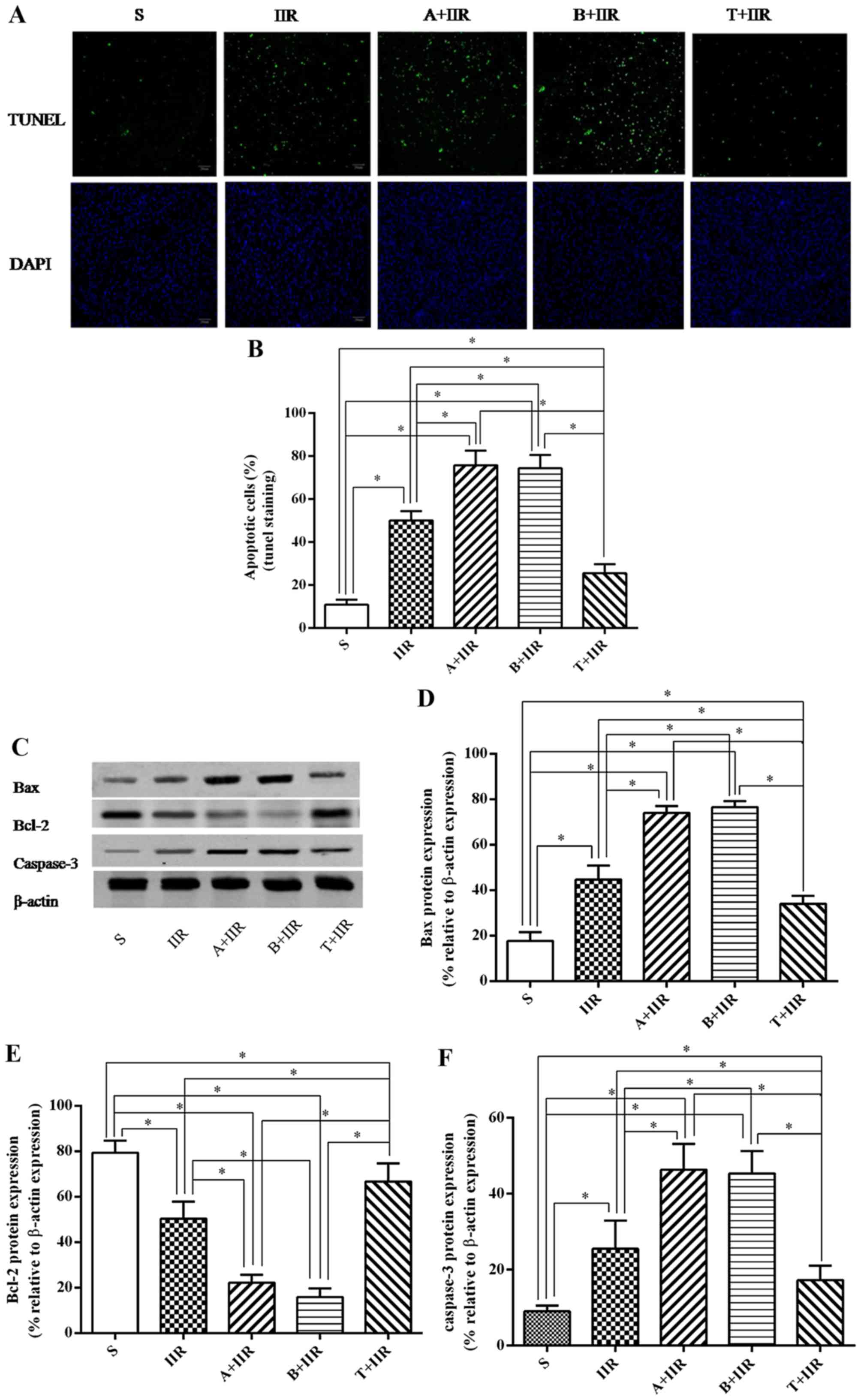
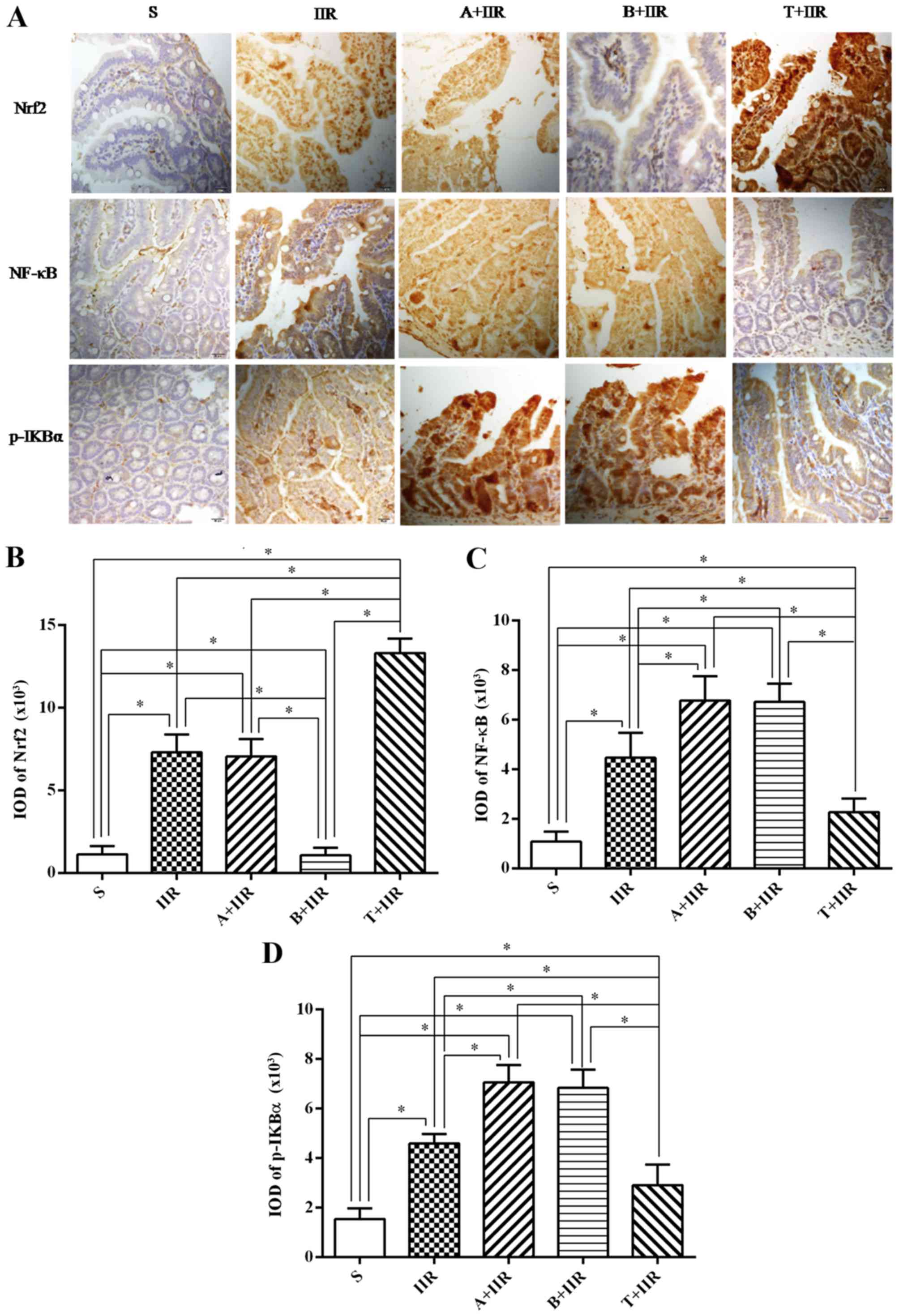
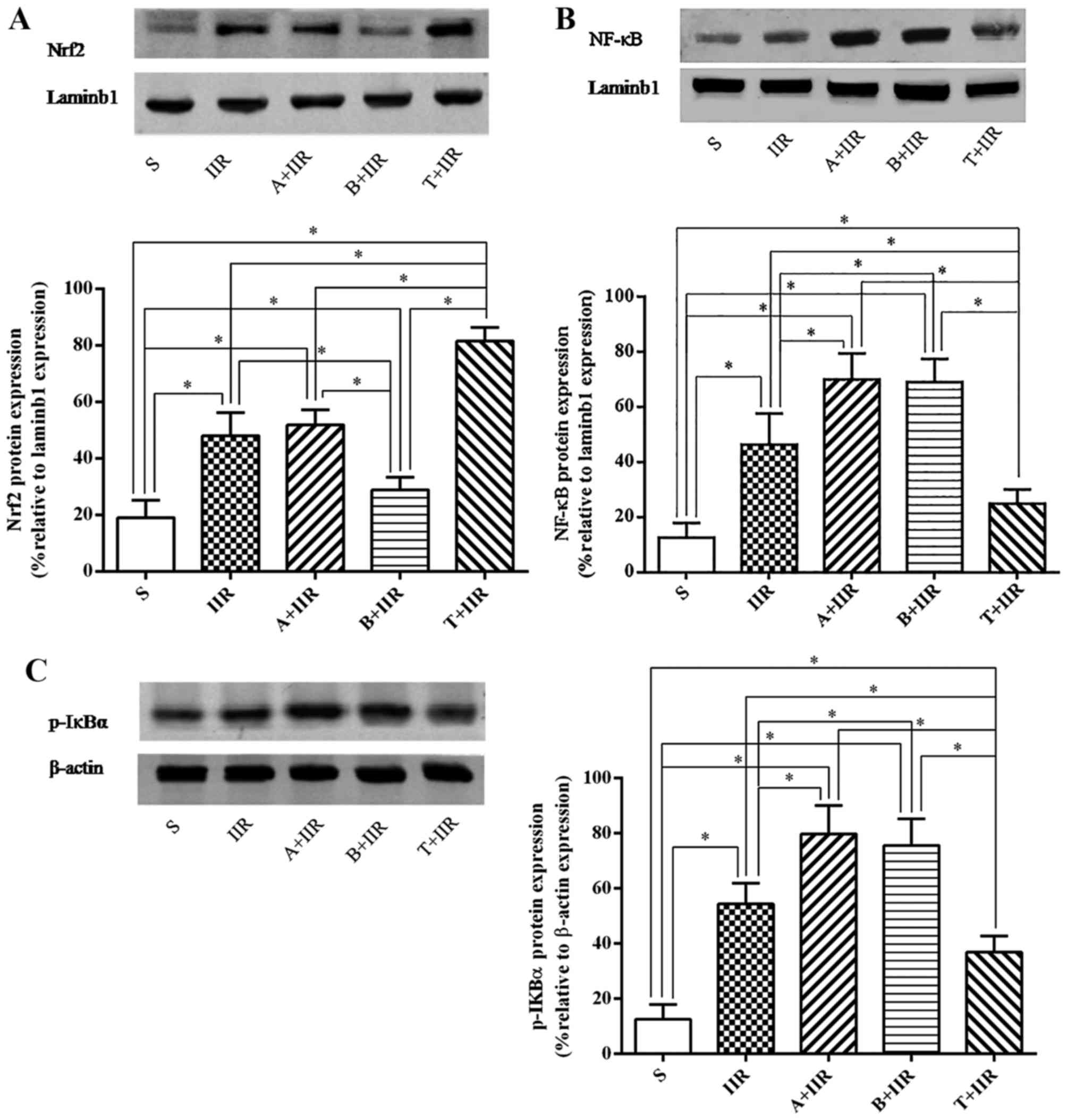
|
1
|
Huang CY, Hsiao JK, Lu YZ, Lee TC and Yu
LC: Anti-apoptotic PI3K/Akt signaling by sodium/glucose transporter
1 reduces epithelial barrier damage and bacterial translocation in
intestinal ischemia. Lab Invest. 91:294–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gerlach UA, Atanasov G, Wallenta L, Polenz
D, Reutzel-Selke A, Kloepfel M, Jurisch A, Marksteiner M,
Loddenkemper C, Neuhaus P, et al: Short-term TNF-alpha inhibition
reduces short-term and long-term inflammatory changes
post-ischemia/reperfusion in rat intestinal transplantation.
