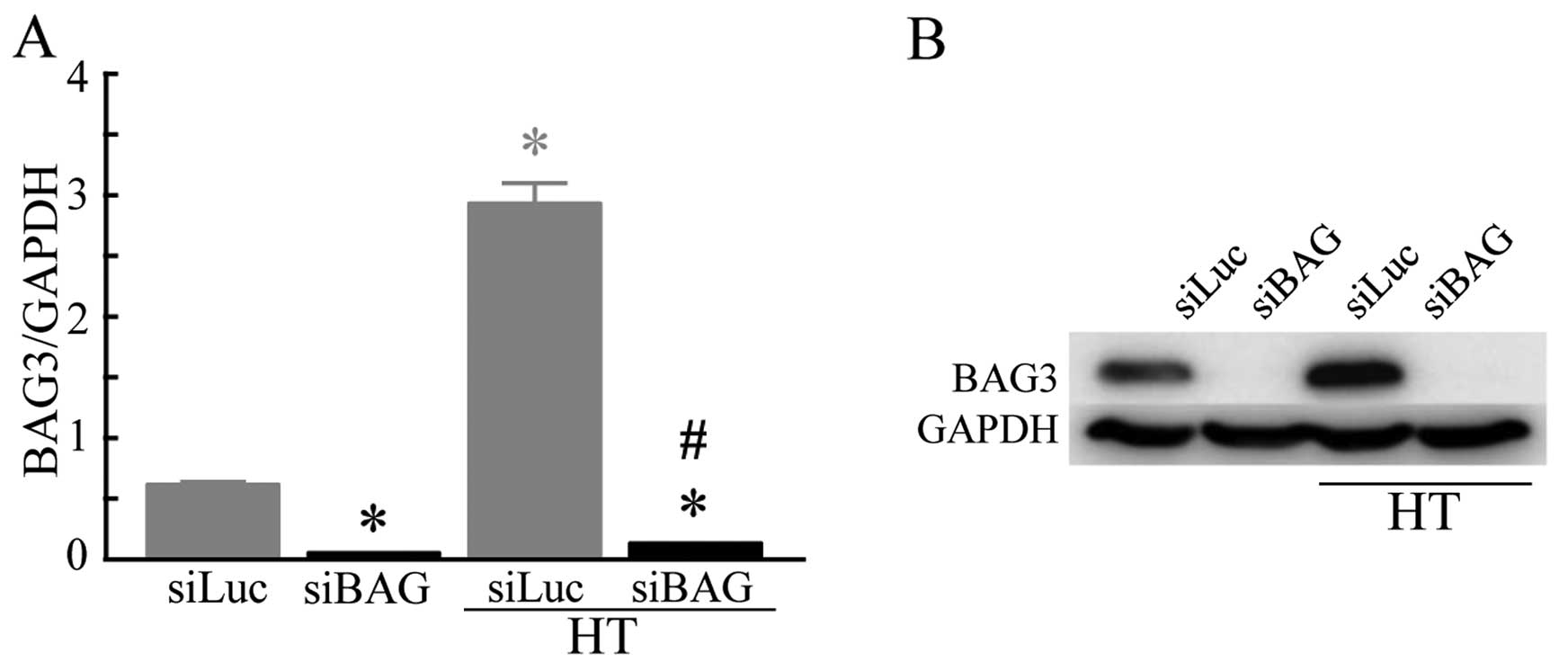
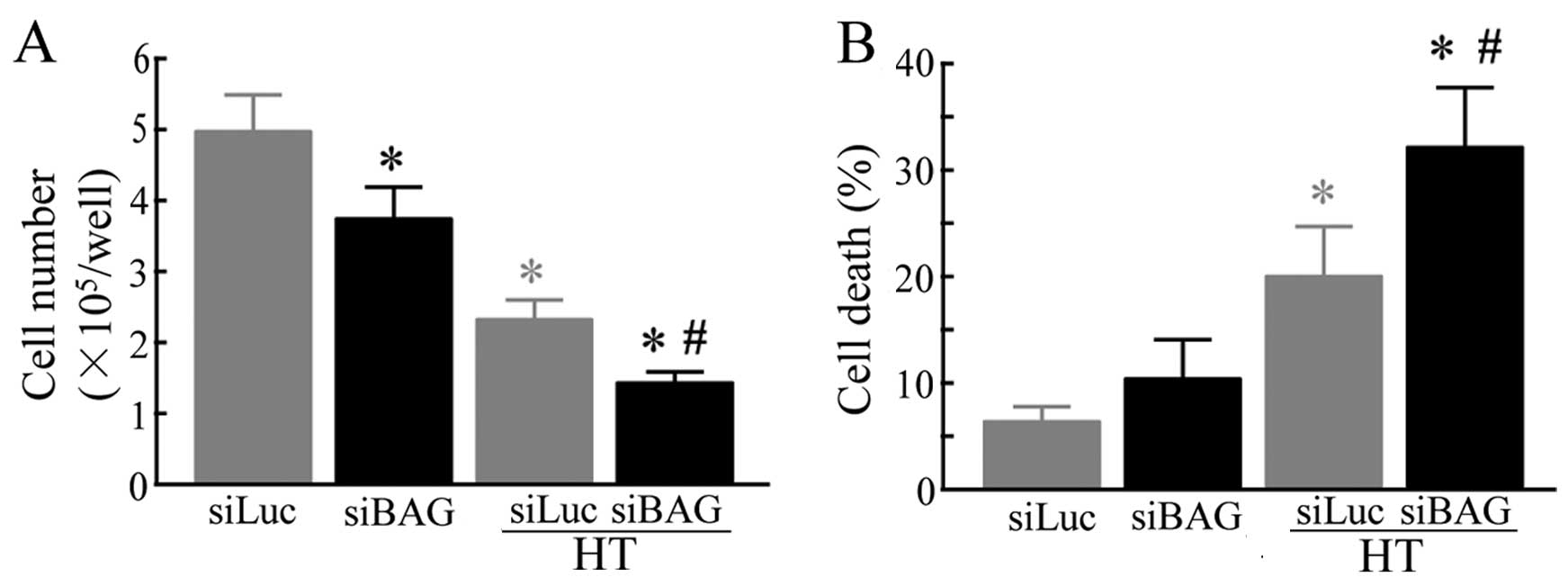
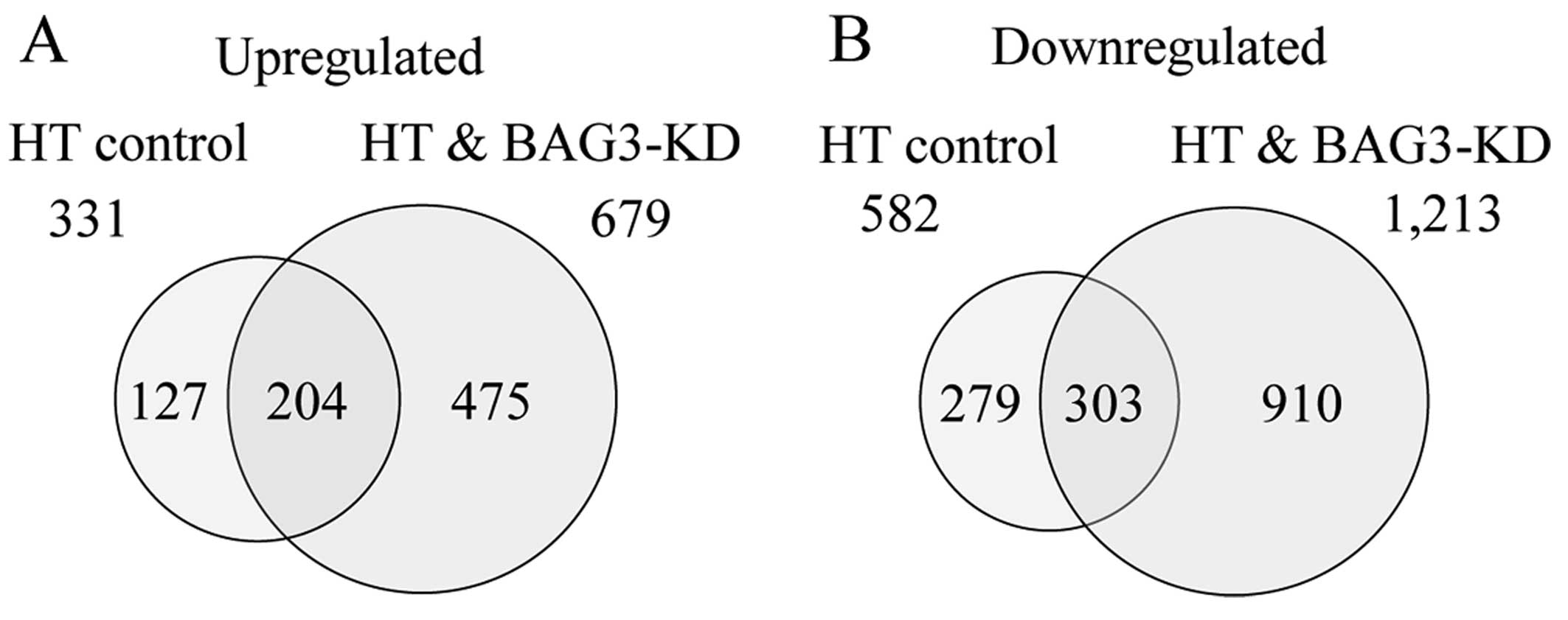
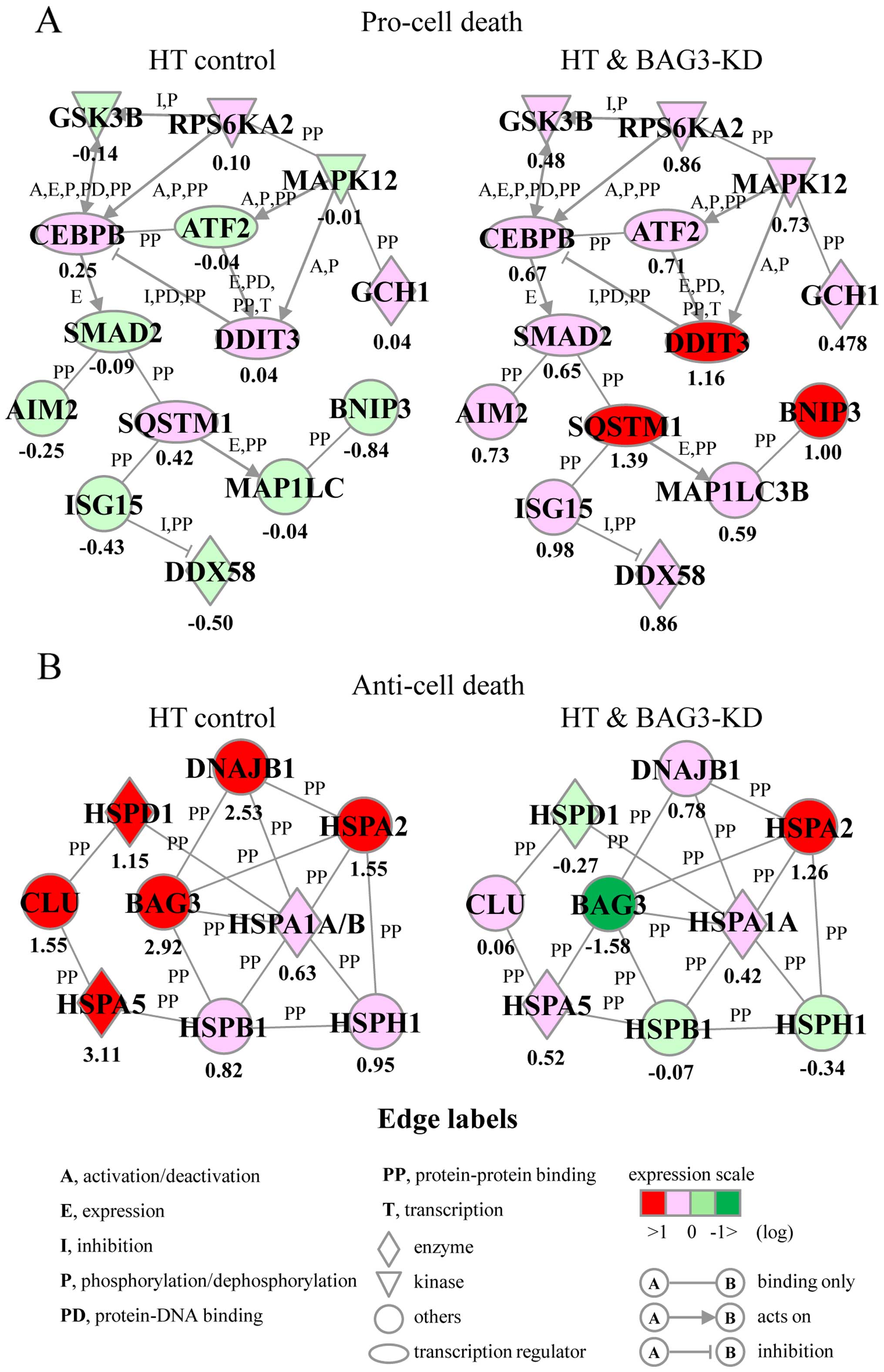
|
1
|
van der Zee J, González González D, van
Rhoon GC, van Dijk JD, van Putten WL and Hart AA: Comparison of
radiotherapy alone with radiotherapy plus hyperthermia in locally
advanced pelvic tumours: a prospective, randomised, multicentre
trial. Dutch Deep Hyperthermia Group. Lancet. 355:1119–1125. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harima Y, Nagata K, Harima K, Ostapenko
VV, Tanaka Y and Sawada S: A randomized clinical trial of radiation
therapy versus thermoradiotherapy in stage IIIB cervical carcinoma.
