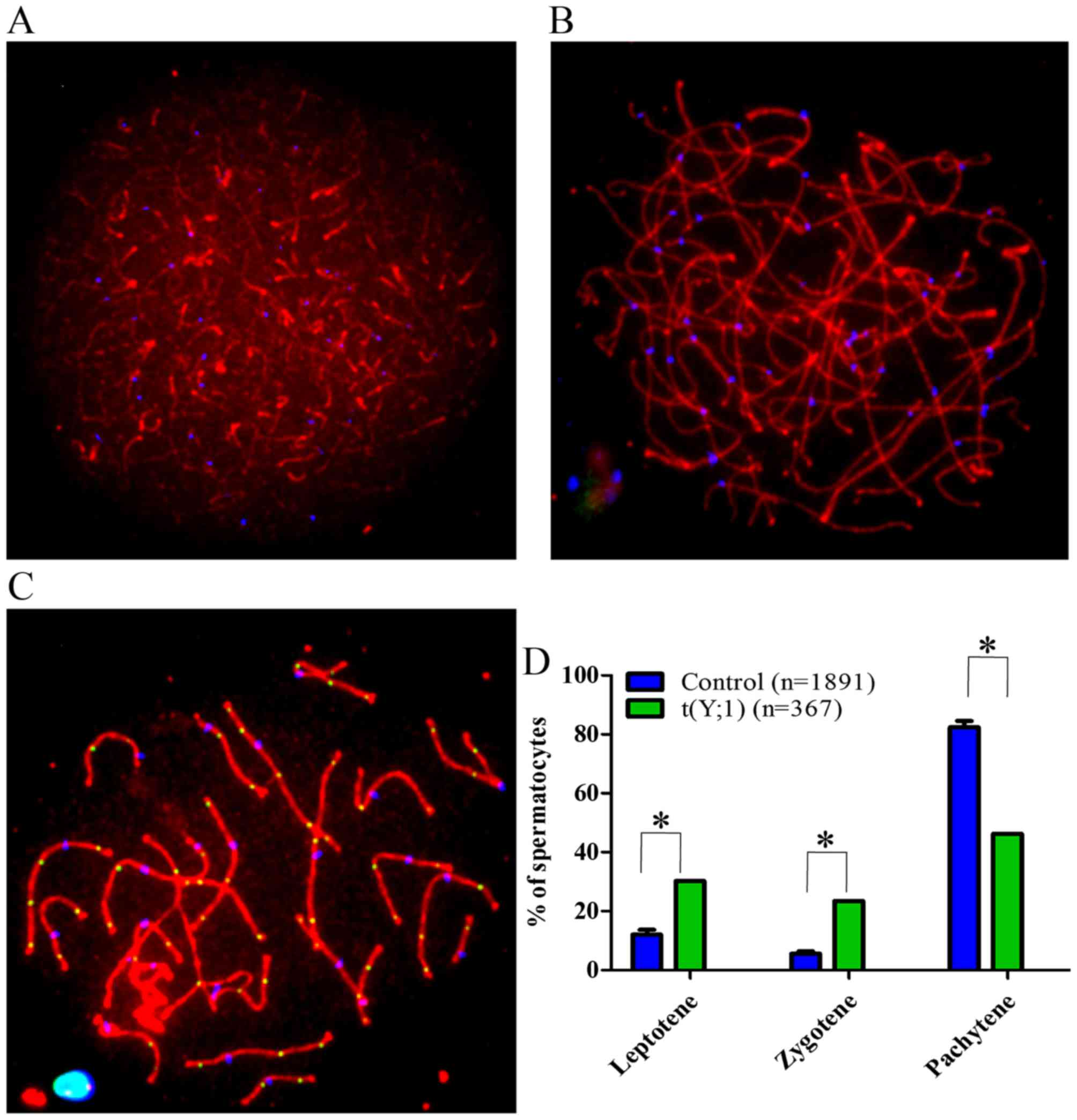
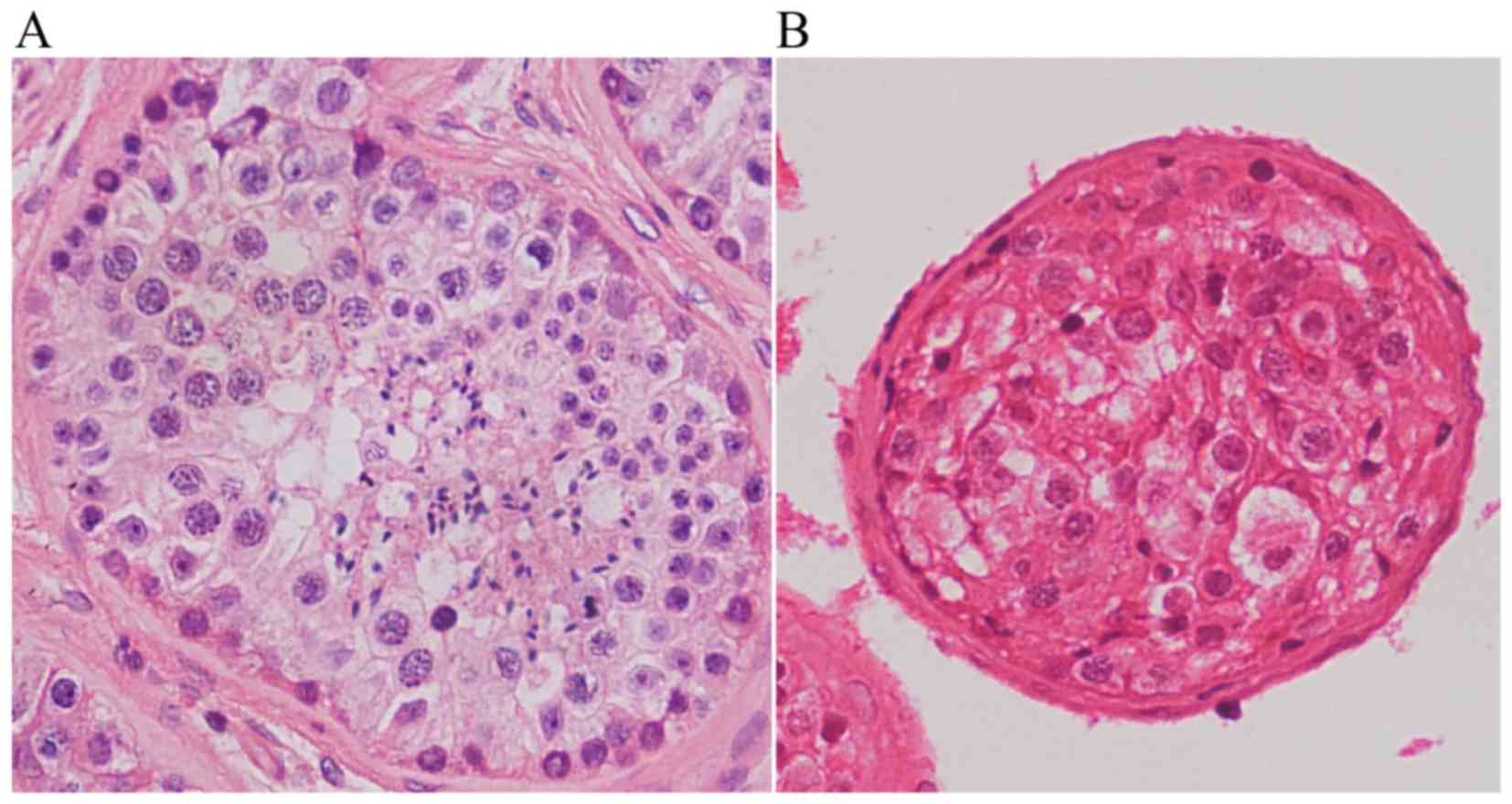
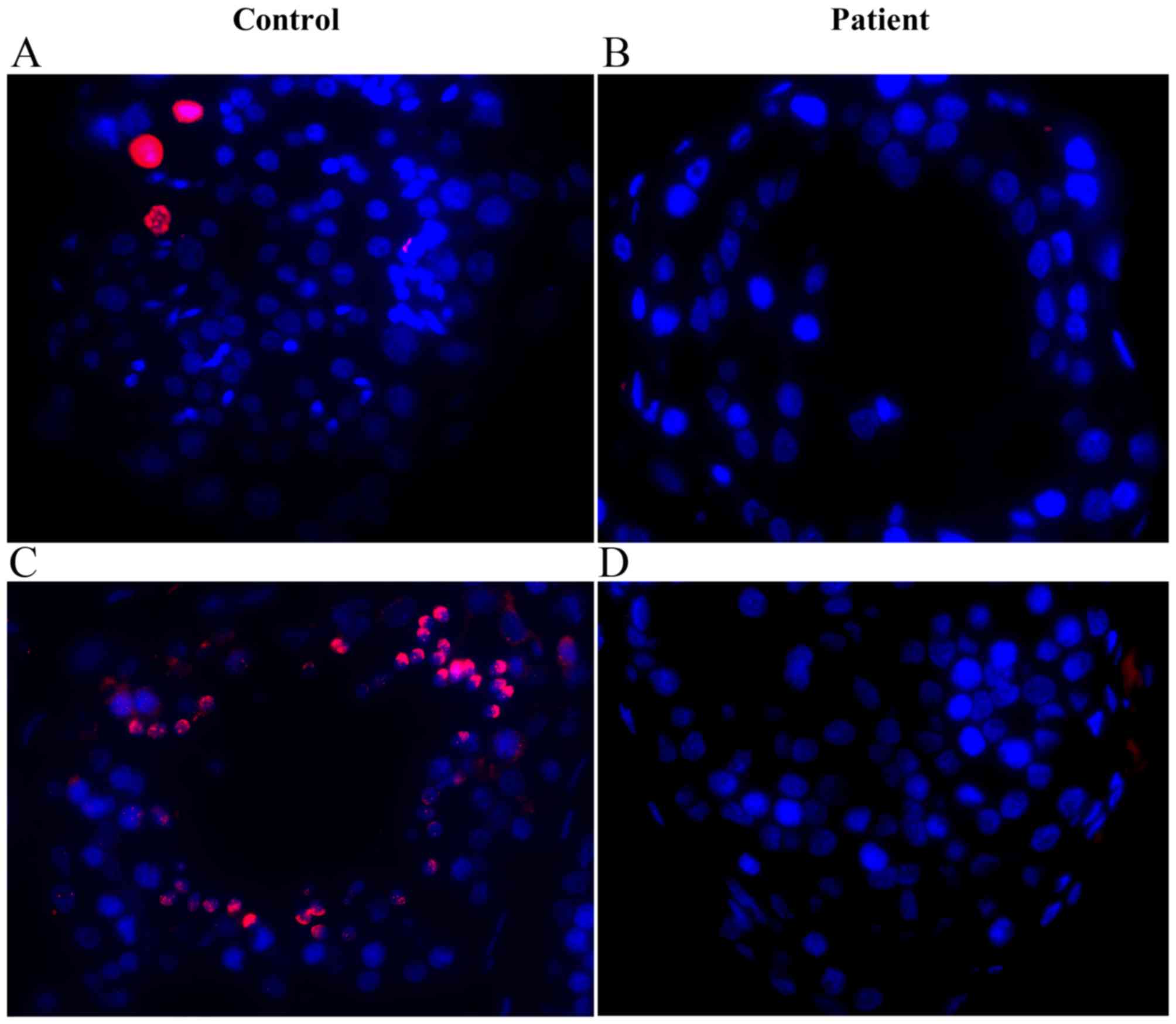
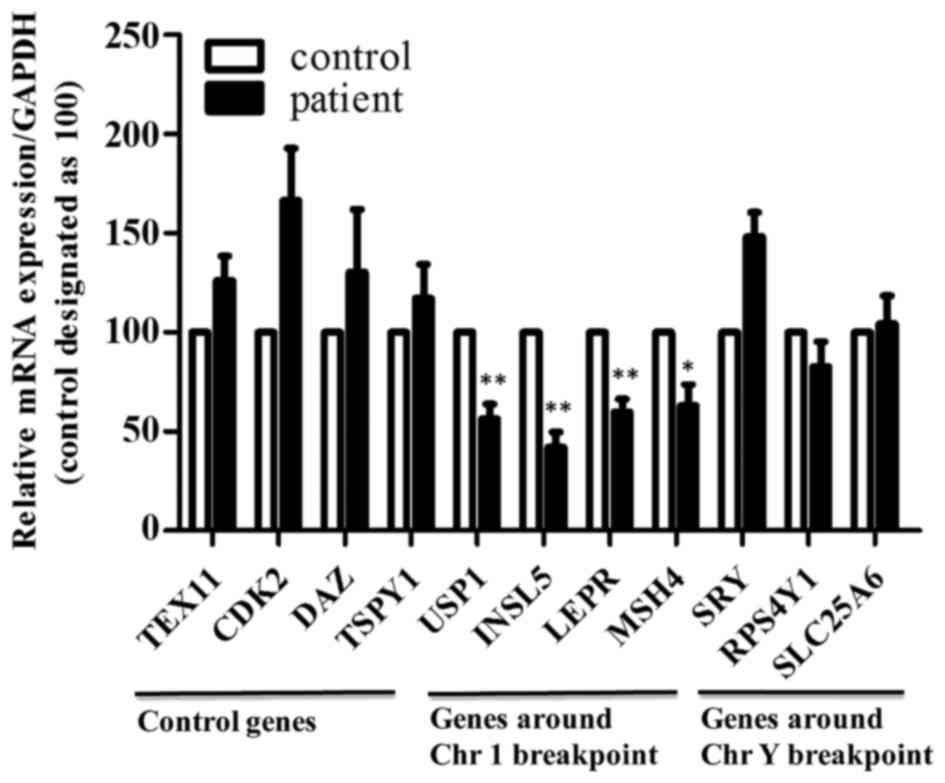
|
1
|
Alves C, Carvalho F, Cremades N, Sousa M
and Barros A: Unique (Y;13) translocation in a male with
oligozoospermia: Cytogenetic and molecular studies. Eur J Hum
Genet. 10:467–474. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsu LY: Phenotype/karyotype correlations
of Y chromosome aneuploidy with emphasis on structural aberrations
in postnatally diagnosed cases. Am J Med Genet. 53:108–140. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alitalo T, Tiihonen J, Hakola P and de la
Chapelle A: Molecular characterization of a Y;15 translocation
segregating in a family. Hum Genet. 79:29–35. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brisset S, Izard V, Misrahi M, Aboura A,
