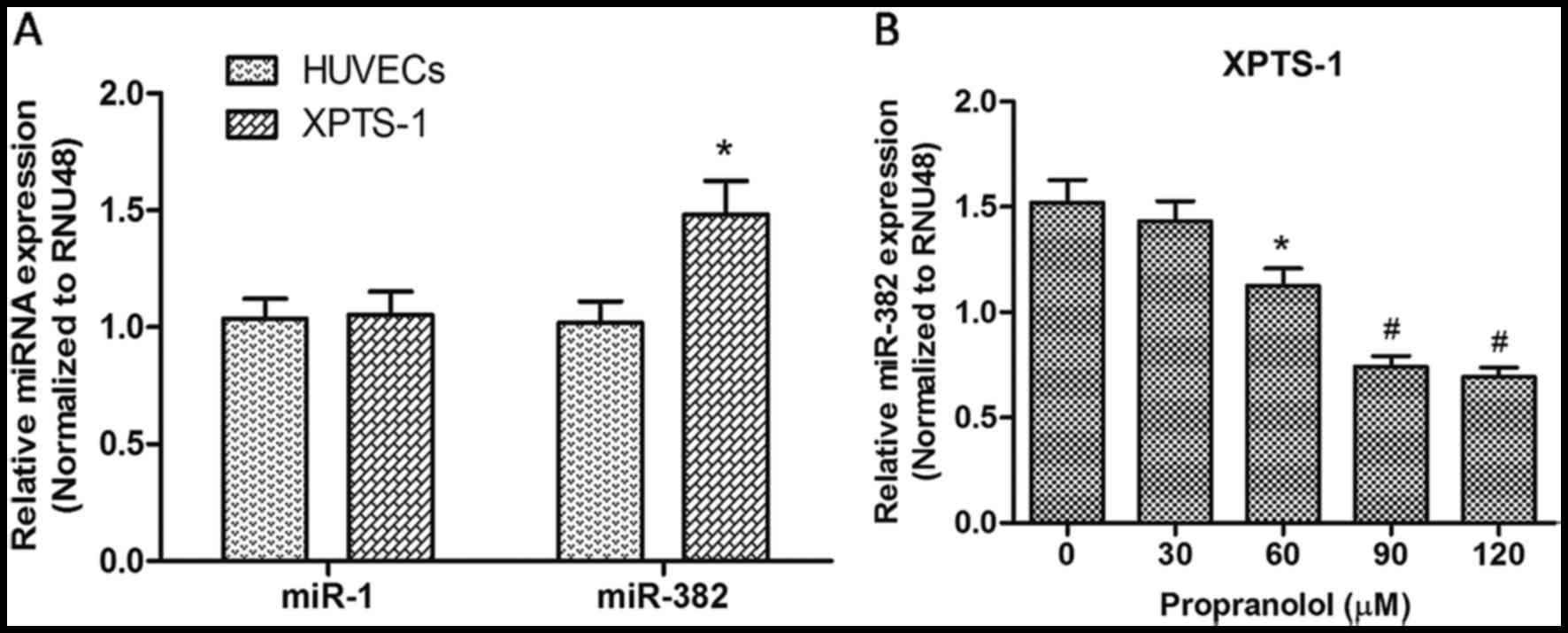
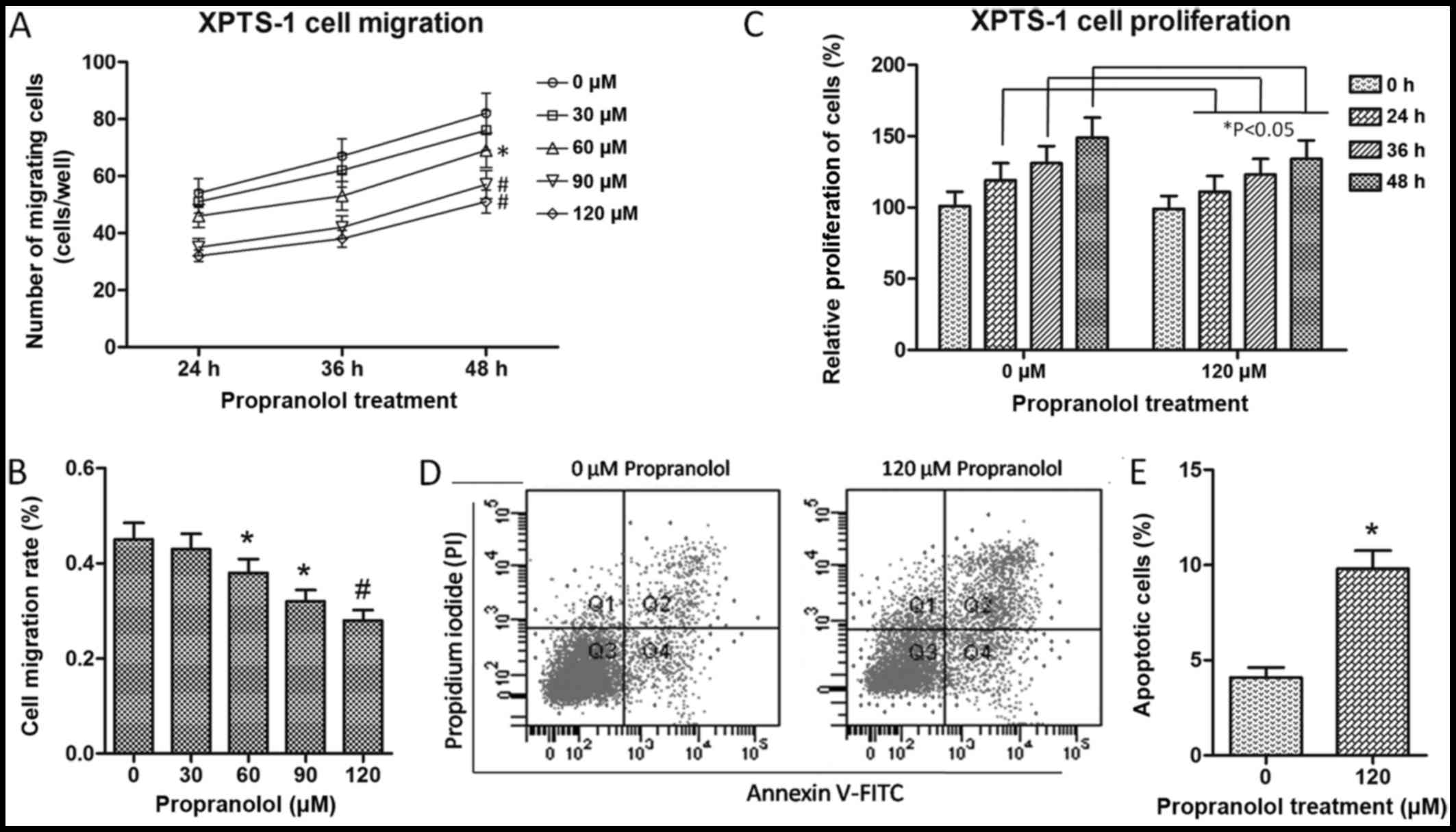
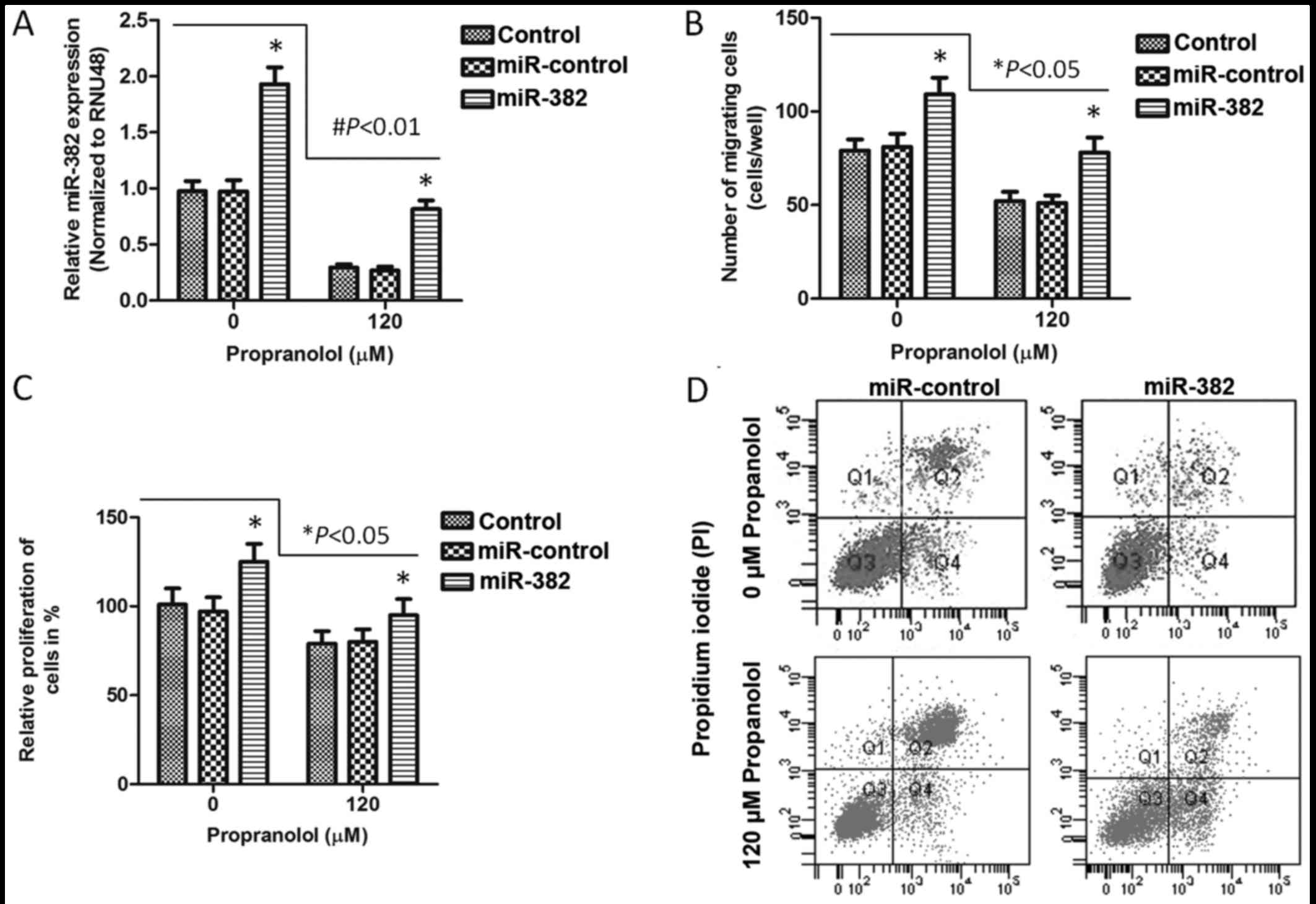
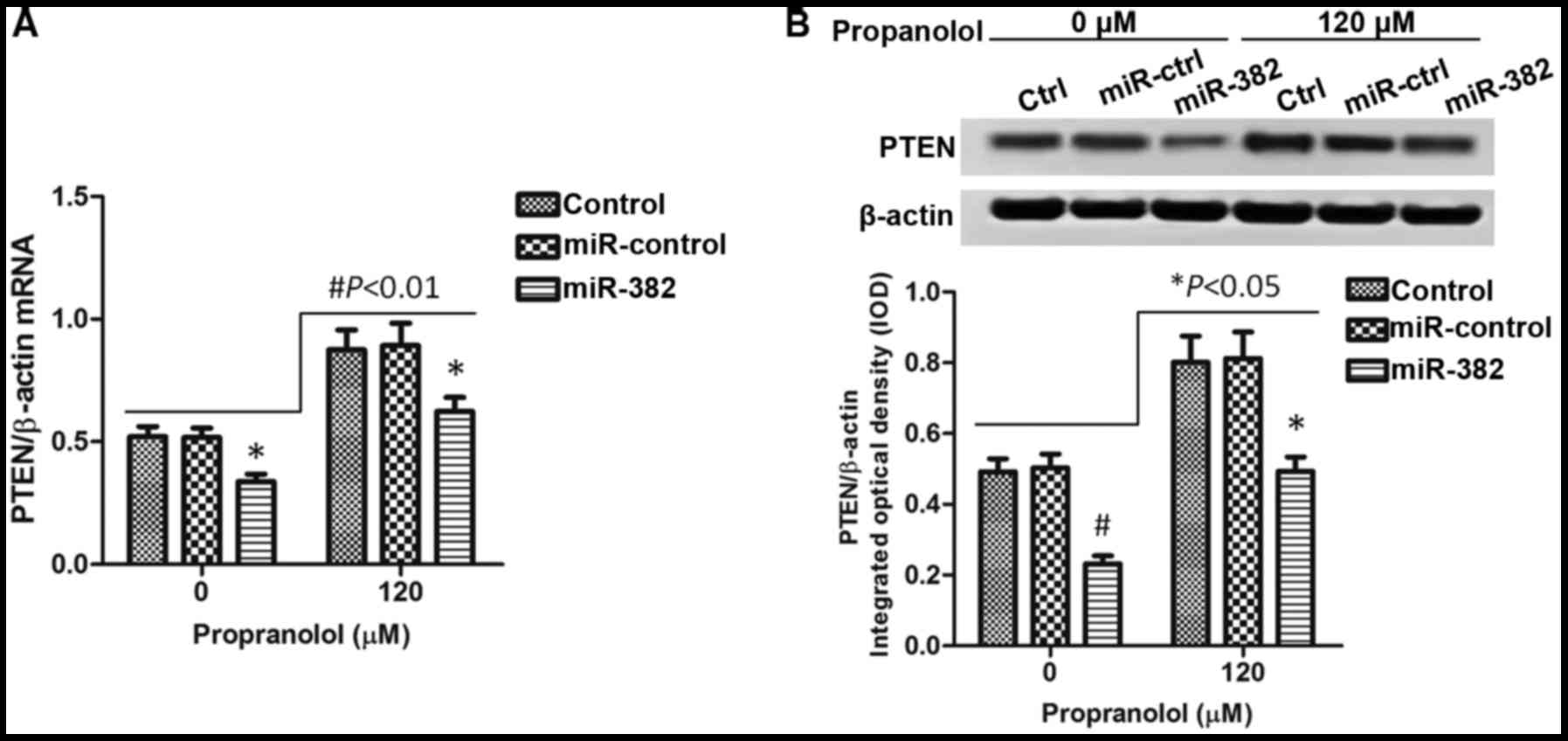
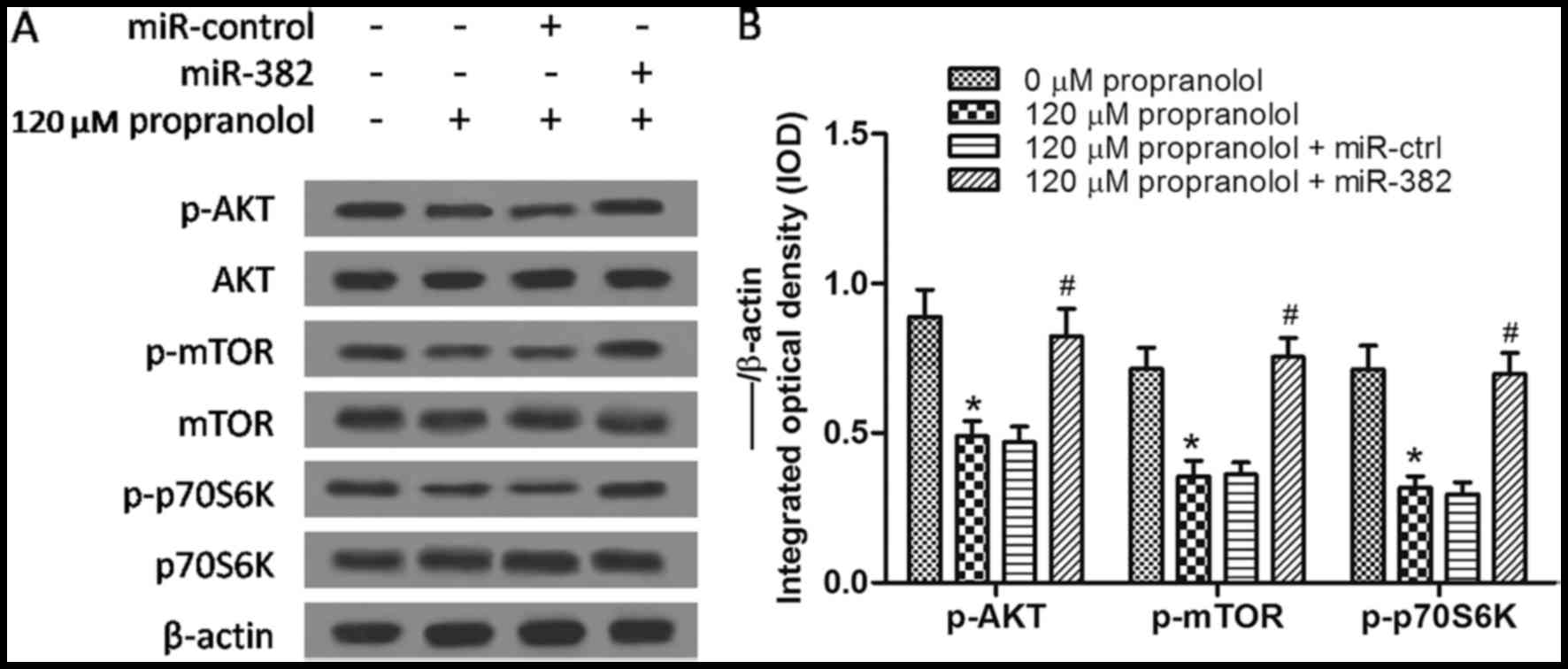
|
1
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Li L, Xu C and Xiang
B: Signaling pathways in the development of infantile hemangioma. J
Hematol Oncol. 7:132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yilmaz L, Dangoisse C and Semaille P:
Infantile hemangioma and propranolol: a therapeutic 'revolution'.
Literature review. Rev Med Brux. 3:4479–4484. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Mulliken JB, Fishman SJ and Burrows PE:
Vascular anomalies. Curr Probl Surg. 37:517–584. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Drolet BA, Esterly NB and Frieden IJ:
Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med. 341:173–181. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Margileth AM and Museles M: Cutaneous
hemangiomas in children. Diagnosis and conservative management.
JAMA. 194:523–526. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Xu C, Li L and Xiang B: The
use of propranolol in the treatment of infantile haemangiomas: an
update on potential mechanisms of action. Br J Dermatol. 172:24–32.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
England RW, Hardy KL, Kitajewski AM, Wong
A, Kitajewski JK, Shawber CJ and Wu JK: Propranolol promotes
accelerated and dysregulated adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells.