Int J Hyperthermia. 17:97–105. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Westermann A, Mella O, Van Der Zee J,
Jones EL, Van Der Steen-Banasik E, Koper P, Uitterhoeve AL, De Wit
R, Van Der Velden J, Burger C, et al: Long-term survival data of
triple modality treatment of stage IIB-III-IVA cervical cancer with
the combination of radiotherapy, chemotherapy and hyperthermia - an
update. Int J Hyperthermia. 28:549–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cihoric N, Tsikkinis A, van Rhoon G,
Crezee H, Aebersold DM, Bodis S, Beck M, Nadobny J, Budach V, Wust
P, et al: Hyperthermia-related clinical trials on cancer treatment
within the http://ClinicalTrials.govurisimpleClinicalTrials.gov
registry. Int J Hyperthermia. 31:609–614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li GC, Mivechi NF and Weitzel G: Heat
shock proteins, thermotolerance, and their relevance to clinical
hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia. 11:459–488. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nollen EA, Brunsting JF, Roelofsen H,
Weber LA and Kampinga HH: In vivo chaperone activity of heat shock
protein 70 and thermotolerance. Mol Cell Biol. 19:2069–2079. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beere HM: 'The stress of dying': the role
of heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
117:2641–2651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lanneau D, Wettstein G, Bonniaud P and
Garrido C: Heat shock proteins: cell protection through protein
triage. Scientific World Journal. 10:1543–1552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ohtsuka K and Hata M: Molecular chaperone
function of mammalian Hsp70 and Hsp40 - a review. Int J
Hyperthermia. 16:231–245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vos MJ, Hageman J, Carra S and Kampinga
HH: Structural and functional diversities between members of the
human HSPB, HSPH, HSPA, and DNAJ chaperone families. Biochemistry.
47:7001–7011. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kabbage M and Dickman MB: The BAG
proteins: a ubiquitous family of chaperone regulators. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 65:1390–1402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taipale M, Tucker G, Peng J, Krykbaeva I,
Lin ZY, Larsen B, Choi H, Berger B, Gingras AC and Lindquist S: A
quantitative chaperone interaction network reveals the architecture
of cellular protein homeostasis pathways. Cell. 158:434–448. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Franceschelli S, Rosati A, Lerose R, De
Nicola S, Turco MC and Pascale M: Bag3 gene expression is regulated
by heat shock factor 1. J Cell Physiol. 215:575–577. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Du ZX, Zhang HY, Meng X, Gao YY, Zou RL,
Liu BQ, Guan Y and Wang HQ: Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces BAG3
expression through activation of heat shock factor 1. J Cell
Physiol. 218:631–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pagliuca MG, Lerose R, Cigliano S and
Leone A: Regulation by heavy metals and temperature of the human
BAG-3 gene, a modulator of Hsp70 activity. FEBS Lett. 541:11–15.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liao Q, Ozawa F, Friess H, Zimmermann A,
Takayama S, Reed JC, Kleeff J and Büchler MW: The anti-apoptotic
protein BAG-3 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and induced by
heat stress in pancreatic cancer cell lines. FEBS Lett.
