|
1
|
Krishnan K, Steptoe AL, Martin HC,
Pattabiraman DR, Nones K, Waddell N, Mariasegaram M, Simpson PT,
Lakhani SR, Vlassov A, et al: miR-139-5p is a regulator of
metastatic pathways in breast cancer. RNA. 19:1767–1780. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Q, Kang X, Yang B, Wang J and Yang
F: Antiangiogenic effect of capecitabine combined with ginsenoside
Rg3 on breast cancer in mice. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
23:647–653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brown RH: Medicine. A reinnervating
microRNA. Science. 326:1494–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo H, Hu X, Ge S, Qian G and Zhang J:
Regulation of RAP1B by miR-139 suppresses human colorectal
carcinoma cell proliferation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1465–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen WX, Hu Q, Qiu MT, Zhong SL, Xu JJ,
Tang JH and Zhao JH: miR-221/222: Promising biomarkers for breast
cancer. Tumour Biol. 34:1361–1370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Zhang H, Chen L, Sun DW, Mao C,
Chen W, Wu JZ, Zhong SL, Zhao JH and Tang JH: β-elemene reverses
chemoresistance of breast cancer via regulating MDR-related
microRNA expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:2027–2037. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ratert N, Meyer HA, Jung M, Lioudmer P,
Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Miller K, Kilic E, Erbersdobler A, Weikert
S, et al: miRNA profiling identifies candidate mirnas for bladder
cancer diagnosis and clinical outcome. J Mol Diagn. 15:695–705.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jia AY, Castillo-Martin M,
Domingo-Domenech J, Bonal DM, Sánchez-Carbayo M, Silva JM and
Cordon-Cardo C: A common MicroRNA signature consisting of miR-133a,
miR-139-3p, and miR-142-3p clusters bladder carcinoma in situ with
normal umbrella cells. Am J Pathol. 182:1171–1179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang R, Liang L, Luo D, Feng Z, Huang Q,
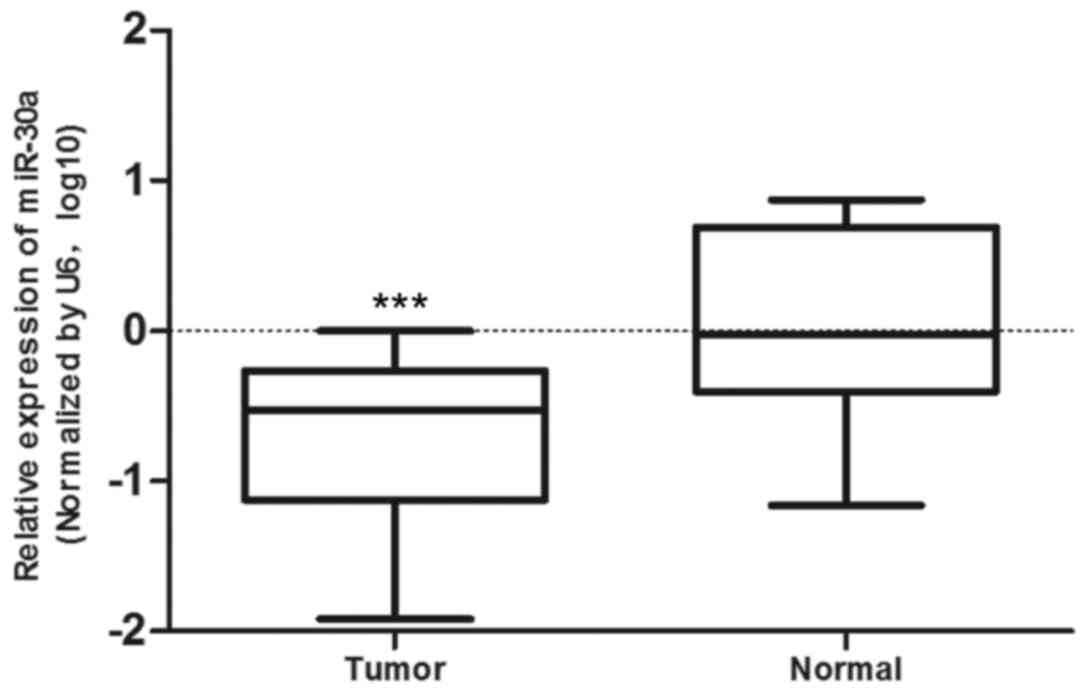
He R, Gan T, Yang L and Chen G: Downregulation of miR-30a is
associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Med Sci Monit.
21:2514–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fu J, Xu X, Kang L, Zhou L, Wang S, Lu J,
Cheng L, Fan Z, Yuan B, Tian P, et al: miR-30a suppresses breast
cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting Eya2. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 445:314–319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dai H, Kang B, Zuo D and Zuo G: Effect of
miR-30a-5p on the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and migration
of SMCC-7721 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Zhonghua Gan
Zang Bing Za Zhi. 22:915–920. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Zhang Q, Tang Q, Qin D, Yu L, Huang R, Lv
G, Zou Z, Jiang XC, Zou C, Liu W, et al: Role of microRNA 30a
targeting insulin receptor substrate 2 in colorectal tumorigenesis.
