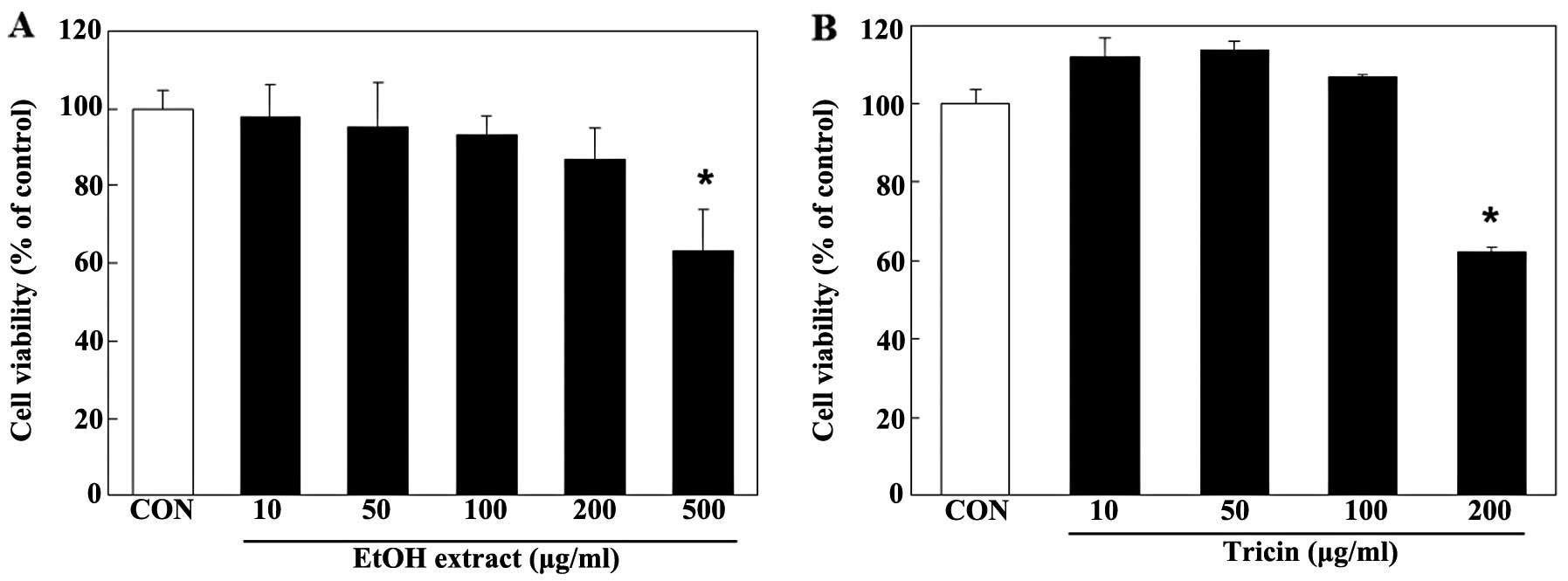
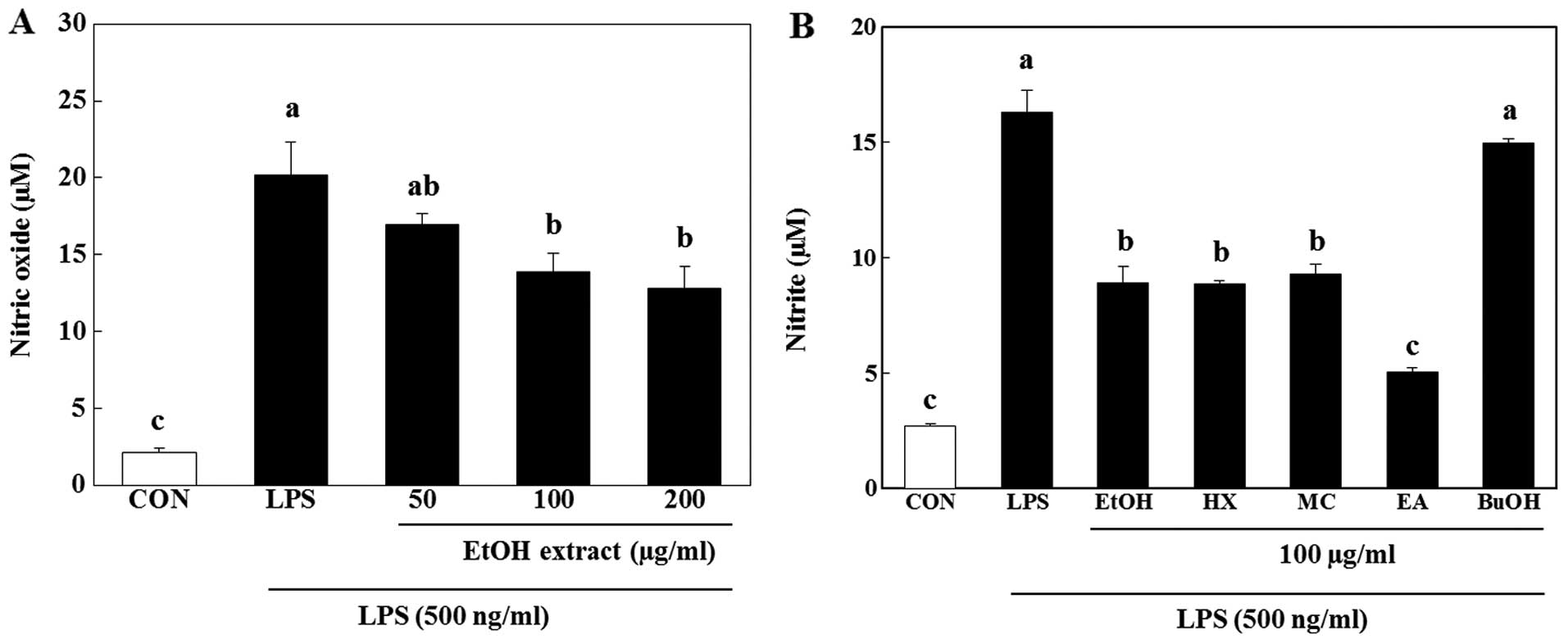
