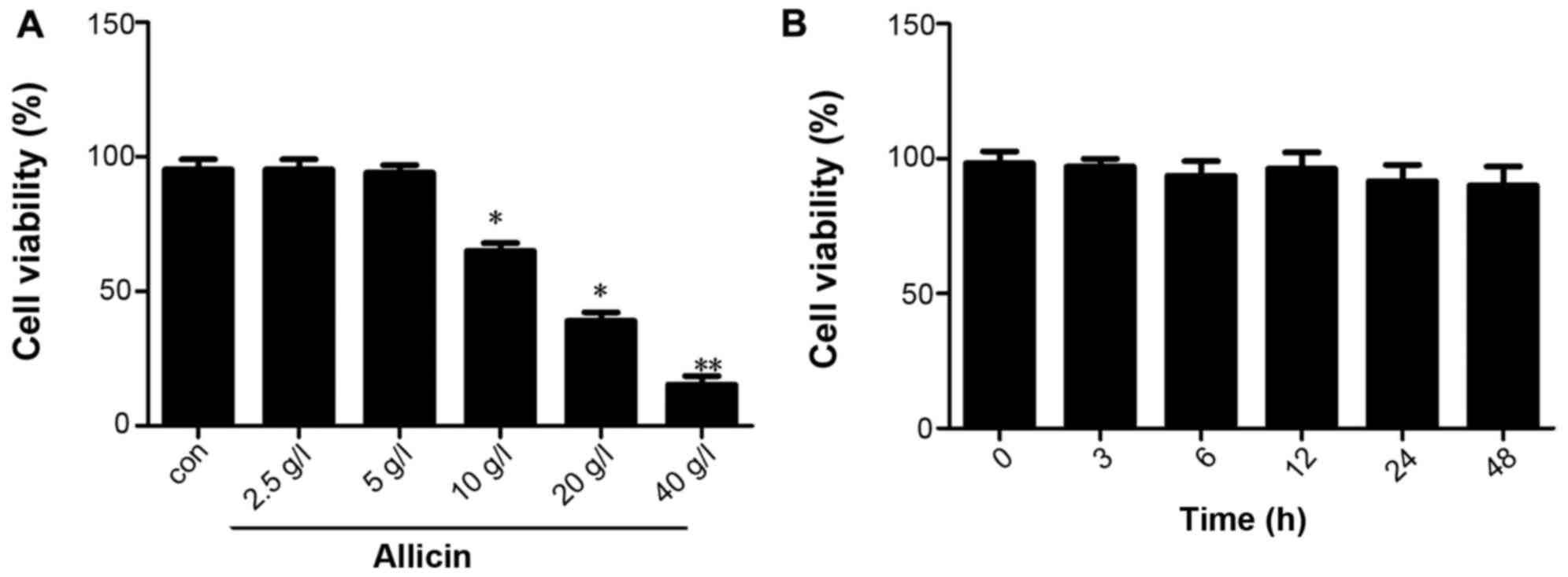
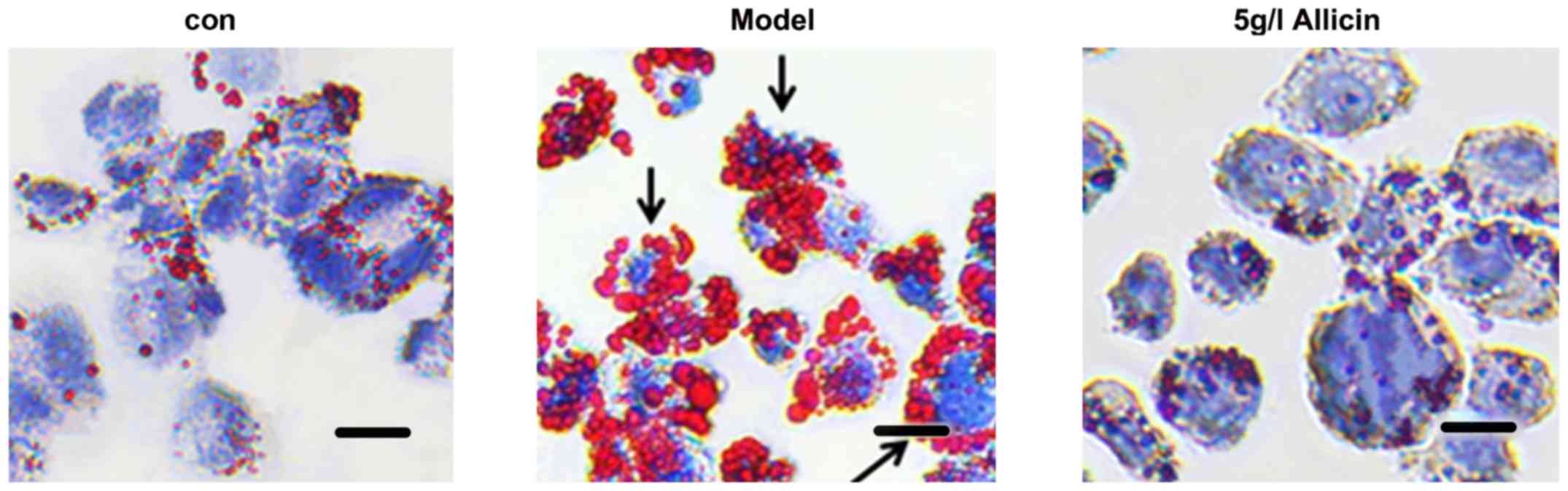
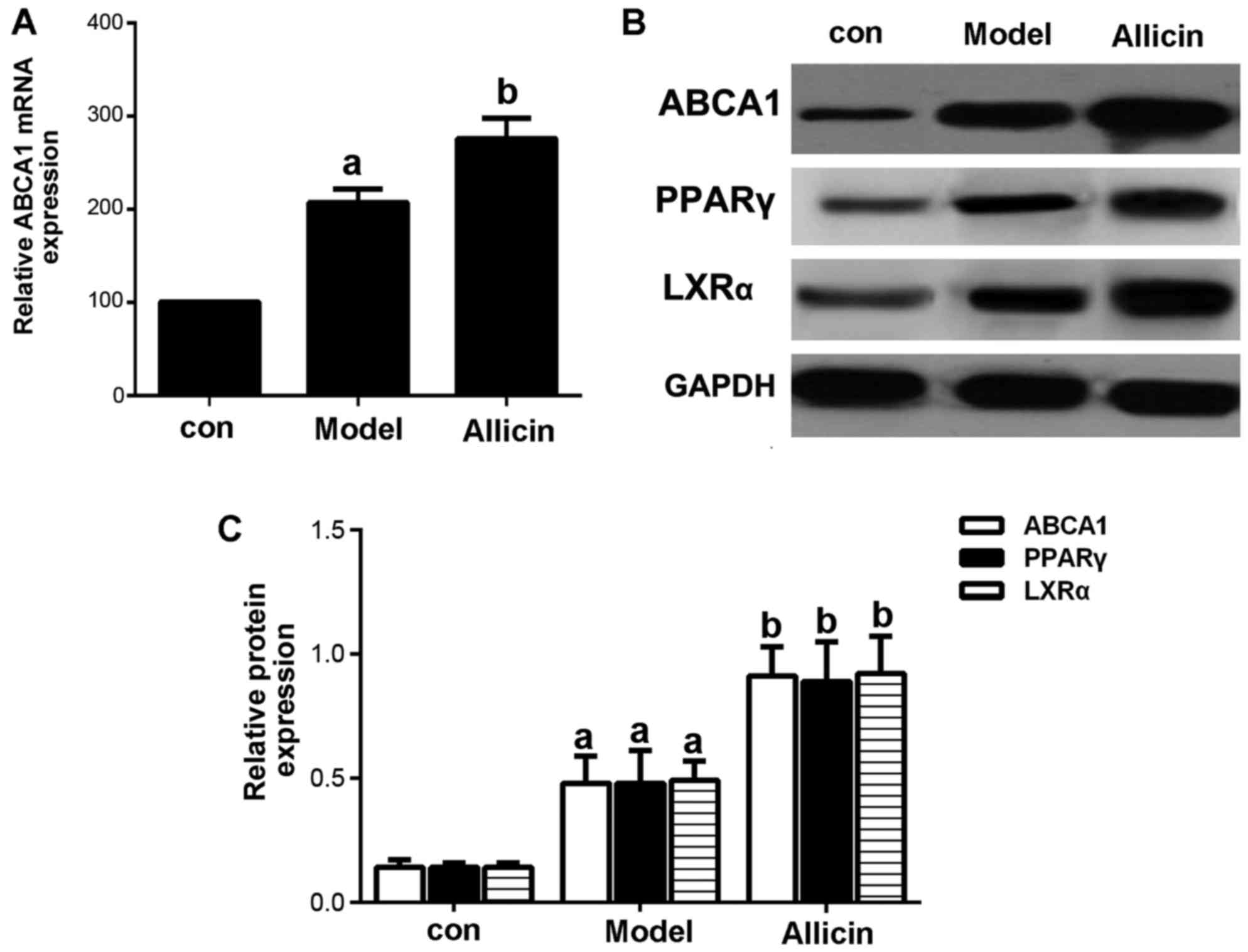
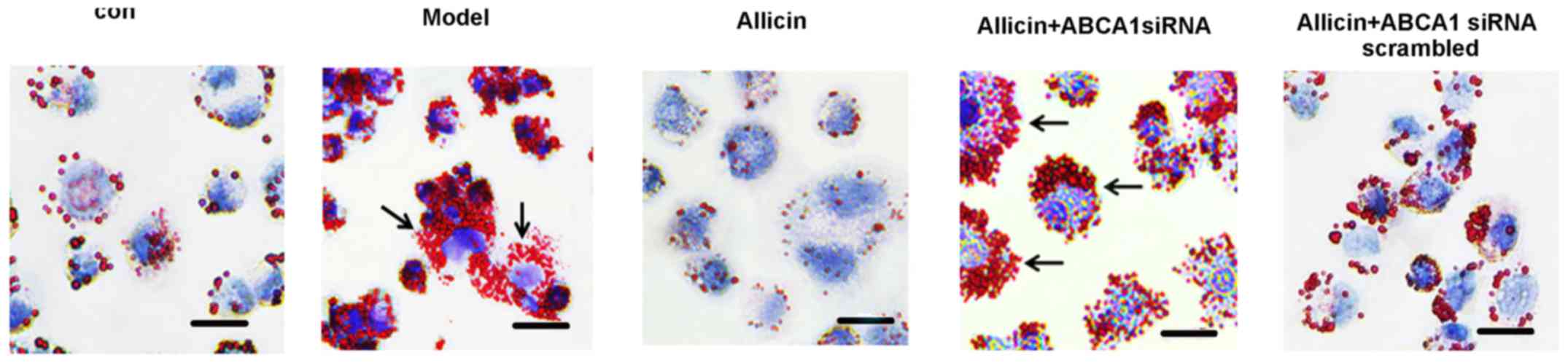
|
1
|
Zeller I and Srivastava S: Macrophage
functions in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 115:e83–e85. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu XH, Fu YC, Zhang DW, Yin K and Tang CK:
Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 424:245–252. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Westerterp M, Bochem AE, Yvan-Charvet L,
Murphy AJ, Wang N and Tall AR: ATP-binding cassette transporters,
atherosclerosis, and inflammation. Circ Res. 114:157–170. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heinecke JW: Small HDL promotes
cholesterol efflux by the ABCA1 pathway in macrophages:
Implications for therapies targeted to HDL. Circ Res.
116:1101–1103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Negi SI, Brautbar A, Virani SS, Anand A,
Polisecki E, Asztalos BF, Ballantyne CM, Schaefer EJ and Jones PH:
A novel mutation in the ABCA1 gene causing an atypical phenotype of
Tangier disease. J Clin Lipidol. 7:82–87. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pervaiz MA, Gau G, Jaffe AS, Saenger AK,
Baudhuin L and Ellison J: A Non-classical presentation of tangier
disease with three ABCA1 mutations. JIMD Rep. 4:109–111. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fitzgerald ML, Mujawar Z and Tamehiro N:
ABC transporters, atherosclerosis and inflammation.
Atherosclerosis. 211:361–370. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang CX and Zhang YL: The target of
regulating the ATP-binding cassette A1 protein (ABCA1): Promoting
ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux in different cells. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 14:623–631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chinetti G, Lestavel S, Bocher V, Remaley
AT, Neve B, Torra IP, Teissier E, Minnich A, Jaye M, Duverger N, et
al: PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma activators induce cholesterol removal
from human macrophage foam cells through stimulation of the ABCA1
pathway. Nat Med. 7:53–58. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schmitz G and Langmann T: Transcriptional
regulatory networks in lipid metabolism control ABCA1 expression.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1735:1–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC,
Nwachukwu ID and Slusarenko AJ: Allicin: Chemistry and biological
properties. Molecules. 19:12591–12618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen S, Tang Y, Qian Y, Chen R, Zhang L,
Wo L and Chai H: Allicin prevents
H2O2-induced apoptosis of HUVECs by
inhibiting an oxidative stress pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:321–329. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sung J, Harfouche Y, De La Cruz M, Zamora
MP, Liu Y, Rego JA and Buckley NE: Garlic (Allium sativum)
stimulates lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha
production from J774A.1 murine macrophages. Phytother Res.
