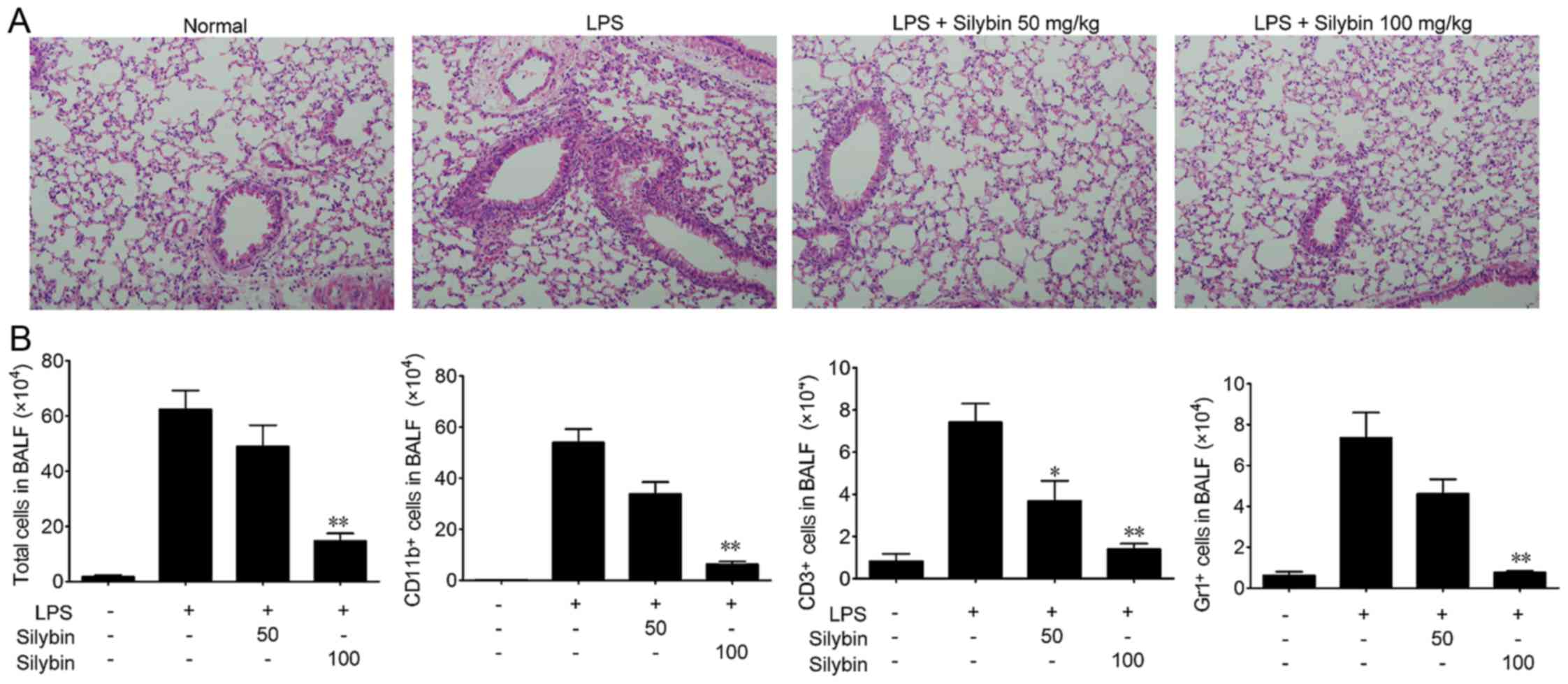
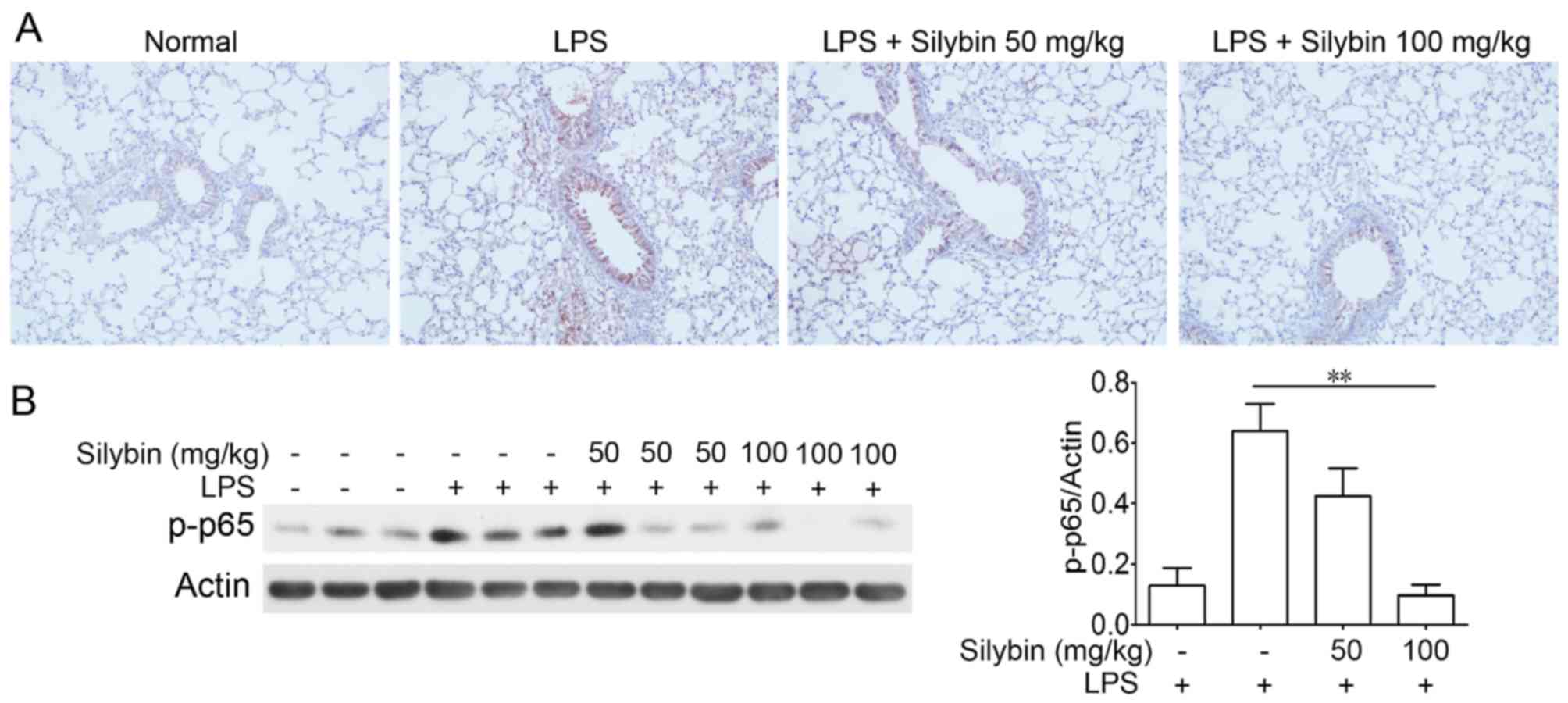
