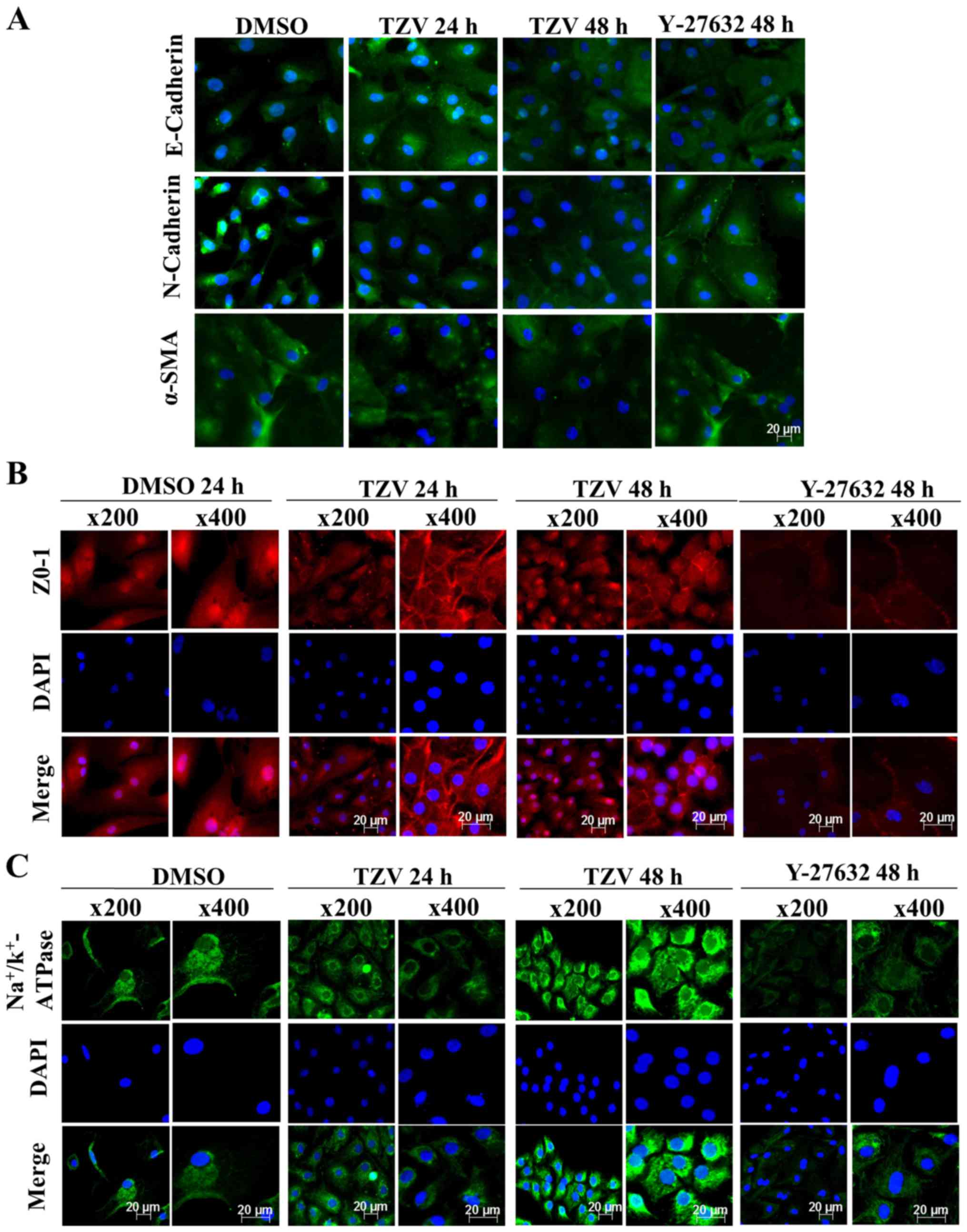
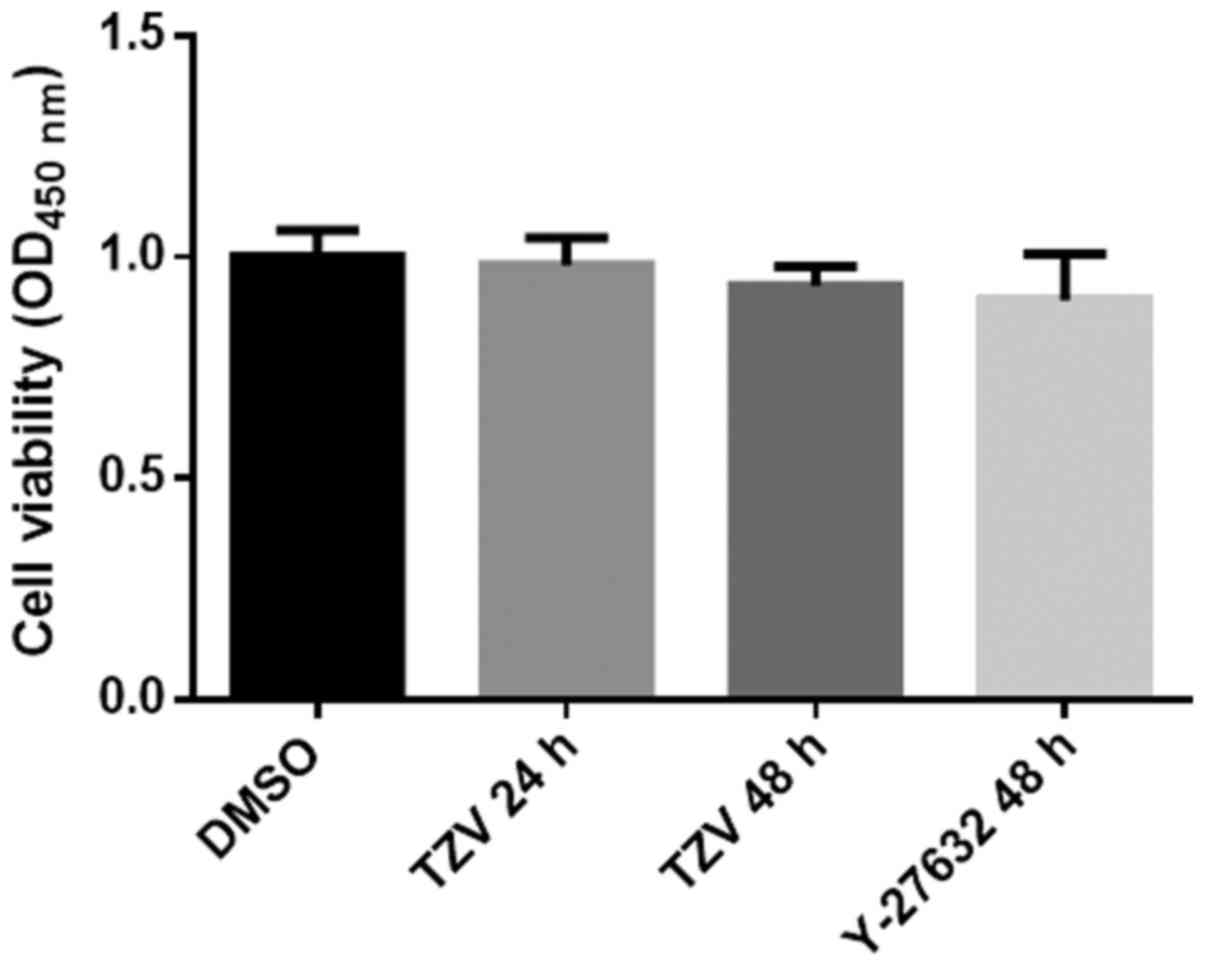
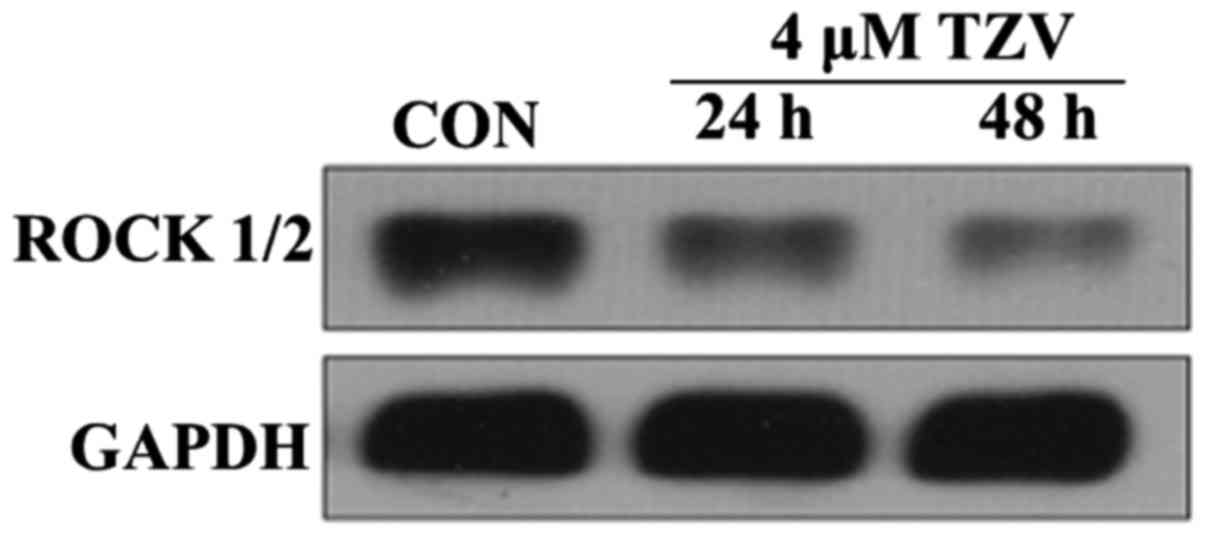
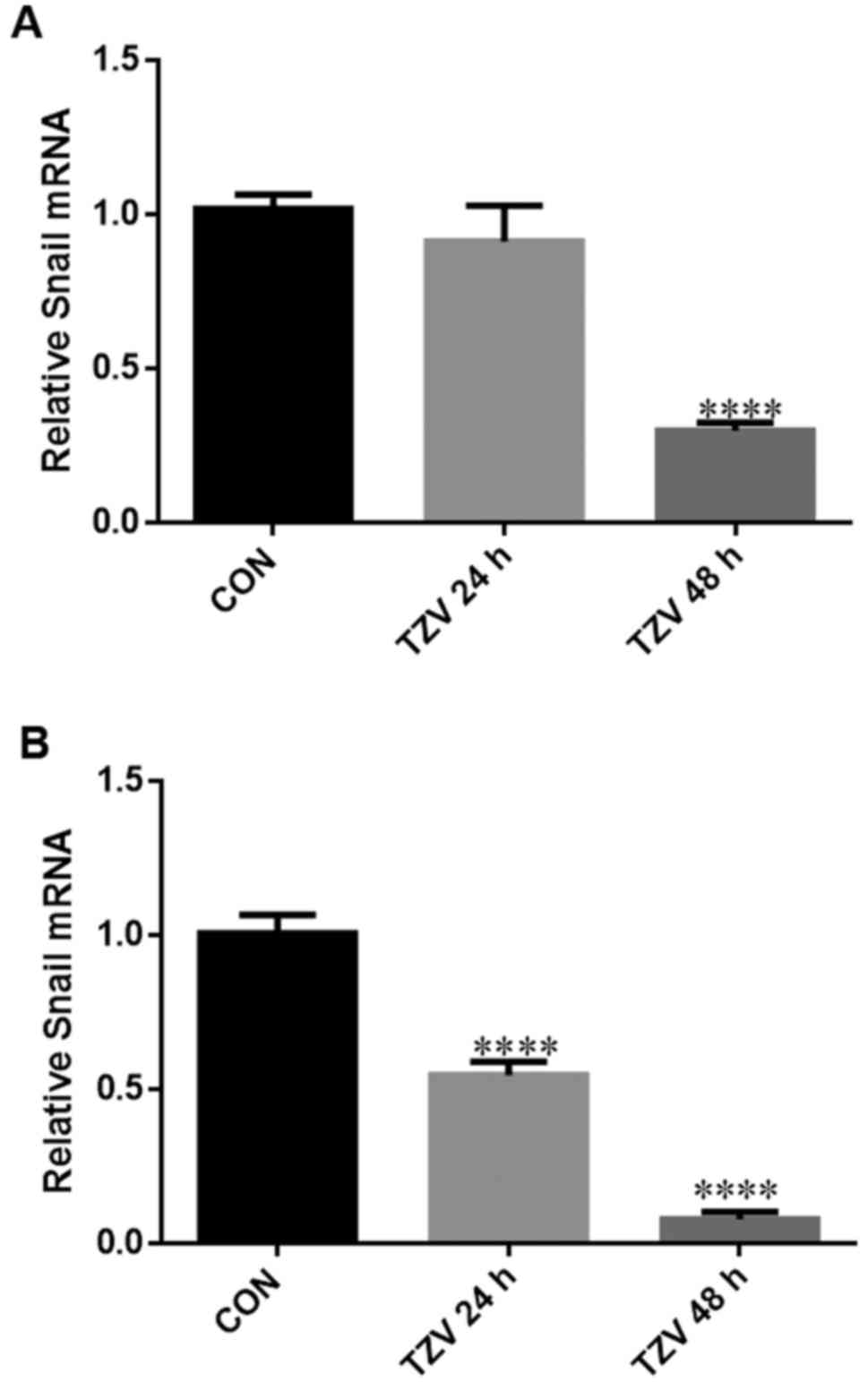
|
1
|
Mishima S: Clinical investigations on the
corneal endothelium-XXXVIII Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am J
Ophthalmol. 93:1–29. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wulle KG: Electron microscopy of the fetal
development of the corneal endothelium and Descemet's membrane of
the human eye. Invest Ophthalmol. 11:897–904. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laing RA, Sanstrom MM, Berrospi AR and
Leibowitz HM: Changes in the corneal endothelium as a function of
age. Exp Eye Res. 22:587–594. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh JS, Haroldson TA and Patel SP:
Characteristics of the low density corneal endothelial monolayer.
Exp Eye Res. 115:239–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He Z, Campolmi N, Gain P, Ha Thi BM,
