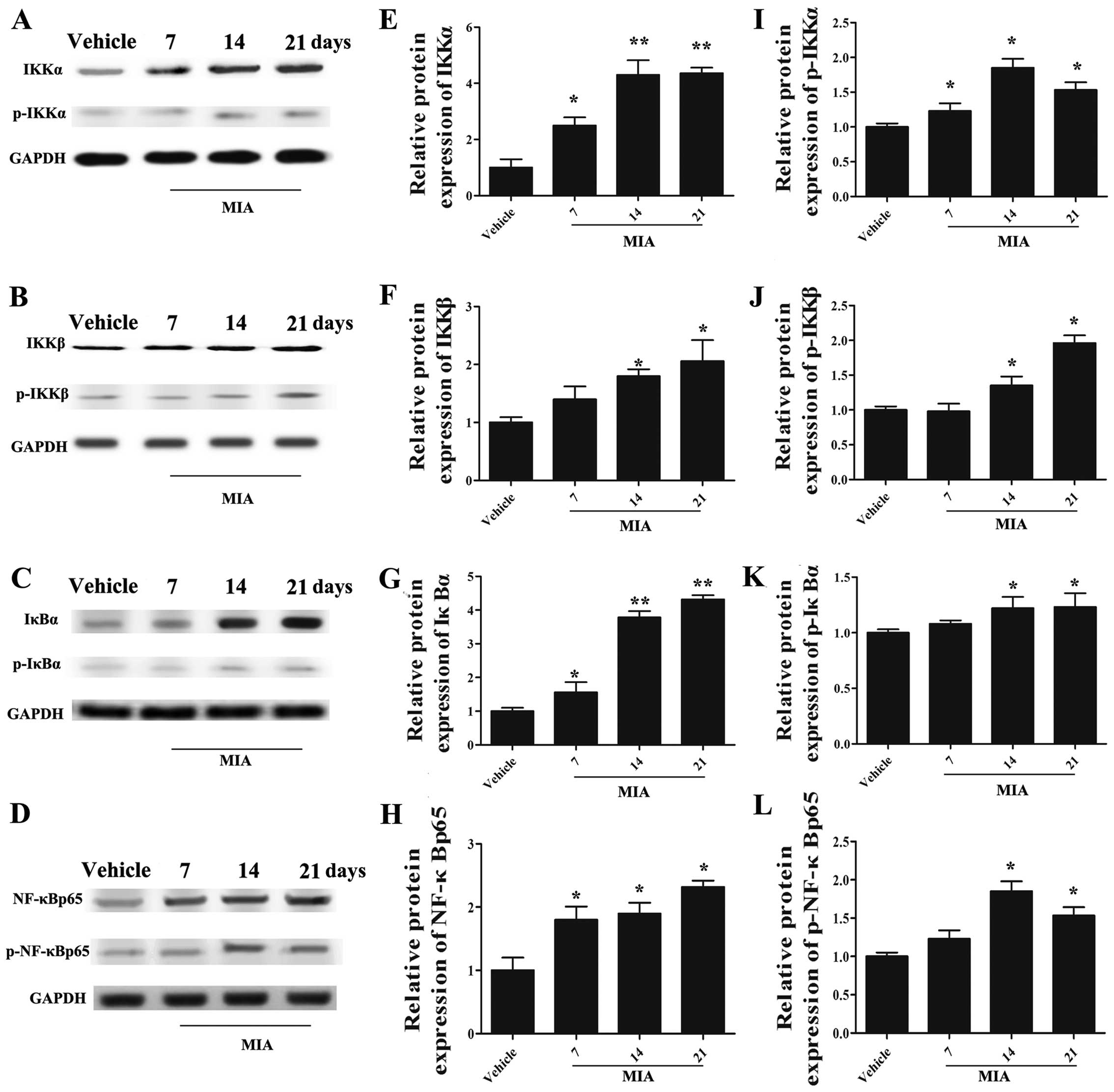
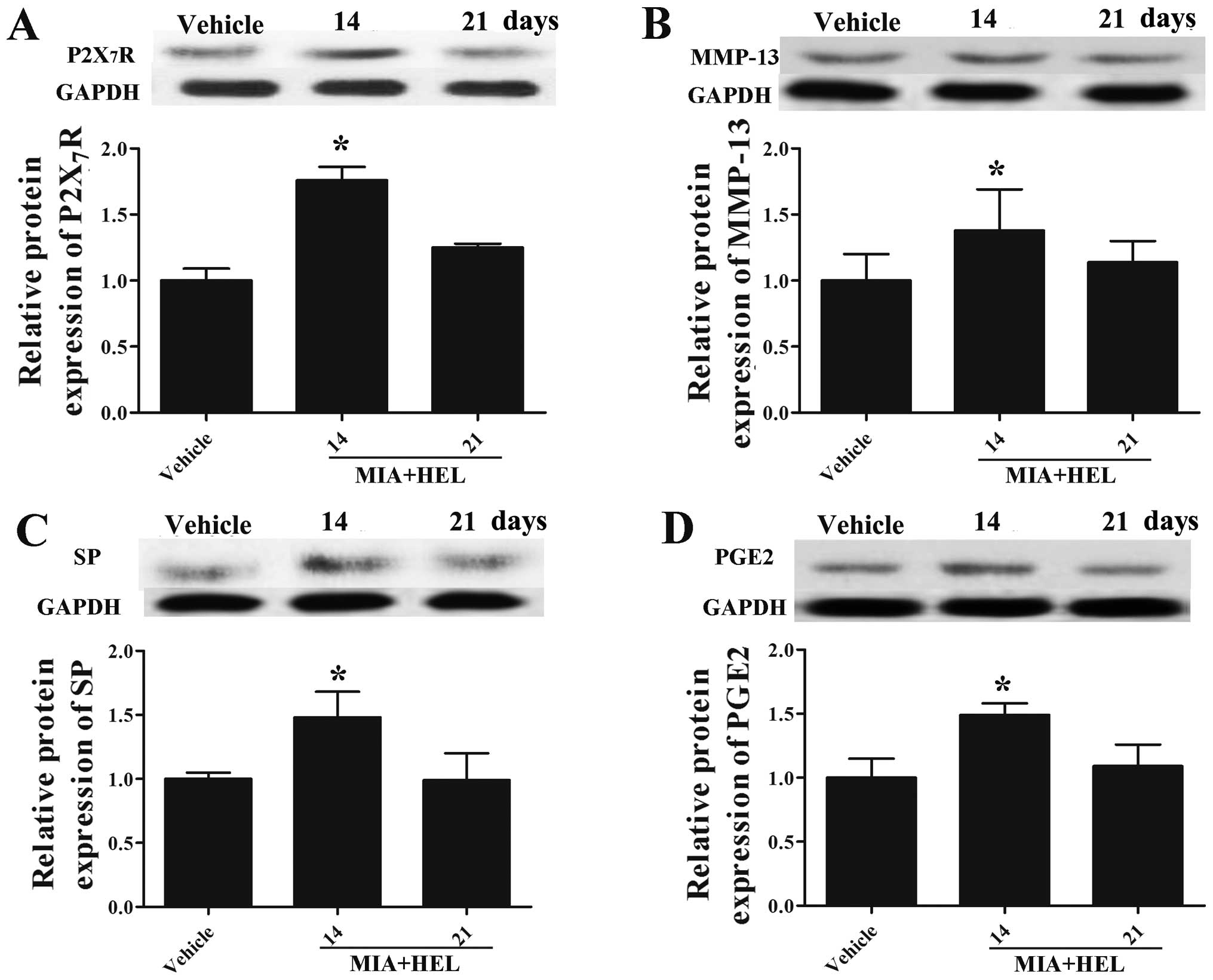
|
1
|
Sinkov V and Cymet T: Osteoarthritis:
understanding the pathophysiology, genetics, and treatments. J Natl
Med Assoc. 95:475–482. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cutolo M and Straub RH: Recent aspects of
gonadal hormone and neurotransmitter interactions with synovial and
immune cells: implications in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
59:657–661. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis and cartilage:
the role of cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2:459–465. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Largo R, Alvarez-Soria MA, Díez-Ortego I,
Calvo E, Sánchez-Pernaute O, Egido J and Herrero-Beaumont G:
Glucosamine inhibits IL-1beta-induced NFkappaB activation in human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 11:290–298.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan Z, Bau B, Yang H, Soeder S and Aigner
T: Freshly isolated osteoarthritic chondrocytes are catabolically
more active than normal chondrocytes, but less responsive to
catabolic stimulation with interleukin-1beta. Arthritis Rheum.
52:136–143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J and
Abramson SB: Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential
implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis
Rheum. 44:1237–1247. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pelletier JP, Fernandes JC, Jovanovic DV,
Reboul P and Martel-Pelletier J: Chondrocyte death in experimental
osteoarthritis is mediated by MEK 1/2 and p38 pathways: role of
cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Rheumatol.
