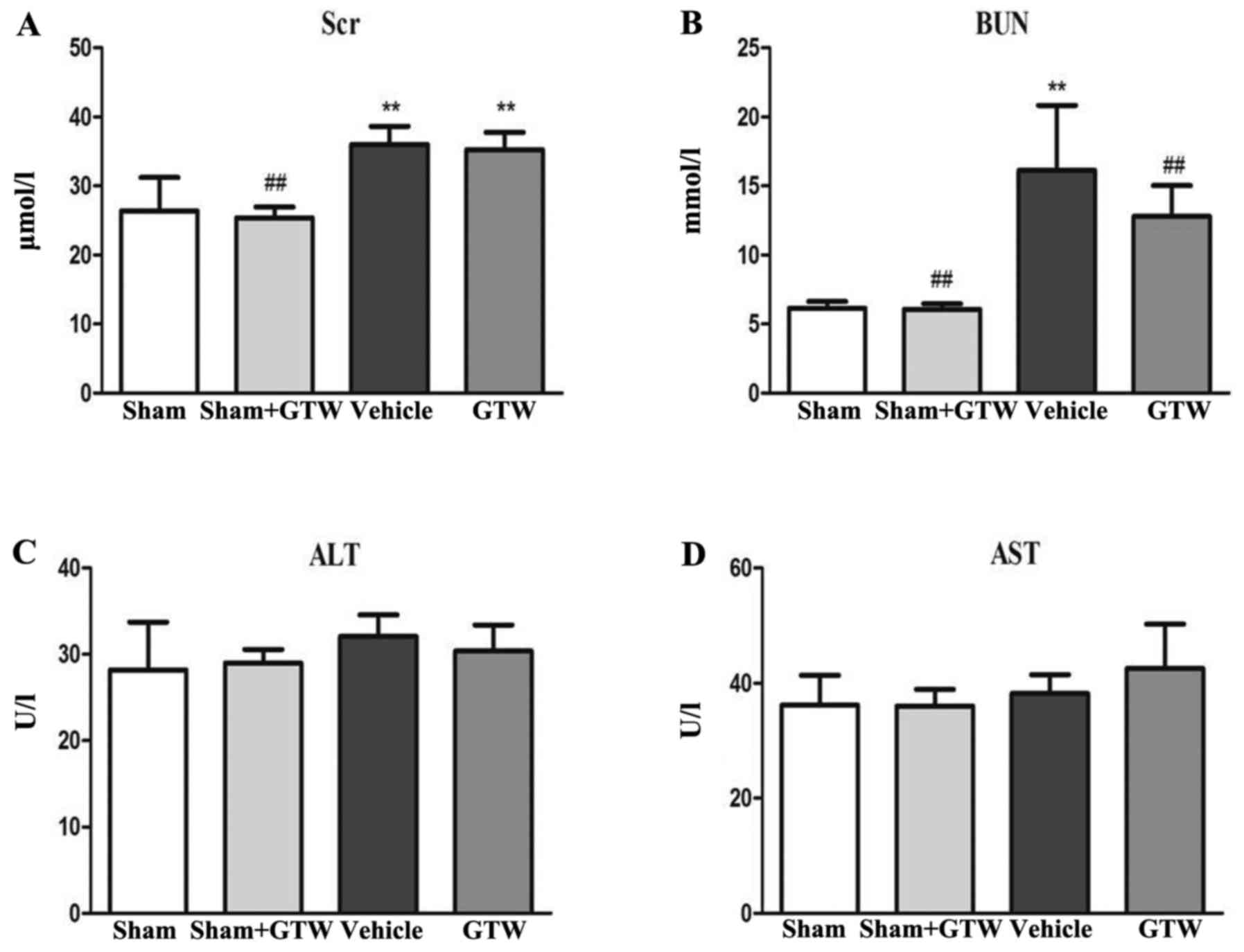
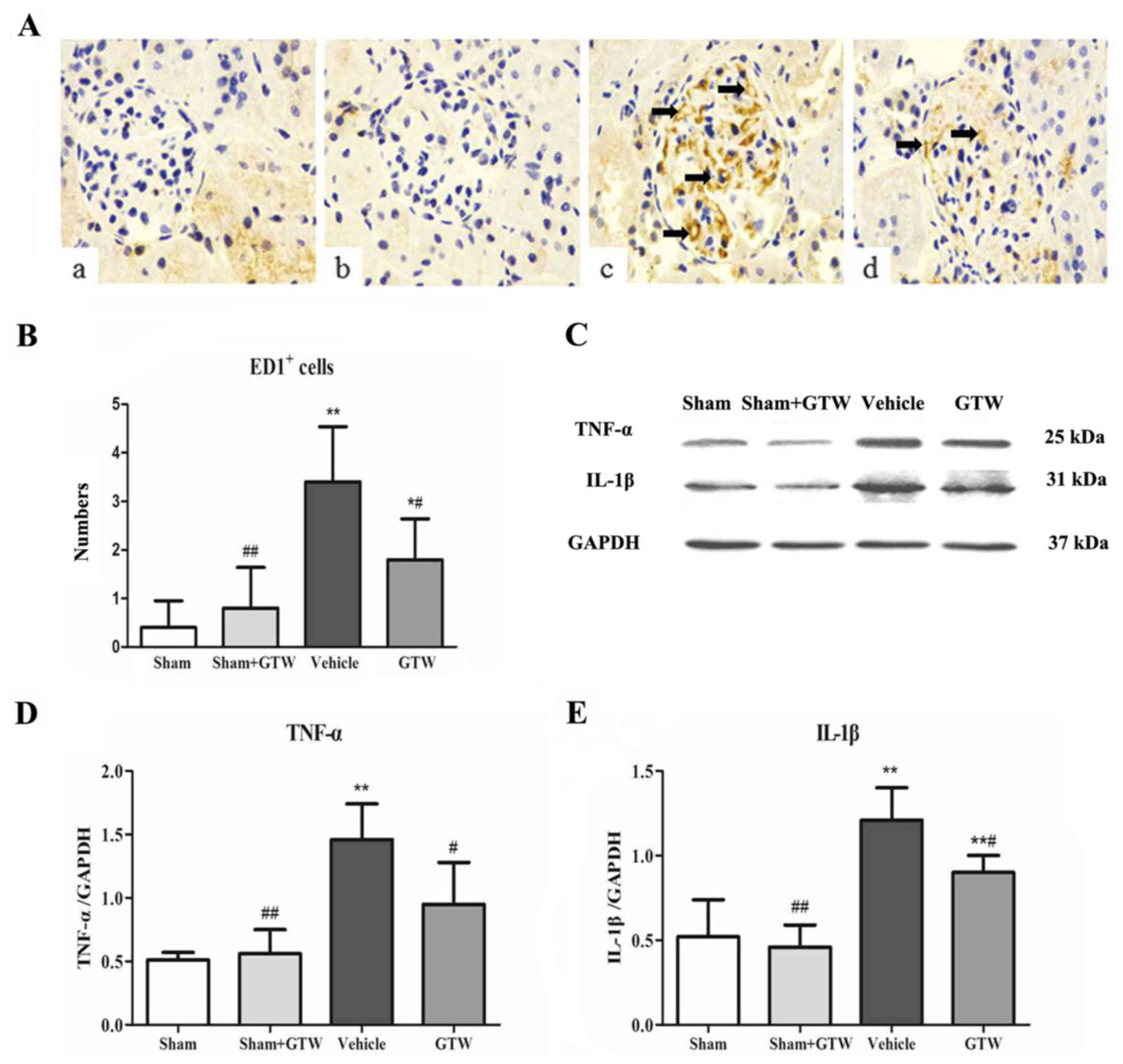
|
1
|
Agrawal NK and Kant S: Targeting
inflammation in diabetes: newer therapeutic options. World J
Diabetes. 5:697–710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C,
Muros de Fuentes M and García-Pérez J: Inflammatory molecules and
pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 7:327–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Utimura R, Fujihara CK, Mattar AL,
Malheiros DM, Noronha IL and Zatz R: Mycophenolate mofetil prevents
the development of glomerular injury in experimental diabetes.
Kidney Int. 63:209–216. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Navarro JF, Mora C, Muros M and García J:
Additive antiproteinuric effect of pentoxifylline in patients with
type 2 diabetes under angiotensin II receptor blockade: a
short-term, randomized, controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:2119–2126. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C,
Muros de Fuentes M, Chahin J, Méndez ML, Gallego E, Macía M, del
Castillo N, Rivero A, Getino MA, et al: Effect of pentoxifylline on
renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with
diabetic kidney disease: The PREDIAN trial. J Am Soc Nephrol.
26:220–229. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Schieven GL: The p38alpha kinase plays a
central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem. 9:1038–1048. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brinker AM, Ma J, Lipsky PE and Raskin I:
Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium
(Celastraceae). Phytochemistry. 68:732–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marks WH: Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F.
versus sulfasalazine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a
well-designed clinical trial of a botanical demonstrating
effectiveness. Fitoterapia. 82:85–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wan YG, Gu LB and Shimizu F: Mechanism of
protective effects of effective components in Ttipterygium
wilfordii Hook. f. on glomerulonephritis. Int J Clin Exp Med.
207:285–288. 2003.In Japanese.
|
|
10
|
Jiang M, Zha Q, Zhang C, Lu C, Yan X, Zhu
W, Liu W, Tu S, Hou L, Wang C, et al: Predicting and verifying
outcome of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. based therapy in
rheumatoid arthritis: from open to double-blinded randomized trial.
