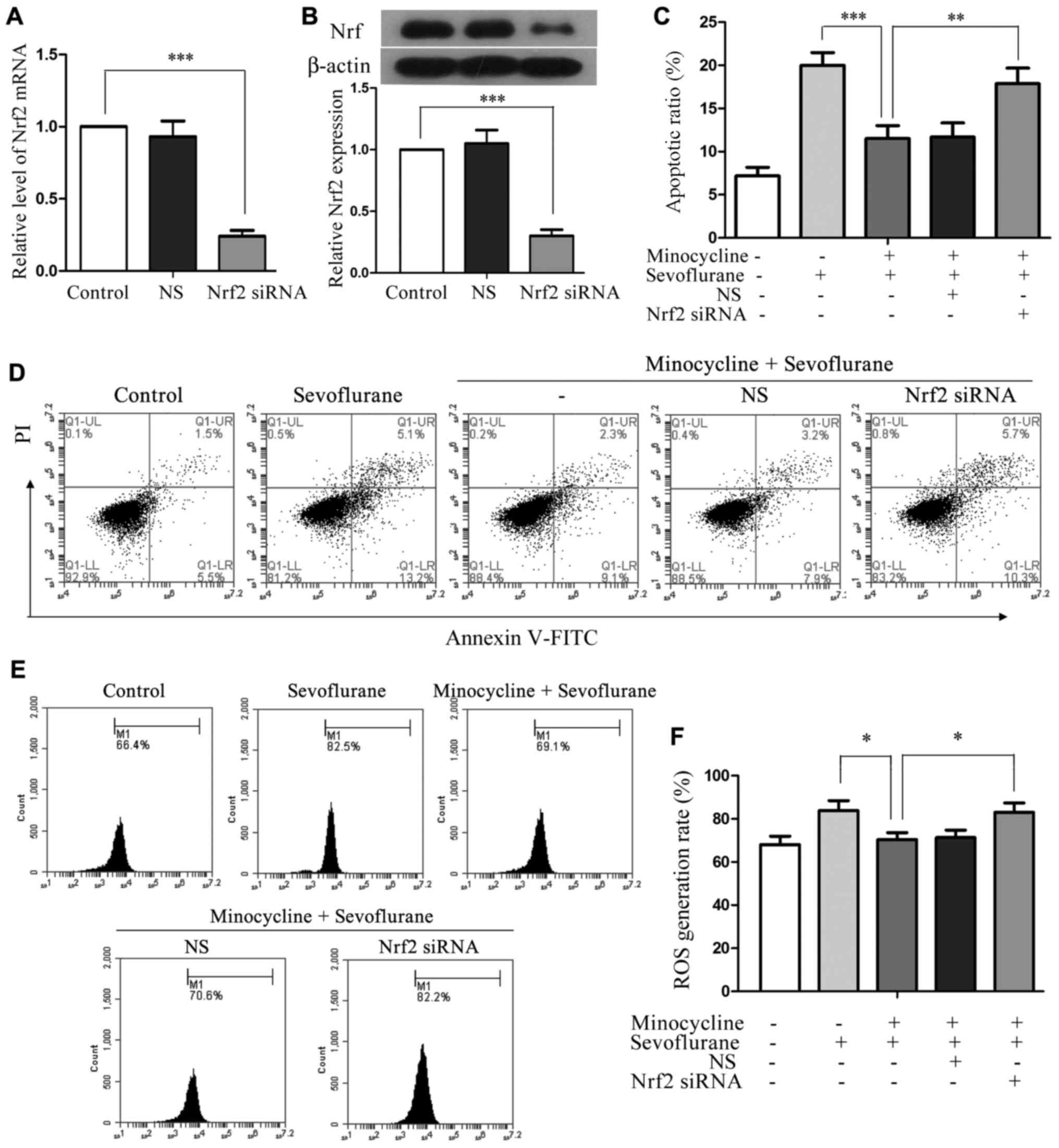
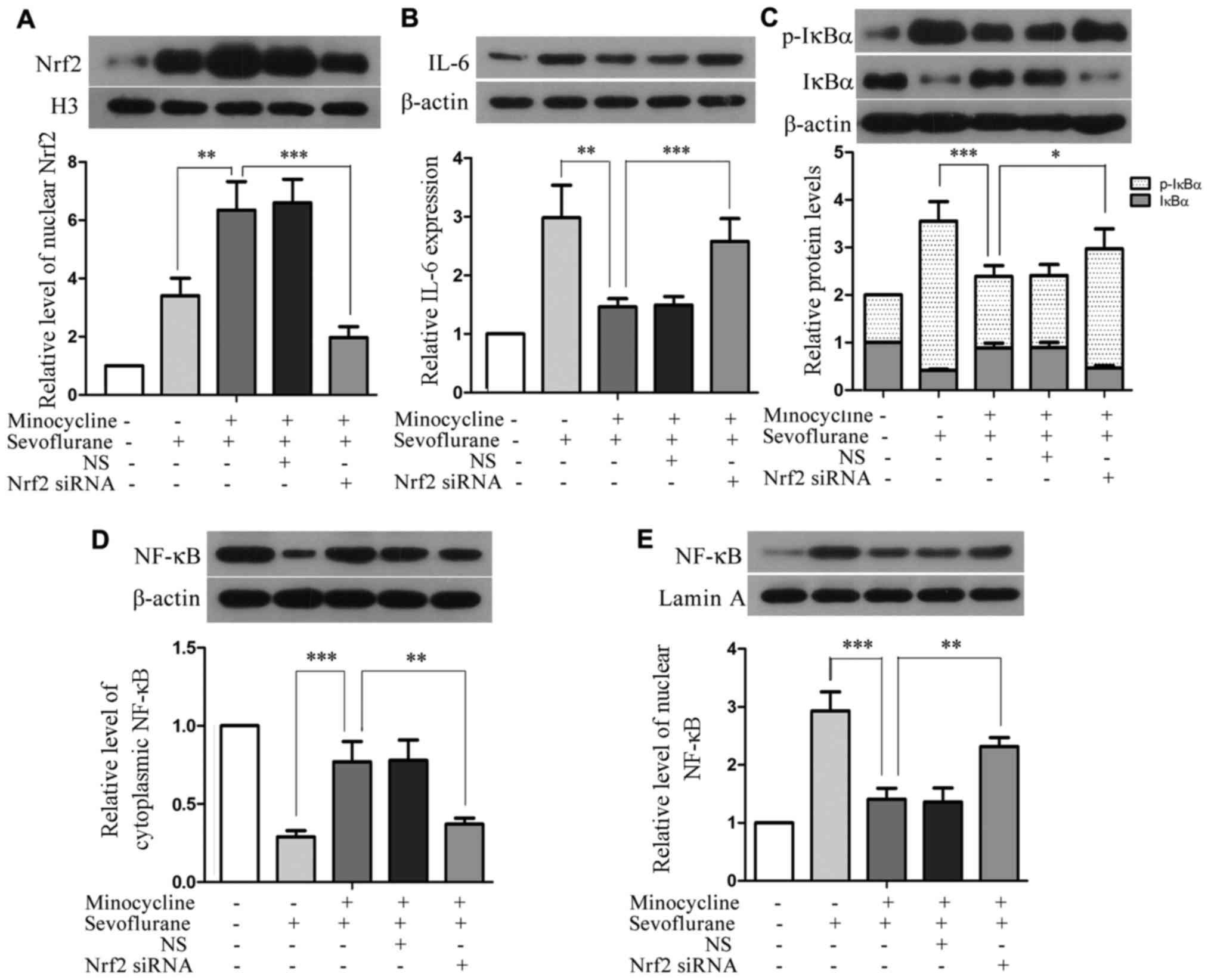
|
1
|
Bittner EA, Yue Y and Xie Z: Brief review:
anesthetic neurotoxicity in the elderly, cognitive dysfunction and
Alzheimer's disease. Can J Anaesth. 58:216–223. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Xiong WX, Zhou GX, Wang B, Xue ZG, Wang L,
Sun HC and Ge SJ: Impaired spatial learning and memory after
sevoflurane-nitrous oxide anesthesia in aged rats is associated
with down-regulated cAMP/CREB signaling. PLoS One. 8:e794082013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Zhang J, Yang L, Dong Y, Zhang Y
and Xie Z: Isoflurane and sevoflurane increase interleukin-6 levels
through the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in neuroglioma cells. Br
J Anaesth. 110(Suppl 1): i82–i91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang LP, Zhu XA and Tso MO: Minocycline
and sulforaphane inhibited lipopolysaccharide-mediated retinal
microglial activation. Mol Vis. 13:1083–1093. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi Y, Kim HS, Shin KY, Kim EM, Kim M,
Kim HS, Park CH, Jeong YH, Yoo J, Lee JP, et al: Minocycline
attenuates neuronal cell death and improves cognitive impairment in
Alzheimer's disease models. Neuropsychopharmacology. 32:2393–2404.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yrjänheikki J, Tikka T, Keinänen R,
Goldsteins G, Chan PH and Koistinaho J: A tetracycline derivative,
minocycline, reduces inflammation and protects against focal
cerebral ischemia with a wide therapeutic window. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:13496–13500. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Desjarlais M, Pratt J, Lounis A, Mounier
C, Haidara K and Annabi B: Tetracycline derivative minocycline
inhibits autophagy and inflammation in concanavalin-a-activated
human hepatoma cells. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 8:63–73. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoon SY, Patel D and Dougherty PM:
Minocycline blocks lipopolysaccharide induced hyperalgesia by
suppression of microglia but not astrocytes. Neuroscience.
