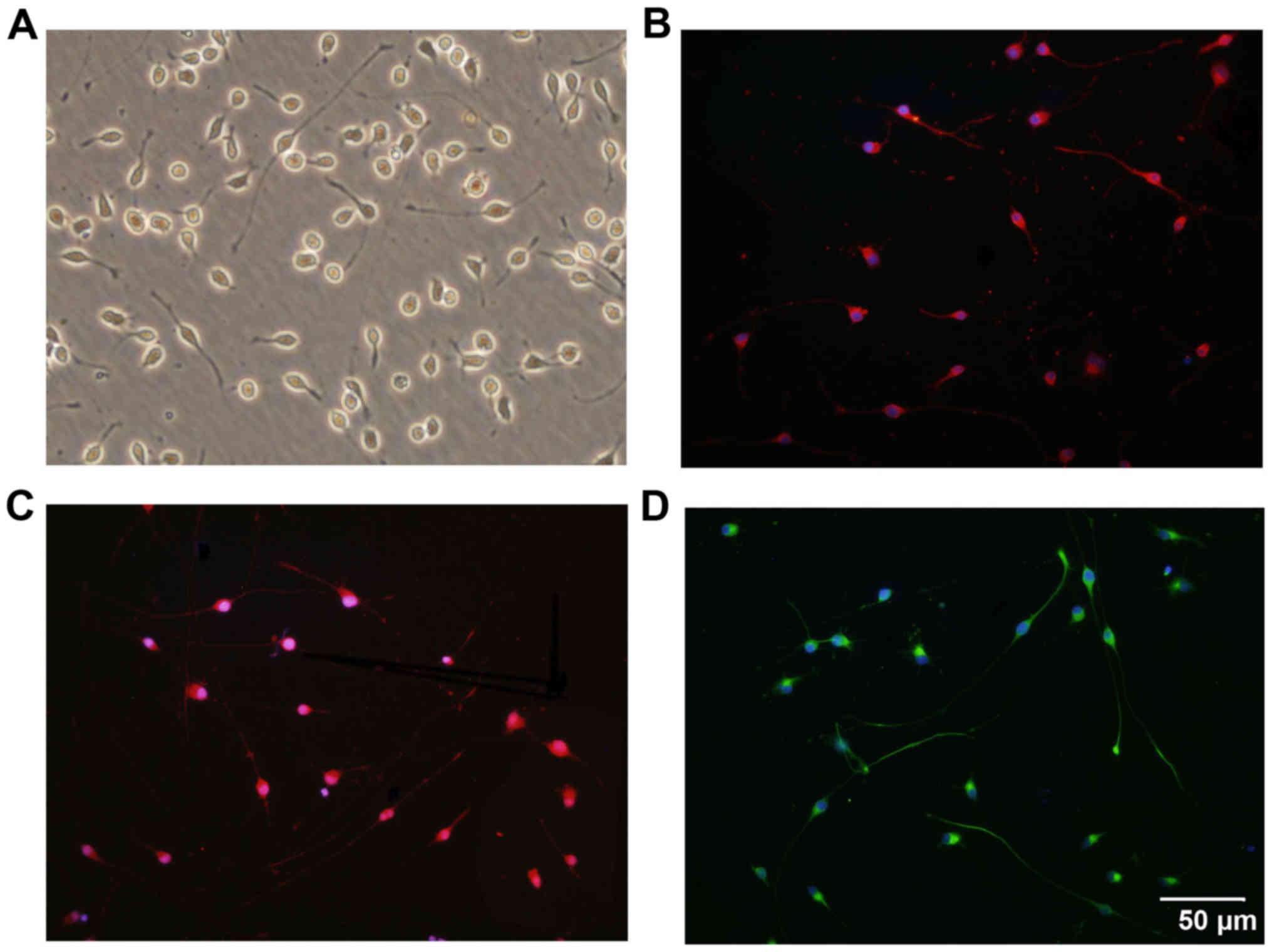
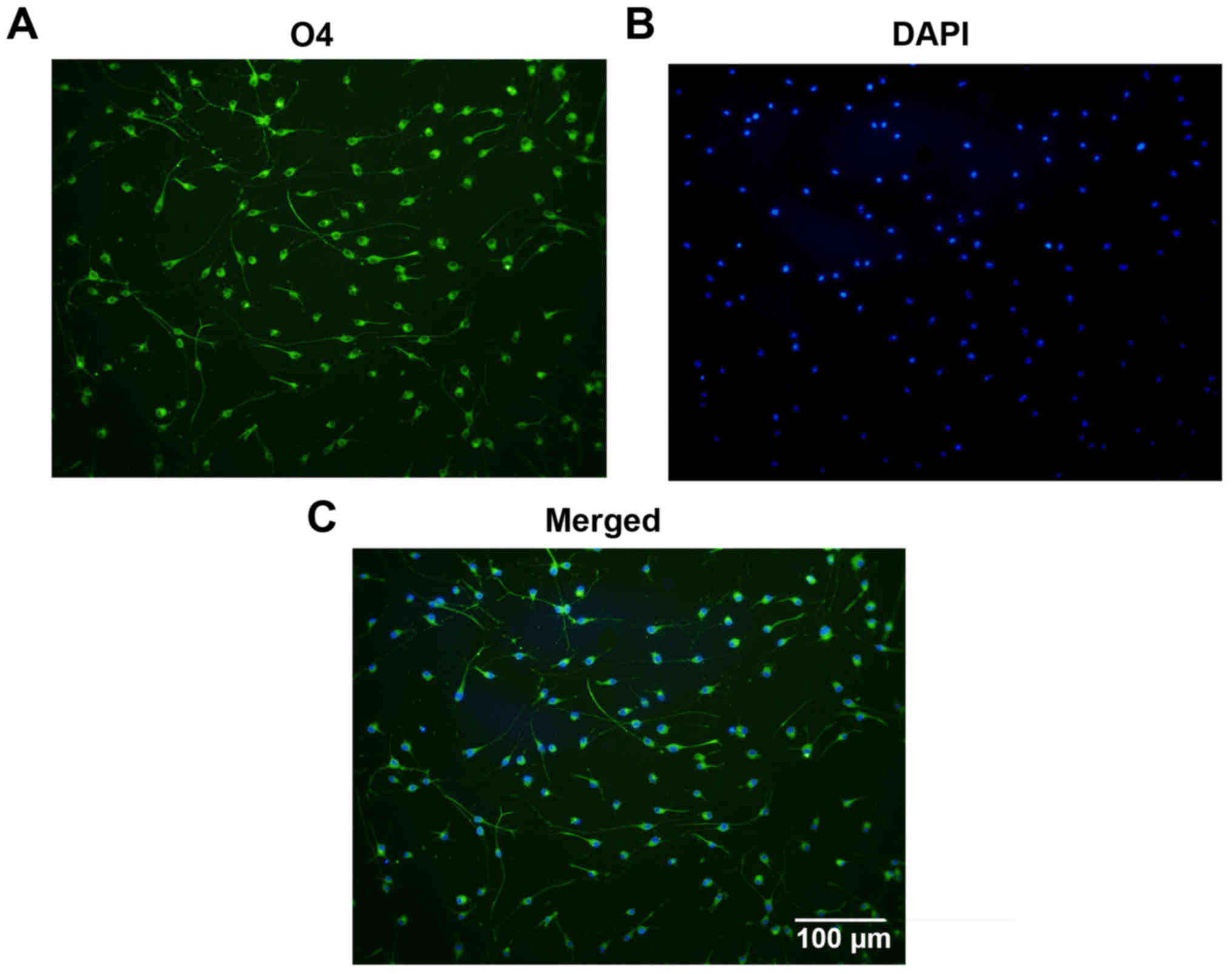
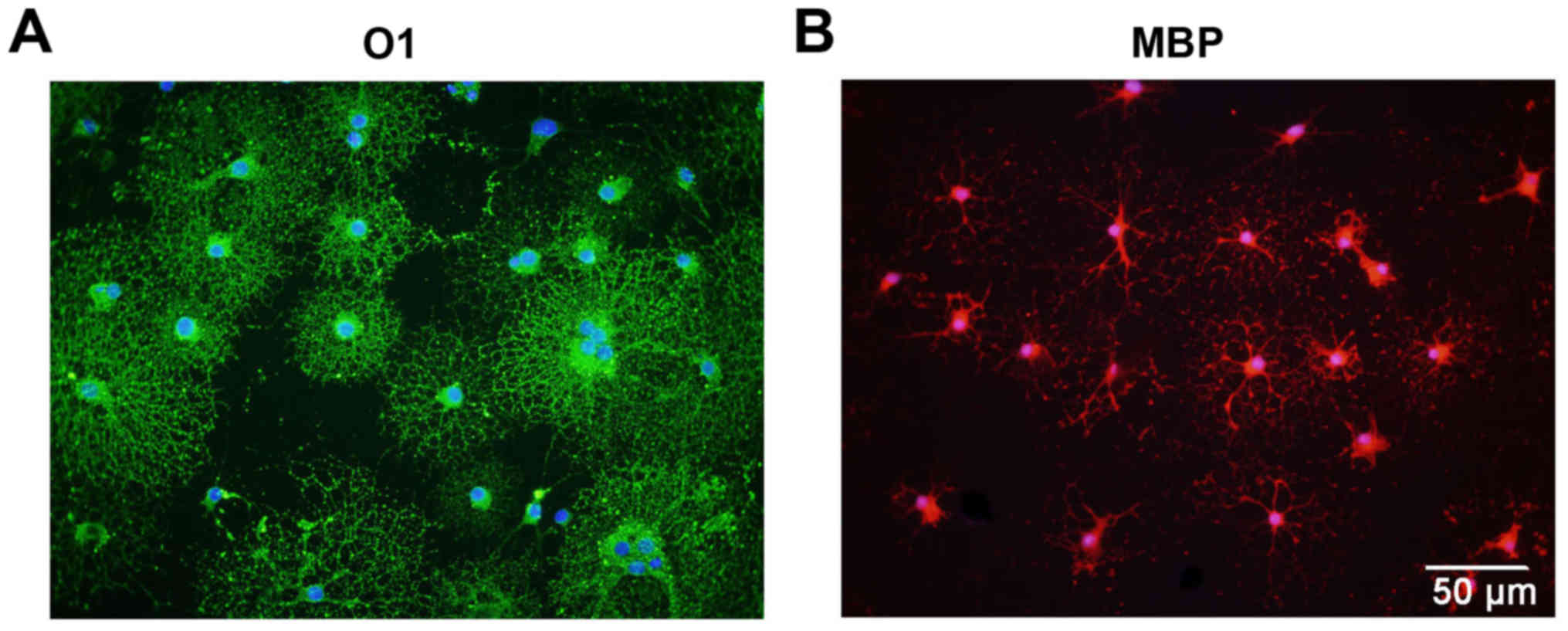
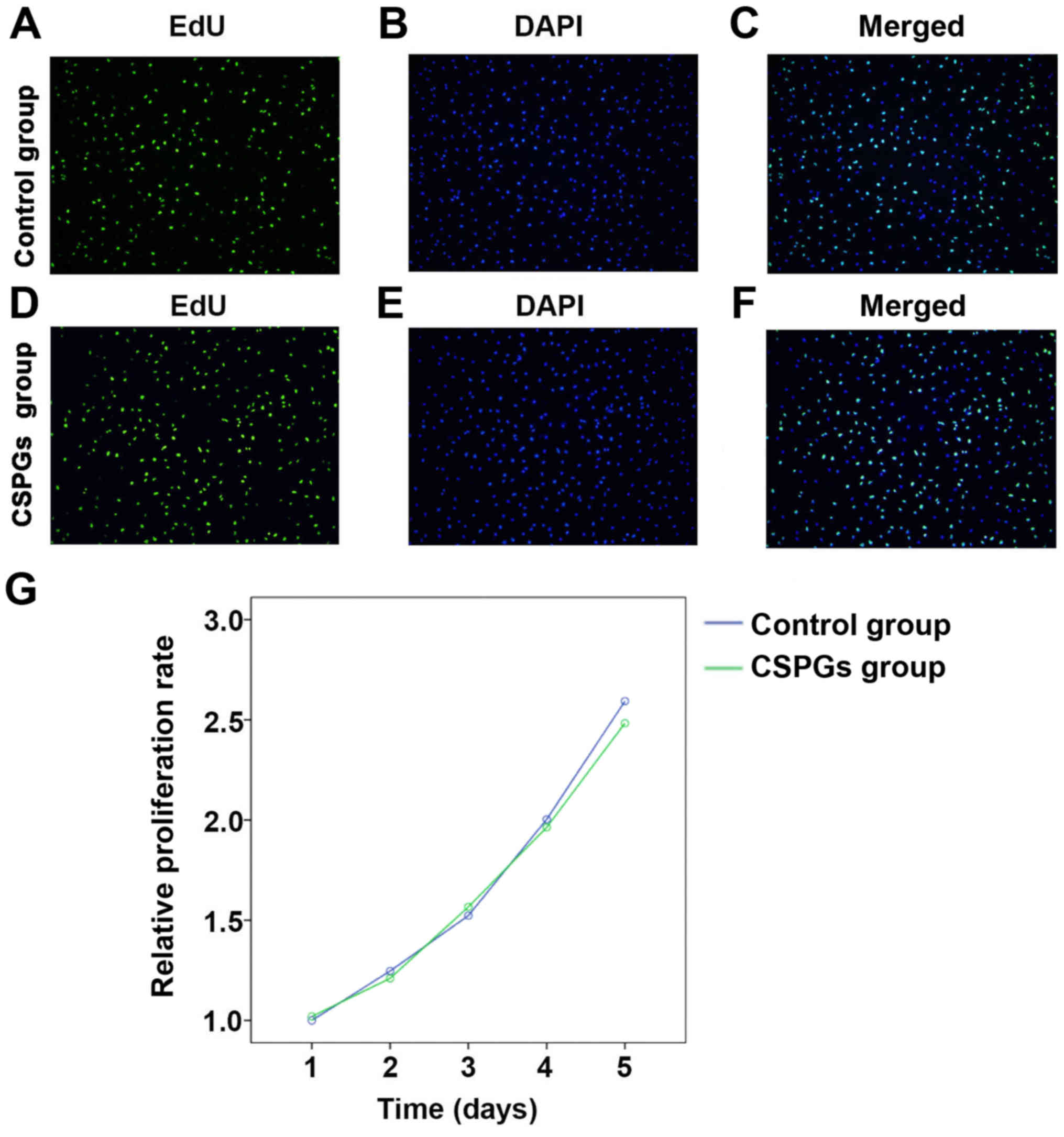
|
1
|
SanGiovanni JP, Allred EN, Mayer DL,
Stewart JE, Herrera MG and Leviton A: Reduced visual resolution
acuity and cerebral white matter damage in very-low-birthweight
infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 42:809–815. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muglia LJ and Katz M: The enigma of
spontaneous preterm birth. N Engl J Med. 362:529–535. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
du Plessis AJ: Neurology of the newborn
infant. Preface. Clin Perinatol. 36:xi–xiii. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wilson-Costello D, Friedman H, Minich N,
Fanaroff AA and Hack M: Improved survival rates with increased
neurodevelop-mental disability for extremely low birth weight
infants in the 1990s. Pediatrics. 115:997–1003. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Groenendaal F, Termote JU, van der
Heide-Jalving M, van Haastert IC and de Vries LS: Complications
affecting preterm neonates from 1991 to 2006: What have we gained?
