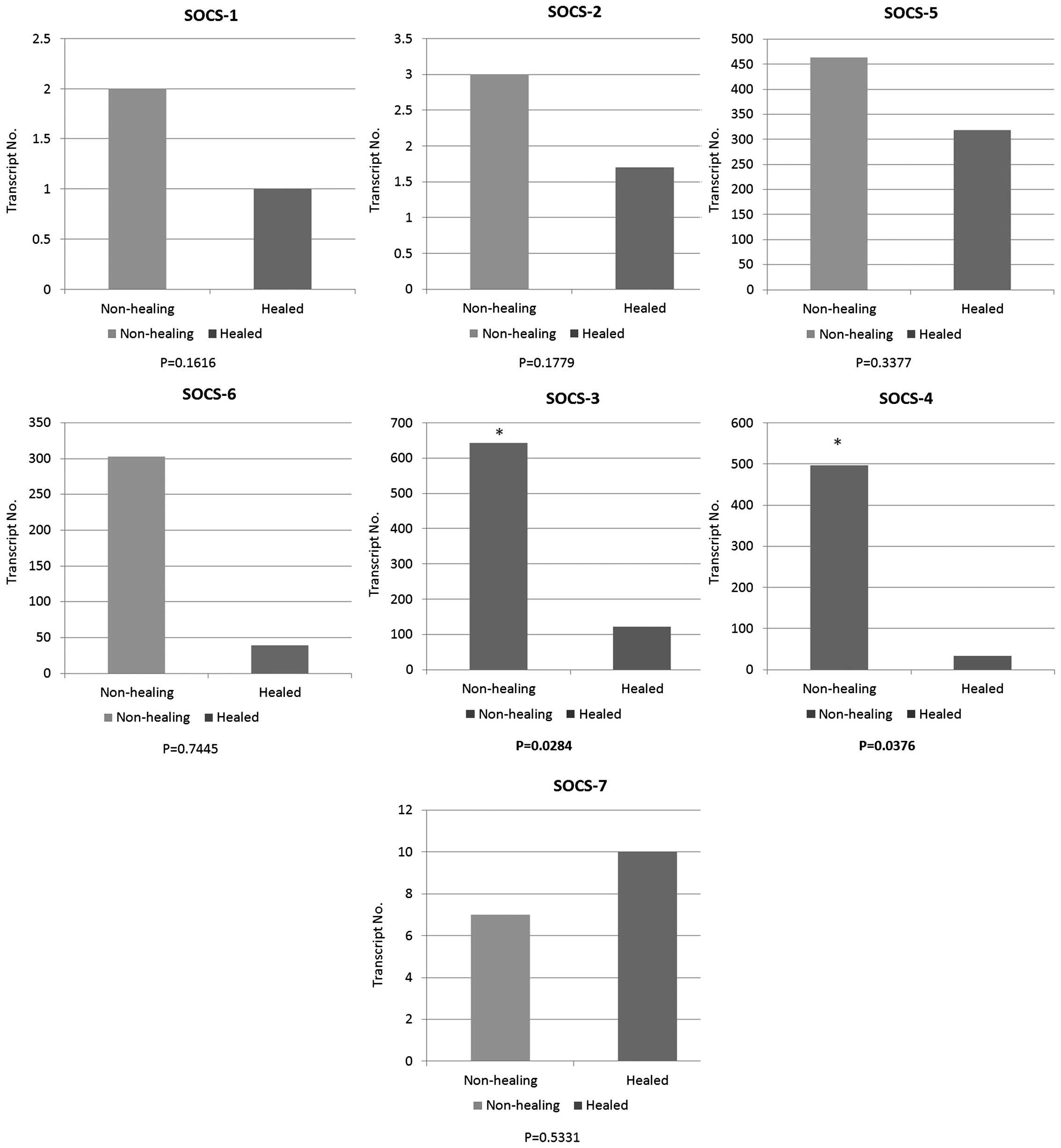
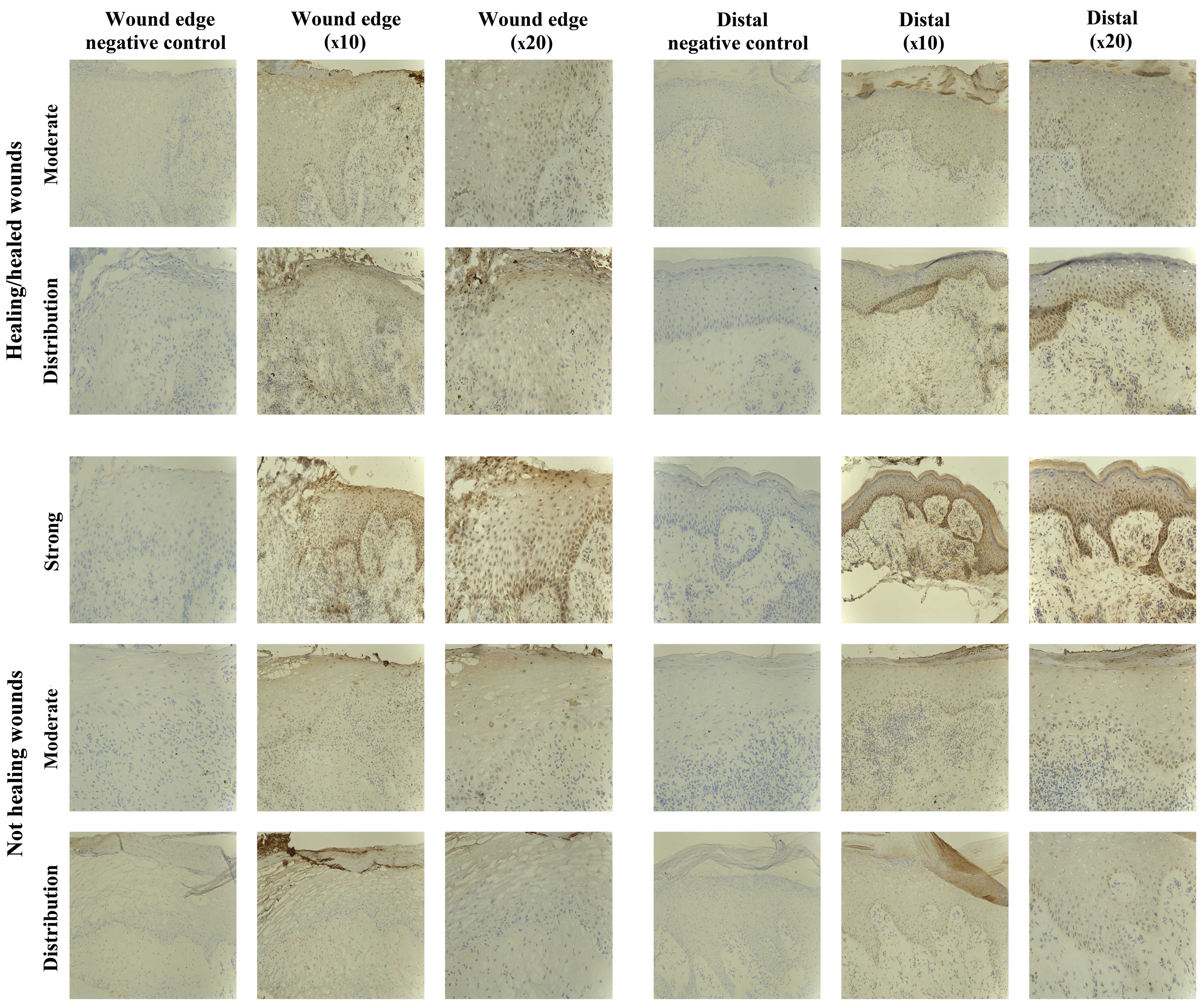
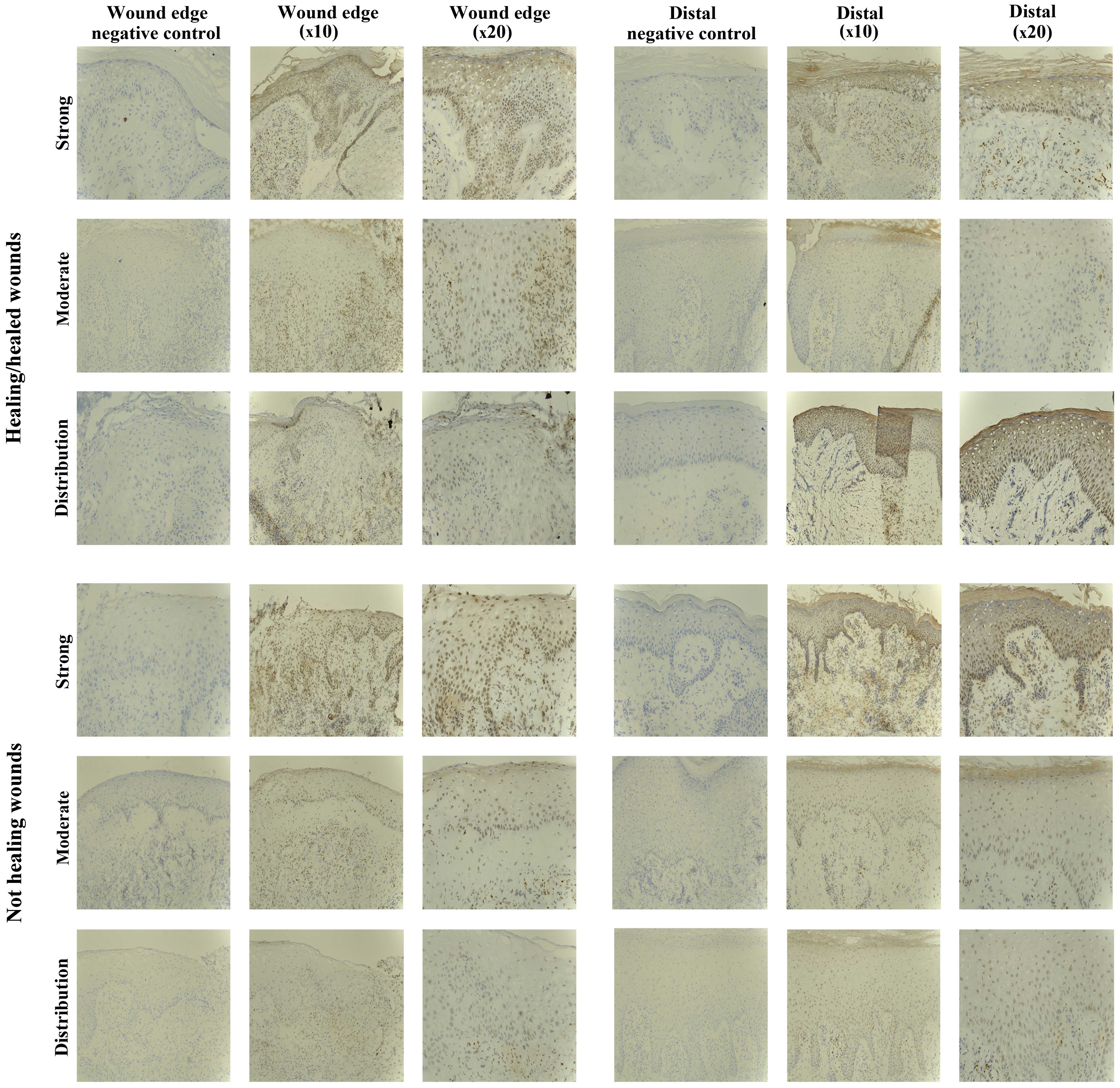
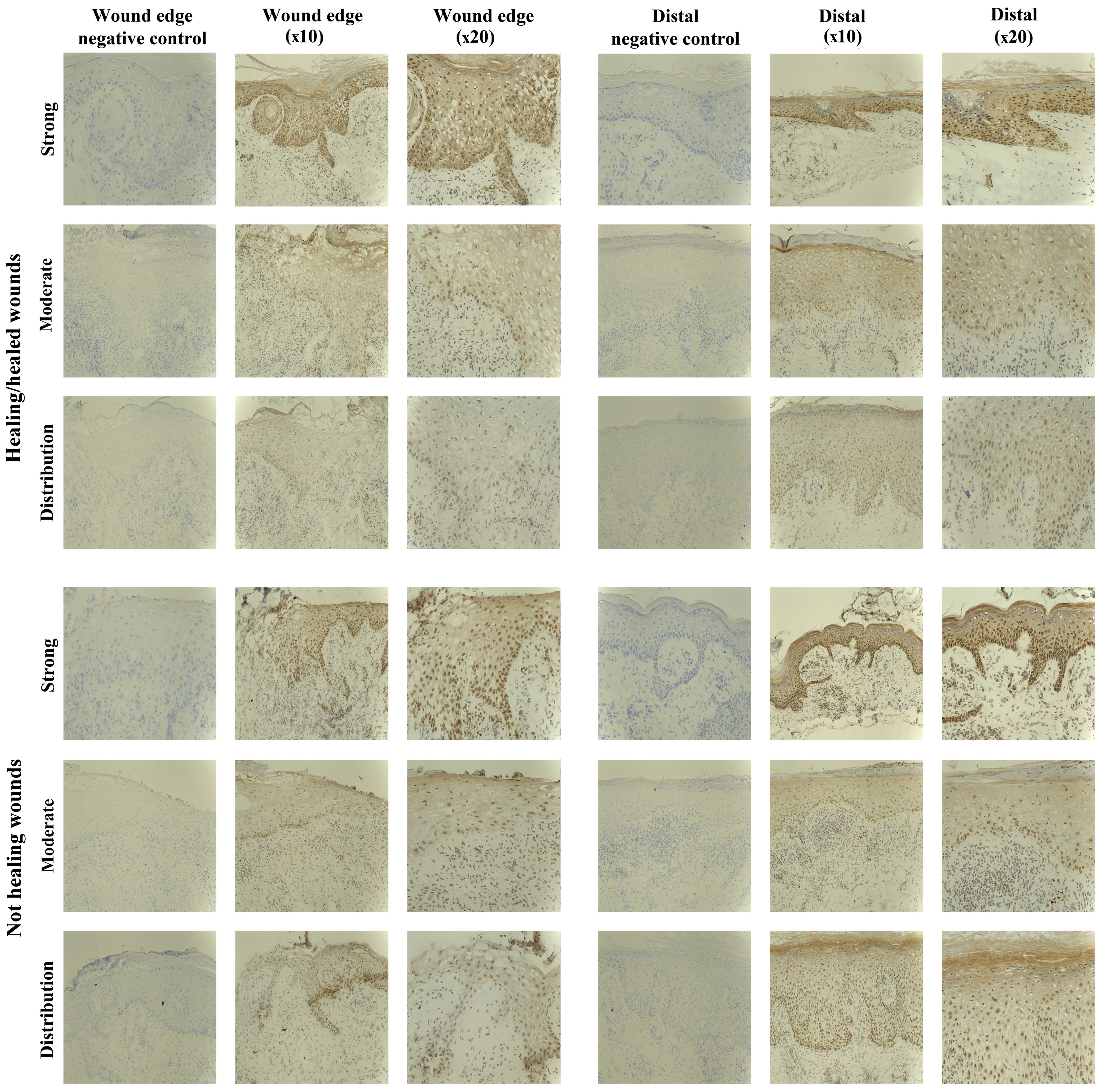
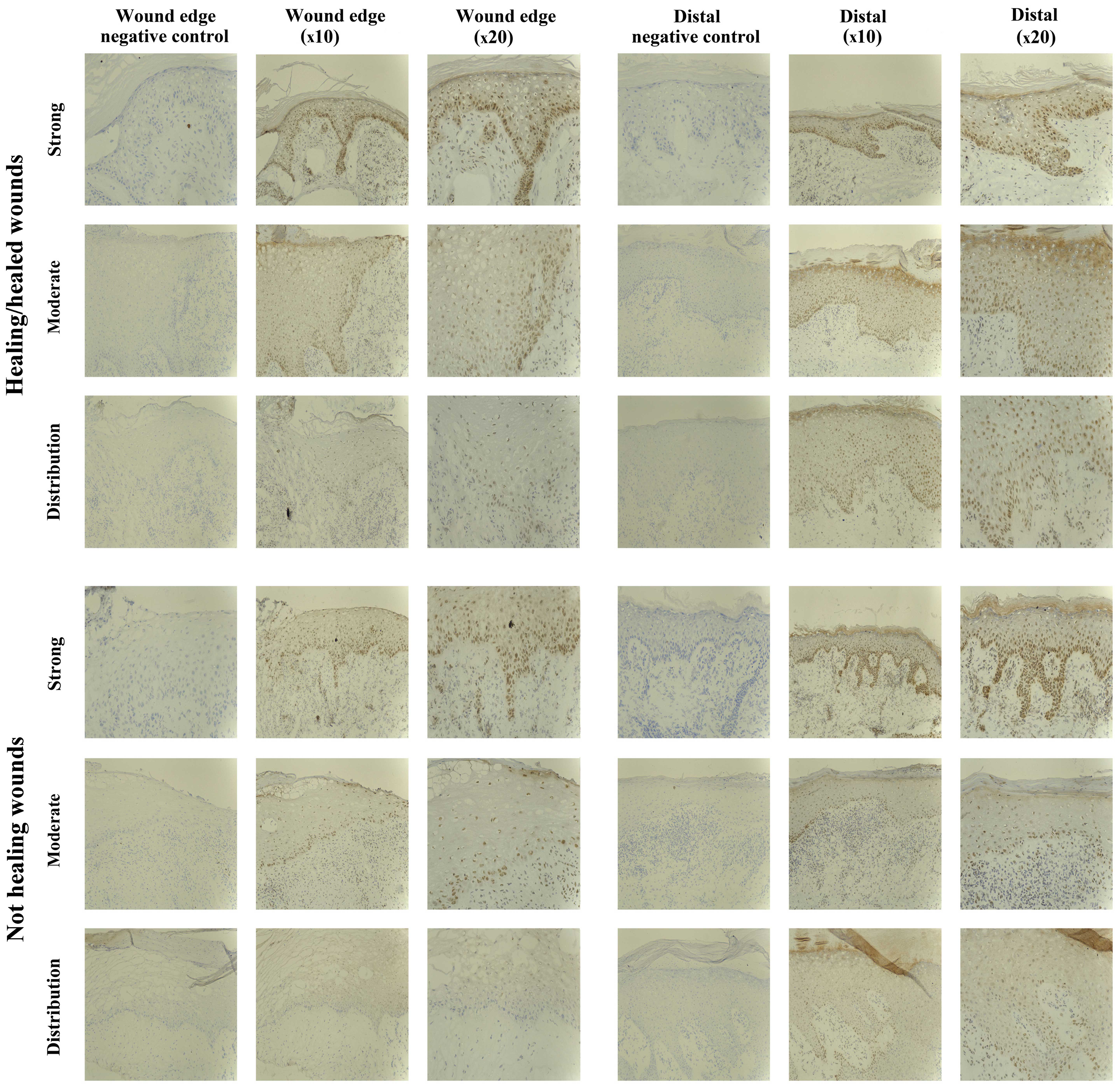
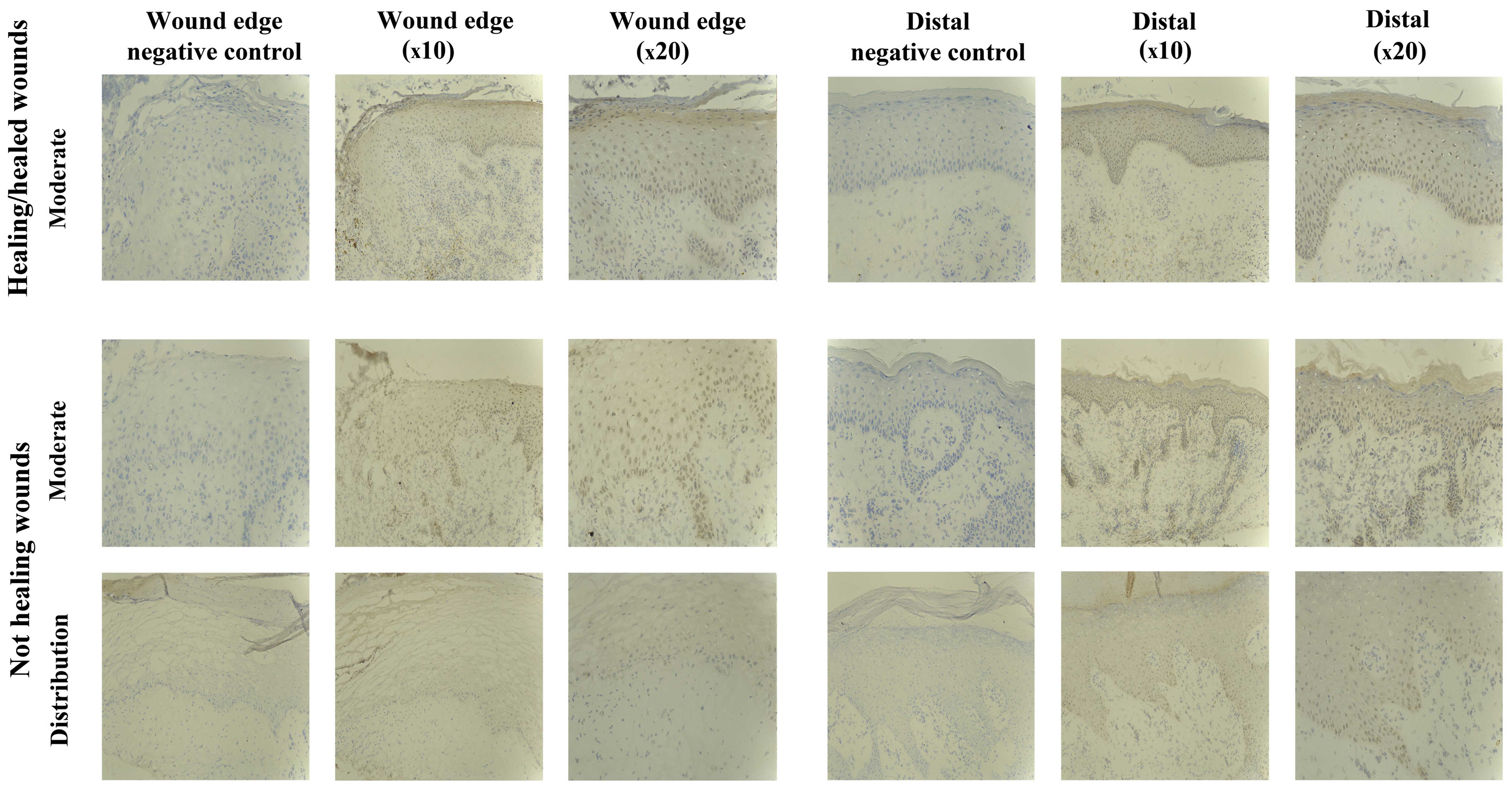
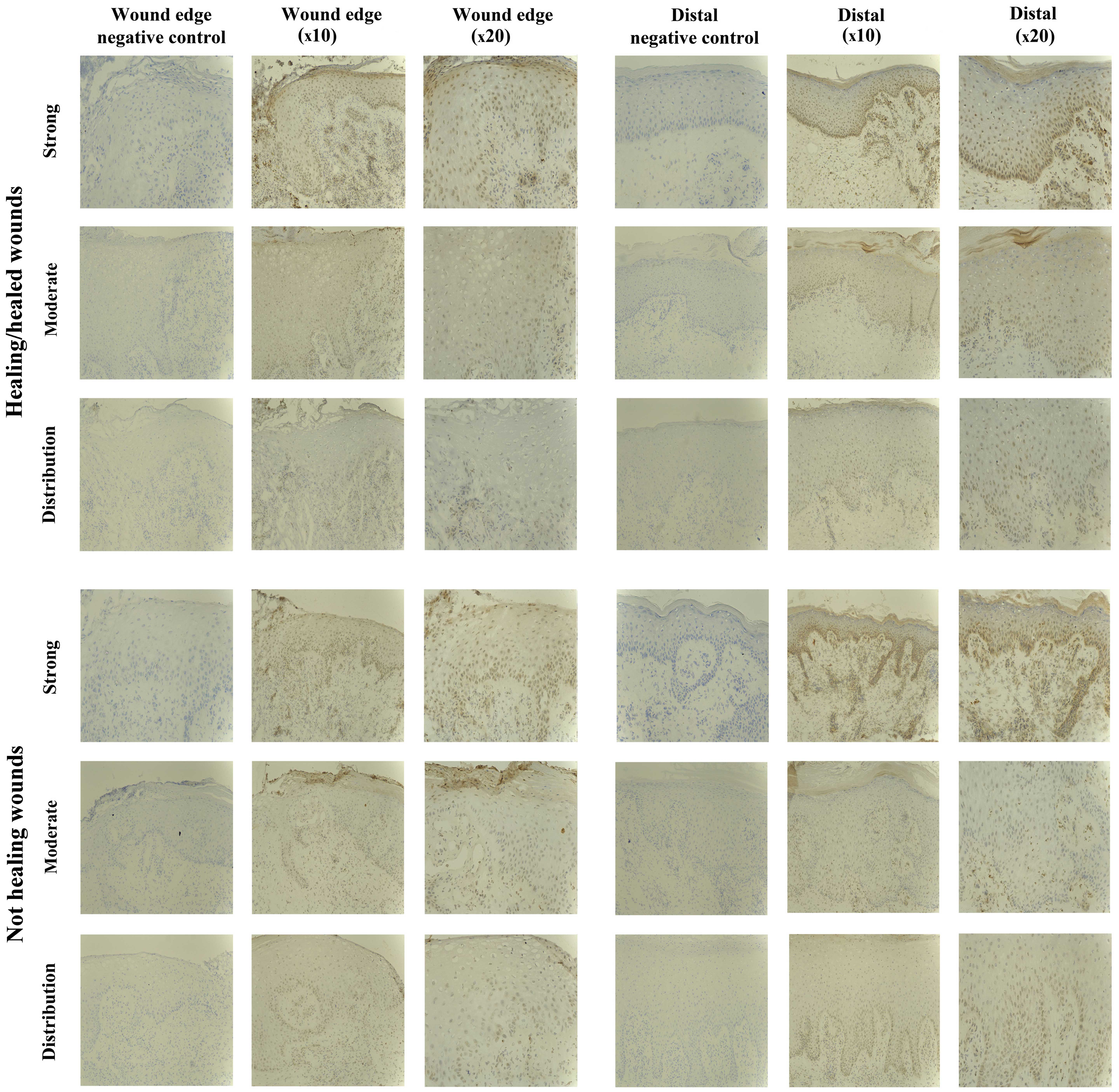
|