Dumollard JM, Duband S, Peoc'h M, Piselli S, Garraud O and Thuret
G: Revisited microanatomy of the corneal endothelial periphery: New
evidence for continuous centripetal migration of endothelial cells
in humans. Stem Cells. 30:2523–2534. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matsuda M, Sawa M, Edelhauser HF, Bartels
SP, Neufeld AH and Kenyon KR: Cellular migration and morphology in
corneal endothelial wound repair. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
26:443–449. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Edelhauser HF: The resiliency of the
corneal endothelium to refractive and intraocular surgery. Cornea.
19:263–273. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan DTH, Dart JKG, Holland EJ and
Kinoshita S: Corneal transplantation. Lancet. 379:1749–1761. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hirata-Tominaga K, Nakamura T, Okumura N,
Kawasaki S, Kay EP, Barrandon Y, Koizumi N and Kinoshita S: Corneal
endothelial cell fate is maintained by LGR5 through the regulation
of hedgehog and Wnt pathway. Stem Cells. 31:1396–1407. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peh GS, Toh KP, Wu FY, Tan DT and Mehta
JS: Cultivation of human corneal endothelial cells isolated from
paired donor corneas. PLoS One. 6:e283102011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okumura N, Kay EP, Nakahara M, Hamuro J,
Kinoshita S and Koizumi N: Inhibition of TGF-β signaling enables
human corneal endothelial cell expansion in vitro for use in
regenerative medicine. PLoS One. 8:e580002013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Engelmann K and Friedl P: Optimization of
culture conditions for human corneal endothelial cells. In Vitro
Cell Dev Biol. 25:1065–1072. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu C and Joyce NC: Proliferative response
of corneal endothelial cells from young and older donors. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:1743–1751. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Engelmann K, Bednarz J and Valtink M:
Prospects for endothelial transplantation. Exp Eye Res. 78:573–578.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McNiven MA: Breaking away: Matrix
remodeling from the leading edge. Trends Cell Biol. 23:16–21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Roy O, Leclerc VB, Bourget JM, Thériault M
and Proulx S: Understanding the process of corneal endothelial
morphological change in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
56:1228–1237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee JG, Ko MK and Kay EP: Endothelial
mesenchymal transformation mediated by IL-1β-induced FGF-2 in
corneal endothelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 95:35–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pipparelli A, Arsenijevic Y, Thuret G,
Gain P, Nicolas M and Majo F: ROCK inhibitor enhances adhesion and
wound healing of human corneal endothelial cells. PLoS One.
