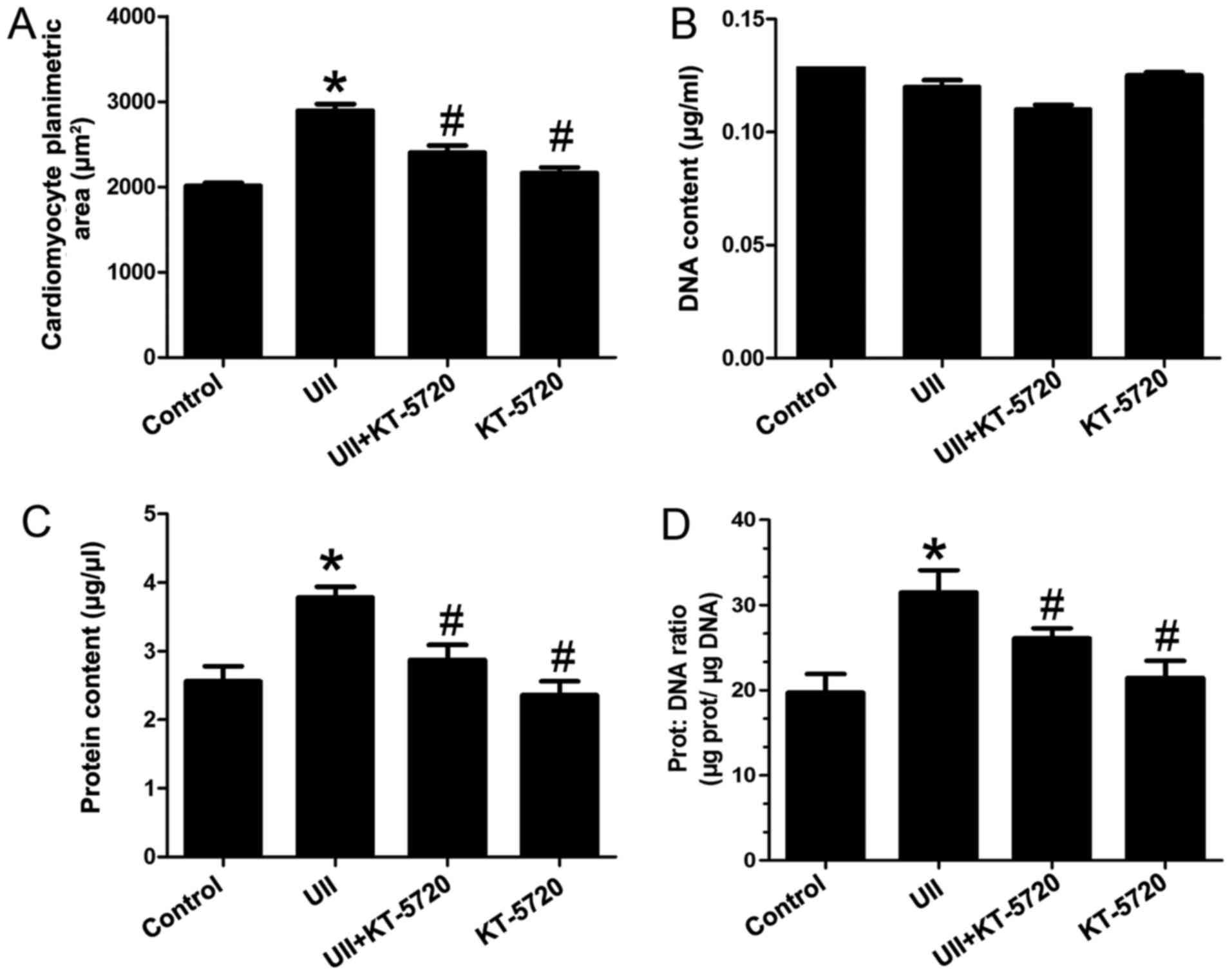
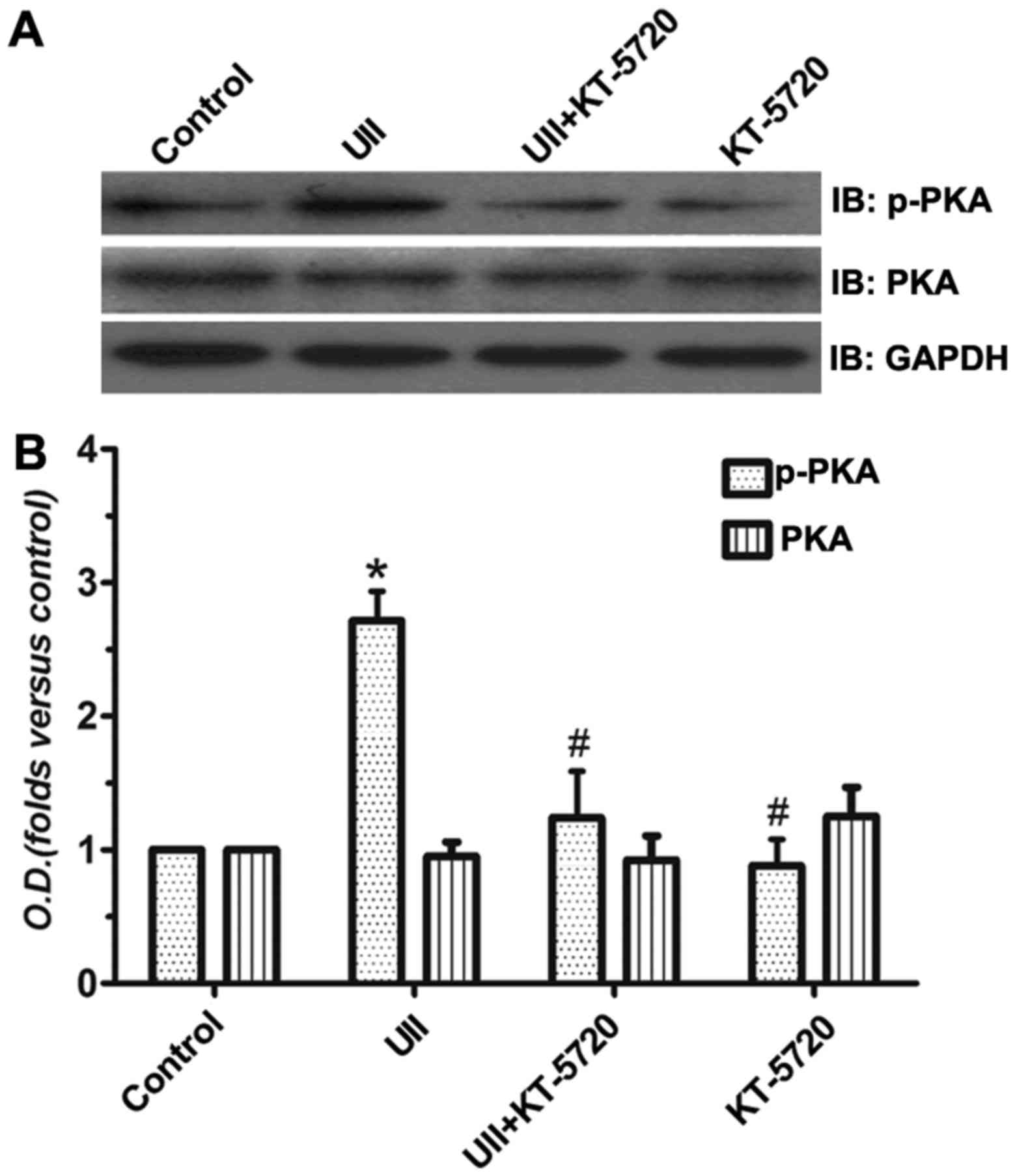
|
1
|
Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB
and Castelli WP: Prognostic implications of echocardiographically
determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N
Engl J Med. 322:1561–1566. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tang S, Chen H, Cheng Y, Nasir MA, Kemper
N and Bao E: The interactive association between heat shock factor
1 and heat shock proteins in primary myocardial cells subjected to
heat stress. Int J Mol Med. 37:56–62. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu C, Dong S and Li Y: Effects of
miRNA-455 on cardiac hypertrophy induced by pressure overload. Int
J Mol Med. 35:893–900. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu P, Yan S, Chen M, Chen A, Yao D, Xu X,
Cai X, Wang L and Huang X: Effects of baicalin on collagen I and
collagen III expression in pulmonary arteries of rats with hypoxic
pulmonary hypertension. Int J Mol Med. 35:901–908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen P, Li F, Xu Z, Li Z and Yi XP:
Expression and distribution of Src in the nucleus of myocytes in
cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Mol Med. 32:165–173. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heineke J and Molkentin JD: Regulation of
cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 7:589–600. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo H, Liu B, Hou L, The E, Li G, Wang D,
Jie Q, Che W and Wei Y: The role of mAKAPβ in the process of
cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II. Int J Mol Med.
