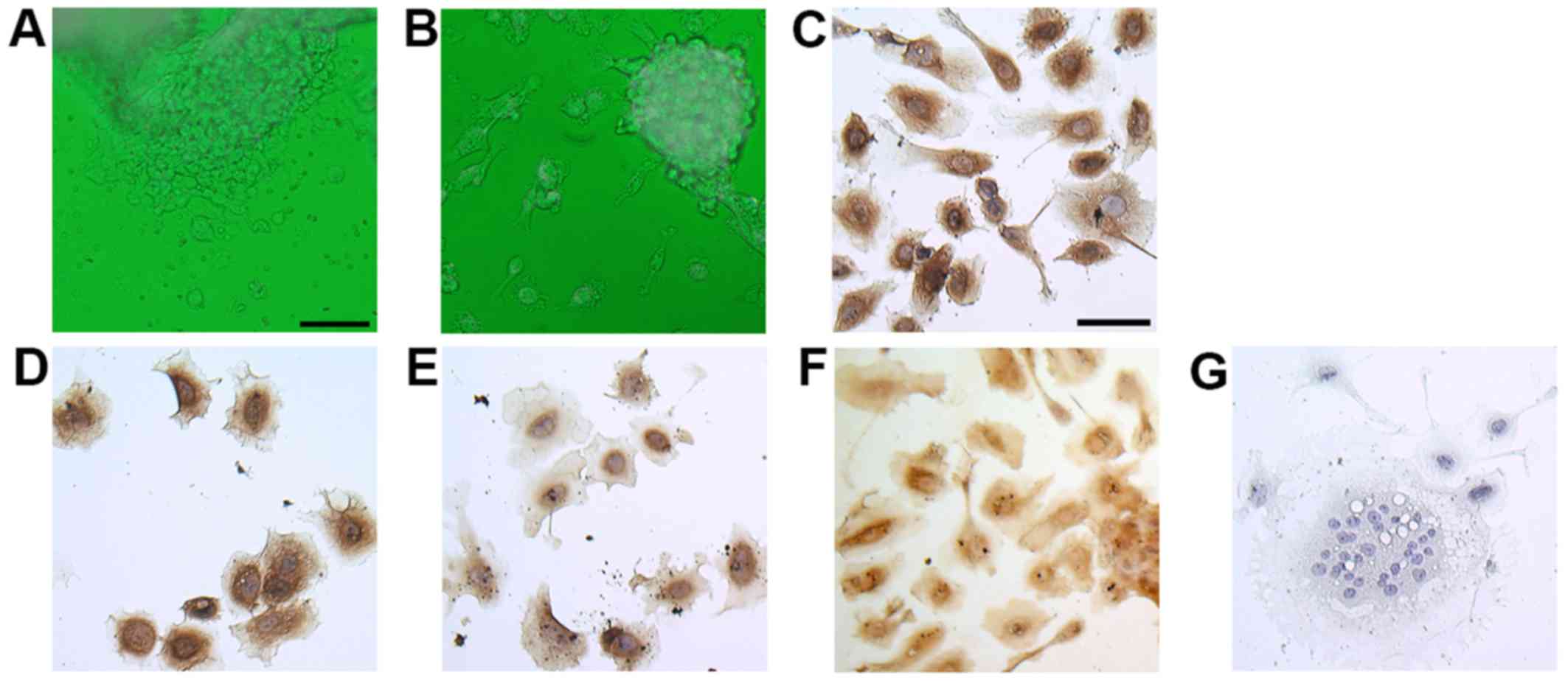
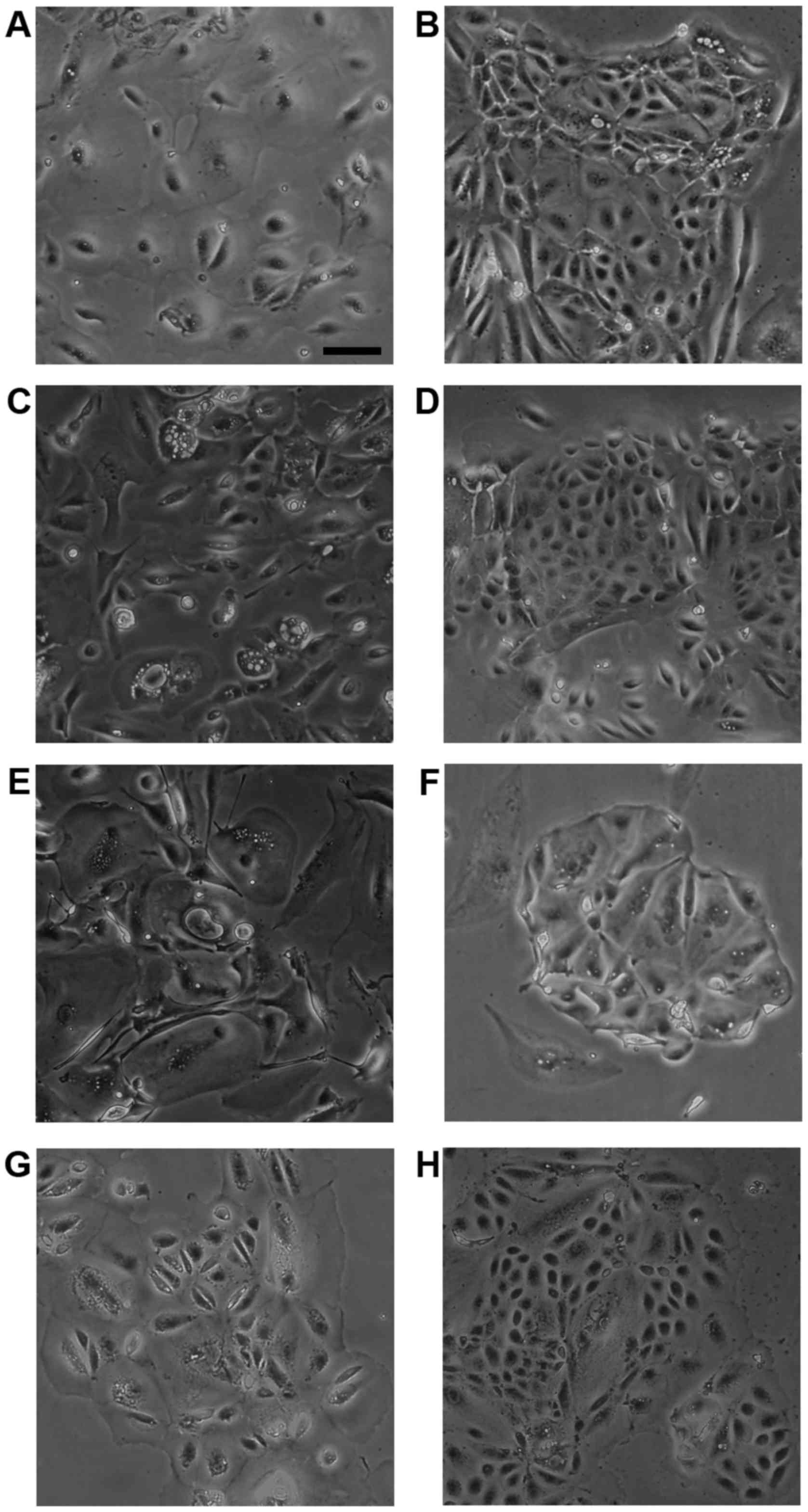
|
1
|
Kajii T and Ohama K: Androgenetic origin
of hydatidiform mole. Nature. 268:633–634. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wake N, Seki T, Fujita H, Okubo H, Sakai
K, Okuyama K, Hayashi H, Shiina Y, Sato H, Kuroda M, et al:
Malignant potential of homozygous and heterozygous complete moles.
