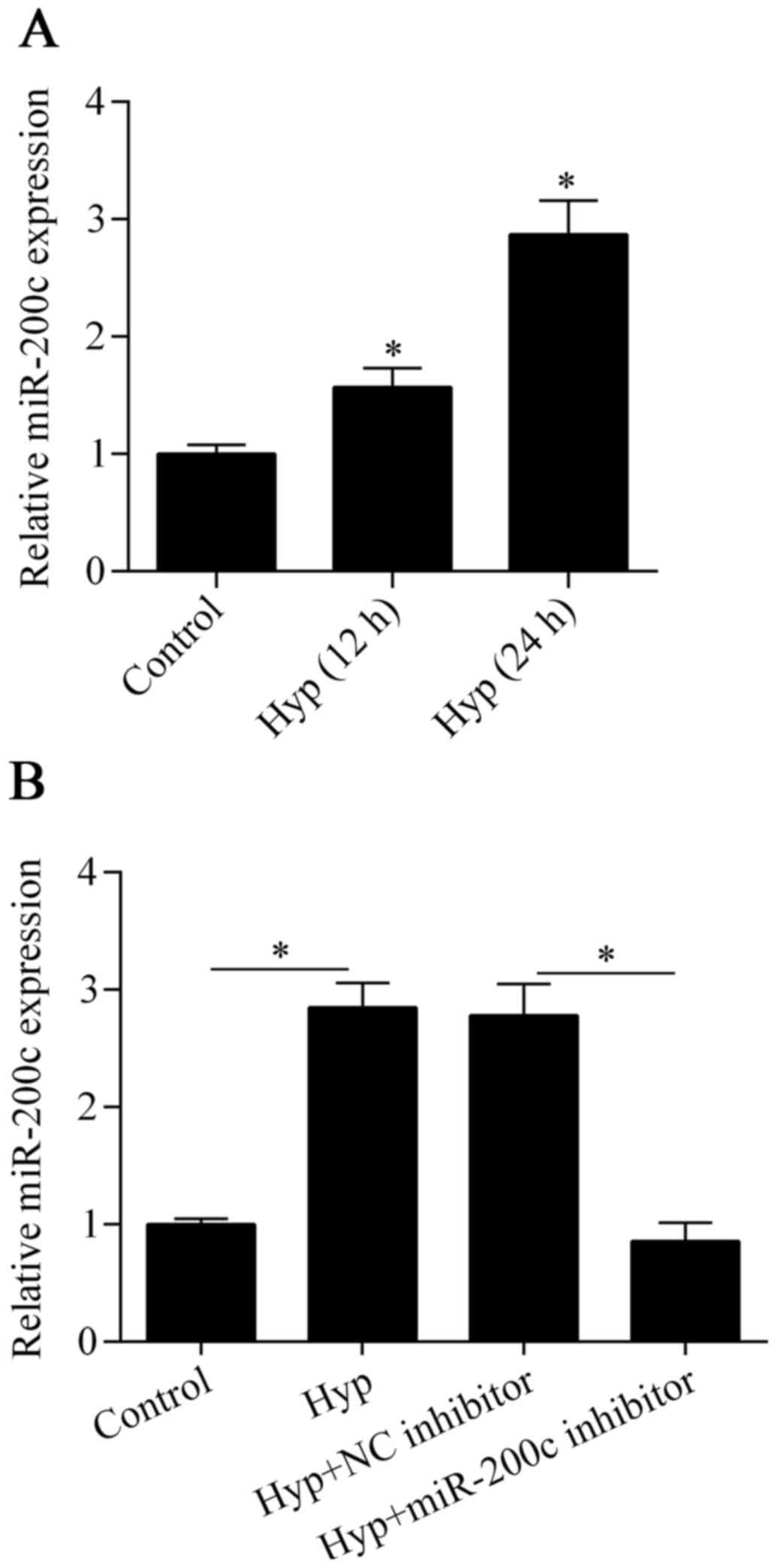
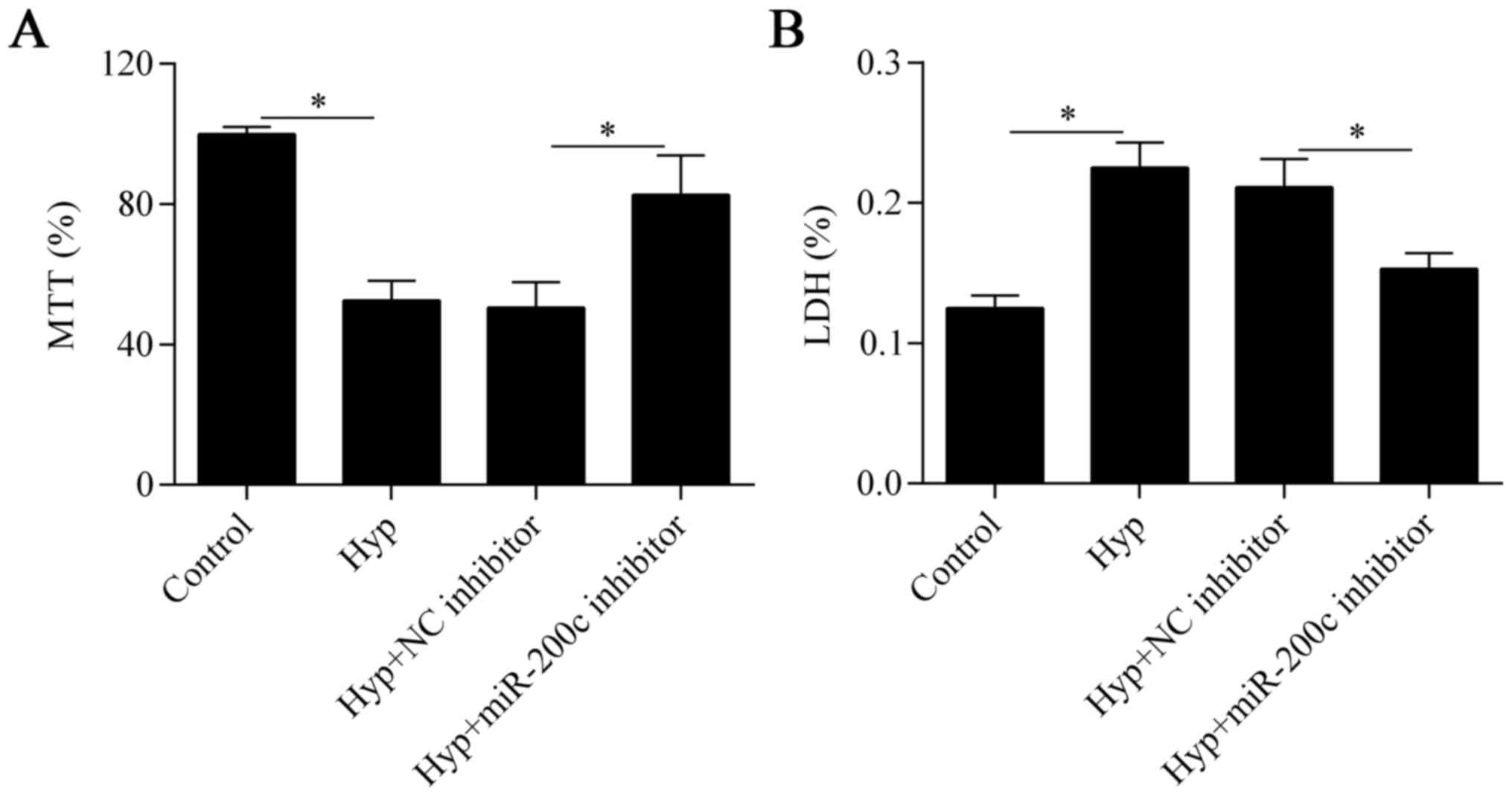
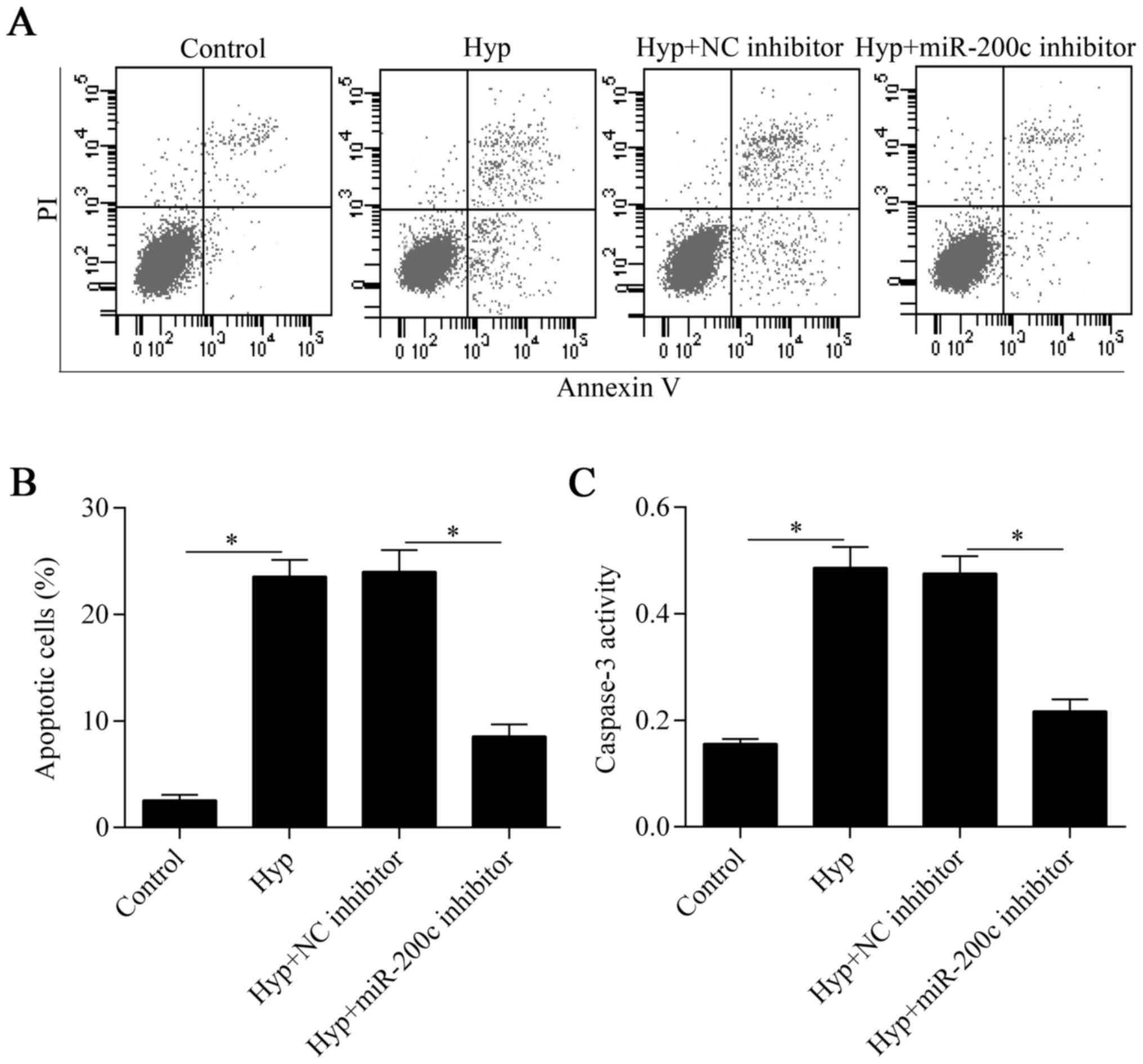
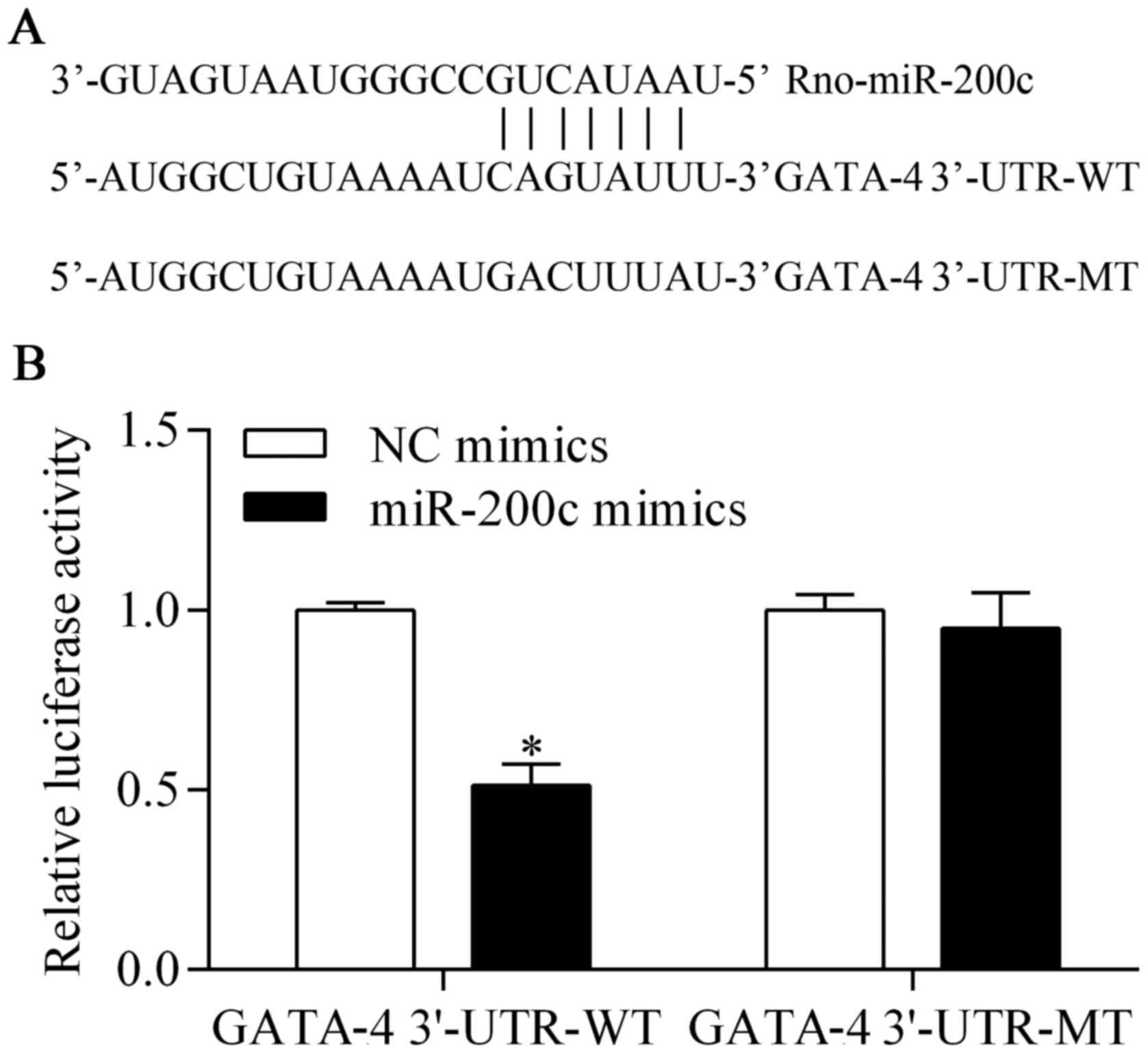
|
1
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Glinka YY and Youdim MB: Inhibition of
mitochondrial complexes I and IV by 6-hydroxydopamine. Eur J
Pharmacol. 292:329–332. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kitsis RN, Peng CF and Cuervo AM: Eat your
heart out. Nat Med. 13:539–541. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang PM, Haunstetter A, Aoki H, Usheva A
and Izumo S: Morphological and molecular characterization of adult
cardiomyocyte apoptosis during hypoxia and reoxygenation. Circ Res.
87:118–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis. Oncotarget.
6:8474–8490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Pan X, Fan Y, Hu X, Liu X, Xiang M
and Wang J: Dysregulated expression of microRNAs and mRNAs in
myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. 7:2291–2304. 2015.
