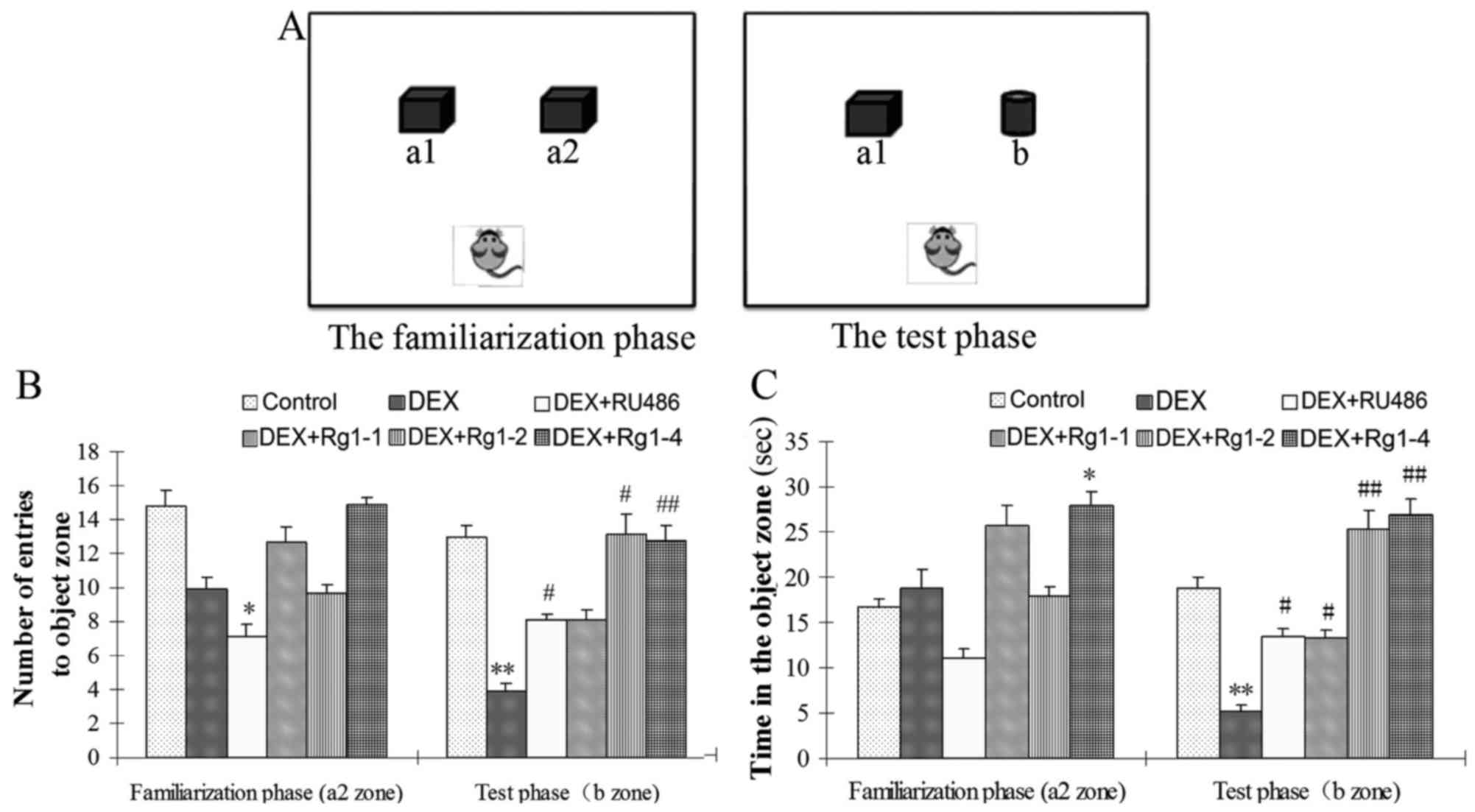
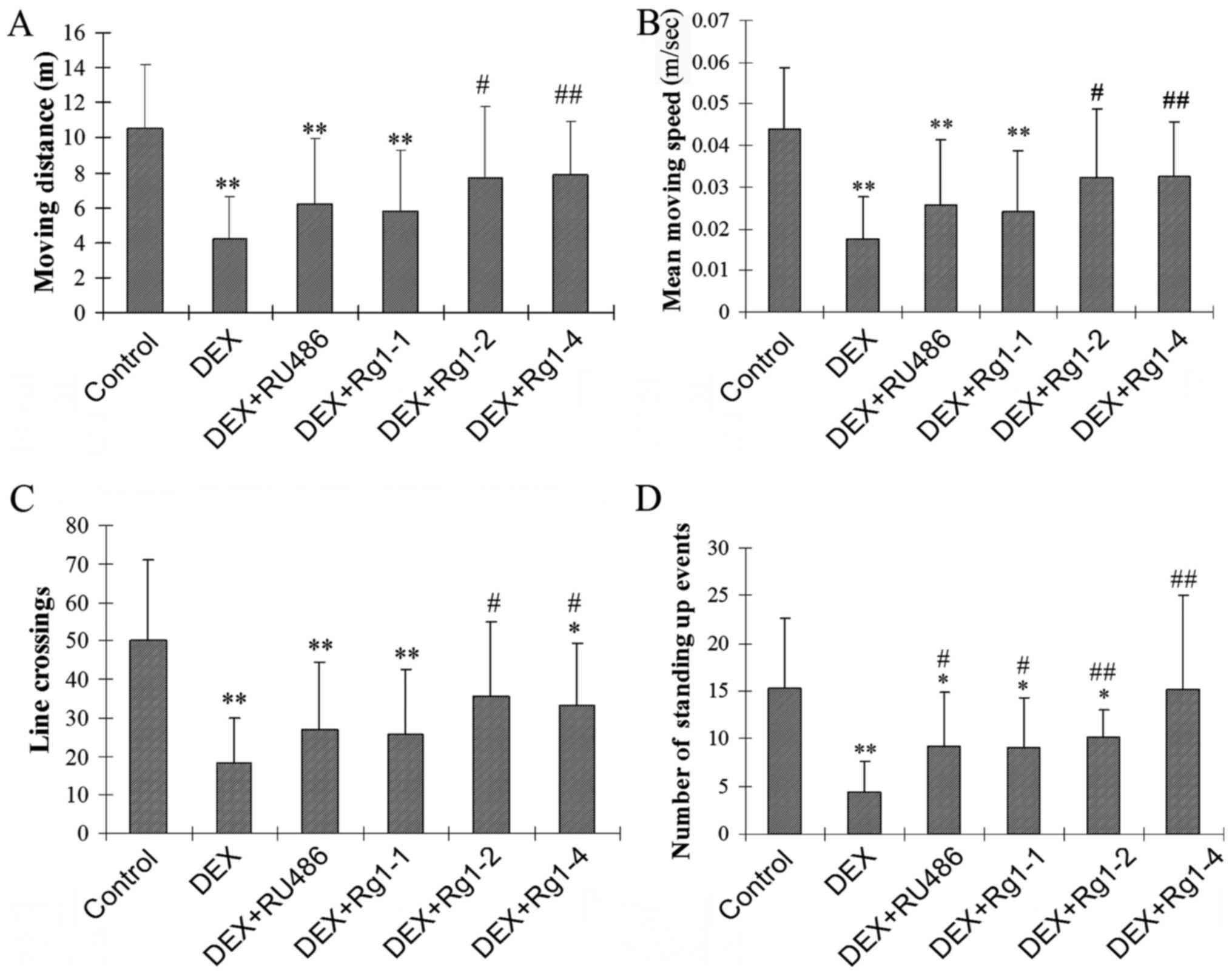
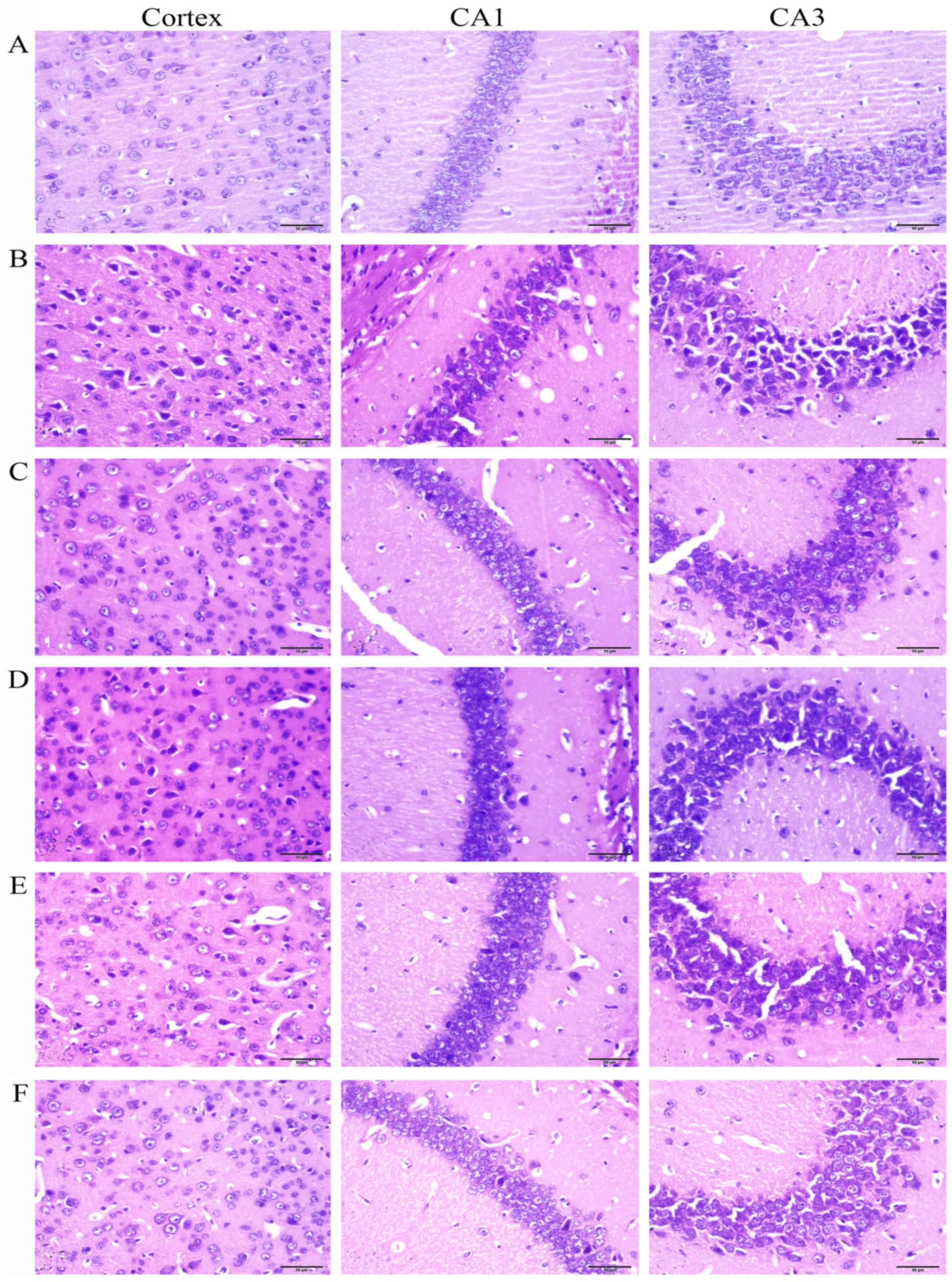
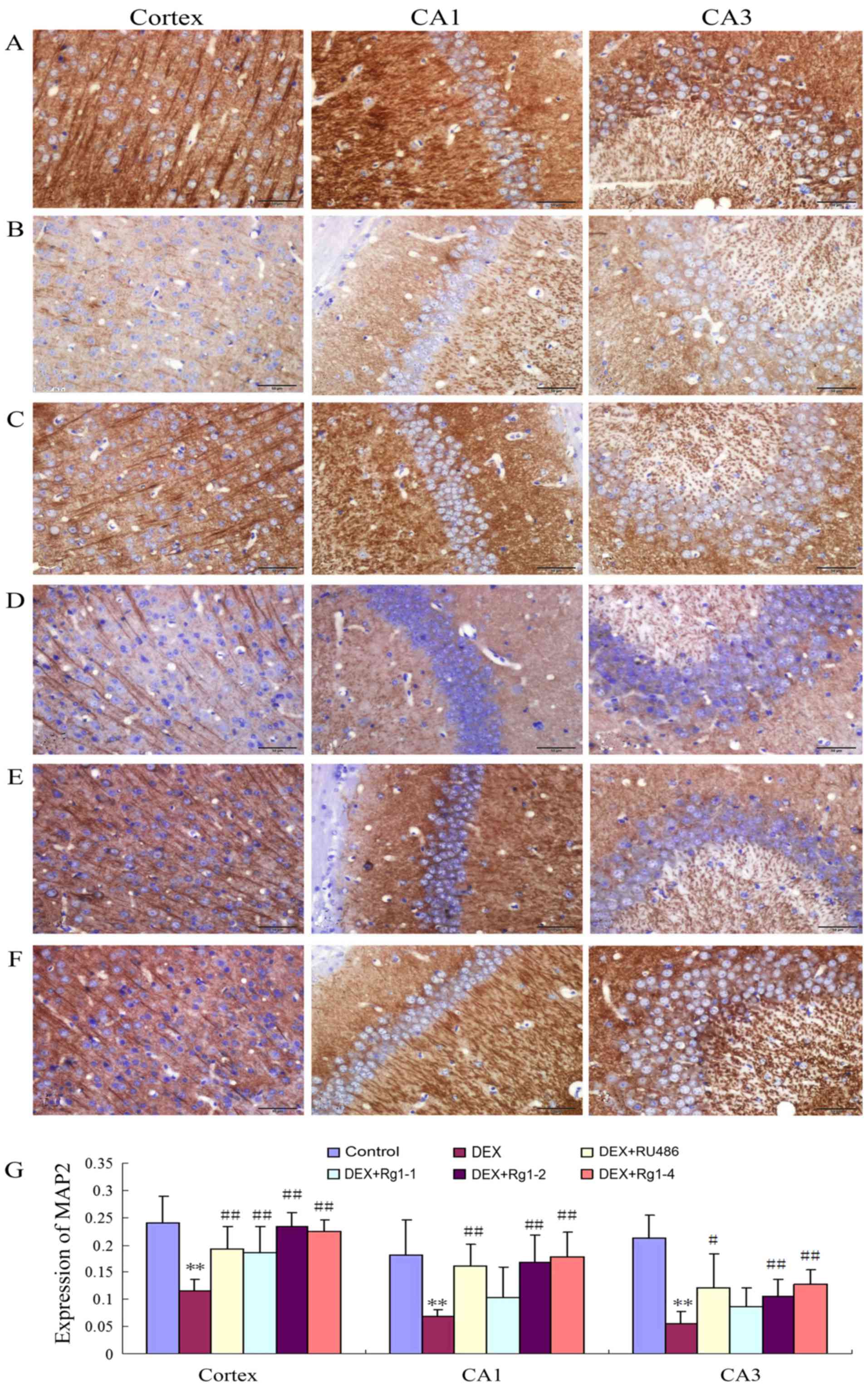
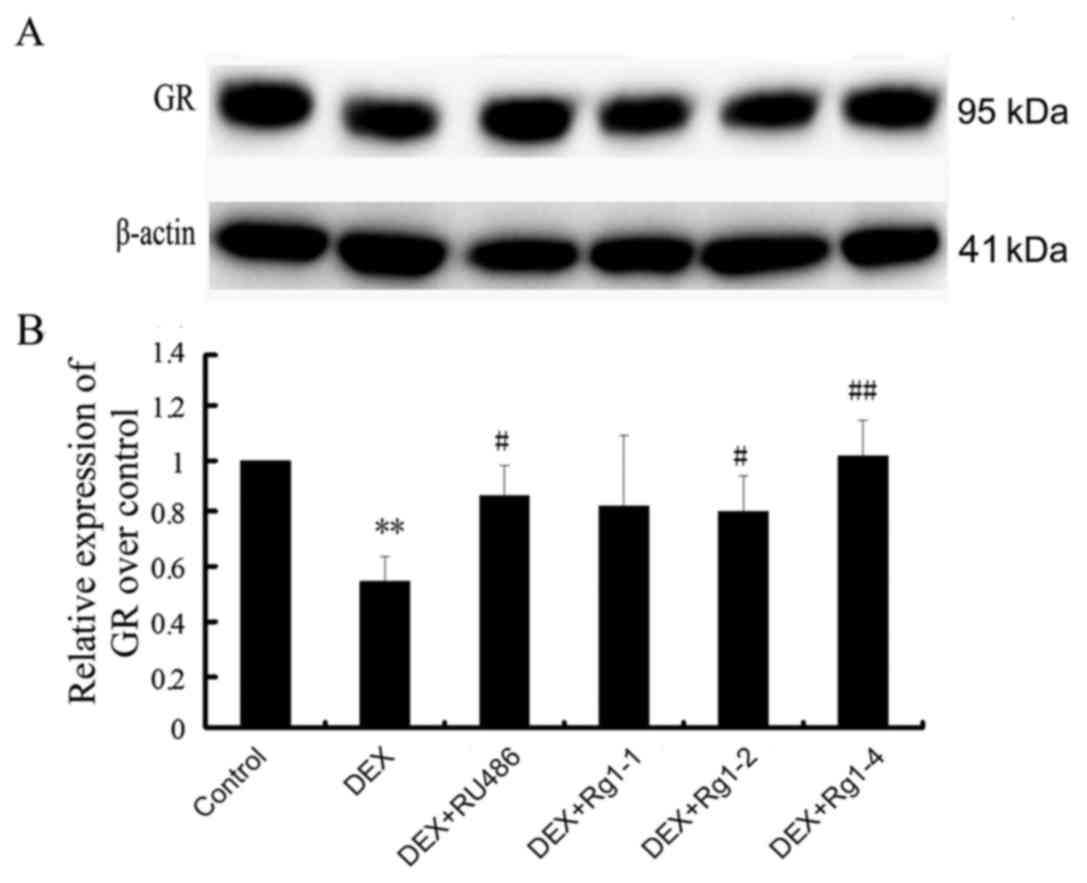
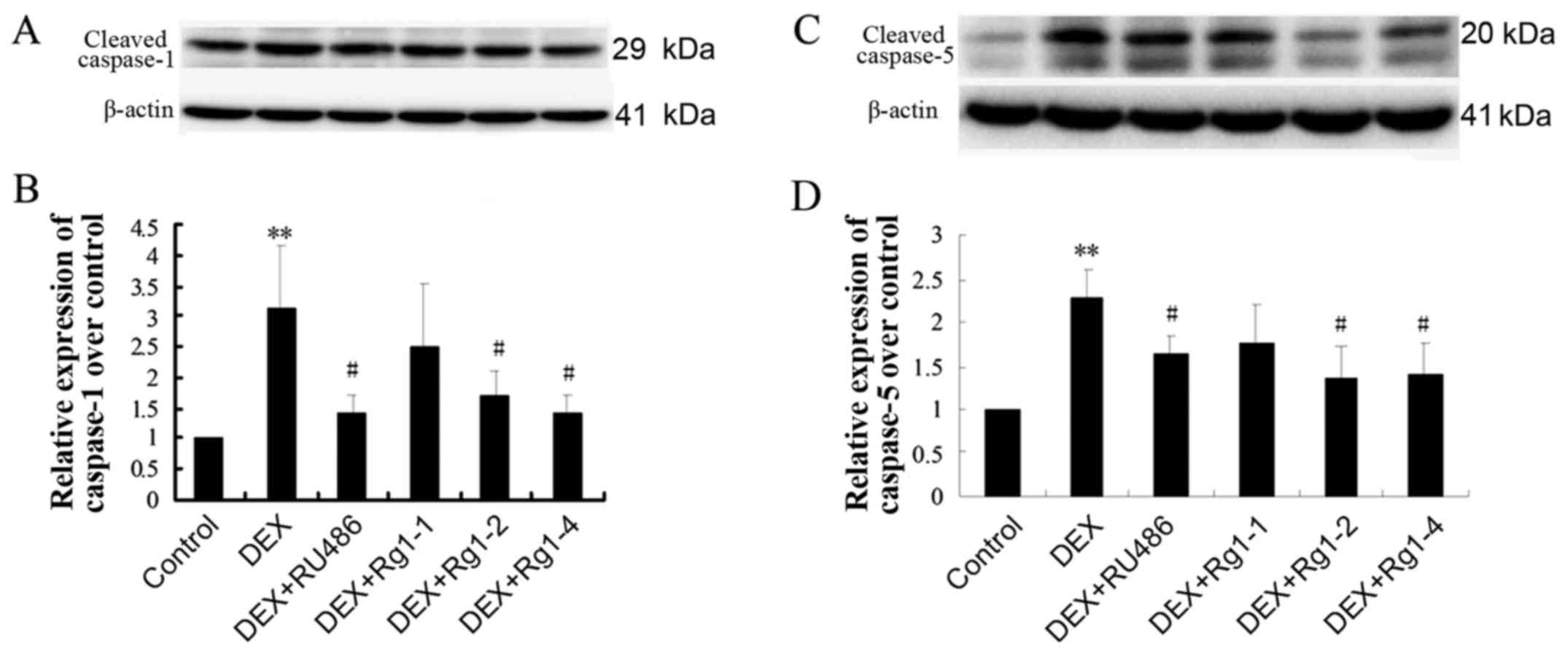
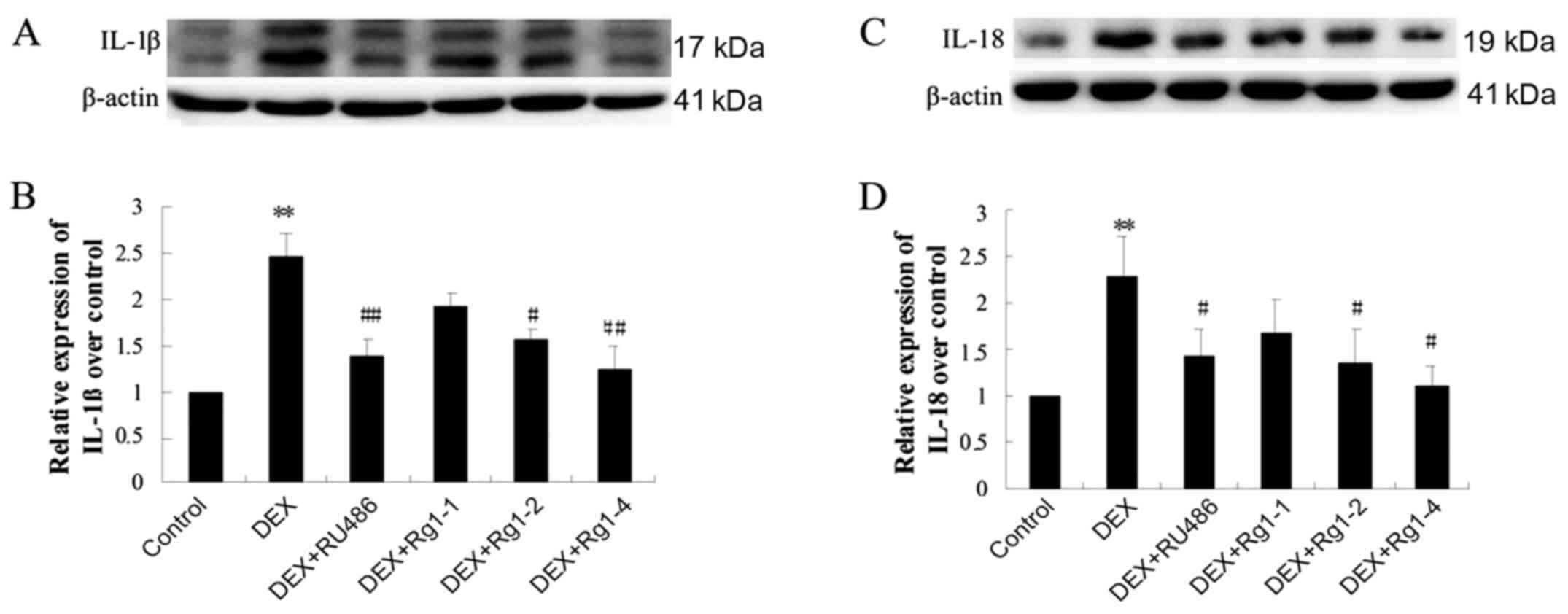
|
1
|
Joshi YB, Chu J and Praticò D: Stress