Cancer Res. 44:1226–1230. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vejerslev LO, Dissing J, Hansen HE and
Poulsen H: Hydatidiform mole: Genetic origin in polyploid
conceptuses. Hum Genet. 76:11–19. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ohama K, Ueda K, Okamoto E, Takenaka M and
Fujiwara A: Cytogenetic and clinicopathologic studies of partial
moles. Obstet Gynecol. 68:259–262. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaneki E, Kobayashi H, Hirakawa T, Matsuda
T, Kato H and Wake N: Incidence of postmolar gestational
trophoblastic disease in androgenetic moles and the morphological
features associated with low risk postmolar gestational
trophoblastic disease. Cancer Sci. 101:1717–1721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seckl MJ, Sebire NJ and Berkowitz RS:
Gestational trophoblastic disease. Lancet. 376:717–729. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kan M, Yamamoto E, Niimi K, Tamakoshi K,
Sekiya Y, Nishino K, Ino K and Kikkawa F: Gestational trophoblastic
neoplasia and pregnancy outcome after routine second curettage for
hydatidiform mole: A retrospective observational study. J Reprod
Med. 61:373–379. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Taillon-Miller P, Bauer-Sardiña I, Zakeri
H, Hillier L, Mutch DG and Kwok PY: The homozygous complete
hydatidiform mole: A unique resource for genome studies. Genomics.
46:307–310. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Steinberg KM, Schneider VA, Graves-Lindsay
TA, Fulton RS, Agarwala R, Huddleston J, Shiryev SA, Morgulis A,
Surti U, Warren WC, et al: Single haplotype assembly of the human
genome from a hydatidiform mole. Genome Res. 24:2066–2076. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kuroda K, Kiyono T, Eitsuka T, Isogai H,
Takahashi K, Donai K, Isogai E and Fukuda T: Establishment of cell
lines derived from the genus Macaca through controlled expression
of cell cycle regulators. J Cell Biochem. 116:205–211. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Donai K, Kiyono T, Eitsuka T, Guo Y,
Kuroda K, Sone H, Isogai E and Fukuda T: Bovine and porcine
fibroblasts can be immortalized with intact karyotype by the
expression of mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4, cyclin D, and
telomerase. J Biotechnol. 176:50–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sasaki R, Narisawa-Saito M, Yugawa T,
Fujita M, Tashiro H, Katabuchi H and Kiyono T: Oncogenic
transformation of human ovarian surface epithelial cells with
defined cellular oncogenes. Carcinogenesis. 30:423–431. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okamoto T, Aoyama T, Nakayama T, Nakamata
T, Hosaka T, Nishijo K, Nakamura T, Kiyono T and Toguchida J:
Clonal heterogeneity in differentiation potential of immortalized
human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
295:354–361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bayasula IA, Iwase A, Kiyono T, Takikawa
S, Goto M, Nakamura T, Nagatomo Y, Nakahara T, Kotani T, Kobayashi
H, et al: Establishment of a human nonluteinized granulosa cell
line that transitions from the gonadotropin-independent to the
gonadotropin-dependent status. Endocrinology. 153:2851–2860. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carey BW, Markoulaki S, Hanna J, Saha K,
Gao Q, Mitalipova M and Jaenisch R: Reprogramming of murine and
human somatic cells using a single polycistronic vector. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:157–162. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Miyoshi H, Blömer U, Takahashi M, Gage FH
and Verma IM: Development of a self-inactivating lentivirus vector.
J Virol. 72:8150–8157. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto E, Ito T, Abe A, Sido F, Ino K,
Itakura A, Mizutani S, Dovat S, Nomura S and Kikkawa F: Ikaros is
expressed in human extravillous trophoblasts and involved in their
migration and invasion. Mol Hum Reprod. 11:825–831. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamamoto E, Ino K, Miyoshi E, Inamori K,
Abe A, Sumigama S, Iwase A, Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Nawa A, et al:
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V regulates extravillous
trophoblast invasion through glycosylation of alpha5beta1 integrin.
Endocrinology. 150:990–999. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Austgulen R, Chedwick L, Vogt Isaksen C,
Vatten L and Craven C: Trophoblast apoptosis in human placenta at
term as detected by expression of a cytokeratin 18 degradation
product of caspase. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 126:1480–1486.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sasagawa M, Yamazaki T, Endo M, Kanazawa K
and Takeuchi S: Immunohistochemical localization of HLA antigens
and placental proteins (alpha hCG, beta hCG CTP, hPL and SP1 in
villous and extravillous trophoblast in normal human pregnancy: A
distinctive pathway of differentiation of extravillous trophoblast.