1
|
Harding KG, Morris HL and Patel GK:
Science, medicine and the future: healing chronic wounds. BMJ.
324:160–163. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Behm B, Babilas P, Landthaler M and
Schreml S: Cytokines, chemokines and growth factors in wound
healing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 26:812–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS,
Brem H and Tomic-Canic M: Growth factors and cytokines in wound
healing. Wound Repair Regen. 16:585–601. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Igaz P, Tóth S and Falus A: Biological and
clinical significance of the JAK-STAT pathway; lessons from
knockout mice. Inflamm Res. 50:435–441. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM and Harrison DA:
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci. 117:1281–1283. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wormald S and Hilton DJ: Inhibitors of
cytokine signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 279:821–824. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Starr R, Willson TA, Viney EM, Murray LJ,
Rayner JR, Jenkins BJ, Gonda TJ, Alexander WS, Metcalf D, Nicola
NA, et al: A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling.
Nature. 387:917–921. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Endo TA, Masuhara M, Yokouchi M, Suzuki R,
Sakamoto H, Mitsui K, Matsumoto A, Tanimura S, Ohtsubo M, Misawa H,
et al: A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK
kinases. Nature. 387:921–924. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Naka T, Narazaki M, Hirata M, Matsumoto T,
Minamoto S, Aono A, Nishimoto N, Kajita T, Taga T, Yoshizaki K, et
al: Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor.
