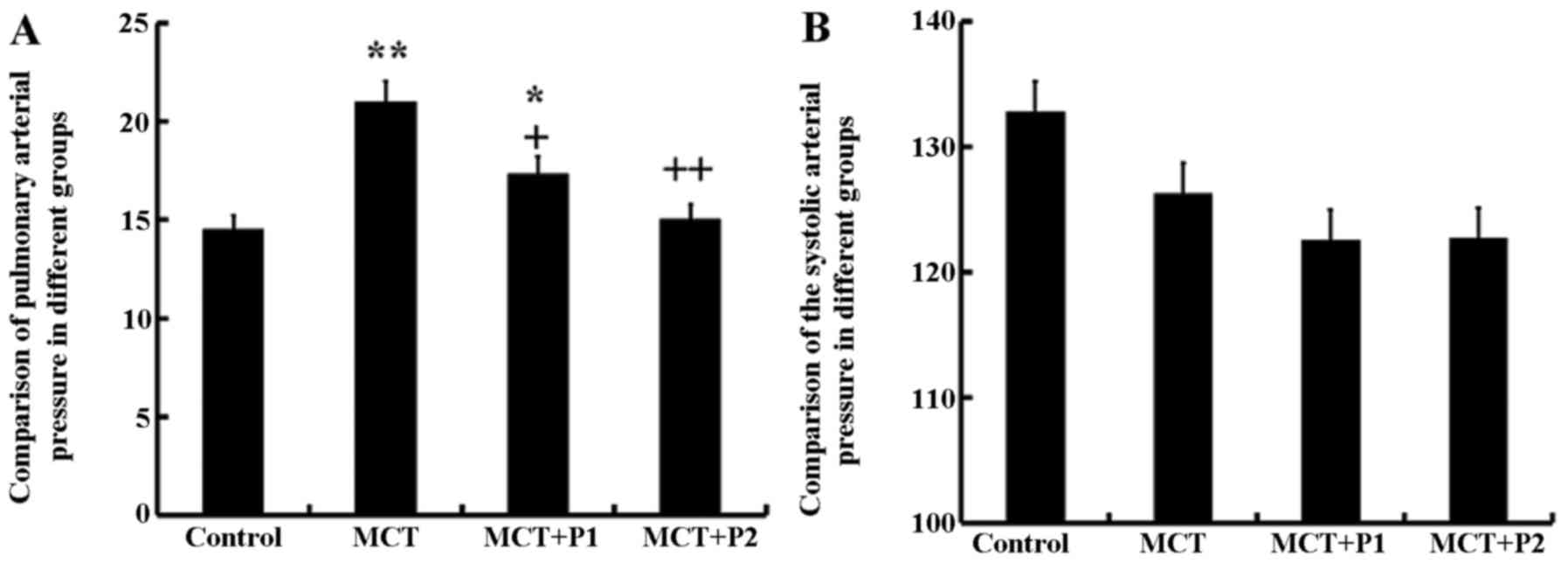
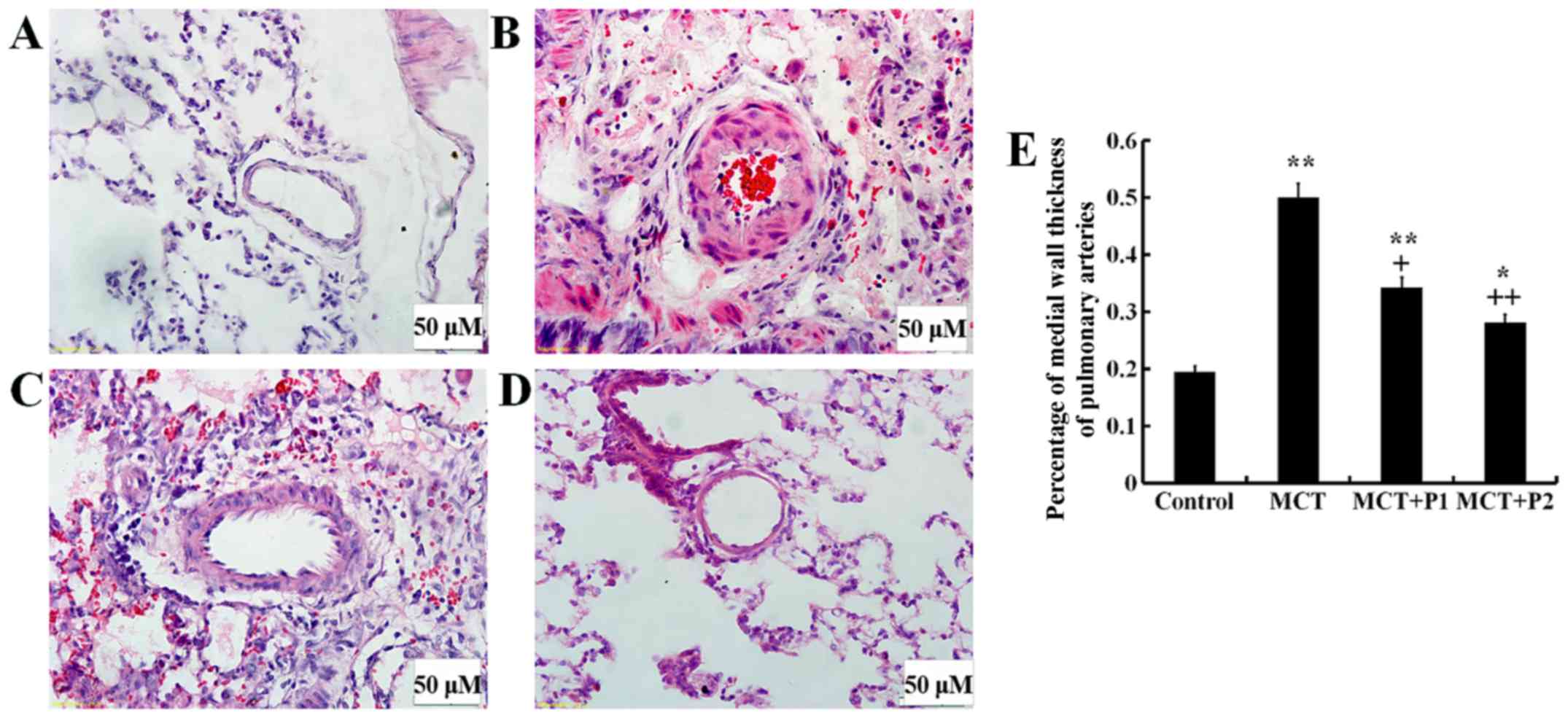
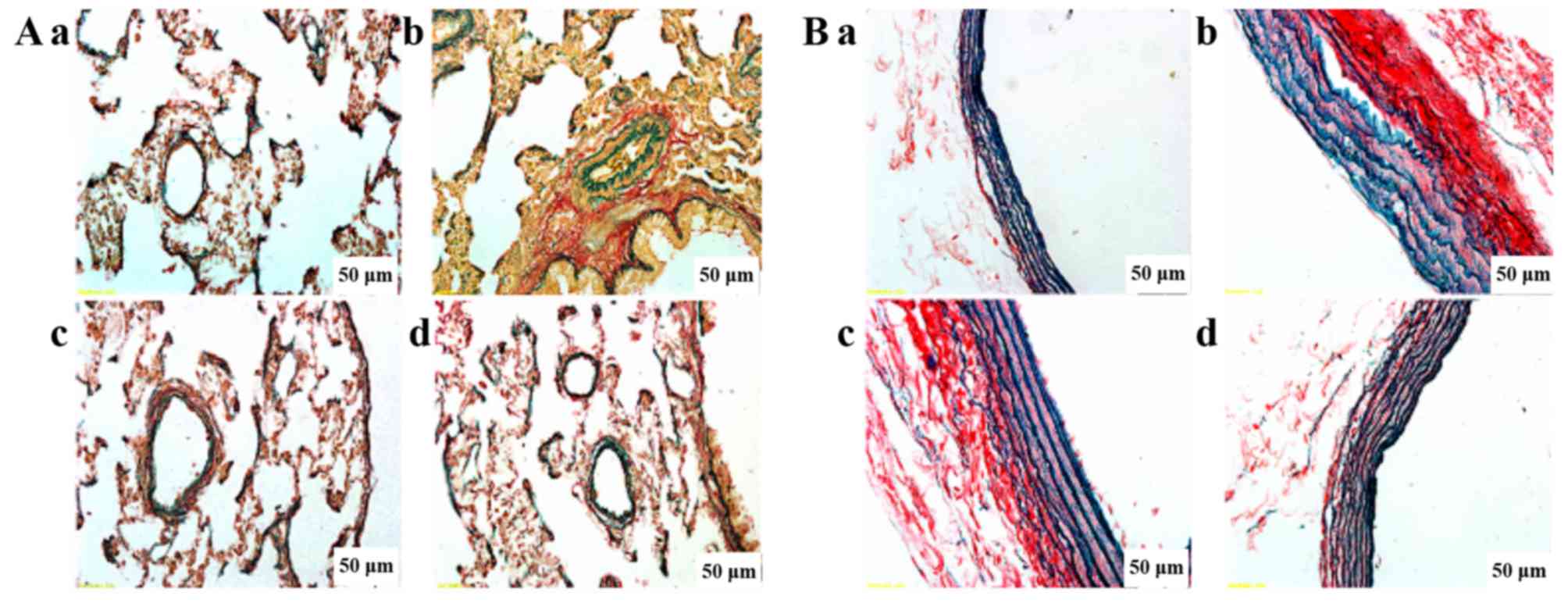
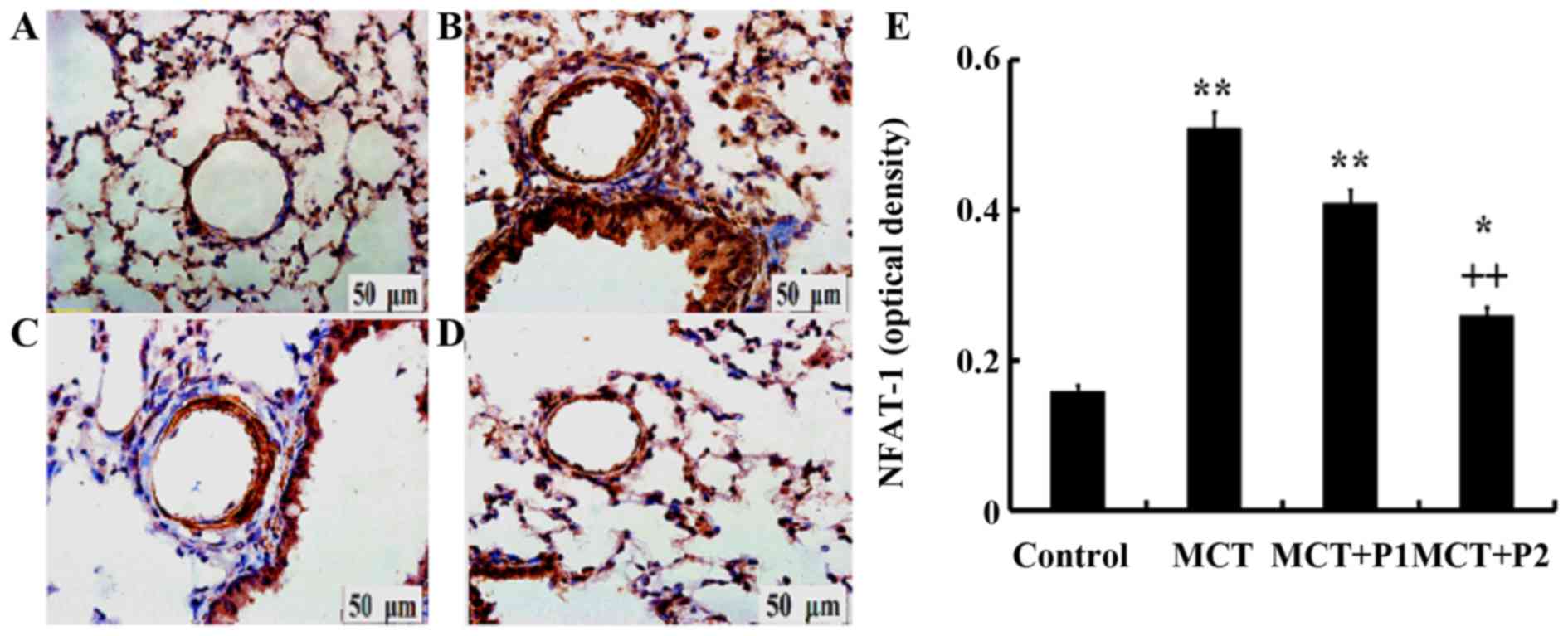
|
1
|
Lai YC, Potoka KC, Champion HC, Mora AL
and Gladwin MT: Pulmonary arterial hypertension: the clinical
syndrome. Circ Res. 115:115–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chaumais MC, Ranchoux B, Montani D,
Dorfmüller P, Tu L, Lecerf F, Raymond N, Guignabert C, Price L,
Simonneau G, et al: N-acetylcysteine improves established
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Respir Res.
15:652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rabinovitch M, Guignabert C, Humbert M and
Nicolls MR: Inflammation and immunity in the pathogenesis of
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res. 115:165–175. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
El Chami H and Hassoun PM: Immune and
inflammatory mechanisms in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Prog
Cardiovasc Dis. 55:218–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu J, Sha M, Wang Q, Ma Y, Geng X, Gao Y,