503:151–157. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yunoki T, Kariya A, Kondo T, Hayashi A and
Tabuchi Y: The combination of silencing BAG3 and inhibition of the
JNK pathway enhances hyperthermia sensitivity in human oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 335:52–57. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yunoki T, Tabuchi Y, Hayashi A and Kondo
T: BAG3 protects against hyperthermic stress by modulating NF-κB
and ERK activities in human retinoblastoma cells. Graefes Arch Clin
Exp Ophthalmol. 253:399–407. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bonelli P, Petrella A, Rosati A, Romano
MF, Lerose R, Pagliuca MG, Amelio T, Festa M, Martire G, Venuta S,
et al: BAG3 protein regulates stress-induced apoptosis in normal
and neoplastic leukocytes. Leukemia. 18:358–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tabuchi Y, Ando H, Takasaki I, Feril LB
Jr, Zhao QL, Ogawa R, Kudo N, Tachibana K and Kondo T:
Identification of genes responsive to low intensity pulsed
ultrasound in a human leukemia cell line Molt-4. Cancer Lett.
246:149–156. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chiappetta G, Ammirante M, Basile A,
Rosati A, Festa M, Monaco M, Vuttariello E, Pasquinelli R, Arra C,
Zerilli M, et al: The antiapoptotic protein BAG3 is expressed in
thyroid carcinomas and modulates apoptosis mediated by tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 92:1159–1163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Festa M, Del Valle L, Khalili K, Franco R,
Scognamiglio G, Graziano V, De Laurenzi V, Turco MC and Rosati A:
BAG3 protein is overexpressed in human glioblastoma and is a
potential target for therapy. Am J Pathol. 178:2504–2512. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rosati A, Graziano V, De Laurenzi V,
Pascale M and Turco MC: BAG3: a multifaceted protein that regulates
major cell pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nymoen DA, Hetland Falkenthal TE, Holth A,
Ow GS, Ivshina AV, Tropé CG, Kuznetsov VA, Staff AC and Davidson B:
Expression and clinical role of chemoresponse-associated genes in
ovarian serous carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 139:30–39. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu P, Xu B, Li J and Lu H: BAG3 gene
silencing sensitizes leukemic cells to bortezomib-induced
apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 583:401–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kariya A, Furusawa Y, Yunoki T, Kondo T
and Tabuchi Y: A microRNA-27a mimic sensitizes human oral squamous
cell carcinoma HSC-4 cells to hyperthermia through downregulation
of Hsp110 and Hsp90. Int J Mol Med. 34:334–340. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:4350–4354. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tabuchi Y, Takasaki I, Doi T, Ishii Y,
Sakai H and Kondo T: Genetic networks responsive to sodium butyrate
in colonic epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 580:3035–3041. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tabuchi Y, Yunoki T, Hoshi N, Suzuki N and
Kondo T: Genes and gene networks involved in sodium
fluoride-elicited cell death accompanying endoplasmic reticulum
stress in oral epithelial cells. Into J Mol Sci. 15:8959–8978.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Baan B, van Dam H, van der Zon GC, Maassen
JA and Ouwens DM: The role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, p38, and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase in insulin-induced Thr69 and
Thr71 phosphorylation of activating transcription factor 2. Mol
Endocrinol. 20:1786–1795. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan HC, Yang CN, Hung YW, Lee WJ, Tien HR,
Shen CC, Sheehan J, Chou CT and Sheu ML: Reciprocal modulation of
C/EBP-α and C/EBP-β by IL-13 in activated microglia prevents
neuronal death. Eur J Immunol. 43:2854–2865. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang X, Batchvarova
N, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H, Stevens JL and Ron D: CHOP is
implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired
function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 12:982–995. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Newman JR and Keating AE: Comprehensive
identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays.
Science. 300:2097–2101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reinke AW, Baek J, Ashenberg O and Keating
AE: Networks of bZIP protein-protein interactions diversified over
a billion years of evolution. Science. 340:730–734. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP and Harper
JW: Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature.
466:68–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tang QQ, Grønborg M, Huang H, Kim JW, Otto
TC, Pandey A and Lane MD: Sequential phosphorylation of CCAAT
enhancer-binding protein beta by MAPK and glycogen synthase kinase
3beta is required for adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:9766–9771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee S, Shuman JD, Guszczynski T,
Sakchaisri K, Sebastian T, Copeland TD, Miller M, Cohen MS, Taunton
J, Smart RC, et al: RSK-mediated phosphorylation in the C/EBPβ
leucine zipper regulates DNA binding, dimerization, and growth
arrest activity. Mol Cell Biol. 30:2621–2635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tibbles LA and Woodgett JR: The
stress-activated protein kinase pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci.