Mol Cell Biol. 35:988–1000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang HY, Li YY, Fu S, Wang XP, Huang MY,
Zhang X, Shao Q, Deng L, Zeng MS, Zeng YX, et al: MicroRNA-30a
promotes invasiveness and metastasis in vitro and in vivo through
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in poor survival of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
239:891–898. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Katz B, Reis ST, Viana NI, Morais DR,
Moura CM, Dip N, Silva IA, Iscaife A, Srougi M and Leite KR:
Comprehensive study of gene and microRNA expression related to
epithelialmesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. PLoS One.
9:e1137002014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tsukamoto O, Miura K, Mishima H, Abe S,
Kaneuchi M, Higashijima A, Miura S, Kinoshita A, Yoshiura K and
Masuzaki H: Identification of endometrioid endometrial
carcinoma-associated microRNAs in tissue and plasma. Gynecol Oncol.
132:715–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Georgas D, Sand D, Hahn
SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Microarray analysis of
microRNA expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J
Dermatol Sci. 68:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng CW, Wang HW, Chang CW, Chu HW, Chen
CY, Yu JC, Chao JI, Liu HF, Ding SL and Shen CY: MicroRNA-30a
inhibits cell migration and invasion by downregulating vimentin
expression and is a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:1081–1093. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brennan K and Brown AM: Is there a role
for Notch signalling in human breast cancer? Breast Cancer Res.
5:69–75. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mittal S, Subramanyam D, Dey D, Kumar RV
and Rangarajan A: Cooperation of Notch and Ras/MAPK signaling
pathways in human breast carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 8:1282009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Won HY, Lee JY, Shin DH, Park JH, Nam JS,
Kim HC and Kong G: Loss of Mel-18 enhances breast cancer stem cell
activity and tumorigenicity through activating Notch signaling
mediated by the Wnt/TCF pathway. FASEB J. 26:5002–5013. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dunwoodie SL, Henrique D, Harrison SM and
Beddington RS: Mouse Dll3: A novel divergent Delta gene which may
complement the function of other Delta homologues during early
pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 124:3065–3076.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Dong Y, Zhu N, Tsoi H, Zhao Z, Wu
CW, Wang K, Zheng S, Ng SS, Chan FK, et al: microRNA-139-5p exerts
tumor suppressor function by targeting NOTCH1 in colorectal cancer.
Mol Cancer. 13:1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sharma A, Paranjape AN, Rangarajan A and
Dighe RR: A monoclonal antibody against human Notch1 ligand-binding
domain depletes subpopulation of putative breast cancer stem-like
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:77–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Al-Hussaini H, Subramanyam D, Reedijk M
and Sridhar SS: Notch signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:9–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bao W, Fu HJ, Xie QS, Wang L, Zhang R, Guo
ZY, Zhao J, Meng YL, Ren XL, Wang T, et al: HER2 interacts with
CD44 to upregulate CXCR4 via epigenetic silencing of microRNA-139
in gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 141:2076–2087. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Au SL, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Tsang FH,
Ng IO and Wong CM: Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically
silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver
cancer metastasis. Hepatology. 56:622–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chappell SA, Walsh T, Walker RA and Shaw
JA: Loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 6q in preinvasive and
early invasive breast carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 75:1324–1329. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Noviello C, Courjal F and Theillet C: Loss
of heterozygosity on the long arm of chromosome 6 in breast cancer:
Possibly four regions of deletion. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1601–1606.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang N, Wang X, Huo Q, Sun M, Cai C, Liu
Z, Hu G and Yang Q: MicroRNA-30a suppresses breast tumor growth and
metastasis by targeting metadherin. Oncogene. 33:3119–3128. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jiang D, Zheng X, Shan W and Shan Y: The
overexpression of miR-30a affects cell proliferation of
chondrosarcoma via targeting Runx2. Tumour Biol. 37:5933–5940.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ronchini C and Capobianco AJ: Notch(ic)-ER
chimeras display hormone-dependent transformation, nuclear
accumulation, phosphorylation and CBF1 activation. Oncogene.
19:3914–3924. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bolós V, Mira E, Martínez-Poveda B, Luxán
G, Cañamero M, Martínez-A C, Mañes S and de la Pompa JL: Notch
activation stimulates migration of breast cancer cells and promotes
tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Speiser J, Foreman K, Drinka E, Godellas
C, Perez C, Salhadar A, Erşahin Ç and Rajan P: Notch-1 and Notch-4
biomarker expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Surg
Pathol. 20:139–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Song Y, Ma W, Zheng W and Yin H:
Decreased microRNA-30a levels are associated with enhanced ABL1 and
BCR-ABL1 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res.
37:349–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li WF, Dai H, Ou Q, Zuo GQ and Liu CA:
Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT
pathway. Tumour Biol. 37:5885–5895. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z,
Quan C, Zhou L, Hu Y, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: miR-139-5p inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR
and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 5:851–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|