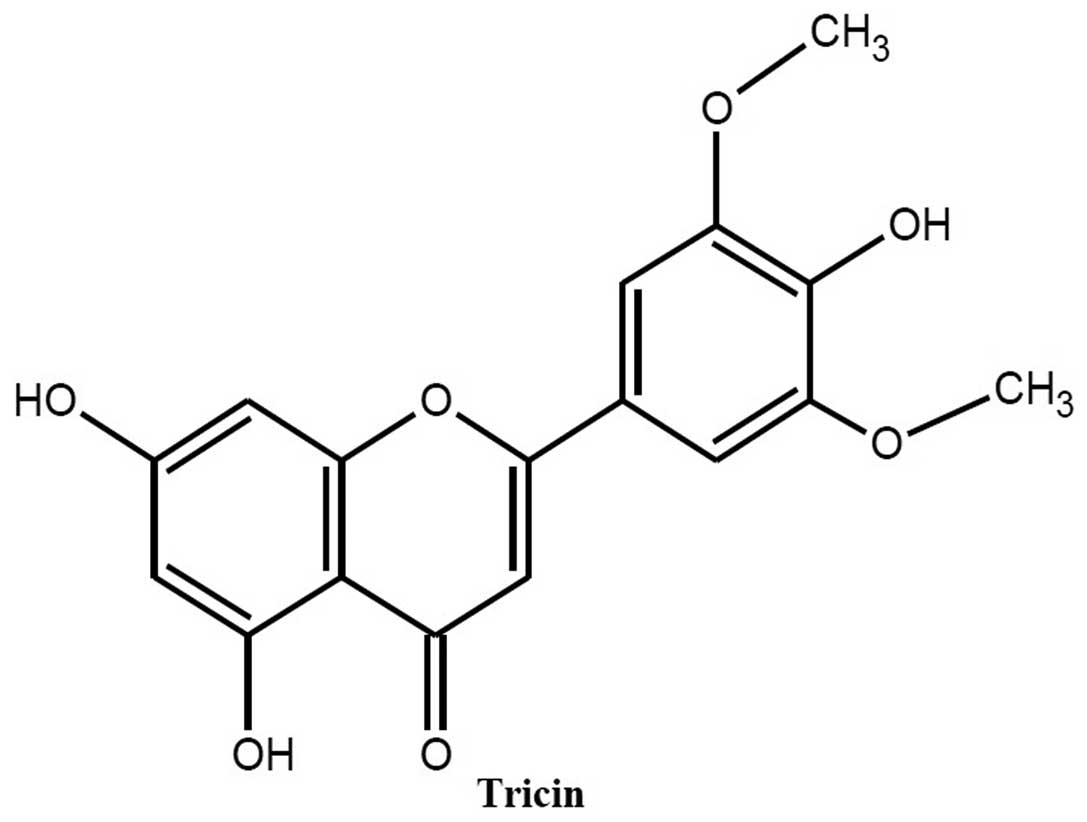