28:2509–2519. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bar-Or D, Rael LT, Thomas GW and Brody EN:
Inflammatory pathways in knee osteoarthritis: potential targets for
treatment. Curr Rheumatol Rev. May 21–2015.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li NG, Shi ZH, Tang YP, Wang ZJ, Song SL,
Qian LH, Qian DW and Duan JA: New hope for the treatment of
osteoarthritis through selective inhibition of MMP-13. Curr Med
Chem. 18:977–1001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lam FF and Ng ES: Substance P and
glutamate receptor antagonists improve the anti-arthritic actions
of dexamethasone in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 159:958–969. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Staunton CA, Lewis R and Barrett-Jolley R:
Ion channels and osteoarthritic pain: potential for novel
analgesics. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 17:3782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Millward-Sadler SJ, Wright MO, Flatman PW
and Salter DM: ATP in the mechanotransduction pathway of normal
human chondrocytes. Biorheology. 41:567–575. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Knight MM, McGlashan SR, Garcia M, Jensen
CG and Poole CA: Articular chondrocytes express connexin 43
hemichannels and P2 receptors - a putative mechanoreceptor complex
involving the primary cilium? J Anat. 214:275–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Varani K, De Mattei M, Vincenzi F, Tosi A,
Gessi S, Merighi S, Pellati A, Masieri F, Ongaro A and Borea PA:
Pharmacological characterization of P2X1 and
P2X3 purinergic receptors in bovine chondrocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:1421–1429. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bravo D, Maturana CJ, Pelissier T,
Hernández A and Constandil L: Interactions of pannexin 1 with NMDA
and P2X7 receptors in central nervous system
pathologies: possible role on chronic pain. Pharmacol Res.
101:86–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dray A and Read SJ: Arthritis and pain.
Future targets to control osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Res Ther.
9:2122007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang K, Zhuang Y, Yan M, Chen H, Ge AQ,
Sun L and Miao B: Effects of riluzole on P2X7R
expression in the spinal cord in rat model of neuropathic pain.
Neurosci Lett. 618:127–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ursu D, Ebert P, Langron E, Ruble C,
Munsie L, Zou W, Fijal B, Qian YW, McNearney TA, Mogg A, et al:
Gain and loss of function of P2X7 receptors: mechanisms,
pharmacology and relevance to diabetic neuropathic pain. Mol Pain.
10:372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sorge RE, Trang T, Dorfman R, Smith SB,
Beggs S, Ritchie J, Austin JS, Zaykin DV, Vander Meulen H, Costigan
M, et al: Genetically determined P2X7 receptor pore formation
regulates variability in chronic pain sensitivity. Nat Med.
18:595–599. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McInnes IB, Cruwys S, Bowers K and
Braddock M: Targeting the P2X7 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis:
biological rationale for P2X7 antagonism. Clin Exp Rheumatol.
32:878–882. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Portales-Cervantes L, Niño-Moreno P,
Doníz-Padilla L, Baranda-Candido L, García-Hernández M,
Salgado-Bustamante M, González-Amaro R and Portales-Pérez D:
Expression and function of the P2X(7) purinergic receptor in
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid
arthritis. Hum Immunol. 71:818–825. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guzman RE, Evans MG, Bove S, Morenko B and
Kilgore K: Mono-iodoacetate-induced histologic changes in
subchondral bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotibial
joints: an animal model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol Pathol.
31:619–624. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beyreuther B, Callizot N and Stöhr T:
Antinociceptive efficacy of lacosamide in the monosodium
iodoacetate rat model for osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Res Ther.
9:R142007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sagar DR, Staniaszek LE, Okine BN,
Woodhams S, Norris LM, Pearson RG, Garle MJ, Alexander SP, Bennett
AJ, Barrett DA, et al: Tonic modulation of spinal hyperexcitability
by the endocannabinoid receptor system in a rat model of
osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Rheum. 62:3666–3676. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Keystone EC, Wang MM, Layton M, Hollis S
and McInnes IB; D1520C00001 Study Team: Clinical evaluation of the
efficacy of the P2X7 purinergic receptor antagonist
AZD9056 on the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in
patients with active disease despite treatment with methotrexate or
sulphasalazine. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:1630–1635. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lyss G, Knorre A, Schmidt TJ, Pahl HL and
Merfort I: The anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone helenalin
inhibits the transcription factor NF-kappaB by directly targeting
p65. J Biol Chem. 273:33508–33516. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bove SE, Calcaterra SL, Brooker RM, Huber
CM, Guzman RE, Juneau PL, Schrier DJ and Kilgore KS: Weight bearing
as a measure of disease progression and efficacy of
anti-inflammatory compounds in a model of monosodium
iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
11:821–830. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fernihough J, Gentry C, Malcangio M, Fox
A, Rediske J, Pellas T, Kidd B, Bevan S and Winter J: Pain related
behaviour in two models of osteoarthritis in the rat knee. Pain.
112:83–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Konttinen YT, Sillat T, Barreto G, Ainola
M and Nordström DC: Osteoarthritis as an autoinflammatory disease
caused by chondrocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. Arthritis
Rheum. 64:613–616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lister MF, Sharkey J, Sawatzky DA,
Hodgkiss JP, Davidson DJ, Rossi AG and Finlayson K: The role of the
purinergic P2X7 receptor in inflammation. J Inflamm (Lond).