hormone leads to memory deficits and altered tau phosphorylation in
a model of Alzh–eimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 31:167–176.
2012.
|
|
2
|
Moceri VM, Kukull WA, Emanuel I, van Belle
G and Larson EB: Early-life risk factors and the development of
Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 54:415–420. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Csernansky JG, Dong H, Fagan AM, Wang L,
Xiong C, Holtzman DM and Morris JC: Plasma cortisol and progression
of dementia in subjects with Alzheimer-type dementia. Am J
Psychiatry. 163:2164–2169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aznar S and Knudsen GM: Depression and
Alzheimer's disease: Is stress the initiating factor in a common
neuropathological cascade? J Alzheimers Dis. 23:177–193. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Kleen JK, Sitomer MT, Killeen PR and
Conrad CD: Chronic stress impairs spatial memory and motivation for
reward without disrupting motor ability and motivation to explore.
Behav Neurosci. 120:842–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Conrad CD, McLaughlin KJ, Harman JS, Foltz
C, Wieczorek L, Lightner E and Wright RL: Chronic glucocorticoids
increase hippocampal vulnerability to neurotoxicity under
conditions that produce CA3 dendritic retraction but fail to impair
spatial recognition memory. J Neurosci. 27:8278–8285. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
MacPherson A, Dinkel K and Sapolsky R:
Glucocorticoids worsen excitotoxin-induced expression of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in hippocampal cultures. Exp Neurol.
