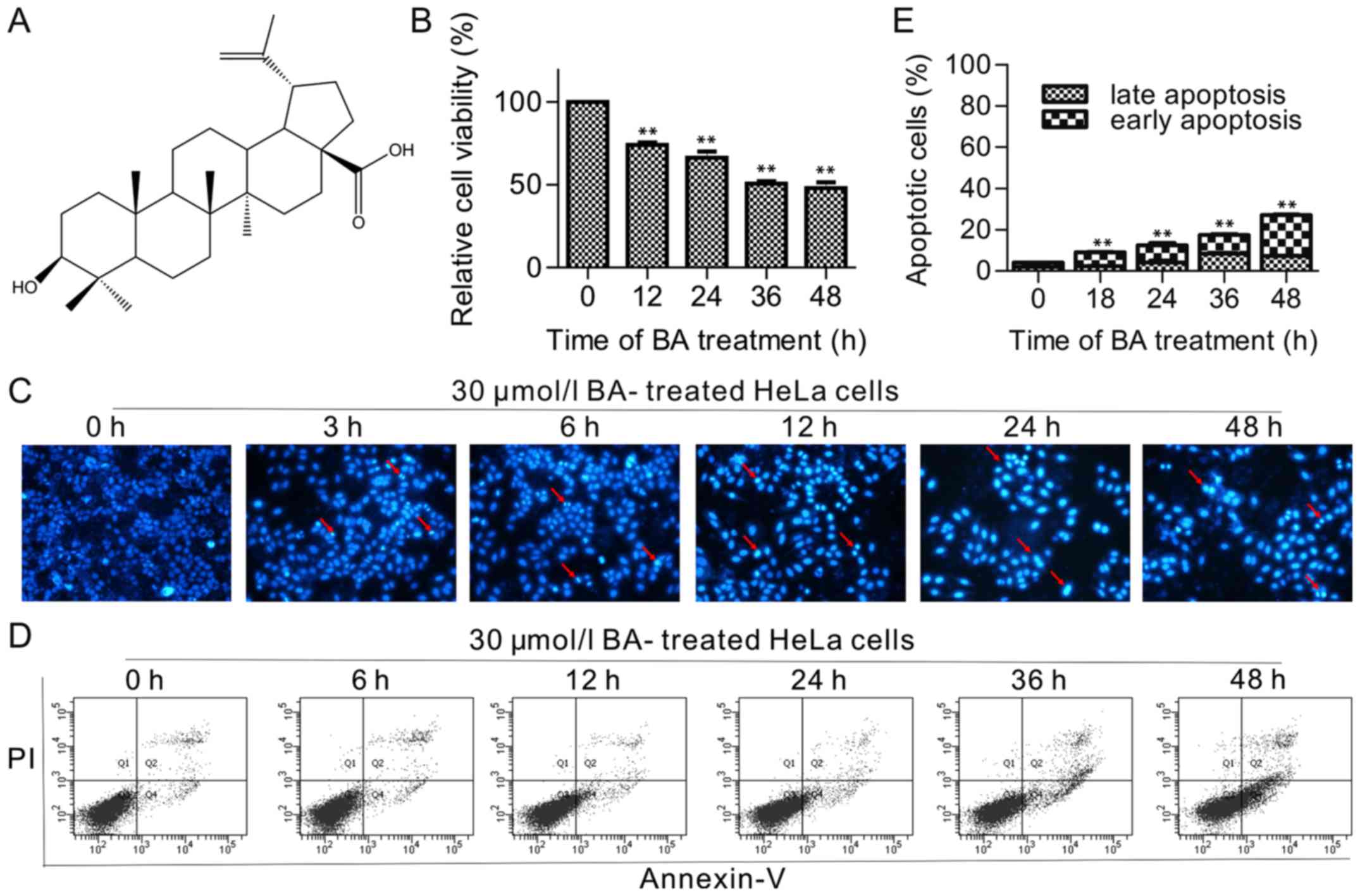
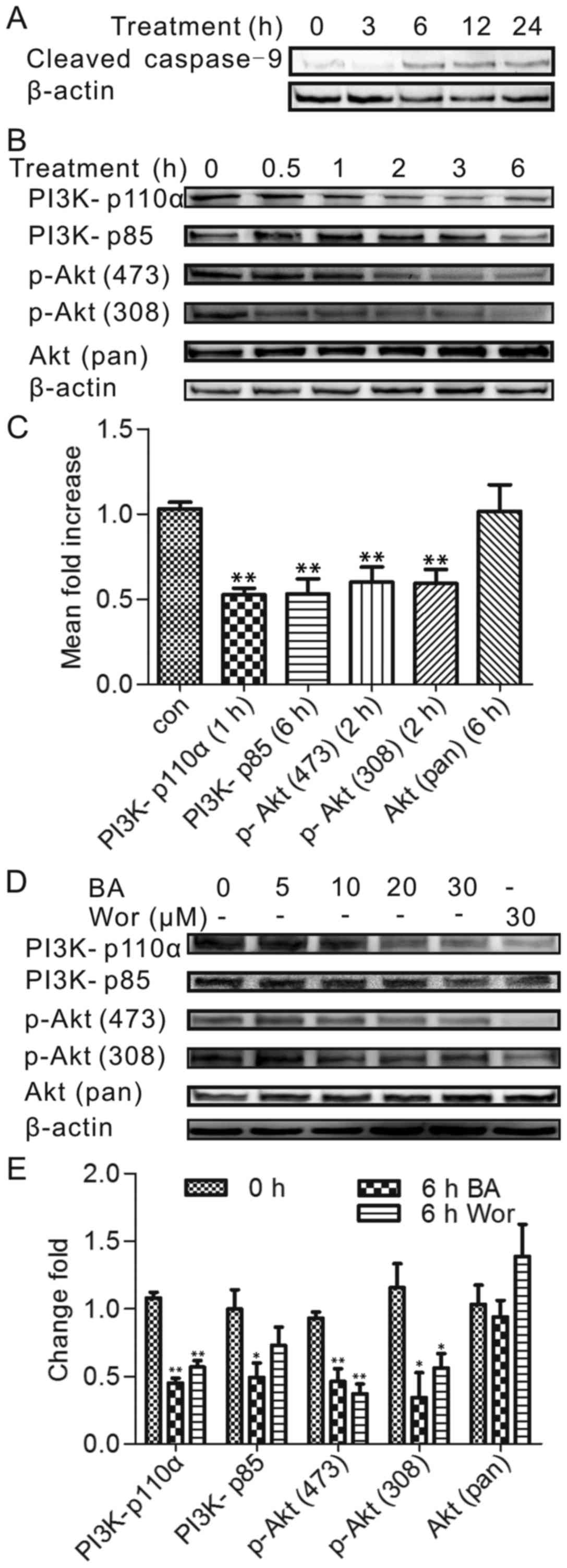
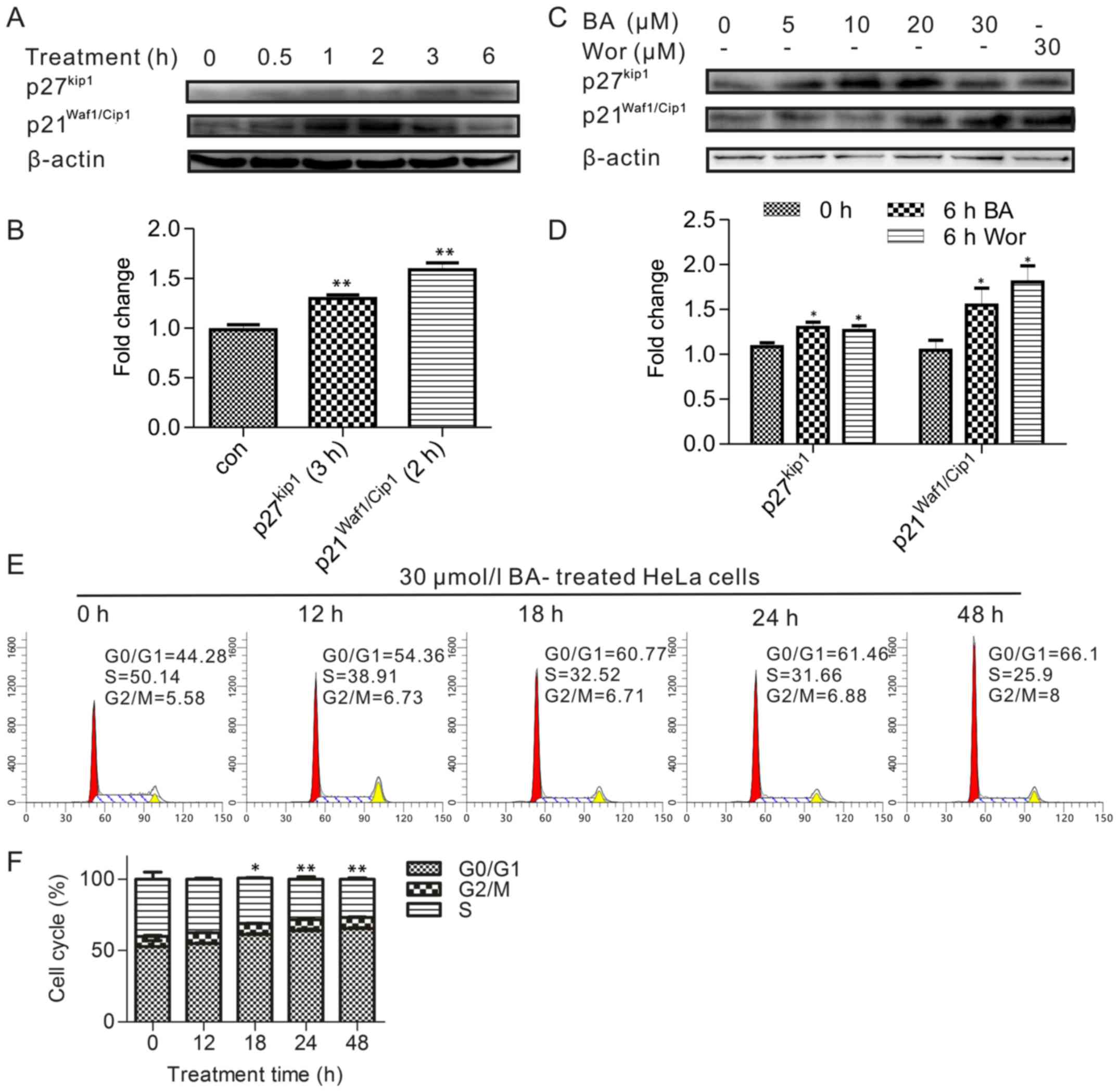
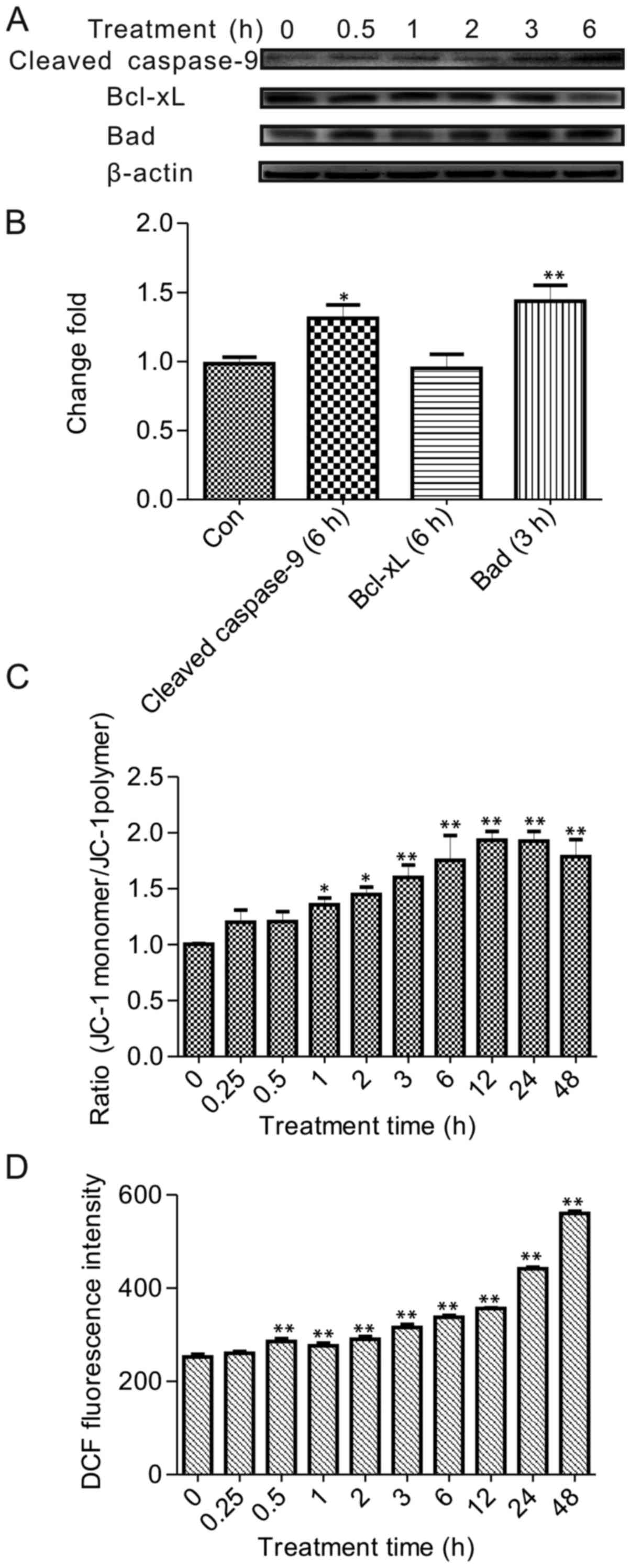
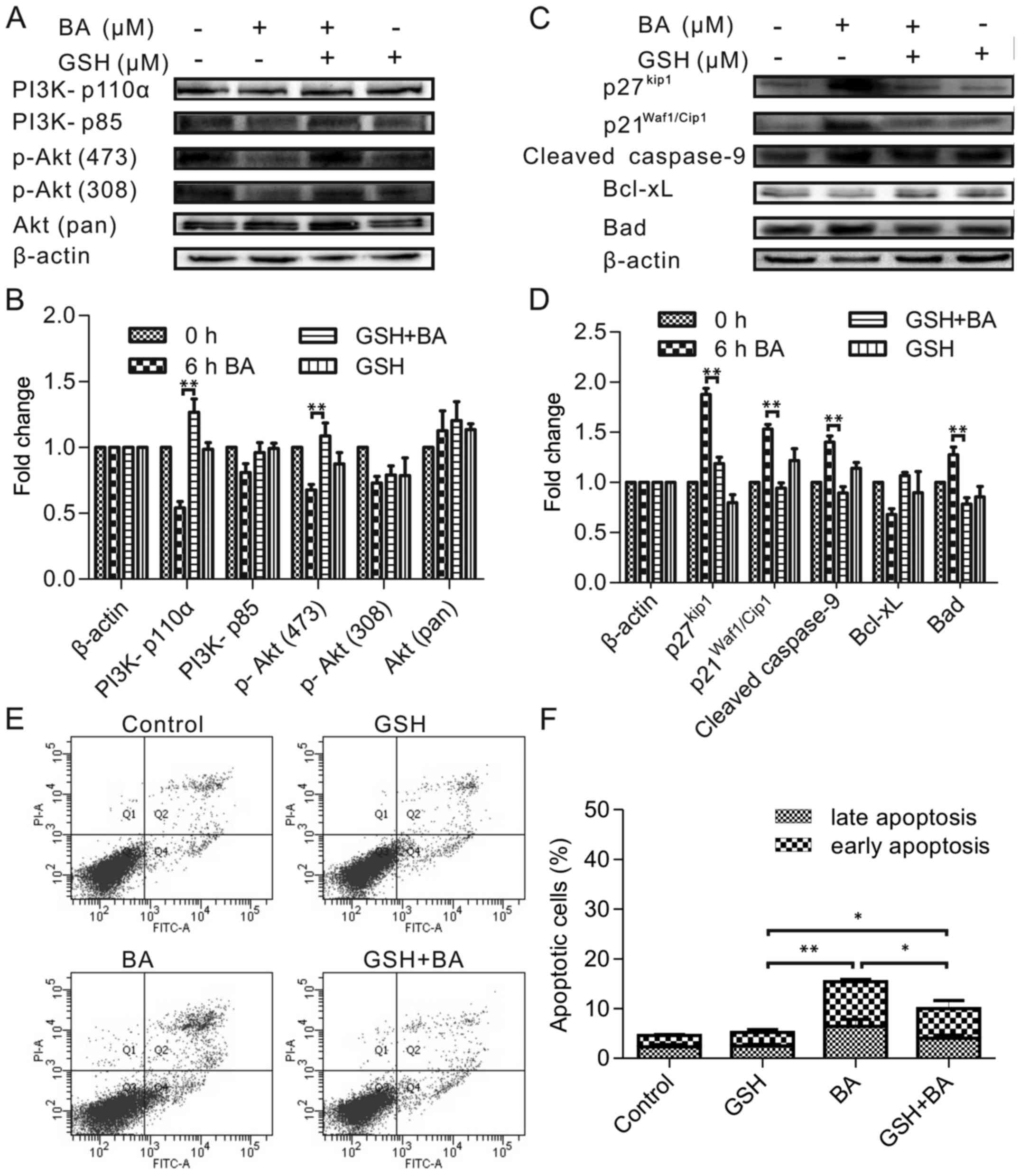
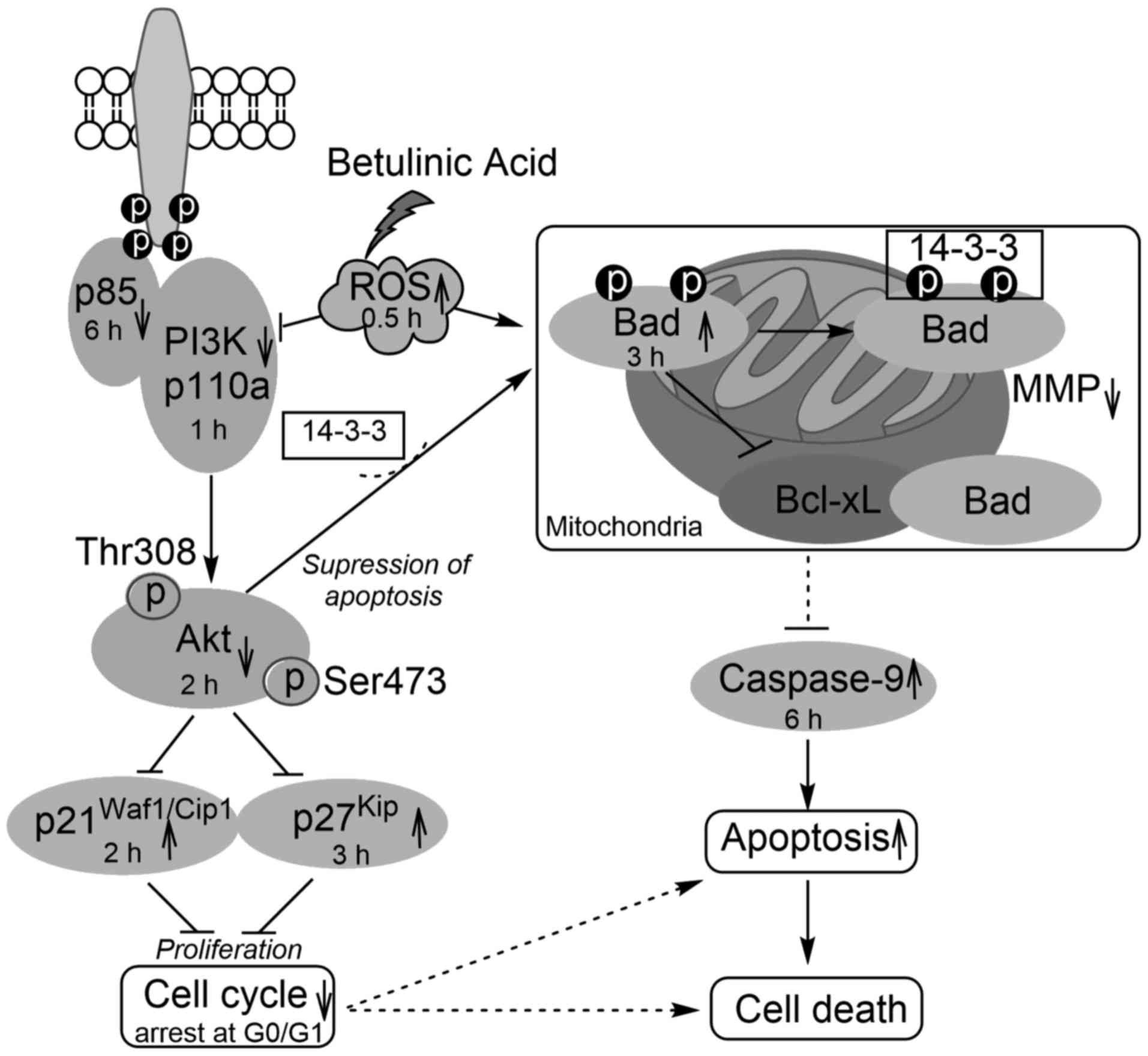
|
1
|
Pisha E, Chai H, Lee IS, Chagwedera TE,
Farnsworth NR, Cordell GA, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Kinghorn AD, Brown
DM, et al: Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of
human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat Med.
