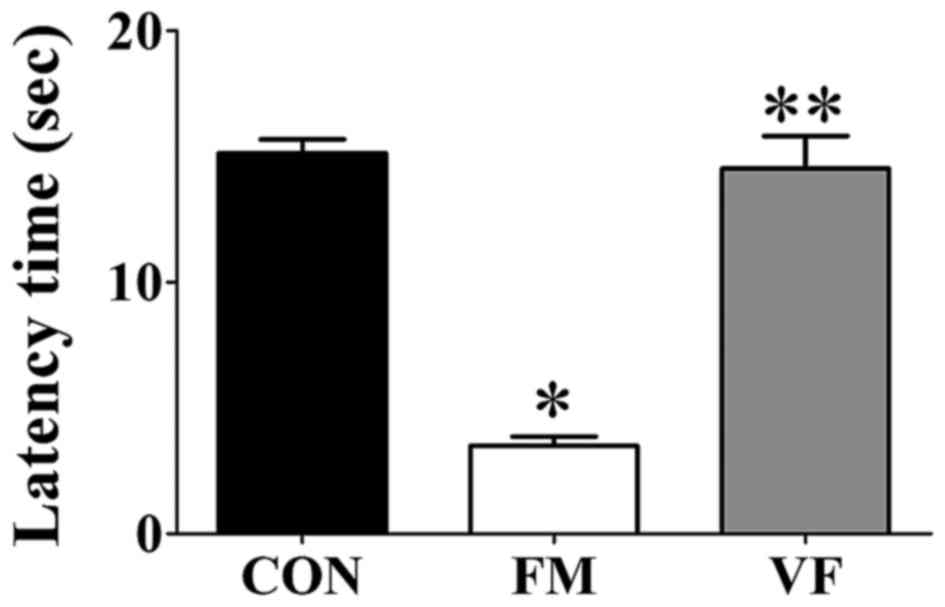