Ann Plast Surg. 73(Suppl 1): S119–S124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Laranjo S, Costa G, Paramés F, Freitas I,
Martins JD, Trigo C and Pinto FF: The role of propranolol in the
treatment of infantile hemangioma. Rev Port Cardiol. 33:289–295.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hou Y, Sun Y, Shan H, Li X, Zhang M, Zhou
X, Xing S, Sun H, Chu W, Qiao G and Lu Y: β-adrenoceptor regulates
miRNA expression in rat heart. Med Sci Monit. 18:BR309–BR314. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gaedcke J, Grade M, Camps J, Søkilde R,
Kaczkowski B, Schetter AJ, Difilippantonio MJ, Harris CC, Ghadimi
BM, Møller S, et al: The rectal cancer microRNAome - microRNA
expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:4919–4930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slattery ML, Wolff E, Hoffman MD, Pellatt
DF, Milash B and Wolff RK: MicroRNAs and colon and rectal cancer:
differential expression by tumor location and subtype. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 50:196–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Shan H, Pan Z, Li X, Li B,
Xu C, Zhang B, Zhang F, Dong D, et al: MicroRNA-1 downregulation by
propranolol in a rat model of myocardial infarction: a new
mechanism for ischaemic cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res.
84:434–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li P, Xiao XE, Xu Q and Guo ZT:
Establishment of human infancy hemangioma-derived endothelial cell
line XPTS-1 and animal model of human infancy hemangioma. Zhonghua
Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 46:129–133. 2011.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han L, Liang XH, Chen LX, Bao SM and Yan
ZQ: SIRT1 is highly expressed in brain metastasis tissues of
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and in positive regulation of
NSCLC cell migration. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:2357–2365.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seok JK, Lee SH, Kim MJ and Lee YM:
MicroRNA-382 induced by HIF-1α is an angiogenic miR targeting the
tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:8062–8072. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Snaddon J, Parkinson EK, Craft JA,
Bartholomew C and Fulton R: Detection of functional PTEN lipid
phosphatase protein and enzyme activity in squamous cell carcinomas
of the head and neck, despite loss of heterozygosity at this locus.
Br J Cancer. 84:1630–1634. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF and
Carnero A: PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis.
28:1379–1386. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haggstrom AN, Drolet BA, Baselga E,
Chamlin SL, Garzon MC, Horii KA, Lucky AW, Mancini AJ, Metry DW,
Newell B, et al: Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas:
clinical characteristics predicting complications and treatment.
Pediatrics. 118:882–887. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Léauté-Labrèze C, Dumas de la Roque E,
Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB and Taïeb A: Propranolol for
severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 358:2649–2651. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Drolet BA, Frommelt PC, Chamlin SL,
Haggstrom A, Bauman NM, Chiu YE, Chun RH, Garzon MC, Holland KE,
Liberman L, et al: Initiation and use of propranolol for infantile
hemangioma: report of a consensus conference. Pediatrics.
131:128–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li W, Xie L, He X, Li J, Tu K, Wei L, Wu
J, Guo Y, Ma X, Zhang P, et al: Diagnostic and prognostic
implications of microRNAs in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 123:1616–1622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abdin AA, Soliman NA and Saied EM: Effect
of propranolol on IL-10, visfatin, Hsp70, iNOS, TLR2, and survivin
in amelioration of tumor progression and survival in Solid Ehrlich
Carcinoma-bearing mice. Pharmacol Rep. 66:1114–1121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miquel J, Bruneau B and Dupuy A:
Successful treatment of multifocal intracerebral and spinal
hemangiomas with propranolol. J Am Acad Dermatol. 70:e83–e84. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto Y, Kounami S, Okuhira H, Nakamura
Y and Furukawa F: Successful treatment of tufted angioma with
propranolol. J Dermatol. 41:1120–1122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lamming DW, Ye L, Sabatini DM and Baur JA:
Rapalogs and mTOR inhibitors as anti-aging therapeutics. J Clin
Invest. 123:980–989. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Benjamin D, Colombi M, Moroni C and Hall
MN: Rapamycin passes the torch: a new generation of mTOR
inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:868–880. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Slomovitz BM and Coleman RL: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5856–5864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|