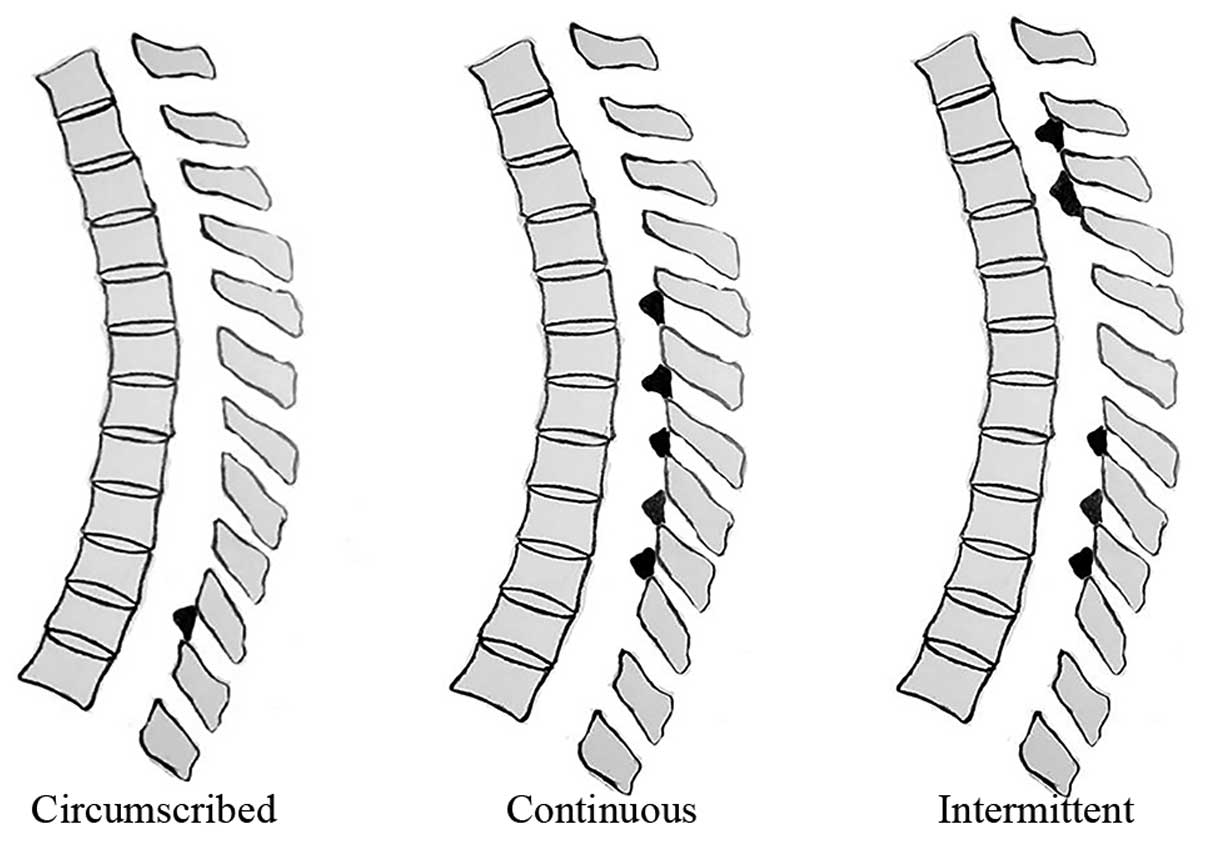
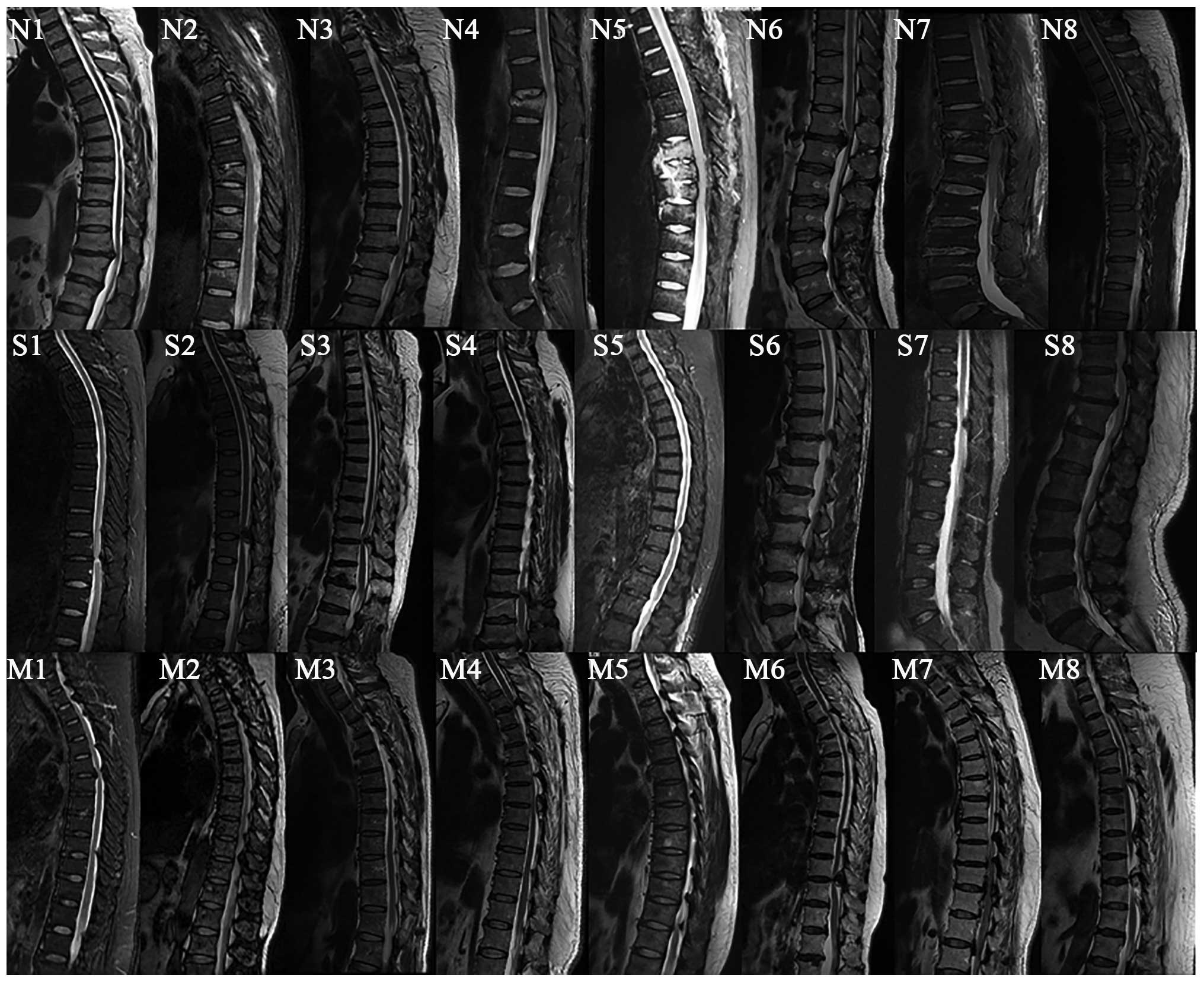
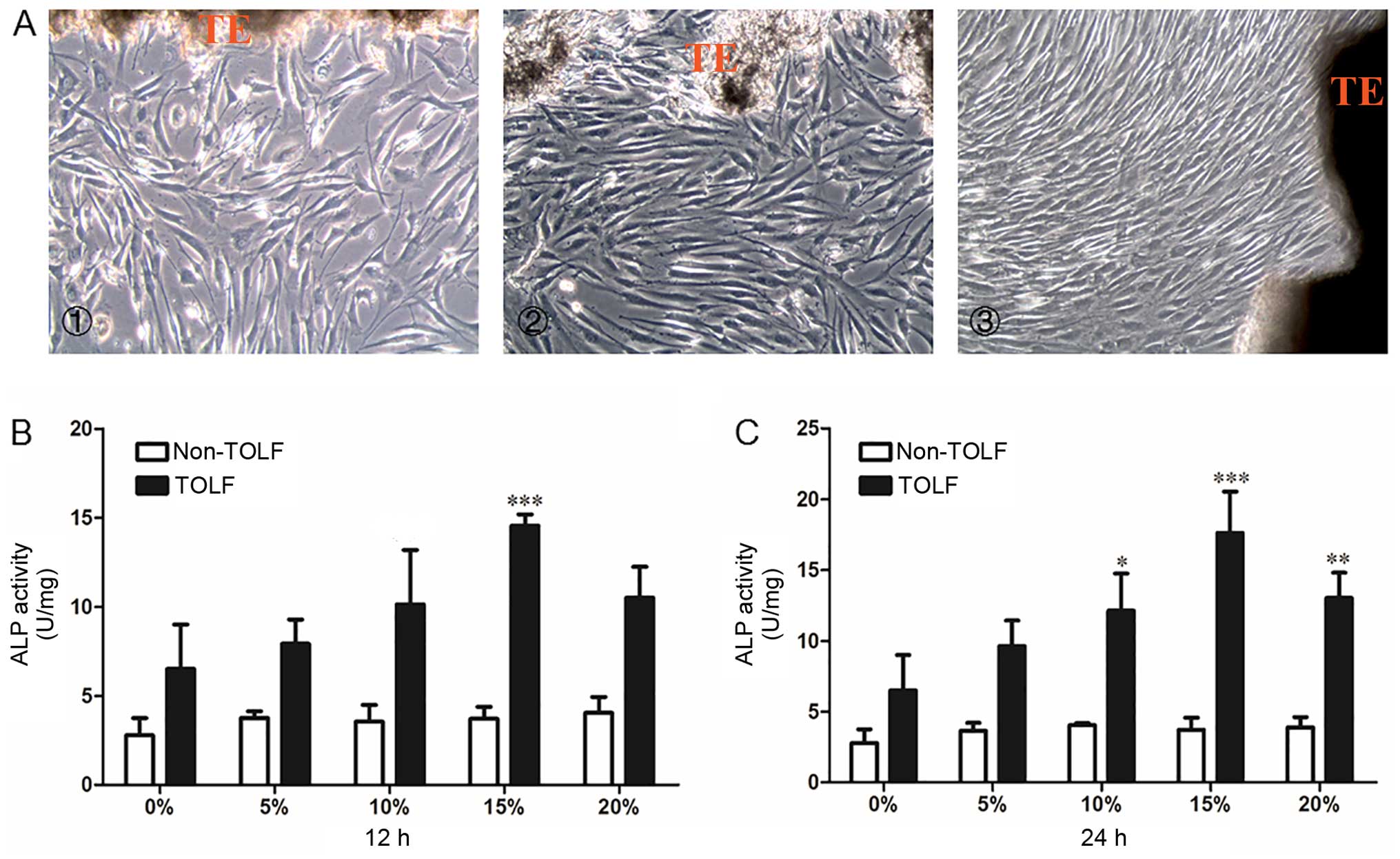
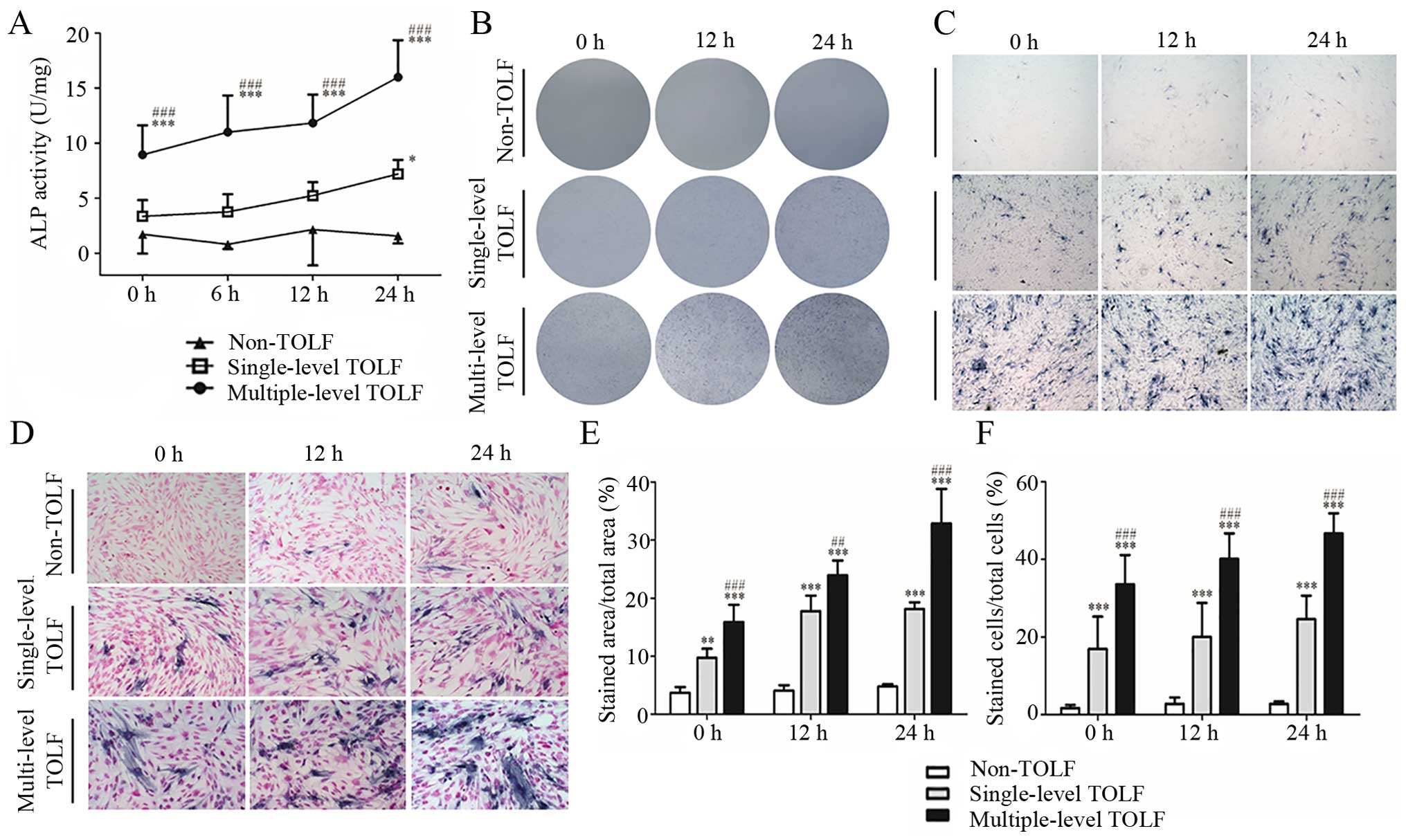
|
1
|
Sato T, Kokubun S, Tanaka Y and Ishii Y:
Thoracic myelopathy in the Japanese: Epidemiological and clinical
observations on the cases in Miyagi Prefecture. Tohoku J Exp Med.
184:1–11. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo JJ, Luk KD, Karppinen J, Yang H and
Cheung KM: Prevalence, distribution, and morphology of ossification
of the ligamentum flavum: A population study of one thousand seven
hundred thirty-six magnetic resonance imaging scans. Spine.
35:51–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kudo S, Ono M and Russell WJ: Ossification
of thoracic ligamenta flava. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 141:117–121.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lang N, Yuan HS, Wang HL, Liao J, Li M,
Guo FX, Shi S and Chen ZQ: Epidemiological survey of ossification
of the ligamentum flavum in thoracic spine: CT imaging observation
of 993 cases. Eur Spine J. 22:857–862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Mobbs RJ and Dvorak M: Ossification of the
ligamentum flavum: diet and genetics. J Clin Neurosci. 14:703–705.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fan D, Chen Z, Chen Y and Shang Y:
Mechanistic roles of leptin in osteogenic stimulation in thoracic
ligament flavum cells. J Biol Chem. 282:29958–29966. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Uchida K, Yayama T, Cai HX, Nakajima H,
Sugita D, Guerrero AR, Kobayashi S, Yoshida A, Chen KB and Baba H:
Ossification process involving the human thoracic ligamentum
flavum: Role of transcription factors. Arthritis Res Ther.