55:1230–1254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Beamer WG, Shultz KL, Coombs HF III,
DeMambro VE, Reinholdt LG, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Canalis E, Rosen CJ
and Donahue LR: BMD regulation on mouse distal chromosome 1,
candidate genes, and response to ovariectomy or dietary fat. J Bone
Miner Res. 26:88–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang EY, Gang H, Aviv Y, Dhingra R,
Margulets V and Kirshenbaum LA: p53 mediates autophagy and cell
death by a mechanism contingent on Bnip3. Hypertension. 62:70–77.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hiscott J, Lin R, Nakhaei P and Paz S:
MasterCARD: a priceless link to innate immunity. Trends Mol Med.
12:53–56. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pickert G, Lim HY, Weigert A, Häussler A,
Myrczek T, Waldner M, Labocha S, Ferreirós N, Geisslinger G, Lötsch
J, et al: Inhibition of GTP cyclohydrolase attenuates tumor growth
by reducing angiogenesis and M2-like polarization of tumor
associated macrophages. Int J Cancer. 132:591–604. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yángüez E, García-Culebras A, Frau A,
Llompart C, Knobeloch KP, Gutierrez-Erlandsson S, García-Sastre A,
Esteban M, Nieto A and Guerra S: ISG15 regulates peritoneal
macrophages functionality against viral infection. PLoS Pathog.
9:e10036322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu Z,
Freundt E, Baehrecke EH and Lenardo M: Autophagic programmed cell
death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4952–4957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lin Y, Zhang B, Liang H, Lu Y, Ai X, Zhang
B and Chen X: JNK inhibitor SP600125 enhances TGF-β-induced
apoptosis of RBE human cholangiocarcinoma cells in a Smad-dependent
manner. Mol Med Rep. 8:1623–1629. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang S, Yang ZJ, Yu C and Sinicrope FA:
Inhibition of mTOR kinase by AZD8055 can antagonize
chemotherapy-induced cell death through autophagy induction and
down-regulation of p62/sequestosome 1. J Biol Chem.
286:40002–40012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Evert BO, Wüllner U and Klockgether T:
Cell death in polyglutamine diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 301:189–204.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Veereshwarayya V, Kumar P, Rosen KM,
Mestril R and Querfurth HW: Differential effects of mitochondrial
heat shock protein 60 and related molecular chaperones to prevent
intracellular beta-amyloid-induced inhibition of complex IV and
limit apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 281:29468–29478. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dix DJ, Allen JW, Collins BW,
Poorman-Allen P, Mori C, Blizard DR, Brown PR, Goulding EH, Strong
BD and Eddy EM: HSP70-2 is required for desynapsis of synaptonemal
complexes during meiotic prophase in juvenile and adult mouse
spermatocytes. Development. 124:4595–4603. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Fu Y, Chan L and Lee AS:
Novel mechanism of anti-apoptotic function of 78-kDa
glucose-regulated protein (GRP78): endocrine resistance factor in
breast cancer, through release of B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) from
BCL-2-interacting killer (BIK). J Biol Chem. 286:25687–25696. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tchivilev I, Madamanchi NR, Vendrov AE,
Niu XL and Runge MS: Identification of a protective role for
protein phosphatase 1cgamma1 against oxidative stress-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
283:22193–22205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saito Y, Yamagishi N, Ishihara K and
Hatayama T: Identification of alpha-tubulin as an
hsp105alpha-binding protein by the yeast two-hybrid system. Exp
Cell Res. 286:233–240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Viard I, Wehrli P, Jornot L, Bullani R,
Vechietti JL, Schifferli JA, Tschopp J and French LE: Clusterin
gene expression mediates resistance to apoptotic cell death induced
by heat shock and oxidative stress. J Invest Dermatol. 112:290–296.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Flanagan L, Whyte L, Chatterjee N and
Tenniswood M: Effects of clusterin over-expression on metastatic
progression and therapy in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 10:1072010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kong DH, Zhang Q, Meng X, Zong ZH, Li C,
Liu BQ, Guan Y and Wang HQ: BAG3 sensitizes cancer cells exposed to
DNA damaging agents via direct interaction with GRP78. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1833:3245–3253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|