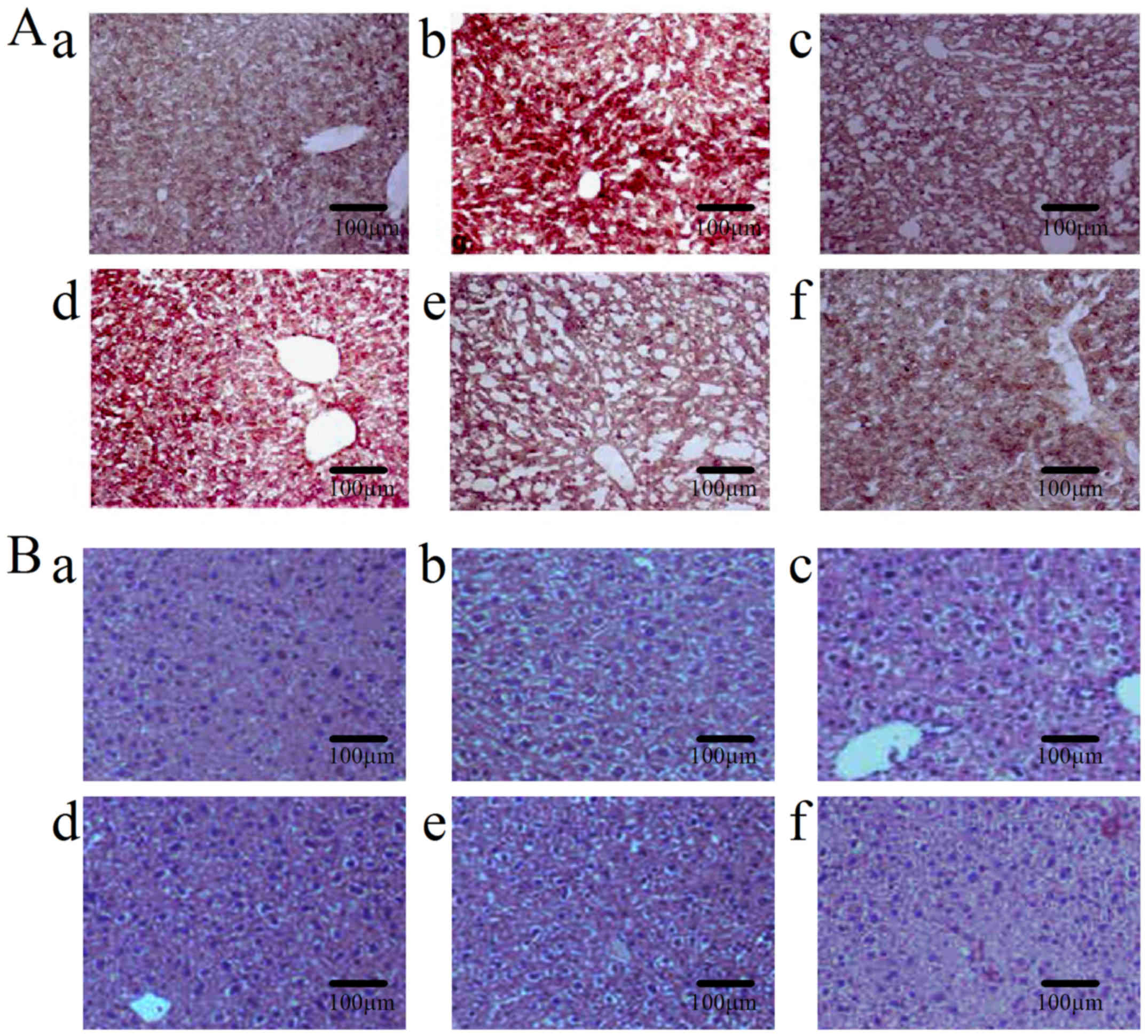
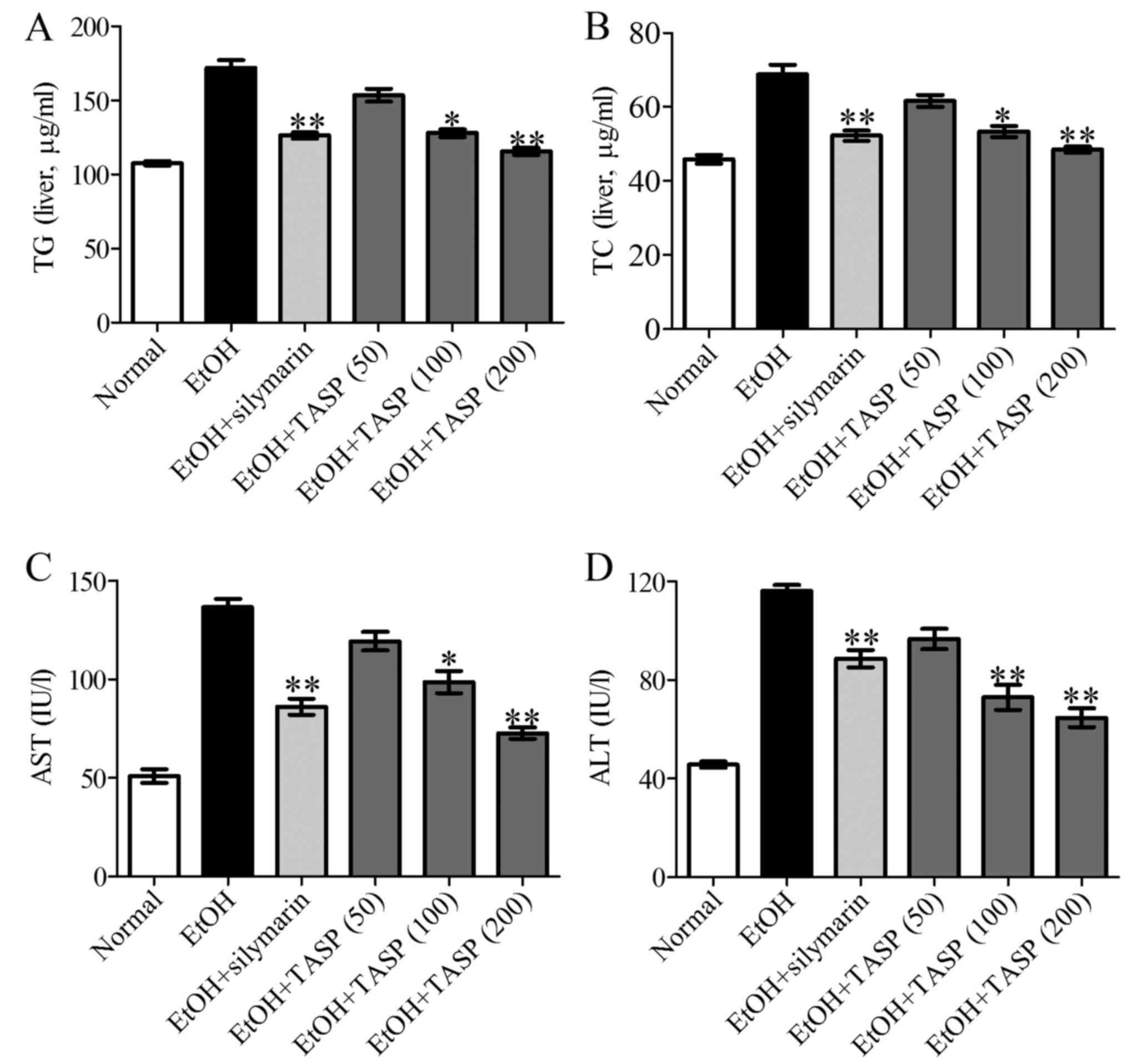
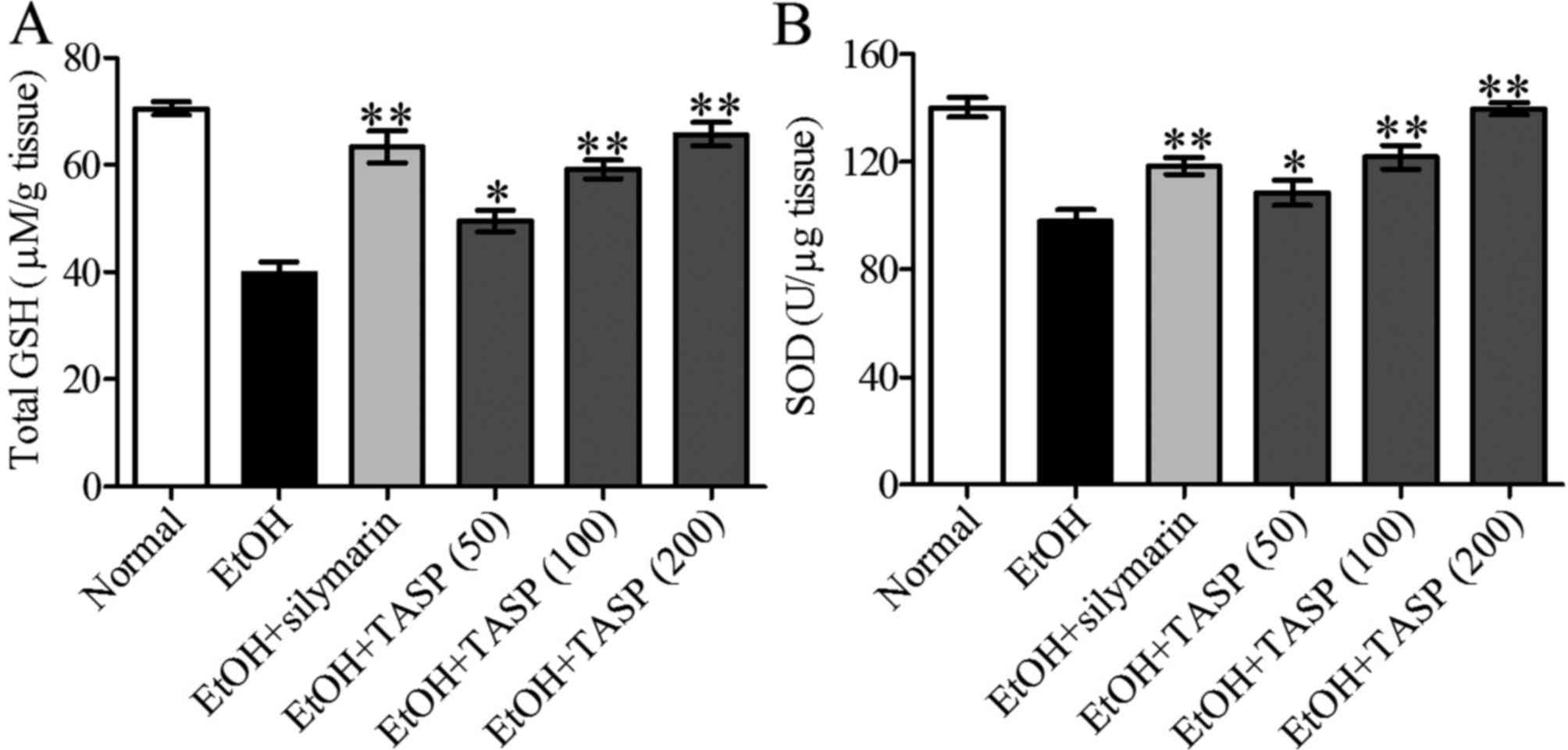
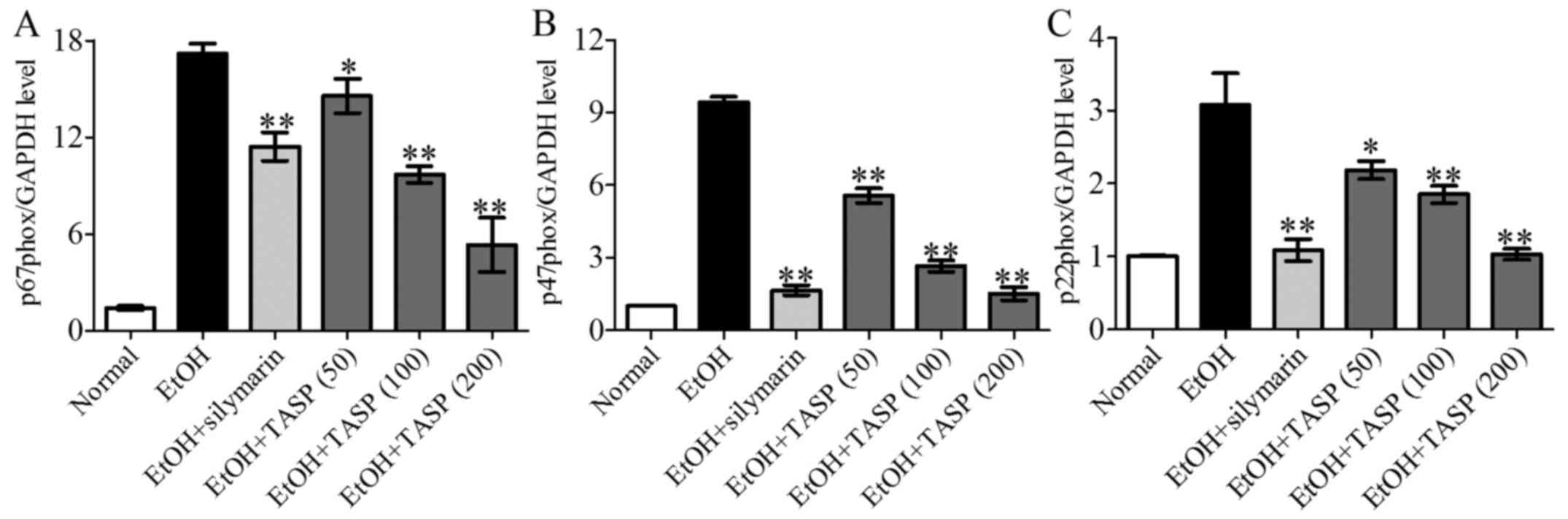
|
1
|
Park SH, Kim CH, Kim DJ, Park JH, Kim TO,
Yang SY, Moon YS, Kim TN, Kim HK, Park HY, et al: Prevalence of
alcoholic liver disease among Korean adults: Results from the
fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,
2009. Subst Use Misuse. 46:1755–1762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arteel G, Marsano L, Mendez C, Bentley F
and McClain CJ: Advances in alcoholic liver disease. Best Pract Res