1:1046–1051. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zuco V, Supino R, Righetti SC, Cleris L,
Marchesi E, Gambacorti-Passerini C and Formelli F: Selective
cytotoxicity of betulinic acid on tumor cell lines, but not on
normal cells. Cancer Lett. 175:17–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rabi T, Shukla S and Gupta S: Betulinic
acid suppresses constitutive and TNFalpha-induced NF-kappaB
activation and induces apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma PC-3
cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:964–973. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eichenmüller M, von Schweinitz D and
Kappler R: Betulinic acid treatment promotes apoptosis in
hepatoblastoma cells. Int J Oncol. 35:873–879. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan DF, Li Q, Rammath N, Beck A, Wiseman
S, Anderson T, al-Salameh A, Brooks J and Bepler G: Prognostic
significance of expression of p53 oncoprotein in primary (stage
I–IIIa) non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 23:1665–1672.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mullauer FB, Kessler JH and Medema JP:
Betulinic acid induces cytochrome c release and apoptosis in a
Bax/Bak-independent, permeability transition pore dependent
fashion. Apoptosis. 14:191–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Eichenmüller M, Hemmerlein B, von
Schweinitz D and Kappler R: Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and
inhibits hedgehog signalling in rhabdomyosarcoma. Br J Cancer.
103:43–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng L, Xia TS, Wang YF, Zhou W, Liang
XQ, Xue JQ, Shi L, Wang Y and Ding Q: The apoptotic effect of D
Rhamnose β-hederin, a novel oleanane-type triterpenoid saponin on
breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e908482014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim JA, Åberg C, de Cárcer G, Malumbres M,
Salvati A and Dawson KA: Low dose of amino-modified nanoparticles
induces cell cycle arrest. ACS Nano. 7:7483–7494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang QH, Liu Y, Wu SS, Cui RR, Yuan LQ
and Liao EY: Ghrelin inhibits the apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells
through ERK and AKT signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
272:591–597. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H,
Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples
survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell.