Feng L and Shen Y and Shen Y: Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3
interacts with 65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in
HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 15:6752015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M: NF-κB
and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev.
246:379–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hoesel B and Schmid JA: The complexity of
NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 12:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vallabhapurapu S and Karin M: Regulation
and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune
system. Annu Rev Immunol. 27:693–733. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB, the first
quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions.
Genes Dev. 26:203–234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang H and Sun SC: NF-κB in inflammation
and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 5:632015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gilmore TD and Wolenski FS: NF-κB: where
did it come from and why? Immunol Rev. 246:14–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Parpaite T, Cardouat G, Mauroux M,
Gillibert-Duplantier J, Robillard P, Quignard JF, Marthan R,
Savineau JP and Ducret T: Effect of hypoxia on TRPV1 and TRPV4
channels in rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflugers
Arch. 468:111–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
de Frutos S, Spangler R, Alò D and Bosc
LV: NFATc3 mediates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
remodeling with alpha-actin up-regulation. J Biol Chem.
282:15081–15089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang C, Li JF, Zhao L, Liu J, Wan J, Wang
YX, Wang J and Wang C: Inhibition of SOC/Ca2+/NFAT
pathway is involved in the anti-proliferative effect of sildenafil
on pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Respir Res. 10:1232009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J and Rao A:
Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes
Dev. 17:2205–2232. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai Y, Wang HM, Liu M, Wang Y, Lian GC,
Zhang XH, Kang J and Wang HL: 4-Chloro-DL-phenylalanine protects
against monocrotaline induced pulmonary vascular remodeling and
lung inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 33:373–382. 2014.
|
|
17
|
Wang HM, Wang Y, Liu M, Bai Y, Zhang XH,
Sun YX and Wang HL: Fluoxetine inhibits monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary arterial remodeling involved in inhibition of RhoA-Rho
kinase and Akt signalling pathways in rats. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 90:1506–1515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li XQ, Wang HM, Yang CG, Zhang XH, Han DD
and Wang HL: Fluoxetine inhibited extracellular matrix of pulmonary
artery and inflammation of lungs in monocrotaline-treated rats.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:217–222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang G, Abate A, George AG, Weng YH and
Dennery PA: Maturational differences in lung NF-kappaB activation
and their role in tolerance to hyperoxia. J Clin Invest.