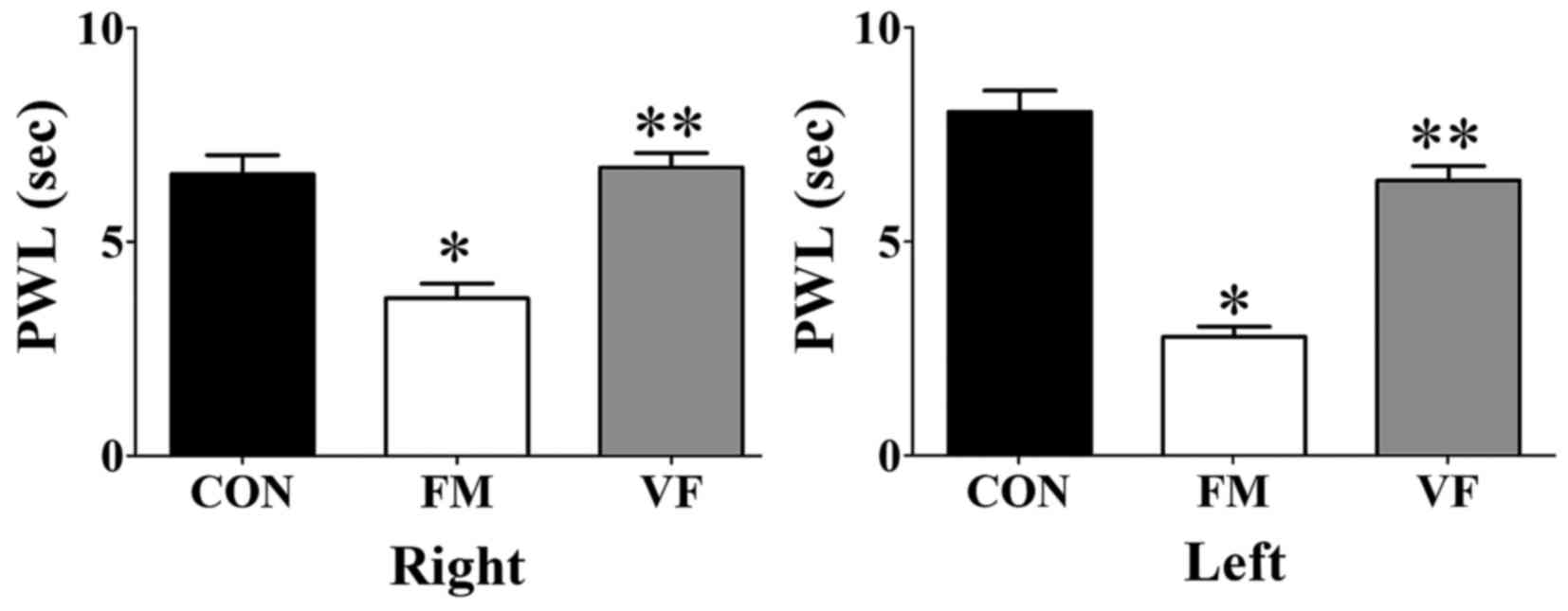
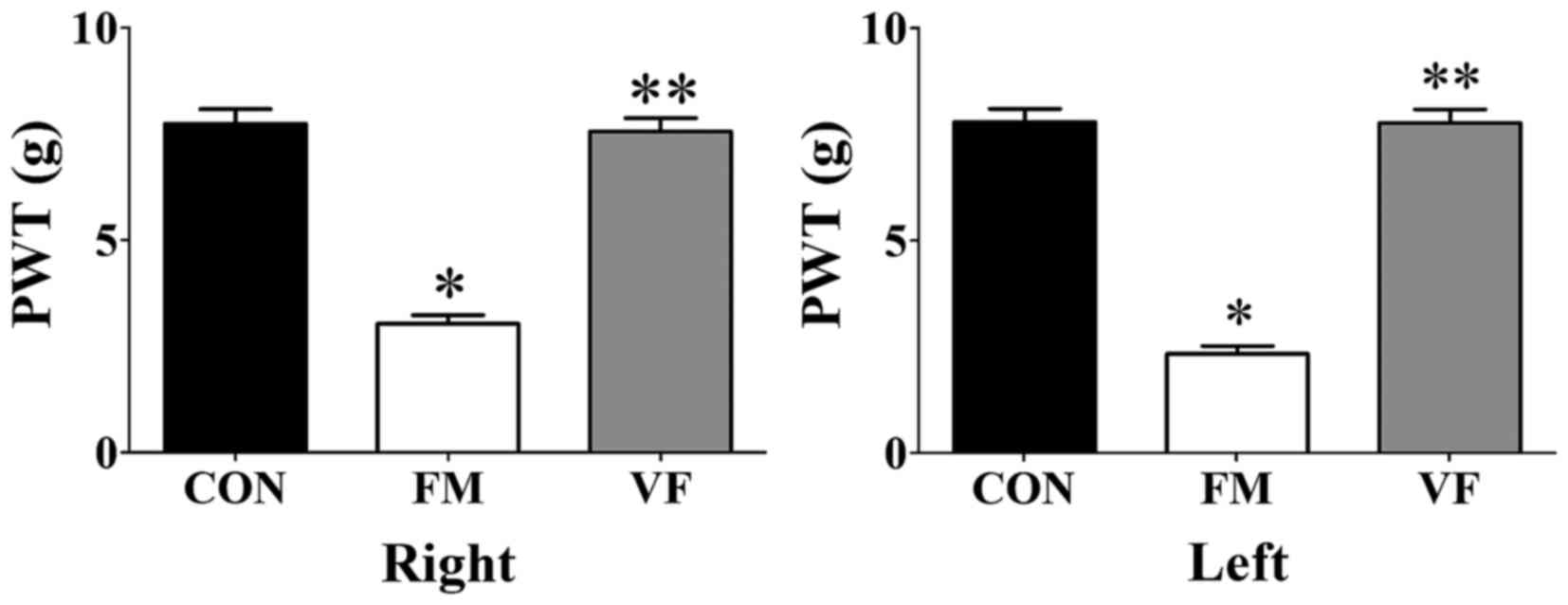