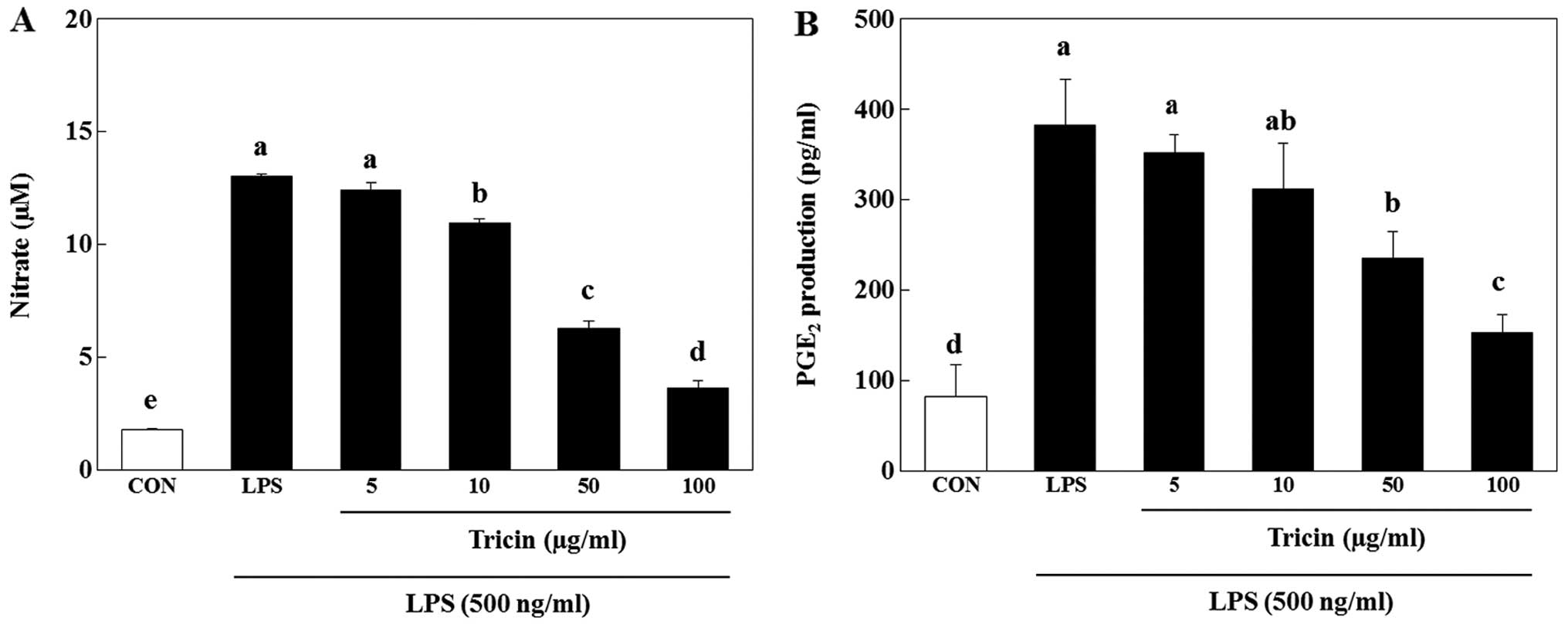
|
1
|
Lee TB: Colored Flora of Korea.