13:R1442011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okada K, Oka S, Tohge K, Ono K, Yonenobu K
and Hosoya T: Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the
ligamentum flavum. Clinicopathologic study and surgical treatment.
Spine. 16:280–287. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maigne JY, Ayral X and Guérin-Surville H:
Frequency and size of ossifications in the caudal attachments of
the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. Role of rotatory
strains in their development. An anatomic study of 121 spines. Surg
Radiol Anat. 14:119–124. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan D, Chen Z, Wang D, Guo Z, Qiang Q and
Shang Y: Osterix is a key target for mechanical signals in human
thoracic ligament flavum cells. J Cell Physiol. 211:577–584. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao R, Yuan W, Yang L, Shi G and Jia L:
Clinical features and surgical outcomes of patients with thoracic
myelopathy caused by multilevel ossification of the ligamentum
flavum. Spine J. 13:1032–1038. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawaguchi Y, Yasuda T, Seki S, Nakano M,
Kanamori M, Sumi S and Kimura T: Variables affecting postsurgical
prognosis of thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the
ligamentum flavum. Spine J. 13:1095–1107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li F, Chen Q and Xu K: Surgical treatment
of 40 patients with thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum.
J Neurosurg Spine. 4:191–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yayama T, Uchida K, Kobayashi S, Kokubo Y,
Sato R, Nakajima H, Takamura T, Bangirana A, Itoh H and Baba H:
Thoracic ossification of the human ligamentum flavum:
Histopathological and immunohistochemical findings around the
ossified lesion. J Neurosurg Spine. 7:184–193. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cai HX, Yayama T, Uchida K, Nakajima H,
Sugita D, Guerrero AR, Yoshida A and Baba H: Cyclic tensile strain
facilitates the ossification of ligamentum flavum through β-catenin
signaling pathway: In vitro analysis. Spine. 37:E639–E646. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim HN, Min WK, Jeong JH, Kim SG, Kim JR,
Kim SY, Choi JY and Park BC: Combination of Runx2 and BMP2
increases conversion of human ligamentum flavum cells into
osteoblastic cells. BMB Rep. 44:446–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kong Q, Ma X, Li F, Guo Z, Qi Q, Li W,
Yuan H, Wang Z and Chen Z: COL6A1 polymorphisms associated with
ossification of the ligamentum flavum and ossification of the
posterior longitudinal ligament. Spine. 32:2834–2838. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Shi G and Yuan W:
RUNX2 polymorphisms associated with OPLL and OLF in the Han
population. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 468:3333–3341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kudo H, Furukawa K, Yokoyama T, Ono A,
Numasawa T, Wada K, Tanaka S, Asari T, Ueyama K, Motomura S and Toh
S: Genetic differences in the osteogenic differentiation potency
according to the classification of ossification of the posterior
longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine. Spine. 36:951–957.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen ZQ, Dang GT, Liu XG and Cai QL: The
choice of treatment for ossification of ligamentum flavum of the
thoracic spine. Chin J Orthop. 19:197–200. 1999.In Chinese.
|
|
21
|
Yin X, Chen Z, Guo Z, Liu X and Yu H:
Tissue transglutaminase expression and activity in human ligamentum
flavum cells derived from thoracic ossification of ligamentum
flavum. Spine. 35:E1018–E1024. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahn DK, Lee S, Moon SH, Boo KH, Chang BK
and Lee JI: Ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Asian Spine J.