Clin Gastroenterol. 17:625–647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kawaratani H, Tsujimoto T, Douhara A,
Takaya H, Moriya K, Namisaki T, Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Fujimoto M
and Fukui H: The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic
liver disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:4951562013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zamora Nava LE, Aguirre Valadez J,
Chávez-Tapia NC and Torre A: Acute-on-chronic liver failure: A
review. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 10:295–303. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu G, Zhang Y, Liu C, Xu D, Zhang R,
Cheng Y, Pan Y, Huang C and Chen Y: Luteolin alleviates alcoholic
liver disease induced by chronic and binge ethanol feeding in mice.
J Nutr. 144:1009–1015. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Knockaert L, Descatoire V, Vadrot N,
Fromenty B and Robin MA: Mitochondrial CYP2E1 is sufficient to
mediate oxidative stress and cytotoxicity induced by ethanol and
acetaminophen. Toxicol In Vitro. 25:475–484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yamashita H, Goto M, Matsui-Yuasa I and
Kojima-Yuasa A: Ecklonia cava polyphenol has a protective effect
against ethanol-induced liver injury in a cyclic AMP-dependent
manner. Mar Drugs. 13:3877–3891. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu T, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Han X and Peng J: Protective effects of dioscin against
alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol. 88:739–753. 2014.
|
|
9
|
Jiang JX and Török NJ: NADPH oxidases in
chronic liver diseases. Adv Hepatol. 2014:7429312014.
|
|
10
|
Xu W, Hellerbrand C, Köhler UA, Bugnon P,
Kan YW, Werner S and Beyer TA: The Nrf2 transcription factor
protects from toxin-induced liver injury and fibrosis. Lab Invest.
