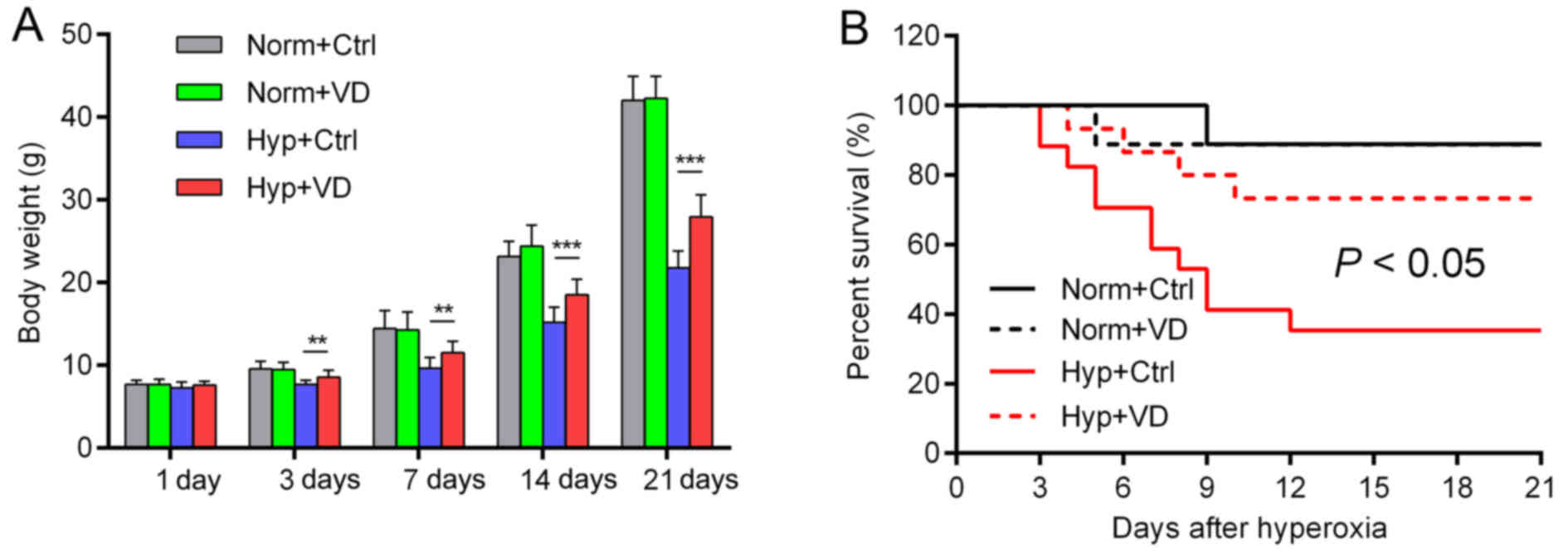
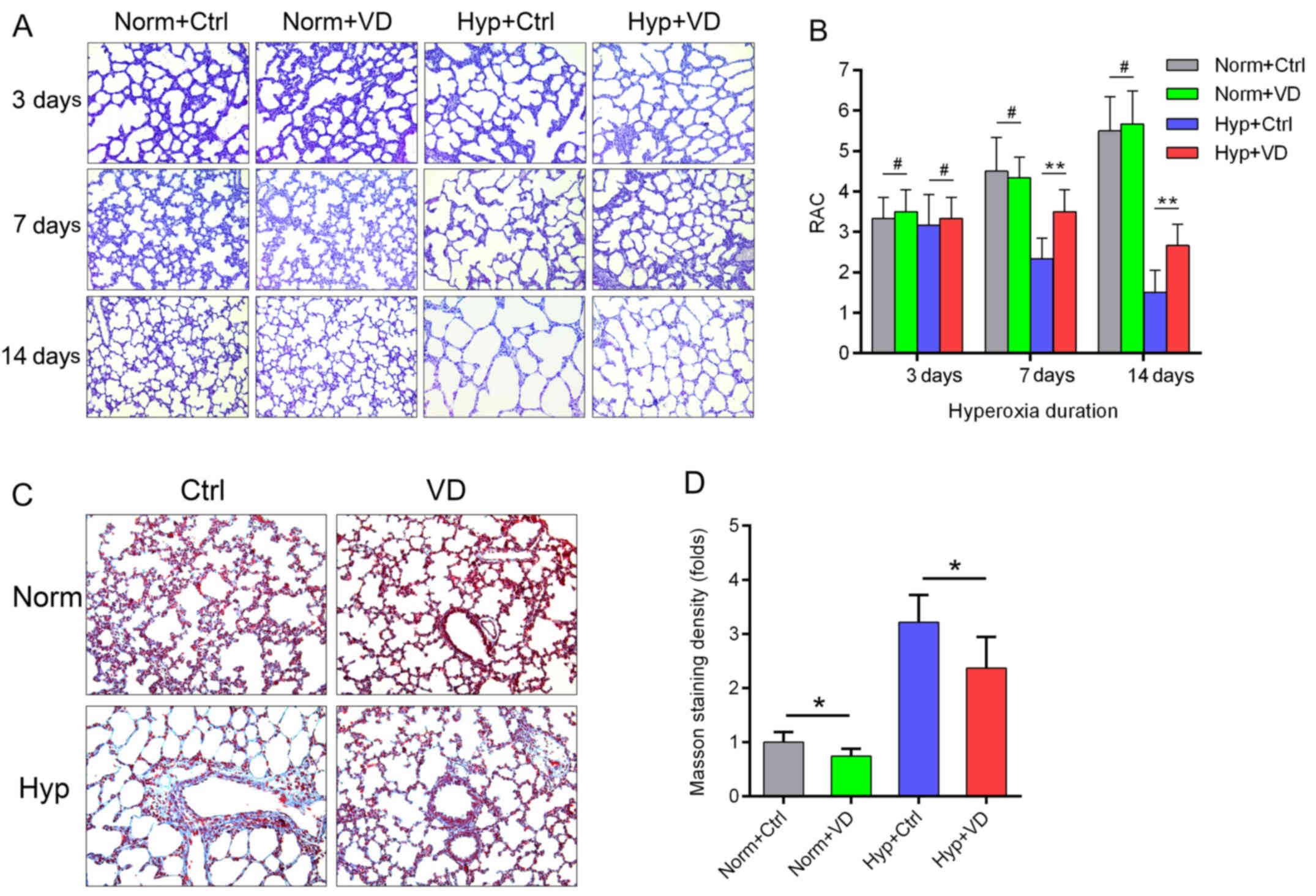
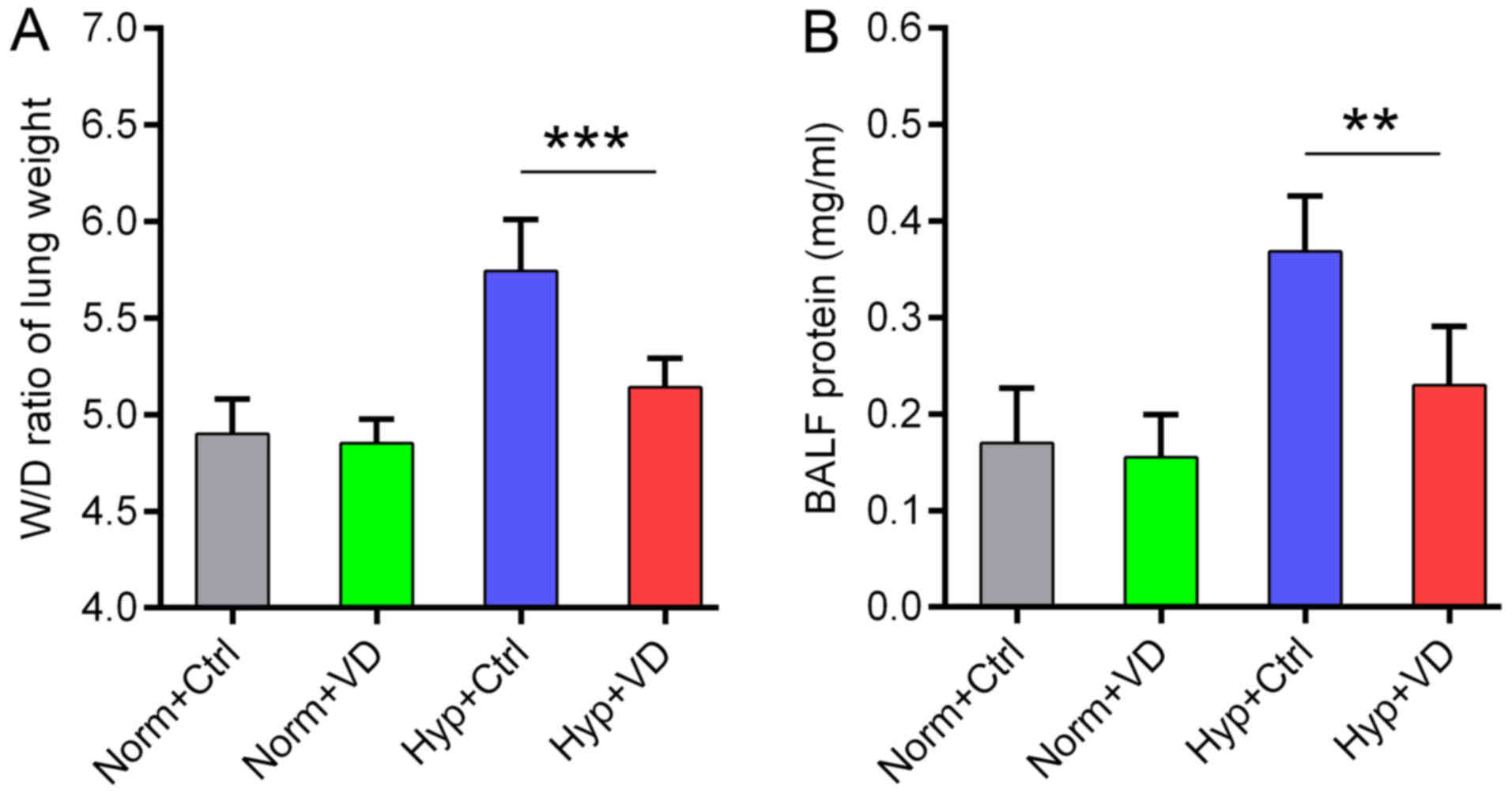
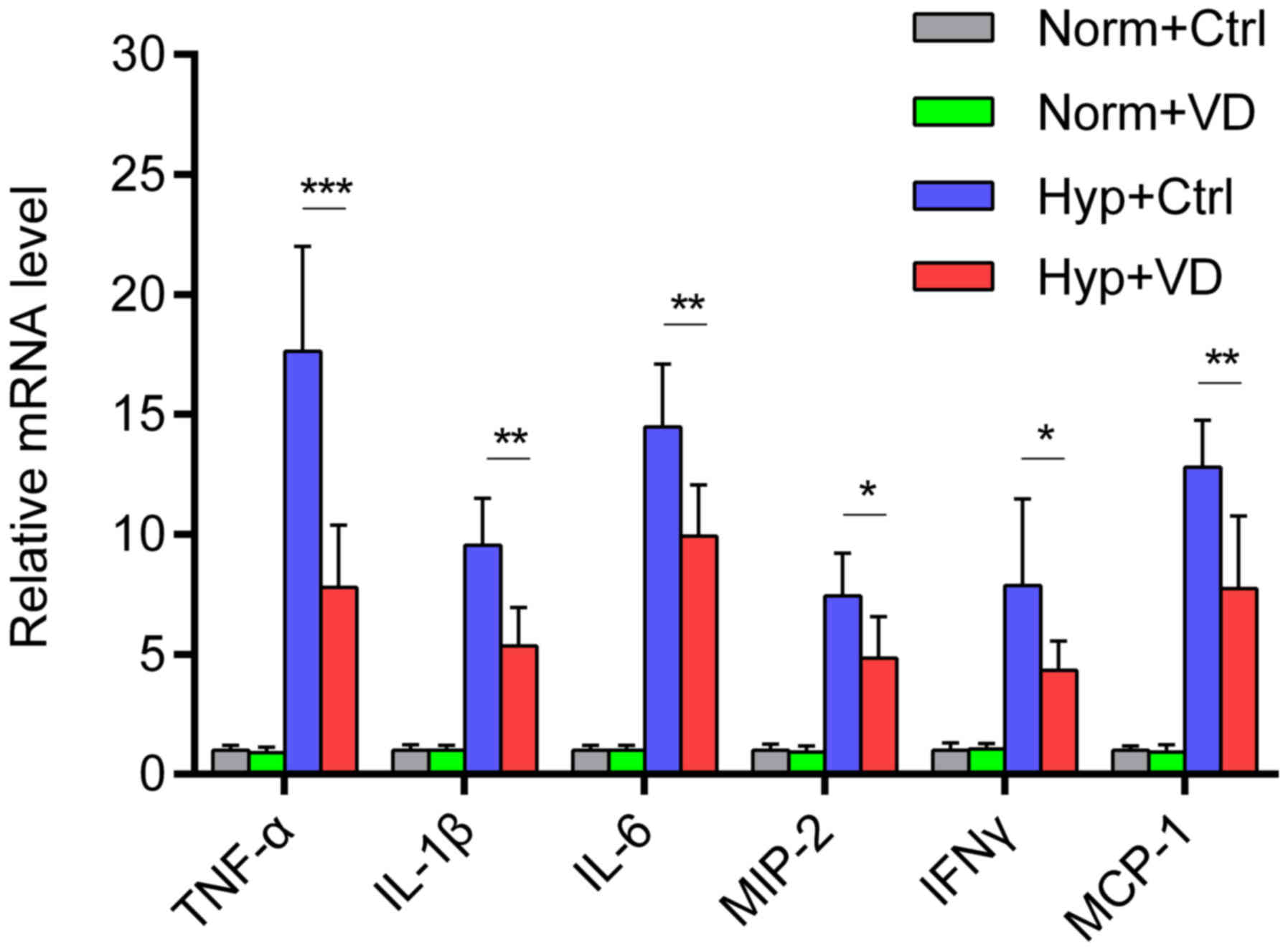
|
1
|
Kair LR, Leonard DT and Anderson JM:
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Rev. 33:255–263. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Balany J and Bhandari V: Understanding the
impact of infection, inflammation and their persistence in the
pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Front Med (Lausanne).
2:902015.
|
|
3
|
Silva DM, Nardiello C, Pozarska A and
Morty RE: Recent advances in the mechanisms of lung alveolarization