Transplantation. 97:732–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim M, Park SW, Kim M, D'Agati VD and Lee
HT: Isoflurane post-conditioning protects against intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury and multiorgan dysfunction via
transforming growth factor-β1 generation. Ann Surg. 255:492–503.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crafts TD, Hunsberger EB, Jensen AR,
Rescorla FJ, Yoder MC and Markel TA: Direct peritoneal
resuscitation improves survival and decreases inflammation after
intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Surg Res.
199:428–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tian S, Guo R, Wei S, Kong Y, Wei X, Wang
W, Shi X and Jiang H: Curcumin protects against the intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury: Involvement of the tight junction
protein ZO-1 and TNF-α related mechanism. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 20:147–152. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Komaravelli N, Tian B, Ivanciuc T,
Mautemps N, Brasier AR, Garofalo RP and Casola A: Respiratory
syncytial virus infection down-regulates antioxidant enzyme
expression by triggering deacetylation-proteasomal degradation of
Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. 88:391–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gallorini M, Petzel C, Bolay C, Hiller KA,
Cataldi A, Buchalla W, Krifka S and Schweikl H: Activation of the
Nrf2-regulated antioxidant cell response inhibits HEMA-induced
oxidative stress and supports cell viability. Biomaterials.
56:114–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boyanapalli SS, Paredes-Gonzalez X,
Fuentes F, Zhang C, Guo Y, Pung D, Saw CL and Kong AN: Nrf2
knockout attenuates the anti-inflammatory effects of phenethyl
isothiocyanate and curcumin. Chem Res Toxicol. 27:2036–2043. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park JH, Choi JW, Ju EJ, Pae AN and Park
KD: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of a natural
compound, shizukahenriol, through Nrf2 activation. Molecules.
20:15989–16003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao W, Sun Z, Wang S, Li Z and Zheng L:
Wnt1 participates in inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide
through upregulating scavenger receptor A and NF-κB. Inflammation.
38:1700–1706. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH and Sanderson CM:
Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response
pathways. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:621–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng QT, Cao C, Wu Y, Liu HM, Li W, Sun Q,
Chen R, Xiao YG, Tang LH, Jiang Y, et al: Ischemic
post-conditioning attenuates acute lung injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in mice: Role of Nrf2. Lab Invest.