91:231–241. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roy B, Pattanaik AK, Das J, Bhutia SK,
Behera B, Singh P and Maiti TK: Role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK
pathway in Concanavalin A induced autophagy in HeLa cells. Chem
Biol Interact. 210:96–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu T, Pang Q, Zhou D, Zhang A, Luo S, Wang
Y and Yan X: Proteomic investigation into betulinic acid-induced
apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cells. PLoS One.
9:e1057682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meinig JM and Peterson BR:
Anticancer/antiviral agent Akt inhibitor-IV massively accumulates
in mitochondria and potently disrupts cellular bioenergetics. ACS
Chem Biol. 10:570–576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargyl-cysteine, increases CSE in
SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a novel anti-cancer
effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One. 6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, Wei A, Naik
E, Fletcher JI, Adams JM and Huang DC: Proapoptotic Bak is
sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by
BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 19:1294–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian F, Ding D and Li D: Fangchinoline
targets PI3K and suppresses PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in SGC7901
cells. Int J Oncol. 46:2355–2363. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goo CK, Lim HY, Ho QS, Too HP, Clement MV
and Wong KP: PTEN/Akt signaling controls mitochondrial respiratory
capacity through 4E-BP1. PLoS One. 7:e458062012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H and Zhao JJ: PI3K
in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and
therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:7–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Brazil DP and Hemmings BA: Ten years of
protein kinase B signalling: A hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem
Sci. 26:657–664. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
del Peso L, González-García M, Page C,
Herrera R and Nuñez G: Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD
through the protein kinase Akt. Science. 278:687–689. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reed SI: Keeping p27(Kip1) in the
cytoplasm: A second front in cancer's war on p27. Cell Cycle.
1:389–390. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nakayama KI and Nakayama K: Ubiquitin
ligases: Cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:369–381.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M:
Cyclin D-dependent kinases, INK4 inhibitors and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1602:73–87. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee SK, Zhang W and Sanderson BJ:
Selective growth inhibition of human leukemia and human
lymphoblastoid cells by resveratrol via cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis induction. J Agric Food Chem. 56:7572–7577. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kang S, Dong SM, Kim BR, Park MS, Trink B,
Byun HJ and Rho SB: Thioridazine induces apoptosis by targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in cervical and endometrial cancer cells.
Apoptosis. 17:989–997. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rzeski W, Stepulak A, Szymański M,
Sifringer M, Kaczor J, Wejksza K, Zdzisińska B and
Kandefer-Szerszeń M: Betulinic acid decreases expression of bcl-2
and cyclin D1, inhibits proliferation, migration and induces
apoptosis in cancer cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
374:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang X, Lu H, Wang Y, Liu C, Zhu W, Zheng
S and Wan F: Taurine induces the apoptosis of breast cancer cells
by regulating apoptosis-related proteins of mitochondria. Int J Mol
Med. 35:218–226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zou Y, Li Q, Jiang L, Guo C, Li Y, Yu Y,
Li Y, Duan J and Sun Z: DNA hypermethylation of CREB3L1 and Bcl-2
associated with the mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis via PI3K/Akt
pathway in human BEAS-2B cells exposure to silica nanoparticles.
PLoS One. 11:e01584752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khan I, Guru SK, Rath SK, Chinthakindi PK,
Singh B, Koul S, Bhushan S and Sangwan PL: A novel triazole
derivative of betulinic acid induces extrinsic and intrinsic
apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Eur J Med Chem.
108:104–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hamanaka RB and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial
reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate
biological outcomes. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:505–513. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Behrend L, Henderson G and Zwacka RM:
Reactive oxygen species in oncogenic transformation. Biochem Soc
Trans. 31:1441–1444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deeb D, Gao X, Jiang H, Janic B, Arbab AS,
Rojanasakul Y, Dulchavsky SA and Gautam SC: Oleanane triterpenoid
CDDO-Me inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells through a ROS-dependent mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol.
79:350–360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chandel NS: Mitochondrial complex III: An
essential component of universal oxygen sensing machinery? Respir
Physiol Neurobiol. 174:175–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chandel NS: Mitochondrial regulation of
oxygen sensing. Adv Exp Med Biol. 661:339–354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|