Hyangmunsa; pp. p5011980
|
|
2
|
Park SH: Unrecorded naturalized plants of
Korea. Korean J Pl Taxon. 23:464–468. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Ahn DJ, Park SG, Son CK, Kim CR and Choi
BS: Growth characteristics and yield of wheat as affected by sowing
methods of seed broadcasting over rice plants and rotavating after
seed broadcasting. J Crop Sci. 39:20–26. 1997.
|
|
4
|
Kim DH, Son BY, Kim SK, Shon GM and Kang
DJ: Effect of over-sowing for labor-saving and on growth response
as affected by different barley and wheat. J Crop Sci. 38:106–116.
1996.
|
|
5
|
Chin MS, Park CS and Ham YS: Ecological
analysis of the water foxtail (Alopecurus aequalis) damage in
barley cultivation on drained paddy fields. J Crop Sci. 19:157–170.
1977.
|
|
6
|
Kim DH, Kim SK, Kim ES, Son BY and Kang
DJ: Weed occurrence and control in simultaneous wheat sowing
culture with rice harvest under no-tilled paddy field. Korean J
Weed Sci. 18:186–190. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Jung JS, Lee JS, Choi CD and Cheung JD: A
study on sod culture using water foxtail (Alopecurus aequalis) in
apple orchard. Kor J Weed Sci. 18:128–135. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Seong KY, Park TS, Cho HS, Seo MC and Jeon
WT: Weed occurrence according to the density of water foxtail in
No-tillage seeding rice paddy fields. Kor J Weed Sci. 32:280–284.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
State Administration of Traditional
Chinese medicine (SATC): The encyclopedia of oriental herbal
medicine. State Adm Tradit Chinesemedicine Shanghai China.
8:7393–7394. 1999.
|
|
10
|
Cho W, Nam JW, Kang HJ, Windono T, Seo EK
and Lee KT: Zedoarondiol isolated from the rhizoma of Curcuma
heyneana is involved in the inhibition of iNOS, COX-2 and
pro-inflammatory cytokines via the downregulation of NF-kappaB
pathway in LPS-stimulated murine macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:1049–1057. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Willoughby DA: Heberden Oration, 1974.
Human arthritis applied to animal models Towards a better therapy.
Ann Rheum Dis. 34:471–478. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dobrovolskaia MA and Vogel SN: Toll
receptors, CD14, and macrophage activation and deactivation by LPS.
Microbes Infect. 4:903–914. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McDaniel ML, Kwon G, Hill JR, Marshall CA
and Corbett JA: Cytokines and nitric oxide in islet inflammation
and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 211:24–32. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim DH, Park SJ, Jung JY, Kim SC and Byun
SH: Antiinflammatory effects of the aqueous extract of
Hwangnyenhaedok-tang in LPS-activated macrophage cells. Korean J
Herbology. 24:47–39. 2009.
|
|
15
|
Willeaume V, Kruys V, Mijatovic T and Huez
G: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production induced by viruses and by
lipopoly-saccharides in macrophages: Similarities and differences.
J Inflamm. 46:1–12. 1996.
|
|
16
|
Moncada S and Higgs EA: Endogenous nitric
oxide: Physiology, pathology and clinical relevance. Eur J Clin
Invest. 21:361–374. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YO, Lee SW, Sohn SH, Kim SY, Oh MS and
Kim SK: Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Eucommia
ulmoides oliver on the LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Hanguk Yakyong
Changmul Hakhoe Chi. 20:381–386. 2012.
|
|
18
|
McCartney-Francis N, Allen JB, Mizel DE,
Albina JE, Xie QW, Nathan CF and Wahl SM: Suppression of arthritis
by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med. 178:749–754.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng GJ, Goodridge HS, Harnett MM, Wei XQ,
Nikolaev AV, Higson AP and Liew FY: Extracellular signal-related
kinase (ERK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases
differentially regulate the lipopolysaccharide-mediated induction
of inducible nitric oxide synthase and IL-12 in macrophages:
Leishmania phosphoglycans subvert macrophage IL-12 production by
targeting ERK MAP kinase. J Immunol. 163:6403–6412. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC,
Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD and Baldwin AS: A nucleosomal function
for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression.