and the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 309:L1239–L1272. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen Y, Li Q, Liu Y, Shu L, Wang N, Wu Y,
Sun X and Wang L: Attenuation of hyperoxia-induced lung injury in
neonatal rats by 1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. Exp Lung
Res. 41:344–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Huang D, Fang F and Xu F: Hyperoxia
induces inflammation and regulates cytokine production in alveolar
epithelium through TLR2/4-NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 20:1399–1410. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang M, Zhao J, Ma X,
Huang T, Pang H, Li J and Song J: Inhibition of TLR4
signalling-induced inflammation attenuates secondary injury after
diffuse axonal injury in rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:47069152016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Perros F, Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: TLR4
signaling in pulmonary stromal cells is critical for inflammation
and immunity in the airways. Respir Res 12:. 125:2011.
|
|
8
|
Liu TJ, Shi YY, Du J, Ge X, Teng X, Liu L,
Wang EB and Zhao Q: Vitamin D treatment attenuates 2, 4,
6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis but not
oxazolone-induced colitis. Sci Rep. 6:328892016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee JW, Kim SC, Ko YS, Lee HY, Cho E, Kim
MG, Jo SK, Cho WY and Kim HK: Renoprotective effect of paricalcitol
via a modulation of the TLR4-NF-κB pathway in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 444:121–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kose M, Bastug O, Sonmez MF, Per S,
Ozdemir A, Kaymak E, Yahşi H and Ozturk MA: Protective effect of
vitamin D against hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 52:69–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shi YY, Liu TJ, Fu JH, Xu W, Wu LL, Hou AN
and Xue XD: Vitamin D/VDR signaling attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by maintaining the
integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier. Mol Med Rep.