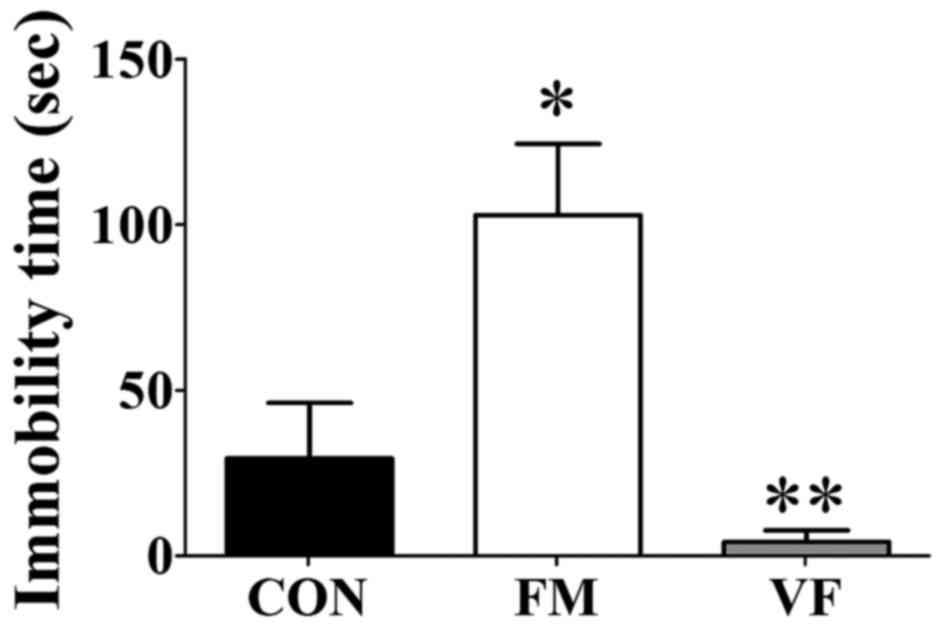