Nature. 423:659–663. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bohuslav J, Kravchenko VV, Parry GC, Erlic
JH, Gerondakis S, Mackman N and Ulevitch RJ: Regulation of an
essential innate immune response by the p50 subunit of NFkappaB. J
Clin Invest. 102:1645–1652. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beinke S and Ley SC: Functions of
NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 in immune cell biology. Biochem J.
382:393–409. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jung HK, Kang BM, Jang JH, Ahn BK, Yeo JH,
Jung WS, Cho JH, Kuk YI, Kyun KH and Cho HW: Inhibitory effect of
Alopecurus aequalis Sobol ethanol extracts on LPS-induced
inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 cells. Hanguk Yakyong Changmul
Hakhoe Chi. 22:98–104. 2014.
|
|
24
|
Zhou J and Ibrahim RK: Tricin-a potential
multifunctional nutraceutical. Phytochem Rev. 9:413–424. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cai H, Al-Fayez M, Tunstall RG, Platton S,
Greaves P, Steward WP and Gescher AJ: The rice bran constituent
tricin potently inhibits cyclooxygenase enzymes and interferes with
intestinal carcinogenesis in ApcMin mice. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:1287–1292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
MacMicking JD, Nathan C, Hom G, Chartrain
N, Fletcher DS, Trumbauer M, Stevens K, Xie QW, Sokol K, Hutchinson
N, et al: Altered responses to bacterial infection and endotoxic
shock in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Cell.
81:641–650. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guzik TJ, Korbut R and Adamek-Guzik T:
Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation.
J Physiol Pharmacol. 54:469–487. 2003.
|
|
28
|
Moncada S, Palmer RM and Higgs EA: Nitric
oxide: Physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol
Rev. 43:109–142. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsao LT, Tsai PS, Lin RH, Huang LJ, Kuo SC
and Wang JP: Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of
inducible nitric oxide synthase by phenolic
(3E)-4-(2-hydroxyphenyl)but-3-en-2-one in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Biochem Pharmacol. 70:618–626. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lowenstein CJ and Padalko E: iNOS (NOS2)
at a glance. J Cell Sci. 117:2865–2867. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Levy D, Höke A and Zochodne DW: Local
expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in an animal model of
neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 260:207–209. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guastadisegni C, Nicolini A, Balduzzi M,
Ajmone-Cat MA and Minghetti L: Modulation of PGE(2) and TNFalpha by
nitric oxide and LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Cytokine.
19:175–180. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kalinski P: Regulation of immune responses
by prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 188:21–28. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Mohanlal S, Parvathy R, Shalini V, Helen A
and Jayalekshmy A: Isolation, characterization and quantification
of tricin and flavonolignans in the medicinal rice Njavara (Oryza
sativa L.), as compared to staple varieties. Plant Foods Hum Nutr.
66:91–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Havsteen B: Flavonoids, a class of natural
products of high pharmacological potency. Biochem Pharmacol.
32:1141–1148. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Verschoyle RD, Greaves P, Cai H, Borkhardt
A, Broggini M, D'Incalci M, Riccio E, Doppalapudi R, Kapetanovic
IM, Steward WP and Gescher AJ: Preliminary safety evaluation of the
putative cancer chemopreventive agent tricin, a naturally occurring
flavone. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 57:1–6. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Oyama T, Yasui Y, Sugie S, Koketsu M,
Watanabe K and Tanaka T: Dietary tricin suppresses
inflammation-related colon carcinogenesis in male Crj: CD-1 mice.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2:1031–1038. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chang CL, Wang GJ, Zhang LJ, Tsai WJ, Chen
RY, Wu YC and Kuo YH: Cardiovascular protective flavonolignans and
flavonoids from Calamus quiquesetinervius. Phytochemistry.
71:271–279. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|