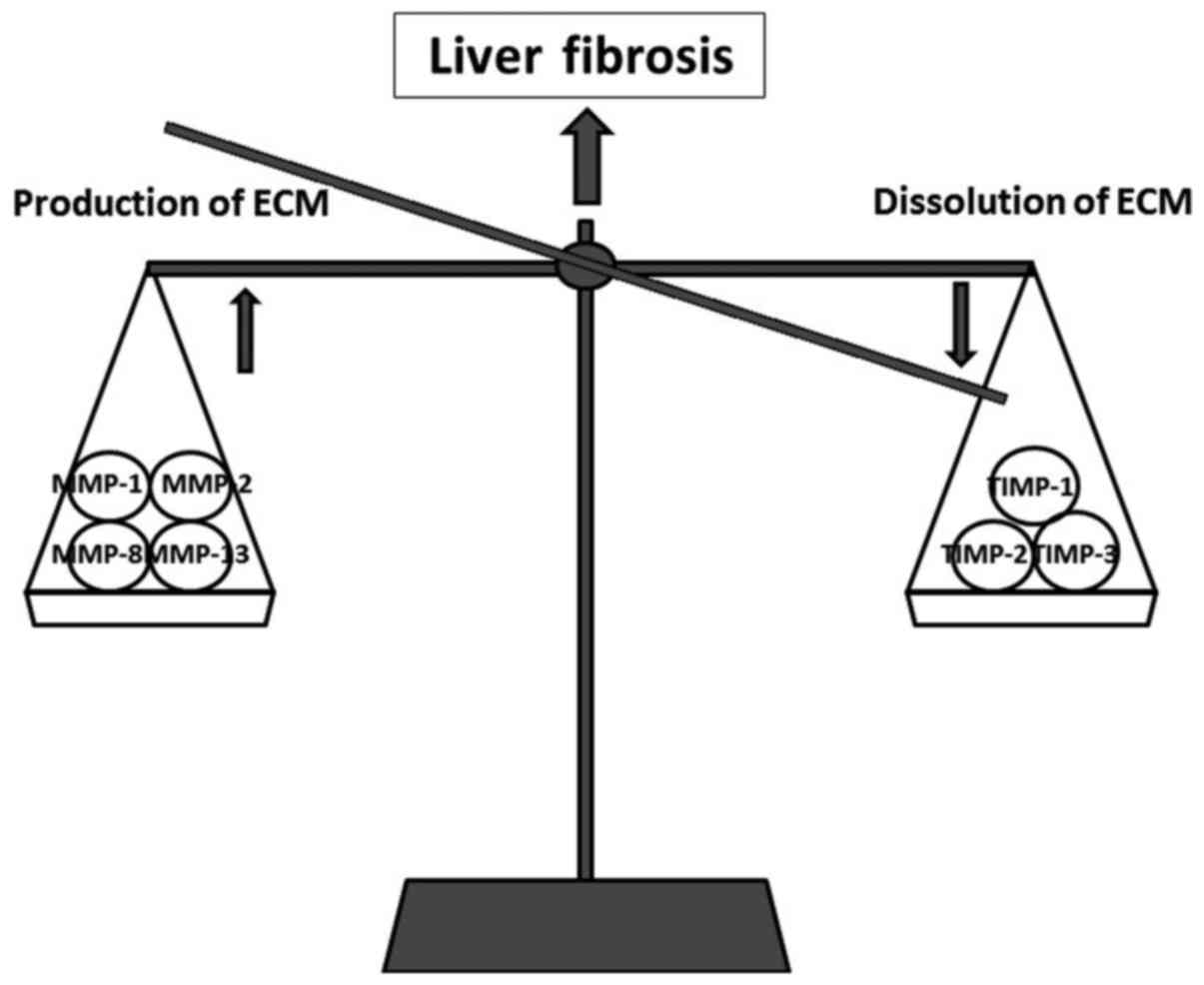
|
1
|
Teli MR, Day CP, Burt AD, Bennett MK and
James OF: Determinants of progression to cirrhosis or fibrosis in
pure alcoholic fatty liver. Lancet. 346:987–990. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lefkowitch JH: Morphology of alcoholic
liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 9:37–53. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cojocariu CE, Trifan AV, Girleanu I and
Stanciu C: Alcoholic liver disease - epidemiology and risk factors.
Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 118:910–917. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Stickel F: Alcoholic cirrhosis and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 815:113–130. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Browning JD and Horton JD: Molecular
mediators of hepatic steatosis and liver injury. J Clin Invest.
114:147–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
MacSween RN and Burt AD: Histologic
spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 6:221–232.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haber PS, Warner R, Seth D, Gorrell MD and
McCaughan GW: Pathogenesis and management of alcoholic hepatitis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:1332–1344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsujimoto T, Kuriyama S, Yamazaki M,
Nakatani Y, Okuda H, Yoshiji H and Fukui H: Augmented
hepatocellular carcinoma progression and depressed Kupffer cell
activity in rat cirrhotic livers. Int J Oncol. 18:41–47. 2001.
|
|
9
|
Kitazawa T, Nakatani Y, Fujimoto M, Tamura
N, Uemura M and Fukui H: The production of tumor necrosis
factor-alpha by macrophages in rats with acute alcohol loading.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 27(Suppl 8): 72S–75S. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rao RK, Seth A and Sheth P: Recent
advances in alcoholic liver disease I. Role of intestinal
permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 286:G881–G884. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Canbay A, Feldstein AE, Higuchi H,
Werneburg N, Grambihler A, Bronk SF and Gores GJ: Kupffer cell
engulfment of apoptotic bodies stimulates death ligand and cytokine
expression. Hepatology. 38:1188–1198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McClain CJ, Song Z, Barve SS, Hill DB and
Deaciuc I: Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease. IV.
Dysregulated cytokine metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 287:G497–G502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao B: Cytokines, STATs and liver disease.
Cell Mol Immunol. 2:92–100. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garcin F, Lau You Hin G, Cote J,
Radouco-Thomas S, Chawla S and Radouco-Thomas C: Aldehyde
dehydrogenase in Drosophila: developmental and functional aspects.
Alcohol. 2:85–89. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lieber CS and DeCarli LM: The role of the
hepatic microsomal ethanol oxidizing system (MEOS) for ethanol
metabolism in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 181:279–287.
1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Neve EP and Ingelman-Sundberg M: Molecular
basis for the transport of cytochrome P450 2E1 to the plasma
membrane. J Biol Chem. 275:17130–17135. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lieber CS: Metabolic consequences of
ethanol. Endocrinologist. 4:127–139. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bilzer M, Roggel F and Gerbes AL: Role of
Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int.
26:1175–1186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Diehl AM: Recent events in alcoholic liver
disease V. Effects of ethanol on liver regeneration. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 288:G1–G6. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hansen J, Cherwitz DL and Allen JI: The
role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in acute endotoxin-induced
hepatotoxicity in ethanol-fed rats. Hepatology. 20:461–474. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aldred A and Nagy LE: Ethanol dissociates
hormone-stimulated cAMP production from inhibition of TNF-alpha
production in rat Kupffer cells. Am J Physiol. 276:G98–G106.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawaratani H, Tsujimoto T, Kitazawa T,
Kitade M, Yoshiji H, Uemura M and Fukui H: Innate immune reactivity
of the liver in rats fed a choline-deficient L-amino-acid-defined
diet. World J Gastroenterol. 14:6655–6661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crespo J, Cayon A, Fernandez-Gil P,
Hernandez-Guerra M, Mayorga M, Dominguez-Diez A,
Fernandez-Escalante JC and Pons-Romero F: Gene expression of tumor
necrosis factor alpha and TNF-receptors, p55 and p75, in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatology. 34:1158–1163.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tilg H, Jalan R, Kaser A, Davies NA,
Offner FA, Hodges SJ, Ludwiczek O, Shawcross D, Zoller H, Alisa A,
et al: Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody therapy
in severe alcoholic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 38:419–425. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akriviadis E, Botla R, Briggs W, Han S,
Reynolds T and Shakil O: Pentoxifylline improves short-term
survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: a double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 119:1637–1648. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iimuro Y, Gallucci RM, Luster MI, Kono H
and Thurman RG: Antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alfa attenuate
hepatic necrosis and inflammation caused by chronic exposure to
ethanol in the rat. Hepatology. 26:1530–1537. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawaratani H, Tsujimoto T, Kitazawa T,
Yoshiji H, Uemura M and Fukui H: Therapeutic effects of cytokine
modulator Y-40138 in the rat alcoholic liver disease model. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:775–783. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong F, Kim WH, Tian Z, Jaruga B, Ishac E,
Shen X and Gao B: Elevated interleukin-6 during ethanol consumption
acts as a potential endogenous protective cytokine against
ethanol-induced apoptosis in the liver: involvement of induction of
Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) proteins. Oncogene. 21:32–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mathurin P, Deng QG, Keshavarzian A,
Choudhary S, Holmes EW and Tsukamoto H: Exacerbation of alcoholic
liver injury by enteral endotoxin in rats. Hepatology.