Sci Rep. 5:97002015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Leishi L: Clinical study of Tripterygium
wilfordii Hook in treating glomerulonephritis (author's transl).
Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 20:216–220. 1981.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu ZH, Li SJ, Wu Y, Zuo K, Wang B, Zeng
CH and Li LS: Treatment of membranous nephropathy with Tripterygium
wilfordii and steroid: a prospective randomized control trial. J
Nephrol Dialy Transpl. 18:303–309. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Ma R, Xu Y, Jiang W and Zhang W:
Combination of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F and angiotensin
receptor blocker synergistically reduces excretion of urinary
podocytes in patients with type 2 diabetic kidney disease.
Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 29:139–146. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu B, Wang Y, Jardine M, Jun M, Lv JC,
Cass A, Liyanage T, Chen HY, Wang YJ and Perkovic V: Tripterygium
preparations for the treatment of CKD: a systematic review and
meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 62:515–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ge Y, Xie H, Li S, Jin B, Hou J, Zhang H,
Shi M and Liu Z: Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F extract: a prospective, randomized,
controlled clinical trial. J Transl Med. 11:1342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao Q, Shen W, Qin W, Zheng C, Zhang M,
Zeng C, Wang S, Wang J, Zhu X and Liu Z: Treatment of db/db
diabetic mice with triptolide: a novel therapy for diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:3539–3547. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang YR, Wan YG, Sun W, Mao ZM, Zhao Q,
Shi XM and Yao J: Effects and mechanisms of multi-glycoside of
Tripterygium wilfordii improving glomerular inflammatory injury by
regulating p38MAPK signaling activation in diabetic nephropathy
rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 39:4102–4109. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Sun W, Wan Y, Che X, He F, Pu H
and Dou C: Preventive effects of multi-glycoside of Tripterygium
wilfordii on glomerular lesions in experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 35:1460–1465. 2010.In
Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li K and Wang S: Fingerprint chromatogram
analysis of extracts from the leaves of Tripterygium wilfordii
Hook. F. by high performance liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci.
28:653–657. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kupchan SM, Court WA, Dailey RG Jr,
Gilmore CJ and Bryan RF: Triptolide and tripdiolide, novel
antileukemic diter-penoid triepoxides from Tripterygium wilfordii.
J Am Chem Soc. 94:7194–7195. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakano K, Yoshida C, Furukawa W, Takaishi
Y and Shishido K: Terpenoids in transformed root culture of
Tripterygium wilfordii. Phytochemistry. 49:1821–1824. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mao ZM, Shen SM, Wan YG, Sun W, Chen HL,
Huang MM, Yang JJ, Wu W, Tang HT and Tang RM: Huangkui capsule
attenuates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy rats through
regulating oxidative stress and p38MAPK/Akt pathways, compared to
α-lipoic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 173:256–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wada J and Makino H: Inflammation and the
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:139–152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Duran-Salgado MB and Rubio-Guerra AF:
Diabetic nephropathy and inflammation. World J Diabetes. 5:393–398.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Navarro-González JF and Mora-Fernández C:
The role of inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 19:433–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan YG, Sun W, Zhen YJ, Che XY, Pu HP,
Wang Y, Li M, Ruan JG and Yan QJ: Multi-glycoside of Tripterygium
wilfordii Hook. f. reduces proteinuria through improving podocyte
slit diaphragm dysfunction in anti-Thy1.1 glomerulonephritis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 136:322–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wan YG, Che XY, Sun W, Huang YR, Meng XJ,
Chen HL, Shi XM, Tu Y, Wu W and Liu YL: Low-dose of multi-glycoside
of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f., a natural regulator of
TGF-β1/Smad signaling activity improves adriamycin induced
glomerulosclerosis in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 151:1079–1089. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wan YG, Zhao Q, Sun W, Zhang HL, Li M, Wei
QX, Wu W, Yue LJ and Wang Q: Contrasting dose-effects of
multi-glycoside of Tripterygium wilfordii HOOK. f. on glomerular
inflammation and hepatic damage in two types of anti-Thy1.1
glomerulonephritis. J Pharmacol Sci. 118:433–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu S and Chen ZJ: Expanding role of
ubiquitination in NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:6–21. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nakagawa T, Sato W, Glushakova O, Heinig
M, Clarke T, Campbell-Thompson M, Yuzawa Y, Atkinson MA, Johnson RJ
and Croker B: Diabetic endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout
mice develop advanced diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
18:539–550. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kodera R, Shikata K, Kataoka HU, Takatsuka
T, Miyamoto S, Sasaki M, Kajitani N, Nishishita S, Sarai K, Hirota
D, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist ameliorates
renal injury through its anti-inflammatory action without lowering
blood glucose level in a rat model of type 1 diabetes.
Diabetologia. 54:965–978. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|