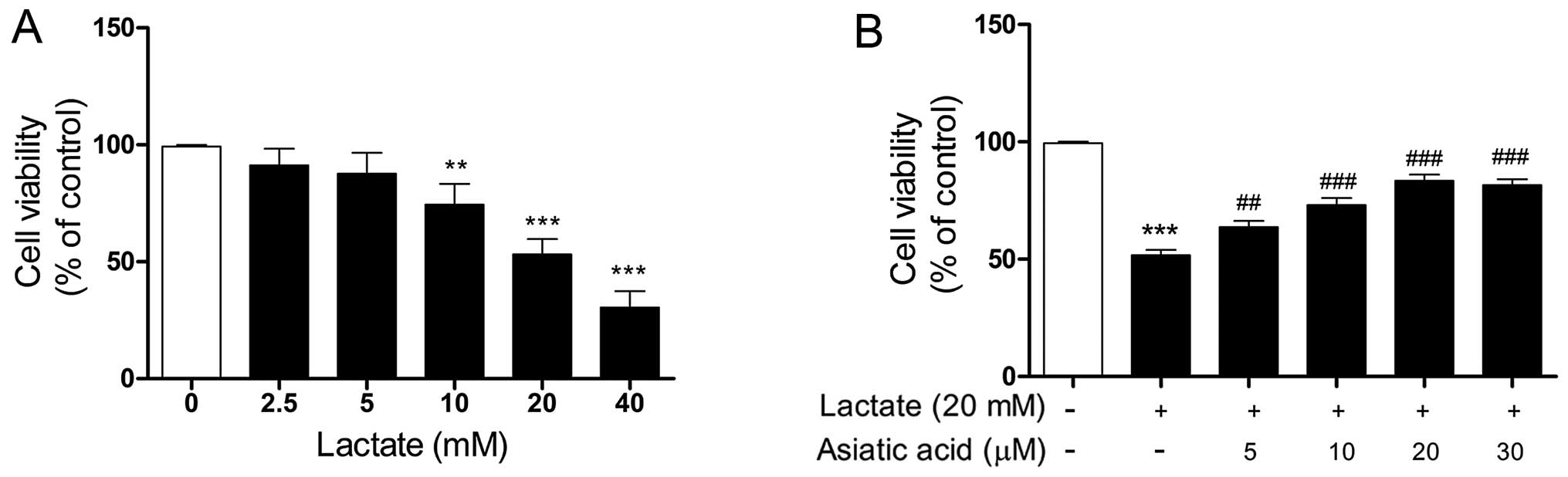
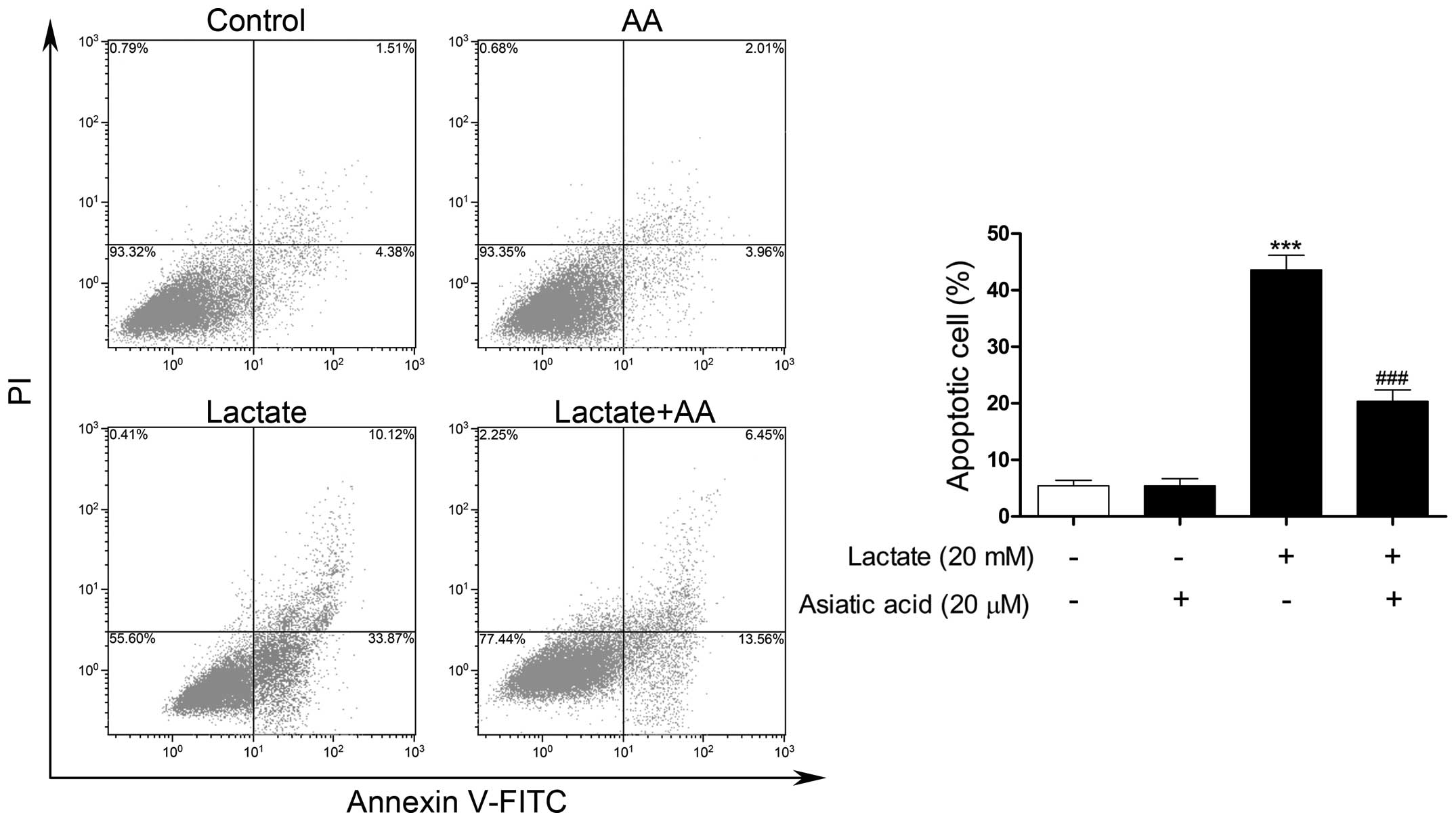
|
1
|
Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M,
Henriksen K, Parvinen M and Voipio-Pulkki LM: Apoptosis in human
acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 95:320–323. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao HK, Yin Z, Zhou N, Feng XY, Gao F and
Wang HC: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition protects the heart
from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of
inflammation and apoptosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 52:286–292.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aharinejad S, Andrukhova O, Lucas T,
Zuckermann A, Wieselthaler G, Wolner E and Grimm M: Programmed cell
death in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy is mediated by
suppression of the apoptosis inhibitor Apollon. Ann Thorac Surg.
86:109–114; discussion 114. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Narula J, Haider N, Virmani R, DiSalvo TG,
Kolodgie FD, Hajjar RJ, Schmidt U, Semigran MJ, Dec GW and Khaw BA:
Apoptosis in myocytes in end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med.
335:1182–1189. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bryant D, Becker L, Richardson J, Shelton
J, Franco F, Peshock R, Thompson M and Giroir B: Cardiac failure in
transgenic mice with myocardial expression of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Circulation. 97:1375–1381. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sayen MR, Gustafsson AB, Sussman MA,
Molkentin JD and Gottlieb RA: Calcineurin transgenic mice have
mitochondrial dysfunction and elevated superoxide production. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 284:C562–C570. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Silva JP, Gustafsson CM, Rustin P