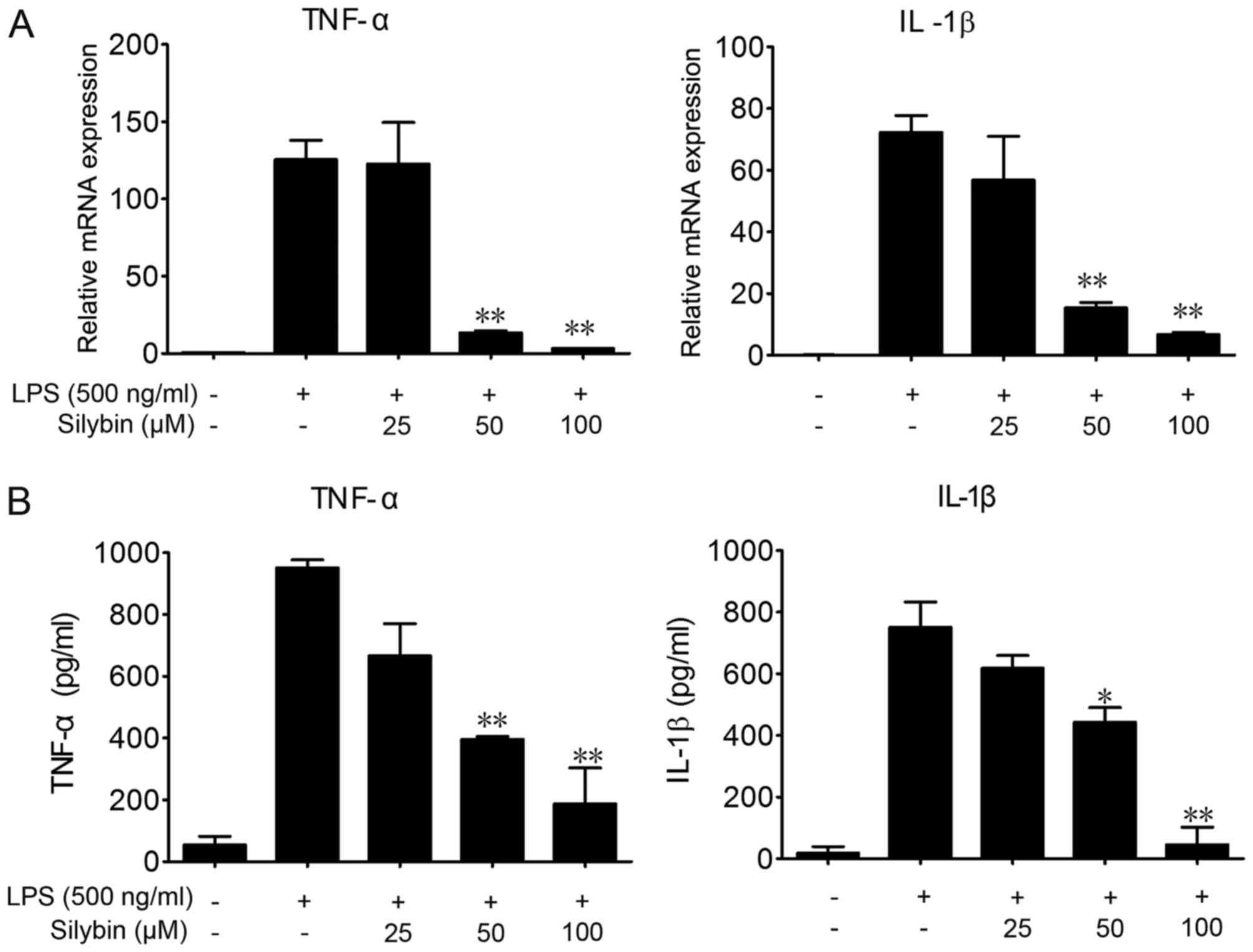
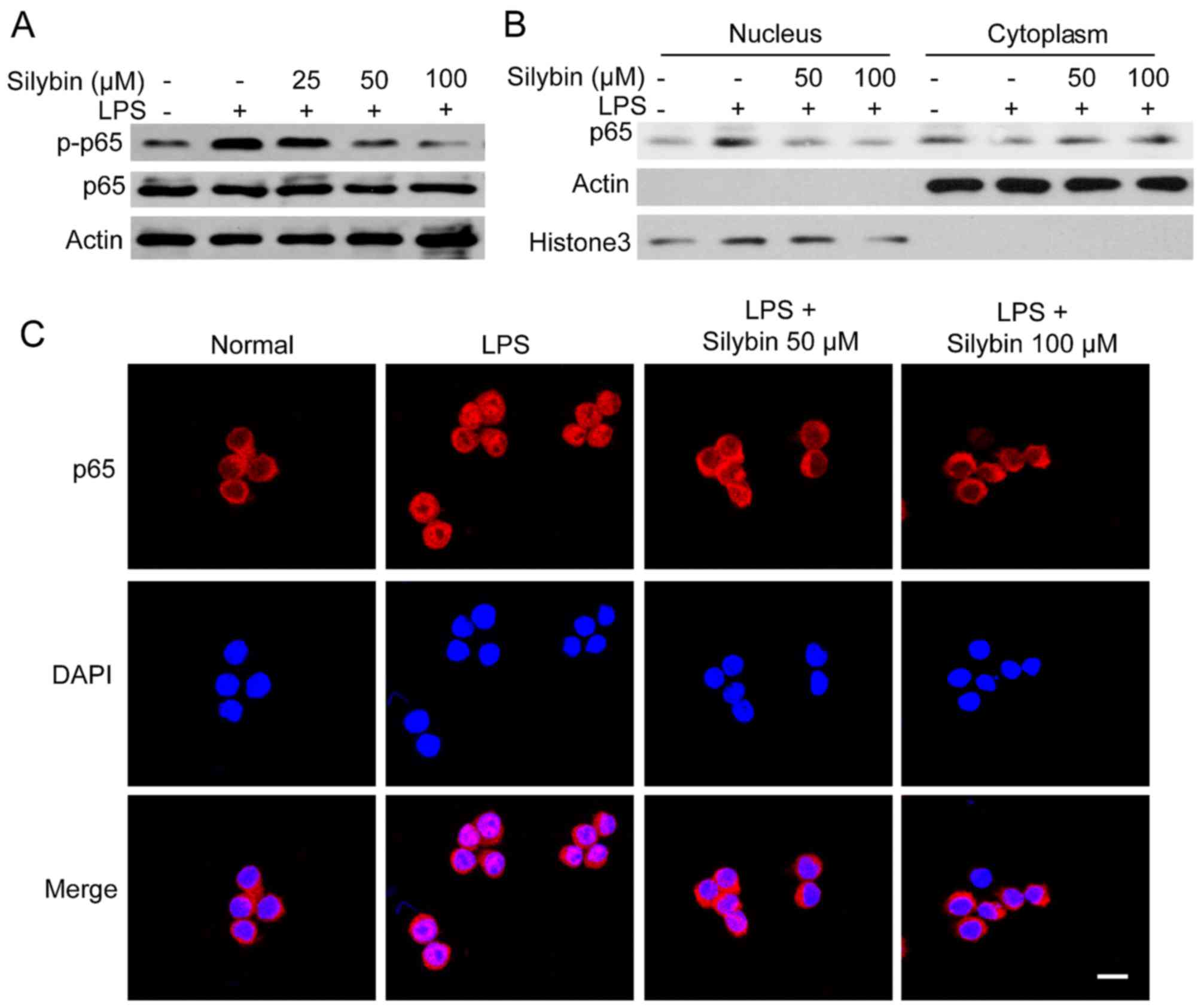
|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Study 2013
Collaborators: Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and
chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.