88:1068–1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma X, Zhao YL, Zhu Y, Chen Z, Wang JB, Li
RY, Chen C, Wei SZ, Li JY, Liu B, et al: Paeonia lactiflora Pall.
protects against ANIT-induced cholestasis by activating Nrf2 via
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:5061–5074.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Neuman MG: Apoptosis in liver disease. Rom
J Gastroenterol. 11:3–7. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SH, Xin MJ, Luyen BTT, Cha JY, Im JY,
Kwon SU, Lim SW, Suh JW, Kim YH, Kim DK, et al: Inhibitory effect
of Triticum aestivum ethanol extract on lipid accumulation in
3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Yakhak Hoeji. 55:478–484. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Wojakowska A, Perkowski J, Góral T and
Stobiecki M: Structural characterization of flavonoid glycosides
from leaves of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using LC/MS/MS
profiling of the target compounds. J Mass Spectrom. 48:329–339.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benedetti S, Primiterra M, Tagliamonte MC,
Carnevali A, Gianotti A, Bordoni A and Canestrari F: Counteraction
of oxidative damage in the rat liver by an ancient grain (Kamut
brand khorasan wheat). Nutrition. 28:436–441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Luyen BT, Tai BH, Thao NP, Cha JY, Lee YM
and Kim YH: A new phenolic component from Triticum aestivum sprouts
and its effects on LPS-stimulated production of nitric oxide and
TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells. Phytother Res. 28:1064–1070. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luyen BT, Thao NP, Tai BH, Lim JY, Ki HH,
Kim DK, Lee YM and Kim YH: Chemical constituents of Triticum
aestivum and their effects on adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1
preadipocytes. Arch Pharm Res. 38:1011–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Poudel B, Ki HH, Luyen BT, Lee YM, Kim YH
and Kim DK: Triticumoside induces apoptosis via caspase-dependent
mitochondrial pathway and inhibits migration through
down-regulation of MMP2/9 in human lung cancer cells. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 48:153–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Poudel B, Nepali S, Xin M, Ki HH, Kim YH,
Kim DK and Lee YM: Flavonoids from Triticum aestivum inhibit
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by upregulating the insig pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 12:3139–3145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang JY, Jeong EY, Kim DK and Lee HS:
Antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory effects in Triticum
aestivum sprouts treated to chilling temperature. J Korean Soc Appl
Biol Chem. 54:644–648. 2011.
|
|
21
|
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee YM, Lee HS and Kim DK:
Polysaccharide isolated from Triticum aestivum stimulates insulin
release from pancreatic cells via the ATP-sensitive K+
channel. Int J Mol Med. 29:913–919. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SH, LY, Lee HS and Kim DK:
Anti-oxidative and anti-hyperglycemia effects of Triticum aestivum
wheat sprout water extracts on the streptozotocin-induced diabetic
mice. Korean J Pharmacogn. 40:408–414. 2009.
|
|
23
|
Zhang K, Gao Y, Zhong M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen
Y, Duan X and Zhu H: Hepatoprotective effects of Dicliptera
chinensis polysaccharides on dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic
fibrosis rats and its underlying mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol.
179:38–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Q, Zhu M, Geng X, Wang H and Ng TB:
Characterization of polysaccharides with antioxidant and
hepatoprotective activities from the edible mushroom Oudemanisella
radicata. Molecules. 22:E2342017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lai DM, Høj PB and Fincher GB:
Purification and characterization of (1→3, 1→4)-beta-glucan
endohydrolases from germinated wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant Mol
Biol. 22:847–859. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lian LH, Wu YL, Song SZ, Wan Y, Xie WX, Li
X, Bai T, Ouyang BQ and Nan JX: Gentiana manshurica Kitagawa
reverses acute alcohol-induced liver steatosis through blocking
sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 maturation. J Agric
Food Chem. 58:13013–13019. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Choi MK, Han JM, Kim HG, Lee JS, Lee JS,
Wang JH, Son SW, Park HJ and Son CG: Aqueous extract of Artemisia
capillaris exerts hepatoprotective action in alcohol-pyrazole-fed
rat model. J Ethnopharmacol. 147:662–670. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nepali S, Son JS, Poudel B, Lee JH, Lee YM
and Kim DK: Luteolin is a bioflavonoid that attenuates
adipocyte-derived inflammatory responses via suppression of nuclear
factor-κB/mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway. Pharmacogn
Mag. 11:627–635. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poudel B, Ki HH, Lee YM and Kim DK:
Collagen I-induced dendritic cells activation is regulated by
TNF-alpha production through down-regulation of IRF4. J Biosci.