13:1186–1194. 2016.
|
|
12
|
Kong J, Zhu X, Shi Y, Liu T, Chen Y, Bhan
I, Zhao Q, Thadhani R and Li YC: VDR attenuates acute lung injury
by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system. Mol
Endocrinol. 27:2116–2125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Verma R, Jung JH and Kim JY:
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 upregulates TLR10 while
downregulating TLR2, 4 and 5 in human monocyte THP-1. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 141:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang H, Zhang Q, Chai Y, Liu Y, Li F, Wang
B, Zhu C, Cui J, Qu H and Zhu Ma: 1,25(OH)2D3
downregulates the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory pahway
and ameliorates liver injury in diabetic rats. J Endocrinol Invest.
38:1083–1091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gambhir V, Kim J, Siddiqui S, Taylor M,
Byford V, Petrof EO, Jones G and Basta S: Influence of 1,
25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 on TLR4-induced activation of antigen
presenting cells is dependent on the order of receptor engagement.
Immunobiology. 216:988–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou AN, Fu JH, Yang HP, Zhu YT, Pan YQ, Xu
SY and Xue XD: Hyperoxia stimulates the transdifferentiation of
type II alveolar epithelial cells in newborn rats. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L861–L872. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reis RB, Nagato AC, Nardeli CR, Matias IC,
Lima WG and Bezerra FS: Alternations in the pulmonary
histoarchitecture of neonatal mice exposed to hyperoxia. J Pediatr
(Rio J). 89:300–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Porzionato A, Sfriso MM, Mazzatenta A,
Macchi V, De Caro R and Di Giulio C: Effects of hyperoxic exposure
on signal transduction pathways in the lung. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 209:106–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Molteni M, Gemma S and Rossetti C: The
role of TLR4 in infectious and non-infectious inflammation.
Mediators Inflamm. 2016:69789362016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
You K, Xu XW, Fu JH, Xu SY, Yue XH, Yu ZL
and Xue XD: Hyperoxia disrupts pulmonary epithelial barrier in
newborn rats via the deterioration of occludin and ZO-1. Respir
Res. 13:362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li C, Fu JH, Liu HY, Yang HP, Yao L, You K
and Xue XD: Hyperoxia arrests pulmonary development in newborn rats
via disruption of endothelial tight junctions and downregulation of
CX40. Mol Med Rep. 10:61–67. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang HP, Fu JH, Xue XD, Yao L, Qiao L, Hou
AN, Jin LL and Xing YJ: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
broncho-pulmonary dysplasia of newborn rats. Pediatr Pulmonol.
49:1112–1123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qureshi ST, Zhang X, Aberg E, Bousette N,
Giaid A, Shan P, Medzhitov RM and Lee PJ: Inducible activation of
TLR4 confers resistance to hyperoxia-induced pulmonary apoptosis. J
Immunol. 176:4950–4958. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Shan P, Qureshi S, Homer R,
Medzhitov R, Noble PW and Lee PJ: Cutting edge: TLR4 deficiency
confers susceptibility to lethal oxidant lung injury. J Immunol.
175:4834–4838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia H, Sodhi CP, Yamaguchi Y, Lu P, Martin
LY, Good M, Zhou Q, Sung J, Fulton WB, Nino DF, et al: Pulmonary
epithelial TLR4 activation leads to lung injury in neonatal
necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol. 197:859–871. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Togbe D, Schnyder-Candrian S, Schnyder B,
Couillin I, Maillet I, Bihl F, Malo D, Ryffel B and Quesniaux VF:
TLR4 gene dosage contributes to endotoxin-induced acute respiratory
inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 80:451–457. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yao T, Ying X, Zhao Y, Yuan A, He Q, Tong
H, Ding S, Liu J, Peng X, Gao E, et al: Vitamin D receptor
activation protects against myocardial reperfusion injury through
inhibition of apoptosis and modulation of autophagy. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:633–650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Zhu T, Liu TJ, Shi YY and Zhao Q: Vitamin
D/VDR signaling pathway ameliorates 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene
sulphonic acid-induced colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial
apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. 35:1213–1218. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeong MS, Kim JY, Lee HI and Seo SJ:
Calcitriol may down-regulate mRNA over-expression of Toll-like
receptor-2 and 4, LL-37 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured
human keratocytes. Ann Dermatol. 26:296–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|