|
|
9
|
Boon RA and Dimmeler S: MicroRNAs in
myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:135–142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hang P, Guo J, Sun C and Du Z: MicroRNAs
as candidate drug targets for cardiovascular diseases. Curr Drug
Targets. Feb 29–2016.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Samanta S, Balasubramanian S, Rajasingh S,
Patel U, Dhanasekaran A, Dawn B and Rajasingh J: MicroRNA: a new
therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 26:407–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zou Y, Liu W, Zhang J and Xiang D: miR-153
regulates apoptosis and autophagy of cardiomyocytes by targeting
Mcl-1. Mol Med Rep. 14:1033–1039. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu H, Jin L, Chen Y and Li J:
Downregulation of microRNA-429 protects cardiomyocytes against
hypoxia-induced apoptosis by increasing Notch1 expression. Int J
Mol Med. 37:1677–1685. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie J, Hu X, Yi C, Hu G, Zhou X and Jiang
H: MicroRNA 451 protects against cardiomyocyte anoxia/reoxygenation
injury by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 expression. Mol Med
Rep. 13:5335–5341. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ke ZP, Xu P, Shi Y and Gao AM: MicroRNA-93
inhibits ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by
targeting PTEN. Oncotarget. 7:28796–28805. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kelley C, Blumberg H, Zon LI and Evans T:
GATA-4 is a novel transcription factor expressed in endocardium of
the developing heart. Development. 118:817–827. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arceci RJ, King AA, Simon MC, Orkin SH and
Wilson DB: Mouse GATA-4: a retinoic acid-inducible GATA-binding
transcription factor expressed in endodermally derived tissues and
heart. Mol Cell Biol. 13:2235–2246. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang Q, De Windt LJ, Witt SA, Kimball TR,
Markham BE and Molkentin JD: The transcription factors GATA4 and
GATA6 regulate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vitro and in vivo. J
Biol Chem. 276:30245–30253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Charron F, Tsimiklis G, Arcand M,
Robitaille L, Liang Q, Molkentin JD, Meloche S and Nemer M:
Tissue-specific GATA factors are transcriptional effectors of the
small GTPase RhoA. Genes Dev. 15:2702–2719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki YJ: Cell signaling pathways for the
regulation of GATA4 transcription factor: implications for cell
growth and apoptosis. Cell Signal. 23:1094–1099. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morimoto T, Hasegawa K, Kaburagi S, Kakita
T, Wada H, Yanazume T and Sasayama S: Phosphorylation of GATA-4 is
involved in alpha 1-adrenergic agonist-responsive transcription of
the endothelin-1 gene in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem.