194:376–383. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim EJ, Pellman B and Kim JJ: Stress
effects on the hippocampus: A critical review. Learn Mem.
22:411–416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rausch WD, Liu S, Gille G and Radad K:
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars).
66:369–375. 2006.
|
|
10
|
Xie CL, Wang WW, Xue XD, Zhang SF, Gan J
and Liu ZG: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
Ginsenoside-Rg1 (G-Rg1) in experimental ischemic stroke. Sci Rep.
5:77902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Xing Y, Gong L, Li H, Wu
Z, Li Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Dong L, et al: Effects of ginsenoside Rg1
or 17β-estradiol on a cognitively impaired, ovariectomized rat
model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience. 220:191–200. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baulieu EE: Contragestion and other
clinical applications of RU 486, an antiprogesterone at the
receptor. Science. 245:1351–1357. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun XC, Ren XF, Chen L, Gao XQ, Xie JX and
Chen WF: Glucocorticoid receptor is involved in the neuroprotective
effect of ginsenoside Rg1 against inflammation-induced dopaminergic
neuronal degeneration in substantia nigra. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 155(Pt A): 94–103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Behl C, Lezoualc'h F, Trapp T, Widmann M,
Skutella T and Holsboer F: Glucocorticoids enhance oxidative
stress-induced cell death in hippocampal neurons in vitro.
Endocrinology. 138:101–106. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCullers DL, Sullivan PG, Scheff SW and
Herman JP: Mifepristone protects CA1 hippocampal neurons following
traumatic brain injury in rat. Neuroscience. 109:219–230. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Green KN, Billings LM, Roozendaal B,
McGaugh JL and LaFerla FM: Glucocorticoids increase amyloid-beta
and tau pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J
Neurosci. 26:9047–9056. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maloney SE, Noguchi KK, Wozniak DF, Fowler
SC and Farber NB: Long-term effects of multiple glucocorticoid
exposures in neonatal mice. Behav Sci (Basel). 1:4–30. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hu W, Zhang Y, Wu W, Yin Y, Huang D, Wang
Y and Li W and Li W: Chronic glucocorticoids exposure enhances
neurodegeneration in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via NLRP-1
inflammasome activation in male mice. Brain Behav Immun. 52:58–70.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Kan H, Yin Y, Wu W, Hu W, Wang M
and Li W and Li W: Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on chronic
restraint stress induced learning and memory impairments in male
mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 120:73–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koros E, Piasecki J, Kostowski W and
Bienkowski P: Saccharin drinking rather than open field behaviour
predicts initial ethanol acceptance in Wistar rats. Alcohol
Alcohol. 33:131–140. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
de Senna PN, Ilha J, Baptista PP, do
Nascimento PS, Leite MC, Paim MF, Gonçalves CA, Achaval M and
Xavier LL: Effects of physical exercise on spatial memory and
astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. Metab
Brain Dis. 26:269–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Frye CA, Paris JJ and Rhodes ME: Engaging
in paced mating, but neither exploratory, anti-anxiety, nor social
behavior, increases 5alpha-reduced progestin concentrations in
midbrain, hippocampus, striatum, and cortex. Reproduction.
133:663–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Antunes M and Biala G: The novel object
recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its
modifications. Cogn Process. 13:93–110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Zotova E, Bharamb—e V, Cheaveau M, Morgan
W, Holmes C, Harris S, Neal JW, Love S, Nicoll JA and Boche D:
Inflammatory components in human Alzheimer–'s disease and after
active amyloid-β42 immunization. Brain. 136:2677–2696. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Calsolaro V and Edison P:
Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: Current evidence and
future directions. Alzheimers Dement. 12:719–732. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morales I, Guzmán-Martínez L,
Cerda-Troncoso C, Farías GA and Maccioni RB: Neuroinflammation in
the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. A rational framework for
the search of novel therapeutic approaches. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:1122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jha S, Srivastava SY, Brickey WJ, Iocca H,
Toews A, Morrison JP, Chen VS, Gris D, Matsushima GK and Ting JP:
The inflammasome sensor, NLRP3, regulates CNS inflammation and
demyelination via caspase-1 and interleukin-18. J Neurosci.