4:52007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gourine AV, Poputnikov DM, Zhernosek N,
Melenchuk EV, Gerstberger R, Spyer KM and Gourine VN: P2 receptor
blockade attenuates fever and cytokine responses induced by
lipopolysaccharide in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 146:139–145. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Catal F, Mete E, Tayman C, Topal E,
Albayrak A and Sert H: A human monoclonal anti-TNF alpha antibody
(adalimumab) reduces airway inflammation and ameliorates lung
histology in a murine model of acute asthma. Allergol Immunopathol
(Madr). 43:14–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Johnsen-Soriano S, Sancho-Tello M, Arnal
E, Díaz-Llopis M, Navea A, Miranda M, Bosch-Morell F and Romero FJ:
Comparison of the acute effects of anti-TNF-alpha drugs on a
uveitis experimental model. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 18:208–215. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Grounds MD, Davies M, Torrisi J,
Shavlakadze T, White J and Hodgetts S: Silencing TNFalpha activity
by using Remicade or Enbrel blocks inflammation in whole muscle
grafts: an in vivo bioassay to assess the efficacy of anti-cytokine
drugs in mice. Cell Tissue Res. 320:509–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hong HS and Son Y: Substance P ameliorates
collagen II-induced arthritis in mice via suppression of the
inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:179–184.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim SJ, Kim JE, Kim SH, Kim SJ, Jeon SJ,
Kim SH and Jung Y: Therapeutic effects of neuropeptide substance P
coupled with self-assembled peptide nanofibers on the progression
of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Biomaterials. 74:119–130. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Malemud CJ, Islam N and Haqqi TM:
Pathophysiological mechanisms in osteoarthritis lead to novel
therapeutic strategies. Cells Tissues Organs. 174:34–48. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schlomann U, Wildeboer D, Webster A,
Antropova O, Zeuschner D, Knight CG, Docherty AJ, Lambert M,
Skelton L, Jockusch H and Bartsch JW: The metalloprotease
disintegrin ADAM8. Processing by autocatalysis is required for
proteolytic activity and cell adhesion. J Biol Chem.
277:48210–48219. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van den Berg WB: Osteoarthritis year 2010
in review: pathomechanisms. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:338–341.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chubinskaya S, Kuettner KE and Cole AA:
Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in normal and damaged
articular cartilage from human knee and ankle joints. Lab Invest.
79:1669–1677. 1999.
|
|
43
|
Csaki C, Mobasheri A and Shakibaei M:
Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol
in human articular chondrocytes: inhibition of IL-1beta-induced
NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Arthritis Res Ther.
11:R1652009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen YJ, Tsai KS, Chan DC, Lan KC, Chen
CF, Yang RS and Liu SH: Honokiol, a low molecular weight natural
product, prevents inflammatory response and cartilage matrix
degradation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res.
32:573–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ding Q, Zhong H, Qi Y, Cheng Y, Li W, Yan
S and Wang X: Anti-arthritic effects of crocin in
interleukin-1β-treated articular chondrocytes and cartilage in a
rabbit osteoarthritic model. Inflamm Res. 62:17–25. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
He C, Chen X, Zhao C, Qie Y, Yan Z and Zhu
X: Eleutheroside E ameliorates arthritis severity in
collagen-induced arthritis mice model by suppressing inflammatory
cytokine release. Inflammation. 37:1533–1543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ferrari D, Wesselborg S, Bauer MK and
Schulze-Osthoff K: Extracellular ATP activates transcription factor
NF-kappaB through the P2Z purinoreceptor by selectively targeting
NF-kappaB p65. J Cell Biol. 139:1635–1643. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chang X, He H, Zhu L, Gao J, Wei T, Ma Z
and Yan T: Protective effect of apigenin on Freund's complete
adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting P2X7/NF-κB
pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 236:41–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Korcok J, Raimundo LN, Ke HZ, Sims SM and
Dixon SJ: Extracellular nucleotides act through P2X7 receptors to
activate NF-kappaB in osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 19:642–651.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kahlenberg JM, Lundberg KC, Kertesy SB, Qu
Y and Dubyak GR: Potentiation of caspase-1 activation by the P2X7
receptor is dependent on TLR signals and requires NF-kappaB-driven
protein synthesis. J Immunol. 175:7611–7622. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Genetos DC, Karin NJ, Geist DJ, Donahue HJ
and Duncan RL: Purinergic signaling is required for fluid shear
stress-induced NF-κB translocation in osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res.
317:737–744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim JE, Kim DS, Jin Ryu H, Il Kim W, Kim
MJ, Won Kim D, Young Choi S and Kang TC: The effect of P2X7
receptor activation on nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation induced by
status epilepticus in the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus. 23:500–514.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|