96:1087–1104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang XJ, Hayes JD, Henderson CJ and Wolf
CR: Identification of retinoic acid as an inhibitor of
transcription factor Nrf2 through activation of retinoic acid
receptor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:19589–19594. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren D, Villeneuve NF, Jiang T, Wu T, Lau
A, Toppin HA and Zhang DD: Brusatol enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated defense mechanism.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1433–1438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
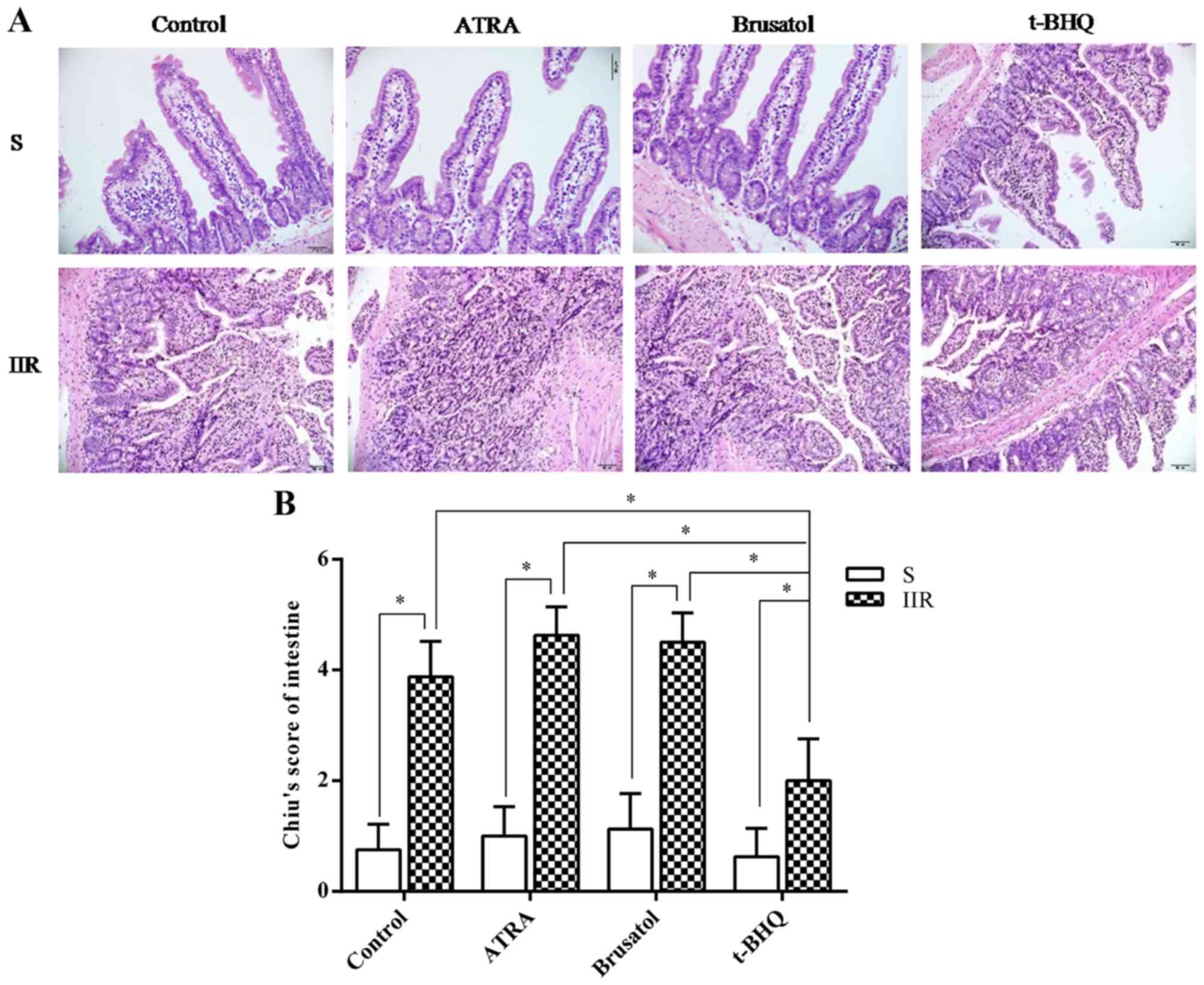
Chiu CJ, McArdle AH, Brown R, Scott HJ and
Gurd FN: Intestinal mucosal lesion in low-flow states. I. A
morphological, hemodynamic, and metabolic reappraisal. Arch Surg.