40:71–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Poudel B, Lim SW, Ki HH, Nepali S, Lee YM
and Kim DK: Dioscin inhibits adipogenesis through the AMPK/MAPK
pathway in 3T3-L1 cells and modulates fat accumulation in obese
mice. Int J Mol Med. 34:1401–1408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang ZH, Liu XQ, Zhang C, He W, Wang H,
Chen YH, Liu XJ, Chen X and Xu DX: Tlr4-mutant mice are resistant
to acute alcohol-induced sterol-regulatory element binding protein
activation and hepatic lipid accumulation. Sci Rep. 6:335132016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma Z, Hou T, Shi W, Liu W and He H:
Inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis: An important mechanism of corn
peptides attenuating liverinjury induced by ethanol. Int J Mol Sci.
16:22062–22080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sugiyama A, Suzuki K, Mitra S, Arashida R,
Yoshida E, Nakano R, Yabuta Y and Takeuchi T: Hepatoprotective
effects of paramylon, a beta-1, 3-D-glucan isolated from Euglena
gracilis Z, on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride
in rats. J Vet Med Sci. 71:885–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neyrinck AM, Mouson A and Delzenne NM:
Dietary supplementation with laminarin, a fermentable marine beta
(1-3) glucan, protects against hepatotoxicity induced by LPS in rat
by modulating immune response in the hepatic tissue. Int
Immunopharmacol. 7:1497–1506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fernández-Checa JC, Kaplowitz N,
García-Ruiz C, Colell A, Miranda M, Marí M, Ardite E and Morales A:
GSH transport in mitochondria: Defense against TNF-induced
oxidative stress and alcohol-induced defect. Am J Physiol.
273:G7–G17. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xiong ZE, Dong WG, Wang BY, Tong QY and Li
ZY: Curcumin attenuates chronic ethanol-induced liver injury by
inhibition of oxidative stress via mitogen-activated protein
kinase/nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 pathway in mice.
Pharmacogn Mag. 11:707–715. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han Y, Xu Q, Hu JN, Han XY, Li W and Zhao
LC: Maltol, a food flavoring agent, attenuates acute
alcohol-induced oxidative damage in mice. Nutrients. 7:682–696.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Leung TM and Nieto N: CYP2E1 and oxidant
stress in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J
Hepatol. 58:395–398. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Jimenez-Lopez JM and Cederbaum AI:
CYP2E1-dependent oxidative stress and toxicity: Role in
ethanol-induced liver injury. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol.
1:671–685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lu Y, Wu D, Wang X, Ward SC and Cederbaum
AI: Chronic alcohol-induced liver injury and oxidant stress are
decreased in cytochrome P4502E1 knockout mice and restored in
humanized cytochrome P4502E1 knock-in mice. Free Radic Biol Med.
49:1406–1416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang J, Tabbi-Anneni I, Gunda V and Wang
L: Transcription factor Nrf2 regulates SHP and lipogenic gene
expression in hepatic lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 299:G1211–G1221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu J, Wang X, Liu R, Liu Y, Zhang T, Fu H
and Hai C: Oleanolic acid co-administration alleviates
ethanol-induced hepatic injury via Nrf-2 and ethanol-metabolizing
modulating in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 221:88–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abdelmegeed MA, Banerjee A, Jang S, Yoo
SH, Yun JW, Gonzalez FJ, Keshavarzian A and Song BJ: CYP2E1
potentiates binge alcohol-induced gut leakiness, steatohepatitis,
and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:1238–1245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cao YW, Jiang Y, Zhang DY, Wang M, Chen
WS, Su H, Wang YT and Wan JB: Protective effects of Penthorum
chinense Pursh against chronic ethanol-induced liver injury in
mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 161:92–98. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gao X, Fan L, Li H, Li J, Liu X, Sun R and
Yu Z: Hepatic injury is associated with cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis with alteration of cyclin A and D1 in ammonium
chloride-induced hyperammonemic rats. Exp Ther Med. 11:427–434.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ducan MB, Yang C, Tanjore H, Boyle PM,
Keskin D, Sugimoto H, Zeisberg M, Olsen BR and Kalluri R: Type XVII
collagen is essential for survival during acute injury in mice. Dis
Model Mech. 4:942–951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Collins JA, Schandi CA, Young KK, Vesely J
and Willingham MC: Major DNA fragmentation is a late event in
apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 45:923–934. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|