Placenta. 8:515–528. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lawler SD, Fisher RA and Dent J: A
prospective genetic study of complete and partial hydatidiform
moles. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 164:1270–1277. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Devergne O, Coulomb-L'Herminé A, Capel F,
Moussa M and Capron F: Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-induced
gene 3, an interleukin-12 p40-related molecule, throughout human
pregnancy: Involvement of syncytiotrophoblasts and extravillous
trophoblasts. Am J Pathol. 159:1763–1776. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niimi K, Yamamoto E, Fujiwara S, Shinjo K,
Kotani T, Umezu T, Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Ino K and Kikkawa F: High
expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase IVa promotes invasion
of choriocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 107:1969–1977. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu H, Hou CC, Luo LF, Hu YJ and Yang WX:
Endometrial stromal cells and decidualized stromal cells: Origins,
transformation and functions. Gene. 551:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Richards RG, Brar AK, Frank GR, Hartman SM
and Jikihara H: Fibroblast cells from term human decidua closely
resemble endometrial stromal cells: Induction of prolactin and
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 expression. Biol
Reprod. 52:609–615. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Telgmann R and Gellersen B: Marker genes
of decidualization: Activation of the decidual prolactin gene. Hum
Reprod Update. 4:472–479. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dunn CL, Kelly RW and Critchley HO:
Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: An enigmatic
transformation. Reprod Biomed Online. 7:151–161. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim JJ, Jaffe RC and Fazleabas AT:
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 expression in baboon
endometrial stromal cells: Regulation by filamentous actin and
requirement for de novo protein synthesis. Endocrinology.
140:997–1004. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lockwood CJ, Krikun G, Caze R, Rahman M,
Buchwalder LF and Schatz F: Decidual cell-expressed tissue factor
in human pregnancy and its involvement in hemostasis and
preeclampsia-related angiogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1127:67–72.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Graham CH, Hawley TS, Hawley RG,
MacDougall JR, Kerbel RS, Khoo N and Lala PK: Establishment and
characterization of first trimester human trophoblast cells with
extended lifespan. Exp Cell Res. 206:204–211. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang YL, Qiu W, Feng HC, Li YX, Zhuang LZ,
Wang Z, Liu Y, Zhou JQ, Zhang DH and Tsao GS: Immortalization of
normal human cytotrophoblast cells by reconstitution of telomeric
reverse transcriptase activity. Mol Hum Reprod. 12:451–460. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li RH and Zhuang LZ: The effects of growth
factors on human normal placental cytotrophoblast cell
proliferation. Hum Reprod. 12:830–834. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katayama M, Kiyono T, Horie K, Hirayama T,
Eitsuka T, Kuroda K, Donai K, Hidema S, Nishimori K and Fukuda T:
Establishment of an immortalized cell line derived from the prairie
vole via lentivirus-mediated transduction of mutant
cyclin-dependent kinase 4, cyclin D, and telomerase reverse
transcriptase. Exp Anim. 65:87–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Kuroda K, Kiyono T, Isogai E, Masuda M,
Narita M, Okuno K and Koyanagi Y: Fukuda T. Immortalization of
fetal bovine colon epithelial cells by expression of human cyclin
D1, mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4, and telomerase reverse
transcriptase: An in vitro model for bacterial infection. PLoS One.
10:e01434732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Inagawa Y, Yamada K, Yugawa T, Ohno S,
Hiraoka N, Esaki M, Shibata T, Aoki K, Saya H and Kiyono T: A human
cancer xenograft model utilizing normal pancreatic duct epithelial
cells conditionally transformed with defined oncogenes.
Carcinogenesis. 35:1840–1846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sundvall L, Lund H, Niemann I, Jensen UB,
Bolund L and Sunde L: Tetraploidy in hydatidiform moles. Hum
Reprod. 28:2010–2020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zygmunt M, Hahn D, Münstedt K, Bischof P
and Lang U: Invasion of cytotrophoblastic JEG-3 cells is stimulated
by hCG in vitro. Placenta. 19:587–593. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|