101:478–483. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
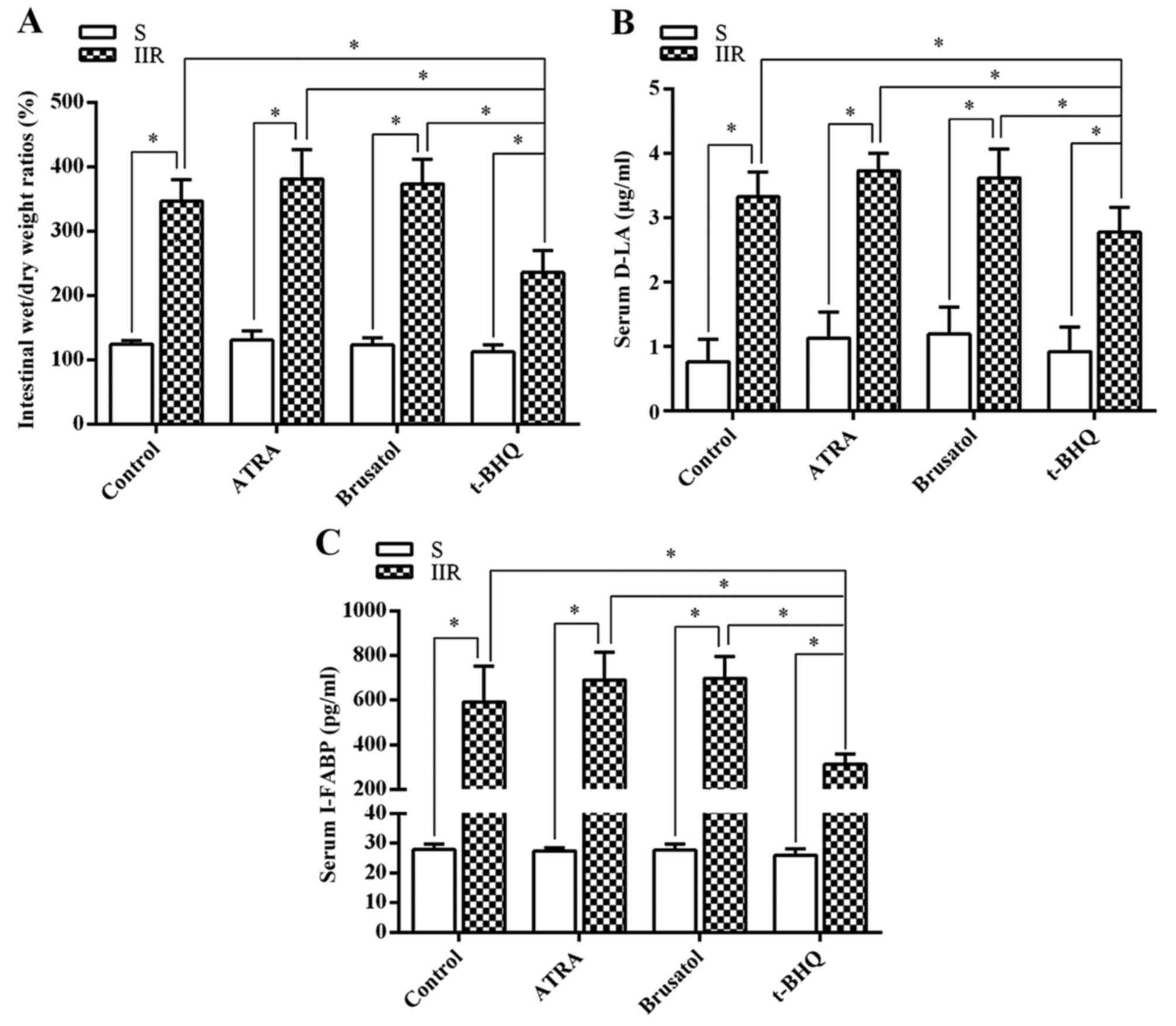
Sun Z, Wang X, Deng X, Lasson A, Wallén R,
Hallberg E and Andersson R: The influence of intestinal ischemia
and reperfusion on bidirectional intestinal barrier permeability,
cellular membrane integrity, proteinase inhibitors, and cell death
in rats. Shock. 10:203–212. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marques GMN, Rasslan R, Belon AR, Carvalho
JG, Felice Neto R, Rasslan S, Utiyama EM and Montero EF:
Pentoxifylline associated to hypertonic saline solution attenuates
inflammatory process and apoptosis after intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 29:735–741. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang X, Bai H, Wang Y, Li J, Zhou Q, Cai
W, Han J, Zhu X, Dong M and Hu D: Deletion of regulatory T cells
supports the development of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion
injuries. J Surg Res. 184:832–837. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang Y, Zhou Z, Meng QT, Sun Q, Su W, Lei
S, Xia Z and Xia ZY: Ginsenoside Rb1 treatment attenuates pulmonary
inflammatory cytokine release and tissue injury following
intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:8437212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schneider KM, Bieghs V, Heymann F, Hu W,
Dreymueller D, Liao L, Frissen M, Ludwig A, Gassler N, Pabst O, et
al: CX3CR1 is a gatekeeper for intestinal barrier integrity in
mice: Limiting steatohepatitis by maintaining intestinal
homeostasis. Hepatology. 62:1405–1416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sheedy JR, Wettenhall RE, Scanlon D,
Gooley PR, Lewis DP, McGregor N, Stapleton DI, Butt HL and DE
Meirleir KL: Increased d-lactic Acid intestinal bacteria in
patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. In Vivo. 23:621–628.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Khadaroo RG, Fortis S, Salim SY, Streutker
C, Churchill TA and Zhang H: I-FABP as biomarker for the early
diagnosis of acute mesenteric ischemia and resultant lung injury.
PLoS One. 9:e1152422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diebel ME, Diebel LN, Manke CW, Liberati
DM and Whittaker JR: Early tranexamic acid administration: A
protective effect on gut barrier function following
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
79:1015–1022. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Santamaría B, Ucero AC, Benito-Martin A,
Vicent MJ, Orzáez M, Celdrán A, Selgas R, Ruíz-Ortega M and Ortiz
A: Biocompatibility reduces inflammation-induced apoptosis in