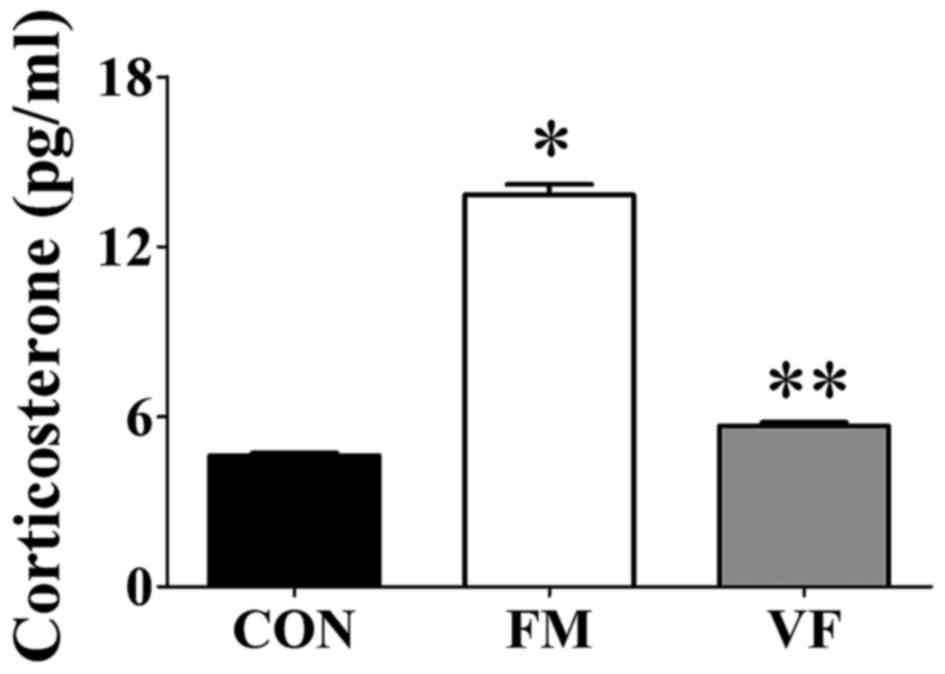
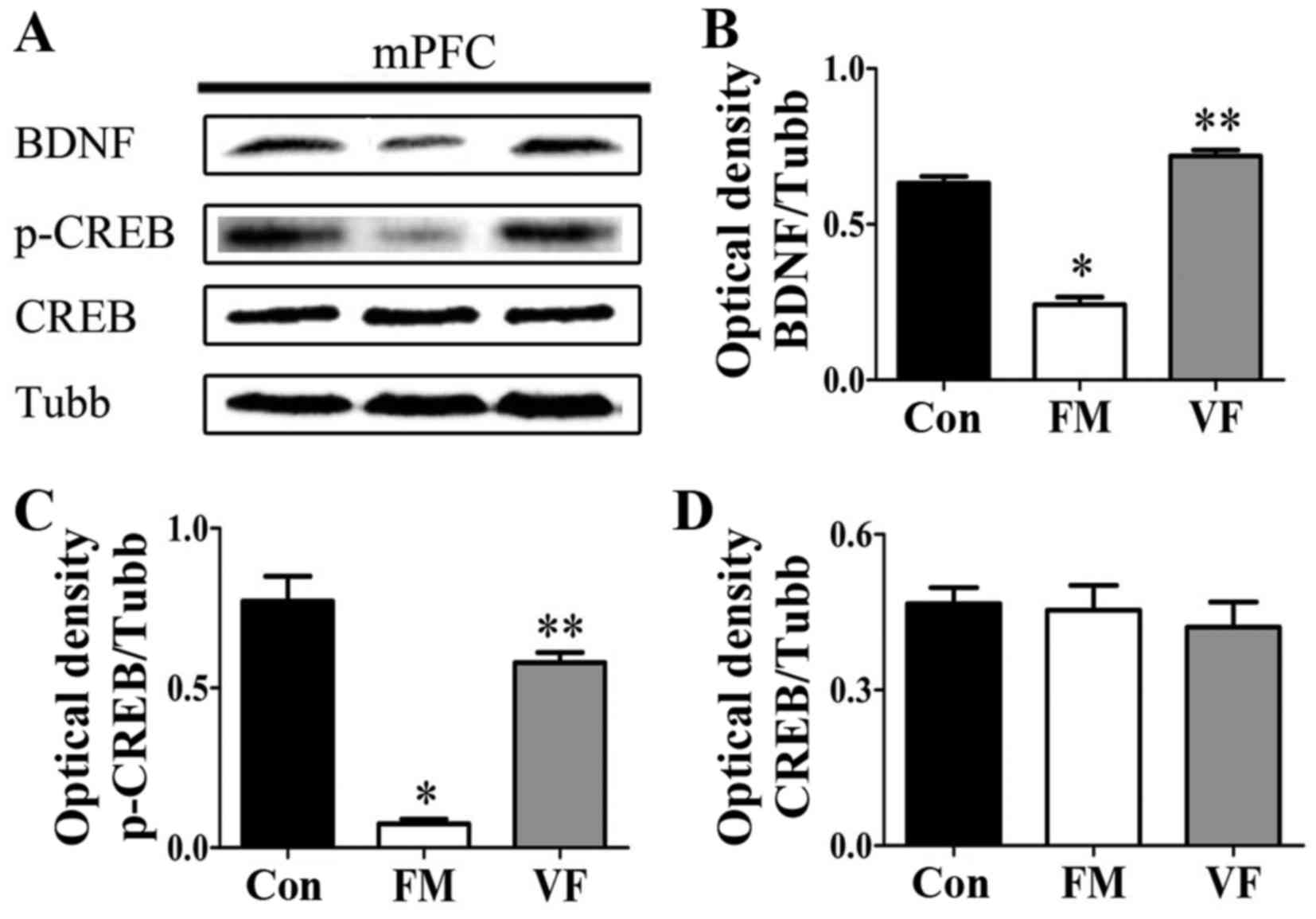