and Larsson NG: Increased in vivo apoptosis in cells lacking
mitochondrial DNA gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:4038–4043. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ and Kitsis RN: The
mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ
Res. 95:957–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee Y and Gustafsson AB: Role of apoptosis
in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis. 14:536–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Halestrap AP and Wilson MC: The
monocarboxylate transporter family - role and regulation. IUBMB
Life. 64:109–119. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Brooks GA, Dubouchaud H, Brown M,
Sicurello JP and Butz CE: Role of mitochondrial lactate
dehydrogenase and lactate oxidation in the intracellular lactate
shuttle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:1129–1134. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gladden LB: Lactate metabolism: A new
paradigm for the third millennium. J Physiol. 558:5–30. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bonen A: The expression of lactate
transporters (MCT1 and MCT4) in heart and muscle. Eur J Appl
Physiol. 86:6–11. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hashimoto T and Brooks GA: Mitochondrial
lactate oxidation complex and an adaptive role for lactate
production. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 40:486–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jóhannsson E, Lunde PK, Heddle C, Sjaastad
I, Thomas MJ, Bergersen L, Halestrap AP, Blackstad TW, Ottersen OP
and Sejersted OM: Upregulation of the cardiac monocarboxylate
transporter MCT1 in a rat model of congestive heart failure.