35:1159–1168. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hill JA and Olson EN: Cardiac plasticity.
N Engl J Med. 358:1370–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chuang CT, Guh JY, Lu CY, Chen HC and
Chuang LY: S100B is required for high glucose-induced pro-fibrotic
gene expression and hypertrophy in mesangial cells. Int J Mol Med.
35:546–552. 2015.
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Si Y and Ma N: Meis1 promotes
poly (rC)-binding protein 2 expression and inhibits angiotensin
II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. IUBMB Life. 68:13–22. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou HM, Zhong ML, Zhang YF, Cui WY, Long
CL and Wang H: Natakalim improves post-infarction left ventricular
remodeling by restoring the coordinated balance between endothelial
function and cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Mol Med. 34:1209–1218.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gong H, Ma H, Liu M, Zhou B, Zhang G, Chen
Z, Jiang G, Yan Y, Yang C, Kanda M, et al: Urotensin II inhibits
the proliferation but not the differentiation of cardiac side
population cells. Peptides. 32:1035–1041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Douglas SA, Tayara L, Ohlstein EH, Halawa
N and Giaid A: Congestive heart failure and expression of
myocardial urotensin II. Lancet. 359:1990–1997. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu JC, Chen CH, Chen JJ and Cheng TH:
Urotensin II induces rat cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via the
transient oxidization of Src homology 2-containing tyrosine
phosphatase and transactivation of epidermal growth factor
receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 76:1186–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Onan D, Pipolo L, Yang E, Hannan RD and
Thomas WG: Urotensin II promotes hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes
via mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Endocrinol.
18:2344–2354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gruson D, Ginion A, Decroly N, Lause P,
Vanoverschelde JL, Ketelslegers JM, Bertrand L and Thissen JP:
Urotensin II induction of adult cardiomyocytes hypertrophy involves
the Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Peptides. 31:1326–1333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maguire JJ and Davenport AP: Is
urotensin-II the new endothelin? Br J Pharmacol. 137:579–588. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Domínguez-Rodríguez A, Díaz I,
Rodríguez-Moyano M, Calderón-Sánchez E, Rosado JA, Ordóñez A and
Smani T: Urotensin-II signaling mechanism in rat coronary artery:
role of STIM1 and Orai1-dependent store operated calcium influx in
vasoconstriction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1325–1332.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Ying J, Jiang D, Chang Z, Li H,
Zhang G, Gong S, Jiang X and Tao J: Urotensin-II receptor
stimulation of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels requires the
βγ subunits of Gi/o-protein and phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-dependent protein kinase C β1 isoform. J Biol Chem.
290:8644–8655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rababa'h A, Singh S, Suryavanshi SV,
Altarabsheh SE, Deo SV and McConnell BK: Compartmentalization role
of A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) in mediating protein kinase
A (PKA) signaling and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Int J Mol Sci.