mesothelial cells exposed to peritoneal dialysis fluid. Blood
Purif. 39:200–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ahmad SF, Attia SM, Bakheet SA, Zoheir KM,
Ansari MA, Korashy HM, Abdel-Hamied HE, Ashour AE and Abd-Allah AR:
Naringin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced acute
lung inflammation through inhibition of NF-κB, STAT3 and
pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancement of IκBα and
anti-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation. 38:846–857. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fan B, Dun SH, Gu JQ, Guo Y and Ikuyama S:
Pycnogenol attenuates the release of proinflammatory cytokines and
expression of perilipin 2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
microglia in part via inhibition of NF-κB and AP-1 activation. PLoS
One. 10:e01378372015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Wang B, Du F, Su X, Sun G, Zhou G,
Bian X and Liu N: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates oxidative
stress and inflammation in obstructive nephropathy via NF-κB and
Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway regulation. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 117:164–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li L, Dong H, Song E, Xu X, Liu L and Song
Y: Nrf2/ARE pathway activation, HO-1 and NQO1 induction by
polychlorinated biphenyl quinone is associated with reactive oxygen
species and PI3K/AKT signaling. Chem Biol Interact. 209:56–67.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Park SY, Kim YH and Park G: Cucurbitacins
attenuate microglial activation and protect from neuroinflammatory
injury through Nrf2/ARE activation and STAT/NF-κB inhibition.
Neurosci Lett. 609:129–136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Keleku-Lukwete N, Suzuki M, Otsuki A,
Tsuchida K, Katayama S, Hayashi M, Naganuma E, Moriguchi T, Tanabe
O, Engel JD, et al: Amelioration of inflammation and tissue damage
in sickle cell model mice by Nrf2 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:12169–12174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin S, Du R, Yin S, Liu X, Xu G and Cao W:
Nrf2 is essential for the anti-inflammatory effect of carbon
monoxide in LPS-induced inflammation. Inflamm Res. 64:537–548.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan H, Wang H, Wang X, Zhu L and Mao L:
The absence of Nrf2 enhances NF-κB-dependent inflammation following
scratch injury in mouse primary cultured astrocytes. Mediators
Inflamm. 2012:2175802012. View Article : Google Scholar
|