Nature. 387:924–929. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Croker BA, Kiu H and Nicholson SE: SOCS
regulation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
19:414–422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alexander WS: Suppressors of cytokine
signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:410–416.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Linossi EM, Babon JJ, Hilton DJ and
Nicholson SE: Suppression of cytokine signaling: the SOCS
perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 24:241–248. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kario E, Marmor MD, Adamsky K, Citri A,
Amit I, Amariglio N, Rechavi G and Yarden Y: Suppressors of
cytokine signaling 4 and 5 regulate epidermal growth factor
receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 280:7038–7048. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krebs DL, Uren RT, Metcalf D, Rakar S,
Zhang JG, Starr R, De Souza DP, Hanzinikolas K, Eyles J, Connolly
LM, et al: SOCS-6 binds to insulin receptor substrate 4, and mice
lacking the SOCS-6 gene exhibit mild growth retardation. Mol Cell
Biol. 22:4567–4578. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Banks AS, Li J, McKeag L, Hribal ML,
Kashiwada M, Accili D and Rothman PB: Deletion of SOCS7 leads to
enhanced insulin action and enlarged islets of Langerhans. J Clin
Invest. 115:2462–2471. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng Y, Sanders AJ, Morgan LD, Harding KG
and Jiang WG: Potential roles of suppressor of cytokine signaling
in wound healing. Regen Med. 11:193–209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasukawa H, Ohishi M, Mori H, Murakami M,
Chinen T, Aki D, Hanada T, Takeda K, Akira S, Hoshijima M, et al:
IL-6 induces an anti-inflammatory response in the absence of SOCS3
in macrophages. Nat Immunol. 4:551–556. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bosanquet DC, Harding KG, Ruge F, Sanders
AJ and Jiang WG: Expression of IL-24 and IL-24 receptors in human
wound tissues and the biological implications of IL-24 on
keratinocytes. Wound Repair Regen. 20:896–903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parr C, Watkins G, Mansel RE and Jiang WG:
The hepatocyte growth factor regulatory factors in human breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:202–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eriksson E: Gene transfer in wound
healing. Adv Skin Wound Care. 13(Suppl 2): 20–22. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Branski LK, Pereira CT, Herndon DN and
Jeschke MG: Gene therapy in wound healing: present status and
future directions. Gene Ther. 14:1–10. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Alexander WS, Starr R, Fenner JE, Scott
CL, Handman E, Sprigg NS, Corbin JE, Cornish AL, Darwiche R,
Owczarek CM, et al: SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon
gamma signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions
of this cytokine. Cell. 98:597–608. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Croker BA, Krebs DL, Zhang JG, Wormald S,
Willson TA, Stanley EG, Robb L, Greenhalgh CJ, Förster I, Clausen
BE, et al: SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat
Immunol. 4:540–545. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lang R, Pauleau AL, Parganas E, Takahashi
Y, Mages J, Ihle JN, Rutschman R and Murray PJ: SOCS3 regulates the
plasticity of gp130 signaling. Nat Immunol. 4:546–550. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kubo M, Hanada T and Yoshimura A:
Suppressors of cytokine signaling and immunity. Nat Immunol.
4:1169–1176. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song MM and Shuai K: The suppressor of
cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and SOCS3 but not SOCS2 proteins
inhibit interferon-mediated antiviral and antiproliferative
activities. J Biol Chem. 273:35056–35062. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Seki Y, Hayashi K, Matsumoto A, Seki N,
Tsukada J, Ransom J, Naka T, Kishimoto T, Yoshimura A and Kubo M:
Expression of the suppressor of cytokine signaling-5 (SOCS5)
negatively regulates IL-4-dependent STAT6 activation and Th2
differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:13003–13008. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pastar I, Stojadinovic O, Yin NC, Ramirez
H, Nusbaum AG, Sawaya A, Patel SB, Khalid L, Isseroff RR and
Tomic-Canic M: Epithelialization in wound healing: a comprehensive
review. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 3:445–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Raja, Sivamani K, Garcia MS and Isseroff
RR: Wound re-epithelialization: modulating keratinocyte migration
in wound healing. Front Biosci. 12:2849–2868. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Linke A, Goren I, Bösl MR, Pfeilschifter J
and Frank S: The suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-3
determines keratinocyte proliferative and migratory potential
during skin repair. J Invest Dermatol. 130:876–885. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Linke A, Goren I, Bösl MR, Pfeilschifter J
and Frank S: Epithelial overexpression of SOCS-3 in transgenic mice
exacerbates wound inflammation in the presence of elevated
TGF-beta1. J Invest Dermatol. 130:866–875. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|