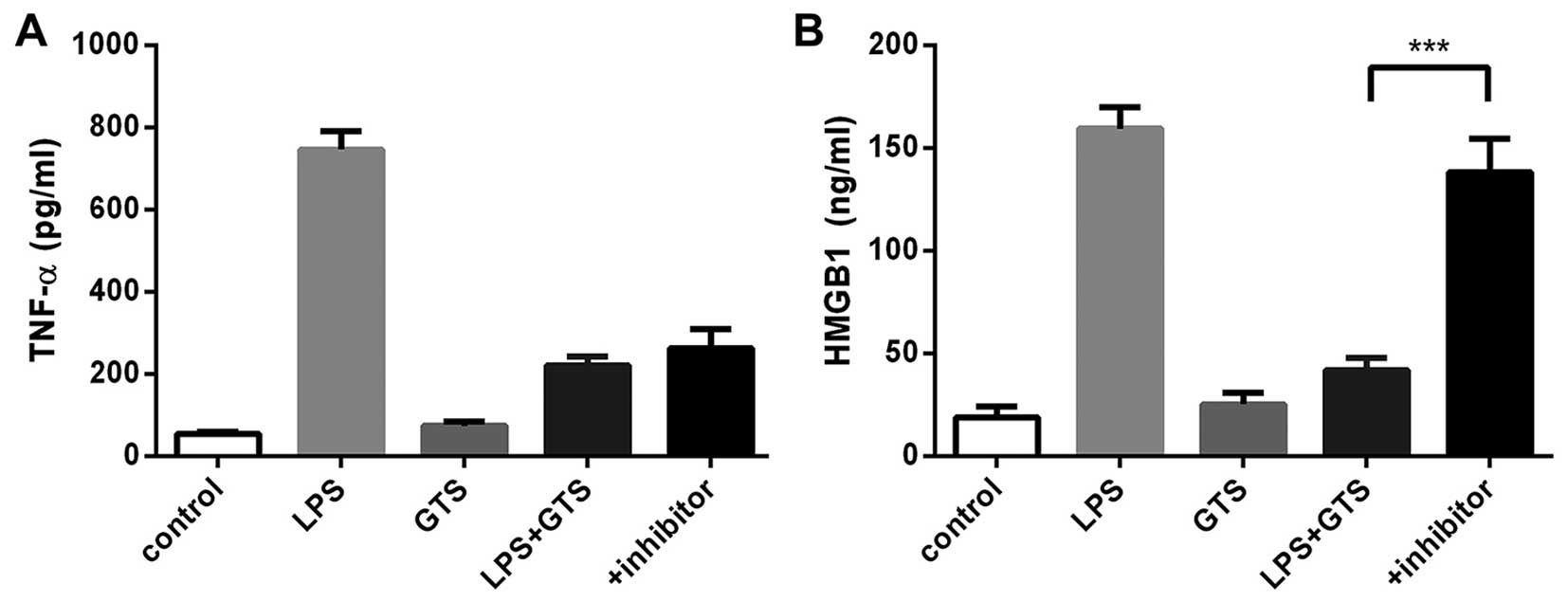
|
1
|
Kang R, Chen R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Wu S, Cao
L, Huang J, Yu Y, Fan XG, Yan Z, et al: HMGB1 in health and
disease. Mol Aspects Med. 40:1–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tracey KJ: The inflammatory reflex.
Nature. 420:853–859. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pavlov VA, Wang H, Czura CJ, Friedman SG
and Tracey KJ: The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing
link in neuroimmunomodulation. Mol Med. 9:125–134. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silman NJ: Rapid diagnosis of sepsis using
biomarker signatures. Crit Care. 17:10202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lyle NH, Pena OM, Boyd JH and Hancock R:
Barriers to the effective treatment of sepsis: antimicrobial
agents, sepsis definitions, and host-directed therapies. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1323:101–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu L, Bao H, Si Y and Wang X: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on early and late cytokines during polymicrobial
sepsis in mice. Inflamm Res. 62:507–514. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Charoensup J, Sermswan RW, Paeyao A,
Promakhejohn S, Punasee S, Chularari C, Krabkraikaew S,
Lertanekawattana S and Wongratanacheewin S: High HMGB1 level is
associated with poor outcome of septicemic melioidosis. Int J
Infect Dis. 28:111–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo ZS, Liu ZQ, Bartlett DL, Tang DL and
Lotze MT: Life after death: targeting high mobility group box 1 in
emergent cancer therapies. Am J Cancer Res. 3:1–20. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang H, Liao H, Ochani M, Justiniani M,
Lin X, Yang L, Al-Abed Y, Wang H, Metz C, Miller EJ, et al:
Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in
experimental sepsis. Nat Med. 10:1216–1221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Connell RM, Rao DS and Baltimore D:
microRNA regulation of inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Immunol.