Acta Paediatr. 99:354–358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Msall ME: Central nervous system
connectivity after extreme prematurity: Understanding autistic
spectrum disorder. J Pediatr. 156:519–521. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Volpe JJ, Kinney HC, Jensen FE and
Rosenberg PA: The developing oligodendrocyte: Key cellular target
in brain injury in the premature infant. Int J Dev Neurosci.
29:423–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Back SA, Luo NL, Mallinson RA, O'Malley
JP, Wallen LD, Frei B, Morrow JD, Petito CK, Roberts CT Jr, Murdoch
GH, et al: Selective vulnerability of preterm white matter to
oxidative damage defined by F2-isoprostanes. Ann Neurol.
58:108–120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khwaja O and Volpe JJ: Pathogenesis of
cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal
Neonatal Ed. 93:F153–F161. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Billiards SS, Haynes RL, Folkerth RD,
Borenstein NS, Trachtenberg FL, Rowitch DH, Ligon KL, Volpe JJ and
Kinney HC: Myelin abnormalities without oligodendrocyte loss in
periventricular leukomalacia. Brain Pathol. 18:153–163. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Back SA, Luo NL, Borenstein NS, Levine JM,
Volpe JJ and Kinney HC: Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide
with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal
white matter injury. J Neurosci. 21:1302–1312. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Galtrey CM and Fawcett JW: The role of
chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in regeneration and plasticity in
the central nervous system. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 54:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Carulli D, Laabs T, Geller HM and Fawcett
JW: Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in neural development and
regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 15:116–120. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Siebert JR and Osterhout DJ: The
inhibitory effects of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on
oligodendrocytes. J Neurochem. 119:176–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
O'Meara RW, Ryan SD, Colognato H and
Kothary R: Derivation of enriched oligodendrocyte cultures and
oligodendrocyte/neuron myelinating co-cultures from post-natal
murine tissues. J Vis Exp. 54:33242011.
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Back SA and Rosenberg PA: Pathophysiology
of glia in perinatal white matter injury. Glia. 62:1790–1815. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Volpe JJ, Kinney HC, Jensen FE and
Rosenberg PA: Reprint of 'The developing oligodendrocyte: Key
cellular target in brain injury in the premature infant'. Int J Dev
Neurosci. 29:565–582. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sirko S, von Holst A, Wizenmann A, Götz M
and Faissner A: Chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans control
proliferation, radial glia cell differentiation and neurogenesis in
neural stem/progenitor cells. Development. 134:2727–2738. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Meara RW, Michalski JP and Kothary R:
Integrin signaling in oligodendrocytes and its importance in CNS
myelination. J Signal Transduct. 2011:3540912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buttery PC and ffrench-Constant C:
Laminin-2/integrin interactions enhance myelin membrane formation
by oligodendrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci. 14:199–212. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Olsen IM and Ffrench-Constant C: Dynamic
regulation of integrin activation by intracellular and
extracellular signals controls oligodendrocyte morphology. BMC
Biol. 3:252005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gu WL, Fu SL, Wang YX, Li Y, Lü HZ, Xu XM
and Lu PH: Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans regulate the growth,
differentiation and migration of multipotent neural precursor cells
through the integrin signaling pathway. BMC Neurosci. 10:1282009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu WM, Chen ZL, North AJ and Strickland S:
Laminin is required for Schwann cell morphogenesis. J Cell Sci.
122:929–936. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Relucio J, Menezes MJ, Miyagoe-Suzuki Y,
Takeda S and Colognato H: Laminin regulates postnatal
oligodendrocyte production by promoting oligodendrocyte progenitor
survival in the subventricular zone. Glia. 60:1451–1467. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|