32:1008–1017. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hawrylowicz CM and O'Garra A: Potential
role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and
asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:271–283. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Louis H, Le Moine O, Goldman M and Deviere
J: Modulation of liver injury by interleukin-10. Acta Gastroenterol
Belg. 66:7–14. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Latvala J, Hietala J, Koivisto H, Jarvi K,
Anttila P and Niemela O: Immune responses to ethanol metabolites
and cytokine profiles differentiate alcoholics with or without
liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 100:1303–1310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Tachibana S, Wang H, Hisada M,
Williams GM, Gao B and Sun Z: Interleukin-6 is an important
mediator for mitochondrial DNA repair after alcoholic liver injury
in mice. Hepatology. 52:2137–2147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rabe B, Chalaris A, May U, Waetzig GH,
Seegert D, Williams AS, Jones SA, Rose-John S and Scheller J:
Transgenic blockade of interleukin 6 transsignaling abrogates
inflammation. Blood. 111:1021–1028. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Miller AM, Wang H, Bertola A, Park O,
Horiguchi N, Ki SH, Yin S, Lafdil F and Gao B:
Inflammation-associated interleukin-6/signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 activation ameliorates alcoholic and
nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in interleukin-10-deficient mice.
Hepatology. 54:846–856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jura J, Wegrzyn P, Korostyński M, Guzik K,
Oczko- Wojciechowska M, Jarzab M, Kowalska M, Piechota M,
Przewłocki R and Koj A: Identification of interleukin-1 and
interleukin-6-responsive genes in human monocyte-derived
macrophages using microarrays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1779:383–389.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G,
Lanzavecchia A and Sallusto F: Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not
transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the
differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells.
Nat Immunol. 8:942–949. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR and
Harrington LE: IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity
of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:821–852. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lafdil F, Miller AM, Ki SH and Gao B: Th17
cells and their associated cytokines in liver diseases. Cell Mol
Immunol. 7:250–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lemmers A, Moreno C, Gustot T, Marechal R,
Degre D, Demetter P, de Nadai P, Geerts A, Quertinmont E,
Vercruysse V, et al: The interleukin-17 pathway is involved in
human alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 49:646–657. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nanji AA, Zhao S, Sadrzadeh SM, Dannenberg
AJ, Tahan SR and Waxman DJ: Markedly enhanced cytochrome P450 2E1
induction and lipid peroxidation is associated with severe liver
injury in fish oil-ethanol-fed rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
18:1280–1285. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ki SH, Park O, Zheng M, Morales-Ibanez O,
Kolls JK, Bataller R and Gao B: Interleukin-22 treatment
ameliorates alcoholic liver injury in a murine model of
chronic-binge ethanol feeding: role of signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3. Hepatology. 52:1291–1300. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dominguez M, Miquel R, Colmenero J, Moreno
M, Garcia-Pagan JC, Bosch J, Arroyo V, Gines P, Caballeria J and
Bataller R: Hepatic expression of CXC chemokines predicts portal
hypertension and survival in patients with alcoholic hepatitis.
Gastroenterology. 136:1639–1650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Simpson KJ, Henderson NC, Bone-Larson CL,
Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM and Kunkel SL: Chemokines in the
pathogenesis of liver disease: so many players with poorly defined
roles. Clin Sci (Lond). 104:47–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jiang Y, Beller DI, Frendl G and Graves
DT: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates adhesion molecule
expression and cytokine production in human monocytes. J Immunol.
148:2423–2428. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fisher NC, Neil DA, Williams A and Adams
DH: Serum concentrations and peripheral secretion of the beta
chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage
inflammatory protein 1alpha in alcoholic liver disease. Gut.
45:416–420. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lu B, Rutledge BJ, Gu L, Fiorillo J,
Lukacs NW, Kunkel SL, North R, Gerard C and Rollins BJ:
Abnormalities in monocyte recruitment and cytokine expression in
monocyte chemoattractant protein 1-deficient mice. J Exp Med.