221:214–224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuang X, Scofield VL, Yan M, Stoica G, Liu
N and Wong PK: Attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and
apoptosis by minocycline prevents retrovirus-induced
neurodegeneration in mice. Brain Res. 1286:174–184. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian Y, Guo S, Wu X, Ma L and Zhao X:
Minocycline alleviates sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in
aged rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:585–594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishii T, Itoh K, Takahashi S, Sato H,
Yanagawa T, Katoh Y, Bannai S and Yamamoto M: Transcription factor
Nrf2 coordinately regulates a group of oxidative stress-inducible
genes in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 275:16023–16029. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lyu JH, Kim KH, Kim HW, Cho SI, Ha KT,
Choi JY, Han CW, Jeong HS, Lee HK, Ahn KS, et al: Dangkwisoo-san,
an herbal medicinal formula, ameliorates acute lung inflammation
via activation of Nrf2 and suppression of NF-kappaB. J
Ethnopharmacol. 140:107–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cuadrado A, Martín-Moldes Z, Ye J and
Lastres-Becker I: Transcription factors NRF2 and NF-kappaB are
coordinated effectors of the Rho family, GTP-binding protein RAC1
during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 289:15244–15258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mahmoud-Awny M, Attia AS, Abd-Ellah MF and
El-Abhar HS: Mangiferin mitigates gastric ulcer in
ischemia/reperfused rats: involvement of PPAR-gamma, NF-kappaB and
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. PLoS One. 10:e01324972015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Franks NP and Lieb WR: Temperature
dependence of the potency of volatile general anesthetics:
implications for in vitro experiments. Anesthesiology. 84:716–720.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jacobson MD: Reactive oxygen species and
programmed cell death. Trends Biochem Sci. 21:83–86. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Heo K, Cho YJ, Cho KJ, Kim HW, Kim HJ,
Shin HY, Lee BI and Kim GW: Minocycline inhibits caspase-dependent
and -independent cell death pathways and is neuroprotective against
hippocampal damage after treatment with kainic acid in mice.
Neurosci Lett. 398:195–200. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Wei Q, Wang CY, Hill WD, Hess DC
and Dong Z: Minocycline up-regulates Bcl-2 and protects against
cell death in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 279:19948–19954. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang C, Li R, Zeng Q, Ding Y, Zou Y, Mao
X, Hu W, Xiong R and Li M: Effect of minocycline postconditioning
and ischemic postconditioning on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury in atherosclerosis rabbits. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog
Med Sci. 32:524–529. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen M, Ona VO, Li M, Ferrante RJ, Fink
KB, Zhu S, Bian J, Guo L, Farrell LA, Hersch SM, et al: Minocycline
inhibits caspase-1 and caspase-3 expression and delays mortality in
a transgenic mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat Med. 6:797–801.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang BP, Le L, Xu LJ and Xiao PG:
Minocycline inhibits ICAD degradation and the NF-kappaB activation
induced by 6-OHDA in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 1586:1–11. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmitz T, Endesfelder S, Chew LJ, Zaak I
and Bührer C: Minocycline protects oligodendroglial precursor cells
against injury caused by oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Neurosci
Res. 90:933–944. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sakon S, Xue X, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T,
Okazaki T, Kojima Y, Piao JH, Yagita H, Okumura K, Doi T, et al:
NF-kappaB inhibits TNF-induced accumulation of ROS that mediate
prolonged MAPK activation and necrotic cell death. EMBO J.
22:3898–3909. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao W, Hodge DR, Wang L, Yang X, Zhang X
and Farrar WL: Co-operative functions between nuclear factors
NF-kappaB and CCAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta (C/EBP-beta)
regulate the IL-6 promoter in autocrine human prostate cancer
cells. Prostate. 61:354–370. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dutta J, Fan Y, Gupta N, Fan G and Gélinas
C: Current insights into the regulation of programmed cell death by
NF-kappaB. Oncogene. 25:6800–6816. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakano H, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S,
Piao JH, Xue X and Okumura K: Reactive oxygen species mediate
crosstalk between NF-kappaB and JNK. Cell Death Differ. 13:730–737.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|