16:218–229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masterson LR, Yu T, Shi L, Wang Y,
Gustavsson M, Mueller MM and Veglia G: cAMP-dependent protein
kinase A selects the excited state of the membrane substrate
phospholamban. J Mol Biol. 412:155–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin Z, Wang X, Zhang L, Zhou H, Wei L and
Dong X: Aspirin attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy by inhibiting the Ca(2+)/Calcineurin-NFAT signaling
pathway. Cardiovasc Ther. 34:21–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fabiato A: Calcium-induced release of
calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol.
245:C1–C14. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bers DM: Cardiac excitation-contraction
coupling. Nature. 415:198–205. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bers DM: Ca transport during contraction
and relaxation in mammalian ventricular muscle. Basic Res Cardiol.
92(Suppl 1): 1–10. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
MacLennan DH and Kranias EG:
Phospholamban: a crucial regulator of cardiac contractility. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:566–577. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang C, Shan XL, Liao YL, Zhao P, Guo W,
Wei HC and Lu R: Effects of stachydrine on norepinephrine-induced
neonatal rat cardiac myocytes hypertrophy and intracellular calcium
transients. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:4742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Giordano A, Romano S, Mallardo M,
D'Angelillo A, Calì G, Corcione N, Ferraro P and Romano MF: FK506
can activate transforming growth factor-beta signalling in vascular
smooth muscle cells and promote proliferation. Cardiovasc Res.
79:519–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maclennan DH: Interactions of the calcium
ATPase with phospholamban and sarcolipin: structure, physiology and
pathophysiology. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 25:600–601. 2004.
|
|
30
|
Irie T, Sips PY, Kai S, Kida K, Ikeda K,
Hirai S, Moazzami K, Jiramongkolchai P, Bloch DB, Doulias PT, et
al: S-nitrosylation of calcium-handling proteins in cardiac
adrenergic signaling and hypertrophy. Circ Res. 117:793–803. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Walsh DA and Van Patten SM: Multiple
pathway signal transduction by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
FASEB J. 8:1227–1236. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shioya T: A simple technique for isolating
healthy heart cells from mouse models. J Physiol Sci. 57:327–335.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamazaki T, Komuro I, Zou Y, Kudoh S,
Mizuno T, Hiroi Y, Shiojima I, Takano H, Kinugawa K, Kohmoto O, et
al: Protein kinase A and protein kinase C synergistically activate
the Raf-1 kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 29:2491–2501.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Komuro I and Yazaki Y: Control of cardiac
gene expression by mechanical stress. Annu Rev Physiol. 55:55–75.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shi H, Han Q, Xu J, Liu W, Chu T and Zhao
L: Urotensin II induction of neonatal cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
involves the CaMKII/PLN/SERCA 2a signaling pathway. Gene. 583:8–14.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tölle M and van der Giet M:
Cardiorenovascular effects of urotensin II and the relevance of the
UT receptor. Peptides. 29:743–763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Douglas SA, Sulpizio AC, Piercy V, Sarau
HM, Ames RS, Aiyar NV, Ohlstein EH and Willette RN: Differential
vasoconstrictor activity of human urotensin-II in vascular tissue
isolated from the rat, mouse, dog, pig, marmoset and cynomolgus
monkey. Br J Pharmacol. 131:1262–1274. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bai XY, Liu XC, Yang Q, Tang XD and He GW:
The interaction between human urotensin II and vasodilator agents
in human internal mammary artery with possible clinical
implications. Ann Thorac Surg. 92:610–616. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shyu KG, Wang BW, Chen WJ, Kuan P and Lin
CM: Angiotensin II mediates urotensin II expression by hypoxia in
cultured cardiac fibroblast. Eur J Clin Invest. 42:17–26. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hassan GS, Chouiali F, Saito T, Hu F,
Douglas SA, Ao Z, Willette RN, Ohlstein EH and Giaid A: Effect of
human urotensin-II infusion on hemodynamics and cardiac function.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 81:125–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|