30:295–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moon HG, Yang J, Zheng Y and Jin Y:
miR-15a/16 regulates macrophage phagocytosis after bacterial
infection. J Immunol. 193:4558–4567. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chatterjee V, Beard RS Jr, Reynolds JJ,
Haines R, Guo M, Rubin M, Guido J, Wu MH and Yuan SY: MicroRNA-147b
regulates vascular endothelial barrier function by targeting ADAM15
expression. PLoS One. 9:e1102862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang HJ, Deng J, Wang JY, Zhang PJ, Xin Z,
Xiao K, Feng D, Jia YH, Liu YN and Xie LX: Serum miR-122 levels are
related to coagulation disorders in sepsis patients. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 52:927–933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tacke F, Roderburg C, Benz F, Cardenas DV,
Luedde M, Hippe HJ, Frey N, Vucur M, Gautheron J, Koch A, et al:
Levels of circulating miR-133a are elevated in sepsis and predict
mortality in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 42:1096–1104.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pavlov VA and Tracey KJ: Controlling
inflammation: the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Biochem
Soc Trans. 34:1037–1040. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic
M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, et al: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of
inflammation. Nature. 421:384–388. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Li Q, Gui H, Xu DP, Yang YL, Su DF
and Liu X: MicroRNA-124 mediates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory
action through inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory
cytokines. Cell Res. 23:1270–1283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Musumeci D, Roviello GN and Montesarchio
D: An overview on HMGB1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents
in HMGB1-related pathologies. Pharmacol Ther. 141:347–357. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jia SZ, Yang Y, Lang J, Sun P and Leng J:
Plasma miR-17-5p, miR-20a and miR-22 are down-regulated in women
with endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 28:322–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Cheng Z, Li-Sha G, Jing-Lin Z, Wen-Wu Z,
Xue-Si C, Xing-Xing C and Yue-Chun L: Protective role of the
cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in a mouse model of viral
myocarditis. PLoS One. 9:e1127192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Koopman FA, Schuurman PR, Vervoordeldonk
MJ and Tak PP: Vagus nerve stimulation: a new bioelectronics
approach to treat rheumatoid arthritis? Best Pract Res Clin
Rheumatol. 28:625–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sitapara RA, Antoine DJ, Sharma L, Patel
VS, Ashby CR Jr, Gorasiya S, Yang H, Zur M and Mantell LL: The α7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves bacterial
clearance in mice by restoring hyperoxia-compromised macrophage
function. Mol Med. 20:238–247. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cai B, Chen F, Ji Y, Kiss L, de Jonge WJ,
Conejero-Goldberg C, Szabo C, Deitch EA and Ulloa L: Alpha7
cholinergic-agonist prevents systemic inflammation and improves
survival during resuscitation. J Cell Mol Med. 13(9B): 3774–3785.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kox M, Pompe JC, Peters E, Vaneker M, van
der Laak JW, van der Hoeven JG, Scheffer GJ, Hoedemaekers CW and
Pickkers P: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21
attenuates ventilator-induced tumour necrosis factor-α production
and lung injury. Br J Anaesth. 107:559–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Yang LH,
Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani K, Lin X, Levi J, Parrish WR,
Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, et al: Selective alpha7-nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine
endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 35:1139–1144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang P, Wang L, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Yuan
Y, Debeb BG, Chen D, Sun Y, You MJ, Liu Y, Dean DC, et al: miR-205
acts as a tumour radiosensitizer by targeting ZEB1 and Ubc13. Nat
Commun. 5:56712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin D, Halilovic A, Yue P, Bellner L, Wang
K, Wang L and Zhang C: Inhibition of miR-205 impairs the
wound-healing process in human corneal epithelial cells by
targeting KIR4.1 (KCNJ10). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:6167–6178.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Orang AV, Safaralizadeh R, Hosseinpour
Feizi MA and Somi MH: Diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-205 in
colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4033–4037. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qiao W, Chen L and Zhang M: MicroRNA-205
regulates the calcification and osteoblastic differentiation of
vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1945–1953.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|