8:e620952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu L, Gao Q, Ni L, Wang M and Shen F:
Fasudil inhibits epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation of
human renal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells induced by high glucose.
Chem Pharm Bull. 61:688–694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park S, Kim D, Jung YG and Roh S:
Thiazovivin, a Rho kinase inhibitor, improves stemness maintenance
of embryo-derived stem-like cells under chemically defined culture
conditions in cattle. Anim Reprod Sci. 161:47–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang H, Liu Z, Ma Y, Zhong C, Yin Q, Zhou
C, Shi L, Cai Y, Zhao H, Wang H, et al: Generation of haploid
embryonic stem cells from Macaca fascicularis monkey parthenotes.
Cell Res. 23:1187–1200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka T, Nishimura D, Wu RC, Amano M, Iso
T, Kedes L, Nishida H, Kaibuchi K and Hamamori Y: Nuclear Rho
kinase, ROCK2, targets p300 acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem.
281:15320–15329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang RY, Guilford P and Thiery JP: Early
events in cell adhesion and polarity during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Sci. 125:4417–4422. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaibuchi K, Kuroda S and Amano M:
Regulation of the cytoskeleton and cell adhesion by the Rho family
GTPases in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:459–486. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Somlyo AP and Somlyo AV: Signal
transduction by G-proteins, rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to
smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J Physiol. 522:177–185.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leung T, Chen XQ, Manser E and Lim L: The
p160 RhoA-binding kinase ROK alpha is a member of a kinase family
and is involved in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton. Mol Cell
Biol. 16:5313–5327. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tominaga T and Barber DL: Na-H exchange
acts downstream of RhoA to regulate integrin-induced cell adhesion
and spreading. Mol Biol Cell. 9:2287–2303. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Olson MF, Ashworth A and Hall A: An
essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle
progression through G1. Science. 269:1270–1272. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang L, Valdez JM, Zhang B, Wei L, Chang
J and Xin L: ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 suppresses dissociation-induced
apoptosis of murine prostate stem/progenitor cells and increases
their cloning efficiency. PLoS One. 6:e182712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olson MF: Applications for ROCK kinase
inhibition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 20:242–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liao JK, Seto M and Noma K: Rho kinase
(ROCK) inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:17–24. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Okumura N, Ueno M, Koizumi N, Sakamoto Y,
Hirata K, Hamuro J and Kinoshita S: Enhancement on primate corneal
endothelial cell survival in vitro by a ROCK inhibitor. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3680–3687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okumura N, Koizumi N, Ueno M, Sakamoto Y,
Takahashi H, Hirata K, Torii R, Hamuro J and Kinoshita S:
Enhancement of corneal endothelium wound healing by Rho-associated
kinase (ROCK) inhibitor eye drops. Br J Ophthalmol. 95:1006–1009.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Okumura N, Koizumi N, Kay EP, Ueno M,
Sakamoto Y, Nakamura S, Hamuro J and Kinoshita S: The ROCK
inhibitor eye drop accelerates corneal endothelium wound healing.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:2493–2502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tokushige H, Inatani M, Nemoto S, Sakaki
H, Katayama K, Uehata M and Tanihara H: Effects of topical
administration of y-39983, a selective rho-associated protein
kinase inhibitor, on ocular tissues in rabbits and monkeys. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:3216–3222. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yilmaz M and Christofori G: EMT, the
cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:15–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Piera-Velazquez S and Jimenez SA:
Molecular mechanisms of endothelial to mesenchymal cell transition
(EndoMT) in experimentally induced fibrotic diseases. Fibrogenesis
Tissue Repair. 5(Suppl 1): S72012.PubMed/NCBI
|