275:13721–13726. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hautala N, Tokola H, Luodonpää M, Puhakka
J, Romppanen H, Vuolteenaho O and Ruskoaho H: Pressure overload
increases GATA4 binding activity via endothelin-1. Circulation.
103:730–735. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kobayashi S, Lackey T, Huang Y, Bisping E,
Pu WT, Boxer LM and Liang Q: Transcription factor gata4 regulates
cardiac BCL2 gene expression in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J.
20:800–802. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim Y, Ma AG, Kitta K, Fitch SN, Ikeda T,
Ihara Y, Simon AR, Evans T and Suzuki YJ: Anthracycline-induced
suppression of GATA-4 transcription factor: implication in the
regulation of cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol. 63:368–377.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rysä J, Tenhunen O, Serpi R, Soini Y,
Nemer M, Leskinen H and Ruskoaho H: GATA-4 is an angiogenic
survival factor of the infarcted heart. Circ Heart Fail. 3:440–450.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bian J, Popovic ZB, Benejam C, Kiedrowski
M, Rodriguez LL and Penn MS: Effect of cell-based intercellular
delivery of transcription factor GATA4 on ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Circ Res. 100:1626–1633. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shan W, Zhang X, Li M, Deng F and Zhang J:
Over expression of miR-200c suppresses invasion and restores
methotrexate sensitivity in lung cancer A549 cells. Gene.
593:265–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boominathan L: The tumor suppressors p53,
p63, and p73 are regulators of microRNA processing complex. PLoS
One. 5:e106152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsieh CH, Jeng JC, Jeng SF, Wu CJ, Lu TH,
Liliang PC, Rau CS, Chen YC and Lin CJ: MicroRNA profiling in
ischemic injury of the gracilis muscle in rats. BMC Musculoskelet
Disord. 11:1232010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Yoon HJ, Jeon D,
Kang KM, Park KH, Bae EK, Kim M, Lee SK, et al: MicroRNAs induced
during ischemic preconditioning. Stroke. 41:1646–1651. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stary CM, Xu L, Sun X, Ouyang YB, White
RE, Leong J, Li J, Xiong X and Giffard RG: MicroRNA-200c
contributes to injury from transient focal cerebral ischemia by
targeting Reelin. Stroke. 46:551–556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Venkatadri R, Muni T, Iyer AK, Yakisich JS
and Azad N: Role of apoptosis-related miRNAs in resveratrol-induced
breast cancer cell death. Cell Death Dis. 7:e21042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cui J, Cheng Y, Zhang P, Sun M, Gao F, Liu
C and Cai J: Downregulation of miR200c promotes radiation-induced
thymic lymphoma by targeting BMI1. J Cell Biochem. 115:1033–1042.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu DS, Lv G, Mei XF, Cao Y, Wang YF, Wang
YS and Bi YL: MiR-200c regulates ROS-induced apoptosis in murine
BV-2 cells by targeting FAP-1. Spinal Cord. Dec 2–2014.Epub ahead
of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Magenta A, Cencioni C, Fasanaro P,
Zaccagnini G, Greco S, Sarra-Ferraris G, Antonini A, Martelli F and
Capogrossi MC: miR-200c is upregulated by oxidative stress and
induces endothelial cell apoptosis and senescence via ZEB1
inhibition. Cell Death Differ. 18:1628–1639. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H, Liu J, Qu D, Wang L, Luo JY, Lau
CW, Liu P, Gao Z, Tipoe GL, Lee HK, et al: Inhibition of miR-200c
restores endothelial function in diabetic mice through suppression
of COX-2. Diabetes. 65:1196–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu Y, Gu C and Huang X: Sevoflurane
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating
microRNA-200c regulation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:1126–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Singh GB, Raut SK, Khanna S, Kumar A,
Sharma S, Prasad R and Khullar M: MicroRNA-200c modulates DUSP-1
expression in diabetes-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Mol Cell
Biochem. 424:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Suzuki YJ and Evans T: Regulation of
cardiac myocyte apoptosis by the GATA-4 transcription factor. Life
Sci. 74:1829–1838. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki YJ: Stress-induced activation of
GATA-4 in cardiac muscle cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 34:1589–1598.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kobayashi S, Volden P, Timm D, Mao K, Xu X
and Liang Q: Transcription factor GATA4 inhibits
doxorubicin-induced autophagy and cardiomyocyte death. J Biol Chem.