Madoux S, Ferlicot S, Schoevaert D, Soufir JC, Frydman R and
Tachdjian G: Cytogenetic, molecular and testicular tissue studies
in an infertile 45, X male carrying an unbalanced (Y;22)
translocation: Case report. Hum Reprod. 20:2168–2172. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gunel M, Cavkaytar S, Ceylaner G and
Batioglu S: Azoospermia and cryptorchidism in a male with a de novo
reciprocal t(Y;16) translocation. Genet Couns. 19:277–280.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang YT, Zhang HG, Wang RX, Yu Y, Zhang
ZH and Liu RZ: Novel Y chromosome breakpoint in an infertile male
with a de novo translocation t(Y;16): A case report. J Assist
Reprod Genet. 29:1427–1430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Conte RA, Kleyman SM, Klein V, Bialer MG
and Verma RS: Characterization of a de novo t(Y;9) (q11.2;q22) by
FISH technique. Ann Genet. 39:10–15. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vásquez-Velásquez AI, Arnaud-López L,
Figuera LE, Padilla-Gutiérrez JR, Rivas F and Rivera H: Ambiguous
genitalia by p9 p deletion inherent to a dic(Y;9)(q12;p24). J Appl
Genet. 46:415–418. 2005.
|
|
9
|
Röpke A, Stratis Y, Dossow-Scheele D,
Wieacker P, Kliesch S and Tüttelmann F: Mosaicism for an unbalanced
Y;21 translocation in an infertile man: A case report. J Assist
Reprod Genet. 30:1553–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun F, Oliver-Bonet M, Turek PJ, Ko E and
Martin RH: Meiotic studies in an azoospermic human translocation
(Y;1) carrier. Mol Hum Reprod. 11:361–364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang H, Wang L, Cui Y, Xu Z, Guo T, Cheng
D, Xu P, Yu W and Shi Q: Meiotic chromosome behavior in a human
male t(8;15) carrier. J Genet Genomics. 41:177–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan Z, Yang Q, Ye N, Wang L, Li J, Yu D,
Cooke HJ and Shi Q: Complex relationship between meiotic
recombination frequency and autosomal synaptonemal complex length
per cell in normal human males. Am J Med Genet A. 158A:581–587.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu B, Hua J, Zhang Y, Jiang X, Zhang H, Ma
T, Zheng W, Sun R, Shen W, Sha J, et al: Proliferating cell nuclear
antigen (PCNA) regulates primordial follicle assembly by promoting
apoptosis of oocytes in fetal and neonatal mouse ovaries. PLoS One.