30:15811–15820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sotiropoulos I, Catania C, Pinto LG, Silva
R, Pollerberg GE, Takashima A, Sousa N and Almeida OF: Stress acts
cumulatively to precipitate Alzheimer's disease-like tau pathology
and cognitive deficits. J Neurosci. 31:7840–7847. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen KC, Blalock EM, Curran-Rauhut MA,
Kadish I, Blalock SJ, Brewer L, Porter NM and Landfield PW:
Glucocorticoid-dependent hippocampal transcriptome in male rats:
Pathway-specific alterations with aging. Endocrinology.
154:2807–2820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Danilczuk Z, Ossowska G, Lupina T, Cieślik
K and Zebrowska-Łupina I: Effect of NMDA receptor antagonists on
behavioral impairment induced by chronic treatment with
dexamethasone. Pharmacol Rep. 57:47–54. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li WZ, Li WP, Yao YY, Zhang W, Yin YY, Wu
GC and Gong HL: Glucocorticoids increase impairments in learning
and memory due to elevated amyloid precursor protein expression and
neuronal apoptosis in 12-month old mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
628:108–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kril JJ, Patel S, Harding AJ and Halliday
GM: Neuron loss from the hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease exceeds
extracellular neurofibrillary tangle formation. Acta Neuropathol.
103:370–376. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang Y, Li X, Zhang L, Liu L, Jing G and
Cai H: Ginsenoside Rg1 suppressed inflammation and neuron apoptosis
by activating PPARγ/HO-1 in hippocampus in rat model of cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2484–2494.
2015.
|
|
34
|
Baxter MG: 'I've seen it all before':
Explaining age-related impairments in object recognition.
Theoretical comment on Burke et al 2010. Behav Neurosci.
124:706–709. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wi S, Yu JH, Kim M and Cho SR: In vivo
expression of reprogramming factors increases hippocampal
neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in chronic hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury. Neural Plast. 2016:25808372016.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Ennaceur A: One-trial object recognition
in rats and mice: Methodological and theoretical issues. Behav
Brain Res. 215:244–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Di Stefano G, Casoli T, Fattoretti P,
Gracciotti N, Solazzi M and Bertoni-Freddari C: Distribution of
map2 in hippocampus and cerebellum of young and old rats by
quantitative immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem.
49:1065–1066. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chauhan N and Siegel G: Age-dependent
organotypic expression of microtubule-associated proteins (MAP1,
MAP2, and MAP5) in rat brain. Neurochem Res. 22:713–719. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sartori AC, Vance DE, Slater LZ and Crowe
M: The impact of inflammation on cognitive function in older
adults: Implications for healthcare practice and research. J
Neurosci Nurs. 44:206–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Frank MG, Miguel ZD, Watkins LR and Maier
SF: Prior exposure to glucocorticoids sensitizes the
neuroinflammatory and peripheral inflammatory responses to E. coli
lipopolysaccharide. Brain Behav Immun. 24:19–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hermoso MA, Matsuguchi T, Smoak K and
Cidlowski JA: Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor alpha
cooperatively regulate toll-like receptor 2 gene expression. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:4743–4756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carter BS, Meng F and Thompson RC:
Glucocorticoid treatment of astrocytes results in temporally
dynamic transcriptome regulation and astrocyte-enriched mRNA
changes in vitro. Physiol Genomics. 44:1188–1200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chrousos GP: Stress and disorders of the
stress system. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 5:374–381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Du J, Cheng B, Zhu X and Ling C:
Ginsenoside Rg1, a novel glucocorticoid receptor agonist of plant
origin, maintains glucocorticoid efficacy with reduced side
effects. J Immunol. 187:942–950. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Martinon F and Tschopp J: NLRs join TLRs
as innate sensors of pathogens. Trends Immunol. 26:447–454. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Franchi L, Eigenbrod T, Muñoz-Planillo R
and Nuñez G: The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that
regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol.
10:241–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic
D, French DM, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S and Dixit VM:
Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors
ASC and Ipaf. Nature. 430:213–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Stutz A, Golenbock DT and Latz E:
Inflammasomes: Too big to miss. J Clin Invest. 119:3502–3511. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Yu JW, Datta P,
Miller B, Jankowski W, Rosenberg S, Zhang J and Alnemri ES: The
pyroptosome: A supramolecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating
inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death
Differ. 14:1590–1604. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Salminen A, Ojala J, Suuronen T,
Kaarniranta K and Kauppinen A: Amyloid-beta oligomers set fire to
inflammasomes and induce Alzheimer's pathology. J Cell Mol Med.
12(6A): 2255–2262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|