285:793–804. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Li HX, Zhou YF, Zhao X, Jiang B and Yang
XJ: GATA-4 protects against hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte injury:
effects on mitochondrial membrane potential. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 92:669–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu B, Gong M, Wang Y, Millard RW, Pasha Z,
Yang Y, Ashraf M and Xu M: Cardiomyocyte protection by GATA-4 gene
engineered mesenchymal stem cells is partially mediated by
translocation of miR-221 in microvesicles. PLoS One. 8:e733042013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yu B, Kim HW, Gong M, Wang J, Millard RW,
Wang Y, Ashraf M and Xu M: Exosomes secreted from GATA-4
overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells serve as a reservoir of
anti-apoptotic microRNAs for cardioprotection. Int J Cardiol.
182:349–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kyrönlahti A, Rämö M, Tamminen M,
Unkila-Kallio L, Butzow R, Leminen A, Nemer M, Rahman N, Huhtaniemi
I, Heikinheimo M, et al: GATA-4 regulates Bcl-2 expression in
ovarian granulosa cell tumors. Endocrinology. 149:5635–5642. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang N, Ye F, Zhu W, Hu D, Xiao C, Nan J,
Su S, Wang Y, Liu M, Gao K, et al: Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein
attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by upregulation of Bcl-2
expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:3040–3049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pikkarainen S, Tokola H, Kerkelä R and
Ruskoaho H: GATA transcription factors in the developing and adult
heart. Cardiovasc Res. 63:196–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jun JH, Shin EJ, Kim JH, Kim SO, Shim JK
and Kwak YL: Erythropoietin prevents hypoxia-induced GATA-4
ubiquitination via phosphorylation of serine 105 of GATA-4. Biol
Pharm Bull. 36:1126–1133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yao CX, Wei QX, Zhang YY, Wang WP, Xue LX,
Yang F, Zhang SF, Xiong CJ, Li WY, Wei ZR, et al: miR-200b targets
GATA-4 during cell growth and differentiation. RNA Biol.
10:465–480. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sowa N, Horie T, Kuwabara Y, Baba O,
Watanabe S, Nishi H, Kinoshita M, Takanabe-Mori R, Wada H, Shimatsu
A, et al: MicroRNA 26b encoded by the intron of small CTD
phosphatase (SCP) 1 has an antagonistic effect on its host gene. J
Cell Biochem. 113:3455–3465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Han M, Yang Z, Sayed D, He M, Gao S, Lin
L, Yoon S and Abdellatif M: GATA4 expression is primarily regulated
via a miR-26b-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism during
cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 93:645–654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu Y, Wang Z and Xiao W: MicroRNA-26a
protects against cardiac hypertrophy via inhibiting GATA4 in rat
model and cultured cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 14:2860–2866.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tony H, Yu K and Qiutang Z: MicroRNA-208a
silencing attenuates doxorubicin induced myocyte apoptosis and
cardiac dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:5970322015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang HN, Chen SY, Hwang SM, Yu CC, Su MW,
Mai W, Wang HW, Cheng WC, Schuyler SC, Ma N, et al: miR-200c and
GATA binding protein 4 regulate human embryonic stem cell renewal
and differentiation. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 12:338–353. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|