6:e160462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ashley T, Plug AW, Xu J, Solari AJ, Reddy
G, Golub EI and Ward DC: Dynamic changes in Rad51 distribution on
chromatin during meiosis in male and female vertebrates.
Chromosoma. 104:19–28. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moens PB, Chen DJ, Shen Z, Kolas N,
Tarsounas M, Heng HH and Spyropoulos B: Rad51 immunocytology in rat
and mouse spermatocytes and oocytes. Chromosoma. 106:207–215. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gonsalves J, Sun F, Schlegel PN, Turek PJ,
Hopps CV, Greene C, Martin RH and Pera RA: Defective recombination
in infertile men. Hum Mol Genet. 13:2875–2883. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vidal F, Navarro J, Templado C, Marina S
and Egozcue J: Development and behavior of synaptonemal complexes
in human spermatocytes by light and electron microscopy. Hum Genet.
68:142–147. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
von Wettstein D, Rasmussen SW and Holm PB:
The synaptonemal complex in genetic segregation. Annu Rev Genet.
18:331–413. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Walpita D, Plug AW, Neff NF, German J and
Ashley T: Bloom's syndrome protein, BLM, colocalizes with
replication protein A in meiotic prophase nuclei of mammalian
spermatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 96:5622–5627. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mahadevaiah SK, Turner JM, Baudat F,
Rogakou EP, de Boer P, Blanco-Rodríguez J, Jasin M, Keeney S,
Bonner WM and Burgoyne PS: Recombinational DNA double-strand breaks
in mice precede synapsis. Nat Genet. 27:271–276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Turner JM, Aprelikova O, Xu X, Wang R, Kim
S, Chandramouli GV, Barrett JC, Burgoyne PS and Deng CX: BRCA1,
histone H2AX phosphorylation, and male meiotic sex chromosome
inactivation. Curr Biol. 14:2135–2142. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perrin A, Douet-Guilbert N, Le Bris MJ,
Keromnes G, Langlois ML, Barrière P, Amice J, Amice V, De
Braekeleer M and Morel F: Segregation of chromosomes in sperm of a
t(X;18) (q11;p11.1) carrier inherited from his mother: Case report.
Hum Reprod. 23:227–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pinho MJ, Neves R, Costa P, Ferrás C,
Sousa M, Alves C, Almeida C, Fernandes S, Silva J, Ferrás L, et al:
Unique t(Y;1) (q12;q12) reciprocal translocation with loss of the
hetero-chromatic region of chromosome 1 in a male with azoospermia
due to meiotic arrest: A case report. Hum Reprod. 20:689–696. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ferguson KA, Chow V and Ma S: Silencing of
unpaired meiotic chromosomes and altered recombination patterns in
an azoospermic carrier of a t(8;13) reciprocal translocation. Hum
Reprod. 23:988–995. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oliver-Bonet M, Ko E and Martin RH: Male
infertility in reciprocal translocation carriers: The sex body
affair. Cytogenet Genome Res. 111:343–346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leng M, Li G, Zhong L, Hou H, Yu D and Shi
Q: Abnormal synapses and recombination in an azoospermic male
carrier of a reciprocal translocation t(1;21). Fertil Steril.
91:1293.e1217–1222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Turner JM: Meiotic sex chromosome
inactivation. Development. 134:1823–1831. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Turner JM, Mahadevaiah SK,
Fernandez-Capetillo O, Nussenzweig A, Xu X, Deng CX and Burgoyne
PS: Silencing of unsynapsed meiotic chromosomes in the mouse. Nat
Genet. 37:41–47. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Baarends WM, Wassenaar E, van der Laan R,
Hoogerbrugge J, Sleddens-Linkels E, Hoeijmakers JH, de Boer P and
Grootegoed JA: Silencing of unpaired chromatin and histone H2A
ubiquitination in mammalian meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1041–1053.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schoenmakers S, Wassenaar E, van Cappellen
WA, Derijck AA, de Boer P, Laven JS, Grootegoed JA and Baarends WM:
Increased frequency of asynapsis and associated meiotic silencing
of heterologous chromatin in the presence of irradiation-induced
extra DNA double strand breaks. Dev Biol. 317:270–281. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Forejt J: Hybrid sterility in the mouse.