Lancet. 386:743–800. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Han S and Mallampalli RK: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome: From mechanism to translation. J
Immunol. 194:855–860. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sadowitz B, Roy S, Gatto LA, Habashi N and
Nieman G: Lung injury induced by sepsis: lessons learned from large
animal models and future directions for treatment. Expert Rev Anti
Infect Ther. 9:1169–1178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson ER and Matthay MA: Acute lung
injury: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med
Pulm Drug Deliv. 23:243–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sweeney RM, Griffiths M and McAuley D:
Treatment of acute lung injury: current and emerging
pharmacological therapies. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 34:487–498.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gekara NO, Dietrich N, Lyszkiewicz M,
Lienenklaus S and Weiss S: Signals triggered by a bacterial
pore-forming toxin contribute to toll-like receptor redundancy in
gram-positive bacterial recognition. J Infect Dis. 199:124–133.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jin LY, Li CF, Zhu GF, Wu CT, Wang J and
Yan SF: Effect of siRNA against NF-kappaB on sepsisinduced acute
lung injury in a mouse model. Mol Med Rep. 10:631–637.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu T, Wang DX, Zhang W, Liao X, Guan X,
Bo H, Sun J, Huang N, He J, Zhang Y, et al: Andrographolide
protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inactivation of
NF-kappaB. PLoS One. 8:e564072013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xiao M, Zhu T, Zhang W, Wang T, Shen YC,
Wan QF and Wen FQ: Emodin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung
injury, involving the inactivation of NF-kappaB in mice. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:19355–19368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Yang X, Liu T, Guan M, Feng X,
Dong W, Chu X, Liu J, Tian X, Ci X, et al: Kaempferol regulates
MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways to attenuate LPS-induced
acute lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:209–216. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rahman A and Fazal F: Blocking NF-kappaB:
An inflammatory issue. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 8:497–503. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Elliott EI and Sutterwala FS: Initiation
and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly.
Immunol Rev. 265:35–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Besnard AG, Guillou N, Tschopp J, Erard F,
Couillin I, Iwakura Y, Quesniaux V, Ryffel B and Togbe D: NLRP3
inflammasome is required in murine asthma in the absence of
aluminum adjuvant. Allergy. 66:1047–1057. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sohn SH, Lee JM, Park S, Yoo H, Kang JW,
Shin D, Jung KH, Lee YS, Cho J and Bae H: The inflammasome
accelerates radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in
mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 39:917–926. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Birrell MA and Eltom S: The role of the
NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of airway disease. Pharmacol
Ther. 130:364–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jia R, Cao L, Du J, Xu P, Jeney G and Yin
G: The protective effect of silymarin on the carbon tetrachloride
(CCl4)-induced liver injury in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 49:155–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sozmen M, Devrim AK, Tunca R, Bayezit M,
Dag S and Essiz D: Protective effects of silymarin on fumonisin B1
induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Vet Sci. 15:51–60. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Schumann J, Prockl J, Kiemer AK, Vollmar
AM, Bang R and Tiegs G: Silibinin protects mice from T
cell-dependent liver injury. J Hepatol. 39:333–340. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tzeng JI, Chen MF, Chung HH and Cheng JT:
Silymarin decreases connective tissue growth factor to improve
liver fibrosis in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. Phytother
Res. 27:1023–1028. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Khan AQ, Khan R, Tahir M, Rehman MU,
Lateef A, Ali F, Hamiza OO, Hasan SK and Sultana S: Silibinin
inhibits tumor promotional triggers and tumorigenesis against
chemically induced two-stage skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino
mice: Possible role of oxidative stress and inflammation. Nutr
Cancer. 66:249–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim BR, Seo HS, Ku JM, Kim G-J, Jeon CY,
Park JH, Jang BH, Park SJ, Shin YC and Ko SG: Silibinin inhibits
the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of
NF-kappaB signaling pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells. Inflamm Res.
62:941–950. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi YH, Jin GY, Guo HS, Piao HM, Li L, Li
GZ, Lin ZH and Yan GH: Silibinin attenuates allergic airway
inflammation in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 427:450–455.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuo FH and Jan TR: Silibinin attenuates
antigen-specific IgE production through the modulation of Th1/Th2
balance in ovalbumin-sensitized BALB/c mice. Phytomedicine.