8:89–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsukamoto N, Maeda T, Miura H, Jingushi S,
Hosokawa A, Harimaya K, Higaki H, Kurata K and Iwamoto Y:
Repetitive tensile stress to rat caudal vertebrae inducing
cartilage formation in the spinal ligaments: A possible role of
mechanical stress in the development of ossification of the spinal
ligaments. J Neurosurg Spine. 5:234–242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iwasawa T, Iwasaki K, Sawada T, Okada A,
Ueyama K, Motomura S, Harata S, Inoue I, Toh S and Furukawa KI:
Pathophysiological role of endothelin in ectopic ossification of
human spinal ligaments induced by mechanical stress. Calcif Tissue
Int. 79:422–430. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakatani T, Marui T, Hitora T, Doita M,
Nishida K and Kurosaka M: Mechanical stretching force promotes
collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum
via transforming growth factor-beta1. J Orthop Res. 20:1380–1386.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hoshi K, Amizuka N, Sakou T, Kurokawa T
and Ozawa H: Fibroblasts of spinal ligaments pathologically
differentiate into chondrocytes induced by recombinant human bone
morphogenetic protein-2: Morphological examinations for
ossification of spinal ligaments. Bone. 21:155–162. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwasaki K, Furukawa KI, Tanno M, Kusumi T,
Ueyama K, Tanaka M, Kudo H, Toh S, Harata S and Motomura S:
Uni-axial cyclic stretch induces Cbfa1 expression in spinal
ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the
posterior longitudinal ligament. Calcif Tissue Int. 74:448–457.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ishida Y and Kawai S: Characterization of
cultured cells derived from ossification of the posterior
longitudinal ligament of the spine. Bone. 14:85–91. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong ZM and Chen JT: Phenotypic
characterization of ligamentum flavum cells from patients with
ossification of ligamentum flavum. Yonsei Med J. 50:375–379. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanno M, Furukawa KI, Ueyama K, Harata S
and Motomura S: Uniaxial cyclic stretch induces osteogenic
differentiation and synthesis of bone morphogenetic proteins of
spinal ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of
the posterior longitudinal ligaments. Bone. 33:475–484. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohishi H, Furukawa K, Iwasaki K, Ueyama K,
Okada A, Motomura S, Harata S and Toh S: Role of prostaglandin I2
in the gene expression induced by mechanical stress in spinal
ligament cells derived from patients with ossification of the
posterior longitudinal ligament. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 305:818–824.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Furukawa K: Current topics in
pharmacological research on bone metabolism: Molecular basis of
ectopic bone formation induced by mechanical stress. J Pharmacol
Sci. 100:201–204. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Wei P, Chen Y, Yang L, Jiang C,
Jiang P and Chen D: Down-regulated expression of vimentin induced
by mechanical stress in fibroblasts derived from patients with
ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J.
23:2410–2415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pagani F, Francucci CM and Moro L: Markers
of bone turnover: Biochemical and clinical perspectives. J
Endocrinol Invest. 28(Suppl 10): 8–13. 2005.
|
|
35
|
Hayashi K, Ishidou Y, Yonemori K, Nagamine
T, Origuchi N, Maeda S, Imamura T, Kato M, Yoshida H, Sampath TK,
et al: Expression and localization of bone morphogenetic proteins
(BMPs) and BMP receptors in ossification of the ligamentum flavum.
Bone. 21:23–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fu H, Doll B, McNelis T and Hollinger JO:
Osteoblast differentiation in vitro and in vivo promoted by
Osterix. J Biomed Mater Res A. 83:770–778. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Komaki M, Karakida T, Abe M, Oida S,
Mimori K, Iwasaki K, Noguchi K, Oda S and Ishikawa I: Twist
negatively regulates osteoblastic differentiation in human
periodontal ligament cells. J Cell Biochem. 100:303–314. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ishijima M, Tsuji K, Rittling SR,
Yamashita T, Kurosawa H, Denhardt DT, Nifuji A, Ezura Y and Noda M:
Osteopontin is required for mechanical stress-dependent signals to
bone marrow cells. J Endocrinol. 193:235–243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Inamasu J and Guiot BH: A review of
factors predictive of surgical outcome for ossification of the
ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine.
5:133–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He S, Hussain N, Li S and Hou T: Clinical
and prognostic analysis of ossified ligamentum flavum in a Chinese
population. J Neurosurg Spine. 3:348–354. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|