187:601–608. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mandrekar P, Ambade A, Lim A, Szabo G and
Catalano D: An essential role for monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 in alcoholic liver injury: regulation of proinflammatory
cytokines and hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology. 54:2185–2197.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sahin H and Wasmuth HE: Chemokines in
tissue fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1041–1048. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Gomperts BN,
Belperio JA and Keane MP: CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 16:593–609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Alfonso-Loeches S, Ureña-Peralta JR,
Morillo-Bargues MJ, Oliver-De La Cruz J and Guerri C: Role of
mitochondria ROS generation in ethanol-induced NLRP3 inflammasome
activation and cell death in astroglial cells. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:2162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Szabo G and Csak T: Inflammasomes in liver
diseases. J Hepatol. 57:642–654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Petrasek J, Iracheta-Vellve A, Saha B,
Satishchandran A, Kodys K, Fitzgerald KA, Kurt-Jones EA and Szabo
G: Metabolic danger signals, uric acid and ATP, mediate
inflammatory cross-talk between hepatocytes and immune cells in
alcoholic liver disease. J Leukoc Biol. 98:249–256. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Petrasek J, Bala S, Csak T, Lippai D,
Kodys K, Menashy V, Barrieau M, Min SY, Kurt-Jones EA and Szabo G:
IL-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent
alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J Clin Invest. 122:3476–3489.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal
T, Junger W, Brohi K, Itagaki K and Hauser CJ: Circulating
mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature.
464:104–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P and
Janeway CA Jr: A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein
signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 388:394–397. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Hoshino K,
Kaisho T, Sanjo H, Takeuchi O, Sugiyama M, Okabe M, Takeda K, et
al: Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like
receptor signaling pathway. Science. 301:640–643. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Petrasek J, Mandrekar P and Szabo G:
Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2010:7103812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Szabo G, Mandrekar P, Petrasek J and
Catalano D: The unfolding web of innate immune dysregulation in
alcoholic liver injury. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 35:782–786. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yin M, Bradford BU, Wheeler MD, Uesugi T,
Froh M, Goyert SM and Thurman RG: Reduced early alcohol-induced
liver injury in CD14-deficient mice. J Immunol. 166:4737–4742.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP,
Jobin C and Brenner DA: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory
signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate
cells. Hepatology. 37:1043–1055. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fujimoto M, Uemura M, Nakatani Y, Tsujita
S, Hoppo K, Tamagawa T, Kitano H, Kikukawa M, Ann T, Ishii Y, et
al: Plasma endotoxin and serum cytokine levels in patients with
alcoholic hepatitis: relation to severity of liver disturbance.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 24(Suppl 4): 48S–54S. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fukui H, Brauner B, Bode JC and Bode C:
Plasma endotoxin concentrations in patients with alcoholic and
non-alcoholic liver disease: reevaluation with an improved
chromogenic assay. J Hepatol. 12:162–169. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gustot T, Lemmers A, Moreno C, Nagy N,
Quertinmont E, Nicaise C, Franchimont D, Louis H, Devière J and Le
Moine O: Differential liver sensitization to toll-like receptor
pathways in mice with alcoholic fatty liver. Hepatology.
43:989–1000. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mandrekar P, Catalano D, White B and Szabo
G: Moderate alcohol intake in humans attenuates monocyte
inflammatory responses: inhibition of nuclear regulatory factor
kappa B and induction of interleukin 10. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
30:135–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hartmann P, Seebauer CT and Schnabl B:
Alcoholic liver disease: the gut microbiome and liver cross talk.
Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 39:763–775. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Keshavarzian A, Holmes EW, Patel M, Iber
F, Fields JZ and Pethkar S: Leaky gut in alcoholic cirrhosis: a
possible mechanism for alcohol-induced liver damage. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:200–207. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bala S, Marcos M, Kodys K, Csak T,
Catalano D, Mandrekar P and Szabo G: Up-regulation of microRNA-155
in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor α
(TNFα) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver
disease. J Biol Chem. 286:1436–1444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kavanaugh MJ, Clark C, Goto M, Kovacs EJ,
Gamelli RL, Sayeed MM and Choudhry MA: Effect of acute alcohol
ingestion prior to burn injury on intestinal bacterial growth and
barrier function. Burns. 31:290–296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Thakur V, McMullen MR, Pritchard MT and
Nagy LE: Regulation of macrophage activation in alcoholic liver
disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22(Suppl 1): S53–S56. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rao R: Endotoxemia and gut barrier
dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 50:638–644.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yan AW, Fouts DE, Brandl J, Stärkel P,
Torralba M, Schott E, Tsukamoto H, Nelson KE, Brenner DA and
Schnabl B: Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of
alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 53:96–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Bull-Otterson L, Feng W, Kirpich I, Wang
Y, Qin X, Liu Y, Gobejishvili L, Joshi-Barve S, Ayvaz T, Petrosino
J, et al: Meta-genomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic
alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG treatment. PLoS One. 8:e530282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Forsyth CB, Farhadi A, Jakate SM, Tang Y,
Shaikh M and Keshavarzian A: Lactobacillus GG treatment ameliorates
alcohol-induced intestinal oxidative stress, gut leakiness, and
liver injury in a rat model of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alcohol.
43:163–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Gratz SW, Mykkanen H and El-Nezami HS:
Probiotics and gut health: a special focus on liver diseases. World
J Gastroenterol. 16:403–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Choudhry MA, Fazal N, Goto M, Gamelli RL
and Sayeed MM: Gut-associated lymphoid T cell suppression enhances
bacterial translocation in alcohol and burn injury. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 282:G937–G947. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Szabo G and Bala S: Alcoholic liver
disease and the gut-liver axis. World J Gastroenterol.
16:1321–1329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hoek JB and Pastorino JG: Ethanol,
oxidative stress, and cytokine-induced liver cell injury. Alcohol.
27:63–68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, Gao W and
Thurman RG: Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following
long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology. 108:218–224. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors in
physiology and medicine. Cell. 148:399–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Nath B and Szabo G: Alcohol-induced
modulation of signaling pathways in liver parenchymal and
nonparenchymal cells: implications for immunity. Semin Liver Dis.
29:166–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Valfrè di Bonzo L, Novo E, Cannito S,
Busletta C, Paternostro C, Povero D and Parola M: Angiogenesis and
liver fibrogenesis. Histol Histopathol. 24:1323–1341.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Novo E, Povero D, Busletta C, Paternostro
C, di Bonzo LV, Cannito S, Compagnone A, Bandino A, Marra F,
Colombatto S, et al: The biphasic nature of hypoxia-induced
directional migration of activated human hepatic stellate cells. J
Pathol. 226:588–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Ciupińska-Kajor M, Hartleb M, Kajor M,
Kukla M, Wyleżoł M, Lange D and Liszka L: Hepatic angiogenesis and
fibrosis are common features in morbidly obese patients. Hepatol
Int. 7:233–240. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Sanz-Cameno P, Trapero-Marugán M, Chaparro
M, Jones EA and Moreno-Otero R: Angiogenesis: from chronic liver
inflammation to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol. 2010:2721702010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Marra F and Tacke F: Roles for chemokines
in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 147:577–594.e1. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Raskopf E, Gonzalez Carmona MA, Van
Cayzeele CJ, Strassburg C, Sauerbruch T and Schmitz V: Toxic damage
increases angiogenesis and metastasis in fibrotic livers via
PECAM-1. Biomed Res Int. 2014:7128932014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Svegliati-Baroni G, Ridolfi F, Di Sario A,
Saccomanno S, Bendia E, Benedetti A and Greenwel P: Intracellular
signaling pathways involved in acetaldehyde-induced collagen and
fibronectin gene expression in human hepatic stellate cells.
Hepatology. 33:1130–1140. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Das SK and Vasudevan DM: Genesis of
hepatic fibrosis and its biochemical markers. Scand J Clin Lab
Invest. 68:260–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gao B and Bataller R: Alcoholic liver
disease: pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets.
Gastroenterology. 141:1572–1585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Nanji AA, Khettry U and Sadrzadeh SM:
Lactobacillus feeding reduces endotoxemia and severity of
experimental alcoholic liver (disease). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med.
205:243–247. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bass NM, Mullen KD, Sanyal A, Poordad F,
Neff G, Leevy CB, Sigal S, Sheikh MY, Beavers K, Frederick T, et
al: Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med.
362:1071–1081. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Mencin A, Kluwe J and Schwabe RF:
Toll-like receptors as targets in chronic liver diseases. Gut.
58:704–720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|