Circulation. 104:729–734. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Halestrap AP, Wang X, Poole RC, Jackson VN
and Price NT: Lactate transport in heart in relation to myocardial
ischemia. Am J Cardiol. 80:17A–25A. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu J, Xu X, Si L, Xue L, Zhang S, Qin J,
Wu Y, Shao Y, Chen Y and Wang X: Intracellular lactate signaling
cascade in atrial remodeling of mitral valvular patients with
atrial fibrillation. J Cardiothorac Surg. 8:342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Evans RK, Schwartz DD and Gladden LB:
Effect of myocardial volume overload and heart failure on lactate
transport into isolated cardiac myocytes. J Appl Physiol (1985).
94:1169–1176. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pittella F, Dutra RC, Junior DD, Lopes MT
and Barbosa NR: Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Centella
asiatica (L) Urb. Int J Mol Sci. 10:3713–3721. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yun KJ, Kim JY, Kim JB, Lee KW, Jeong SY,
Park HJ, Jung HJ, Cho YW, Yun K and Lee KT: Inhibition of
LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-kappa B
inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the
IKK and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:431–441. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Krishnamurthy RG, Senut MC, Zemke D, Min
J, Frenkel MB, Greenberg EJ, Yu SW, Ahn N, Goudreau J, Kassab M, et
al: Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene from Centella asiatica,
is neuroprotective in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J
Neurosci Res. 87:2541–2550. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang LX, He RH, Yang G, Tan JJ, Zhou L,
Meng XM, Huang XR and Lan HY: Asiatic acid inhibits liver fibrosis
by blocking TGF-beta/Smad signaling in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One.
7:e313502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Si L, Xu J, Yi C, Xu X, Wang F, Gu W,
Zhang Y and Wang X: Asiatic acid attenuates cardiac hypertrophy by
blocking transforming growth factor-β1-mediated hypertrophic
signaling in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 34:499–506.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Wu J, Dou Y, Xia B, Rong W,
Rimbach G and Lou Y: Asiatic acid protects primary neurons against
C2-ceramide-induced apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 679:51–59. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brooks GA, Brown MA, Butz CE, Sicurello JP
and Dubouchaud H: Cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondria have a
monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. J Appl Physiol (1985).
87:1713–1718. 1999.
|
|
26
|
Butz CE, McClelland GB and Brooks GA: MCT1
confirmed in rat striated muscle mitochondria. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 97:1059–1066. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hashimoto T, Hussien R and Brooks GA:
Colocalization of MCT1, CD147, and LDH in mitochondrial inner
membrane of L6 muscle cells: Evidence of a mitochondrial lactate
oxidation complex. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 290:E1237–E1244.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martinov V, Rizvi SM, Weiseth SA, Sagave
J, Bergersen LH and Valen G: Increased expression of
monocarboxylate transporter 1 after acute ischemia of isolated,
perfused mouse hearts. Life Sci. 85:379–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hashimoto T, Hussien R, Oommen S, Gohil K
and Brooks GA: Lactate sensitive transcription factor network in L6
cells: Activation of MCT1 and mitochondrial biogenesis. FASEB J.
21:2602–2612. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong D, Kim TS, Lee JW, Kim KT, Kim HJ,
Kim IH and Kim IY: Blocking of acidosis-mediated apoptosis by a
reduction of lactate dehydrogenase activity through antisense mRNA
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 289:1141–1149. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kubasiak LA, Hernandez OM, Bishopric NH
and Webster KA: Hypoxia and acidosis activate cardiac myocyte death
through the Bcl-2 family protein BNIP3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:12825–12830. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|