29:288–294. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gonen A, Harats D, Rabinkov A, Miron T,
Mirelman D, Wilchek M, Weiner L, Ulman E, Levkovitz H, Ben-Shushan
D, et al: The antiatherogenic effect of allicin: Possible mode of
action. Pathobiology. 72:325–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lin XL, Liu MH, Hu HJ, Feng HR, Fan XJ,
Zou WW, Pan YQ, Hu XM and Wang Z: Curcumin enhanced cholesterol
efflux by upregulating ABCA1 expression through AMPK-SIRT1-LXRα
signaling in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. DNA Cell Biol.
34:561–572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin X, Freeman SR, Vaisman B, Liu Y, Chang
J, Varsano N, Addadi L, Remaley A and Kruth HS: ABCA1 contributes
to macrophage deposition of extracellular cholesterol. J Lipid Res.
56:1720–1726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mo SJ, Son EW, Rhee DK and Pyo S:
Modulation of TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression, NO and
H2O2 production by alginate, allicin and
ascorbic acid in human endothelial cells. Arch Pharm Res.
26:244–251. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li RK, Li JF, Zhou XR, Yin M, Zhang L and
Pan J: Effects of allicin on plasma lipid metabolism of
atherosclerotic mice. Chin J Clin (Electronic Version). 1:29–33.
2007.
|
|
19
|
Li C, Lun W, Zhao X, Lei S, Guo Y, Ma J
and Zhi F: Allicin alleviates inflammation of
trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced rats and suppresses p38 and
JNK pathways in Caco-2 cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2015:4346922015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu X, Li Q, Pang L, Huang G, Huang J, Shi
M, Sun X and Wang Y: Arctigenin promotes cholesterol efflux from
THP-1 macrophages through PPAR-γ/LXR-α signaling pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 441:321–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu XY, Lu Q, Ouyang XP, Tang SL, Zhao GJ,
Lv YC, He PP, Kuang HJ, Tang YY, Fu Y, et al: Apelin-13 increases
expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 via activating
protein kinase C α signaling in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam
cells. Atherosclerosis. 226:398–407. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Westerterp M, Murphy AJ, Wang M, Pagler
TA, Vengrenyuk Y, Kappus MS, Gorman DJ, Nagareddy PR, Zhu X,
Abramowicz S, et al: Deficiency of ATP-binding cassette
transporters A1 and G1 in macrophages increases inflammation and
accelerates atherosclerosis in mice. Circ Res. 112:1456–1465. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He Y, Zhang L, Li Z, Gao H, Yue Z, Liu Z,
Liu X, Feng X and Liu P: RIP140 triggers foam-cell formation by
repressing ABCA1/G1 expression and cholesterol efflux via liver X
receptor. FEBS Lett. 589:455–460. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Baron M, Bouhlel MA,
Vanhoutte J, Copin C, Sebti Y, Derudas B, Mayi T, Bories G,
Tailleux A, et al: Human atherosclerotic plaque alternative
macrophages display low cholesterol handling but high phagocytosis
because of distinct activities of the PPARγ and LXRα pathways. Circ
Res. 108:985–995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen SG, Xiao J, Liu XH, Liu MM, Mo ZC,
Yin K, Zhao GJ, Jiang J, Cui LB, Tan CZ, et al: Ibrolipim increases
ABCA1/G1 expression by the LXRα signaling pathway in THP-1
macrophage-derived foam cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:1343–1349.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kappus MS, Murphy AJ, Abramowicz S, Ntonga
V, Welch CL, Tall AR and Westerterp M: Activation of liver X
receptor decreases atherosclerosis in Ldlr−/− mice in
the absence of ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1 in
myeloid cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:279–284. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ma AZ, Song ZY and Zhang Q: Cholesterol
efflux is LXRα isoform-dependent in human macrophages. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 14:802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Parikh M, Patel K, Soni S and Gandhi T:
Liver X receptor: A cardinal target for atherosclerosis and beyond.
J Atheroscler Thromb. 21:519–531. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Monsalve FA, Pyarasani RD, Delgado-Lopez F
and Moore-Carrasco R: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:5496272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng X, Liu X, Song L, He Y, Li X and
Zhang H: Atorvastatin inhibits macrophage-derived foam cell
formation by suppressing the activation of PPARγ and NF-κB pathway.
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 34:896–900. 2014.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baranowski M, Blachnio-Zabielska AU,
Zabielski P, Harasim E, Harasiuk D, Chabowski A and Gorski J: Liver
X receptor agonist T0901317 enhanced peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-delta expression and fatty acid
oxidation in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol Pharmacol. 64:289–297.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|