16:271–276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Schroder K and Tschopp J: The
Inflammasomes. Cell. 140:821–832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sutterwala FS, Ogura Y, Szczepanik M,
Lara-Tejero M, Lichtenberger GS, Grant EP, Bertin J, Coyle AJ,
Galán JE, Askenase PW, et al: Critical role for
NALP3/CIAS1/Cryopyrin in innate and adaptive immunity through its
regulation of caspase-1. Immunity. 24:317–327. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sorbara MT and Girardin SE: Mitochondrial
ROS fuel the inflammasome. Cell Res. 21:558–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jangra A, Kasbe P, Pandey SN, Dwivedi S,
Gurjar SS, Kwatra M, Mishra M, Venu AK, Sulakhiya K, Gogoi R, et
al: Hesperidin and silibinin ameliorate aluminum-induced
neurotoxicity: modulation of antioxidants and inflammatory
cytokines level in mice hippocampus. Biol Trace Elem Res.
168:462–471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan WJ, Tan YC, Xu JC, Tang XP, Zhang C,
Zhang PB and Ren ZQ: Protective effects of silibinin and its
possible mechanism of action in mice exposed to chronic
unpredictable mild stress. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 23:245–250. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Duan S, Guan X, Lin R, Liu X, Yan Y, Lin
R, Zhang T, Chen X, Huang J, Sun X, et al: Silibinin inhibits
acetylcholinesterase activity and amyloid beta peptide aggregation:
A dual-target drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 36:1792–1807. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raghu R, Jesudas B, Bhavani G, Ezhilarasan
D and Karthikeyan S: Silibinin mitigates zidovudine-induced
hepatocellular degenerative changes, oxidative stress and
hyperlipidaemia in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 34:1031–1042. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Braun DL, Rauch A, Aouri M, Durisch N,
Eberhard N, Anagnostopoulos A, Ledergerber B, Müllhaupt B, Metzner
KJ, Decosterd L, et al: A lead-in with silibinin prior to
triple-therapy translates into favorable treatment outcomes in
difficult-to-treat HIV/hepatitis C coinfected patients. PLoS One.
10:e01330282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheung CWY, Gibbons N, Johnson DW and
Nicol DL: Silibinin - A promising new treatment for cancer.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 10:186–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Momeny M, Malehmir M, Zakidizaji M,
Ghasemi R, Ghadimi H, Shokrgozar MA, Emami AH, Nafissi S,
Ghavamzadeh A and Ghaffari SH: Silibinin inhibits invasive
properties of human glioblastoma U87MG cells through suppression of
cathepsin B and nuclear factor kappa B-mediated induction of matrix
metalloproteinase 9. Anticancer Drugs. 21:252–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li L, Zeng J, Gao Y and He DL: Targeting
silibinin in the antiproliferative pathway. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 19:243–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hakansson HF, Smailagic A, Brunmark C,
Miller-Larsson A and Lal H: Altered lung function relates to
inflammation in an acute LPS mouse model. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
25:399–406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mouratis MA, Magkrioti C, Oikonomou N,
Katsifa A, Prestwich GD, Kaffe E and Aidinis V: Autotaxin and
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. PLoS One. 10:e01336192015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
No authors listed. Ventilation with lower
tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. N Engl J Med. 342:1301–1308.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
McKenna S and Wright CJ: Inhibiting
IkappaBbeta-NFkappaB signaling attenuates the expression of select
pro-inflammatory genes. J Cell Sci. 128:2143–2155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee IT and Yang CM: Inflammatory
signalings involved in airway and pulmonary diseases. Mediators
Inflamm. 2013:7912312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alvira CM: Nuclear factor-kappa-B
signaling in lung development and disease: One pathway, numerous
functions. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 100:202–216. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Petrilli V, Papin S and Tschopp J: The
inflammasome. Curr Biol. 15:R5812005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wen H, Ting JP and O'Neill LA: A role for
the NLRP3 inflammasome in metabolic diseases - did Warburg miss
inflammation? Nat Immunol. 13:352–357. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shaw PJ, McDermott MF and Kanneganti TD:
Inflammasomes and autoimmunity. Trends Mol Med. 17:57–64. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
45
|
Martinon F: Signaling by ROS drives
inflammasome activation. Eur J Immunol. 40:616–619. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|