114:669–678. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dürk T, Duerschmied D, Müller T, Grimm M,
Reuter S, Vieira RP, Ayata K, Cicko S, Sorichter S, Walther DJ, et
al: Production of serotonin by tryptophan hydroxylase 1 and release
via platelets contribute to allergic airway inflammation. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 187:476–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Bie JJ, Henricks PA, Cruikshank WW,
Hofman G, Jonker EH, Nijkamp FP and Van Oosterhout AJ: Modulation
of airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilia by selective
histamine and 5-HT receptor antagonists in a mouse model of
allergic asthma. Br J Pharmacol. 124:857–864. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Macian F: NFAT proteins: key regulators of
T-cell development and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:472–484. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bonnet S, Rochefort G, Sutendra G, Archer
SL, Haromy A, Webster L, Hashimoto K, Bonnet SN and Michelakis ED:
The nuclear factor of activated T cells in pulmonary arterial
hypertension can be therapeutically targeted. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:11418–11423. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li M, Liu Y, Sun X, Li Z, Liu Y, Fang P,
He P, Shi H, Xie M, Wang X, et al: Sildenafil inhibits
calcineurin/NFATc2-mediated cyclin A expression in pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 89:644–649. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang HJ, Hong SH, Kang KH, Park C and Choi
YH: Anti-inflammatory effects of Hwang-Heuk-San, a traditional
Korean herbal formulation, on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine
macrophages. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:4472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu Q, Chen Y, Auger-Messier M and
Molkentin JD: Interaction between NFκB and NFAT coordinates cardiac
hypertrophy and pathological remodeling. Circ Res. 110:1077–1086.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun SC, Ganchi PA, Ballard DW and Greene
WC: NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha:
evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science.
259:1912–1915. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng B, Ling J, Lee AJ, Wang Z, Chang Z,
Jin W, Kang Y, Zhang R, Shim D, Wang H, et al: Defective feedback
regulation of NF-kappaB underlies Sjogren's syndrome in mice with
mutated kappaB enhancers of the IkappaBalpha promoter. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:15193–15198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: a key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tamura R, Chen Y, Shinozaki M, Arao K,
Wang L, Tang W, Hirano S, Ogura H, Mitsui T, Taketani S, et al:
Eudesmane-type sesquiterpene lactones inhibit multiple steps in the
NF-κB signaling pathway induced by inflammatory cytokines. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 22:207–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Foulds S, Galustian C, Mansfield AO and
Schachter M: Transcription factor NF kappa B expression and
postsurgical organ dysfunction. Ann Surg. 233:70–78. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bhatia M, Brady M, Shokuhi S, Christmas S,
Neoptolemos JP and Slavin J: Inflammatory mediators in acute
pancreatitis. J Pathol. 190:117–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim KN, Ko SC, Ye BR, Kim MS, Kim J, Ko
EY, Cho SH, Kim D, Heo SJ and Jung WK:
5-Bromo-2-hydroxy-4-methyl-benzaldehyde inhibited LPS-induced
production of pro-inflammatory mediators through the inactivation
of ERK, p38 and NF-κB pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Chem Biol
Interact. 258:108–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu G, Feng L, Song P, Xu F, Li A, Wang Y,
Shen Y, Wu X, Luo Q, Wu X, et al: Isomeranzin suppresses
inflammation by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization through the
NF-κB and ERK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 38:175–185. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Suzuki YJ, Day RM and Fanburg BL:
Rho kinase-induced nuclear translocation of ERK1/ERK2 in smooth
muscle cell mitogenesis caused by serotonin. Circ Res. 95:579–586.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu YL, Huang CC, Chang CC, Chou CY, Lin
SY, Wang IK, Hsieh DJ, Jong GP, Huang CY and Wang CM:
Hyper-phosphate-induced myocardial hypertrophy through the
GATA-4/NFAT-3 signaling pathway is attenuated by ERK inhibitor
treatment. Cardiorenal Med. 5:79–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|