Trends Genet. 12:412–417. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Homolka D, Jansa P and Forejt J:
Genetically enhanced asynapsis of autosomal chromatin promotes
transcriptional dysregulation and meiotic failure. Chromosoma.
121:91–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
33
|
Burgoyne PS, Mahadevaiah SK and Turner JM:
The consequences of asynapsis for mammalian meiosis. Nat Rev Genet.
10:207–216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mahadevaiah SK, Bourc'his D, de Rooij DG,
Bestor TH, Turner JM and Burgoyne PS: Extensive meiotic asynapsis
in mice antagonises meiotic silencing of unsynapsed chromatin and
consequently disrupts meiotic sex chromosome inactivation. J Cell
Biol. 182:263–276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Manterola M, Page J, Vasco C, Berríos S,
Parra MT, Viera A, Rufas JS, Zuccotti M, Garagna S and
Fernández-Donoso R: A high incidence of meiotic silencing of
unsynapsed chromatin is not associated with substantial pachytene
loss in heterozygous male mice carrying multiple simple
robertsonian translocations. PLoS Genet. 5:e10006252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mark M, Jacobs H, Oulad-Abdelghani M,
Dennefeld C, Féret B, Vernet N, Codreanu CA, Chambon P and
Ghyselinck NB: STRA8-deficient spermatocytes initiate, but fail to
complete, meiosis and undergo premature chromosome condensation. J
Cell Sci. 121:3233–3242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zimmermann C, Romero Y, Warnefors M,
Bilican A, Borel C, Smith LB, Kotaja N, Kaessmann H and Nef S: Germ
cell-specific targeting of DICER or DGCR8 reveals a novel role for
endo-siRNAs in the progression of mammalian spermatogenesis and
male fertility. PLoS One. 9:e1070232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Subramanian VV and Hochwagen A: The
meiotic checkpoint network: Step-by-step through meiotic prophase.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 6:a0166752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Harewood L, Schütz F, Boyle S, Perry P,
Delorenzi M, Bickmore WA and Reymond A: The effect of
translocation-induced nuclear reorganization on gene expression.
Genome Res. 20:554–564. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kleinjan DA and van Heyningen V:
Long-range control of gene expression: Emerging mechanisms and
disruption in disease. Am J Hum Genet. 76:8–32. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Wang W: Emergence of a DNA-damage response
network consisting of Fanconi anaemia and BRCA proteins. Nat Rev
Genet. 8:735–748. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim JM, Parmar K, Huang M, Weinstock DM,
Ruit CA, Kutok JL and D'Andrea AD: Inactivation of murine Usp1
results in genomic instability and a Fanconi anemia phenotype. Dev
Cell. 16:314–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Burnicka-Turek O, Mohamed BA, Shirneshan
K, Thanasupawat T, Hombach-Klonisch S, Klonisch T and Adham IM:
INSL5-deficient mice display an alteration in glucose homeostasis
and an impaired fertility. Endocrinology. 153:4655–4665. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tartaglia LA: The leptin receptor. J Biol
Chem. 272:6093–6096. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Luca C, Kowalski TJ, Zhang Y, Elmquist
JK, Lee C, Kilimann MW, Ludwig T, Liu SM and Chua SC Jr: Complete
rescue of obesity, diabetes, and infertility in db/db mice by
neuron-specific LEPR-B transgenes. J Clin Invest. 115:3484–3493.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Paquis-Flucklinger V, Santucci-Darmanin S,
Paul R, Saunières A, Turc-Carel C and Desnuelle C: Cloning and
expression analysis of a meiosis-specific MutS homolog: The human
MSH4 gene. Genomics. 44:188–194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Winand NJ, Panzer JA and Kolodner RD:
Cloning and characterization of the human and Caenorhabditis
elegans homologs of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae MSH5 gene.
Genomics. 53:69–80. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kneitz B, Cohen PE, Avdievich E, Zhu L,
Kane MF, Hou H Jr, Kolodner RD, Kucherlapati R, Pollard JW and
Edelmann W: MutS homolog 4 localization to meiotic chromosomes is
required for chromosome pairing during meiosis in male and female
mice. Genes Dev. 14:1085–1097. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|