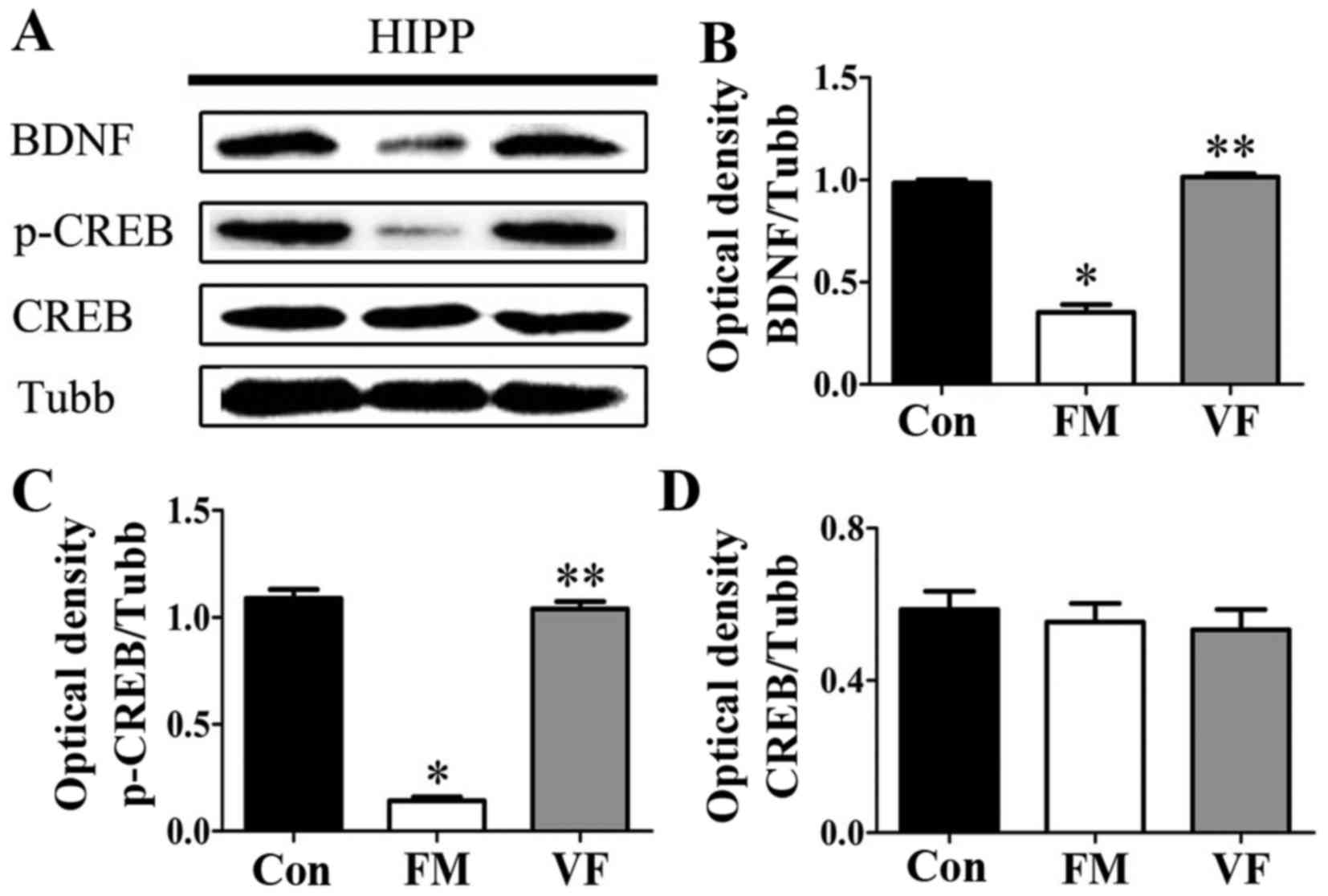
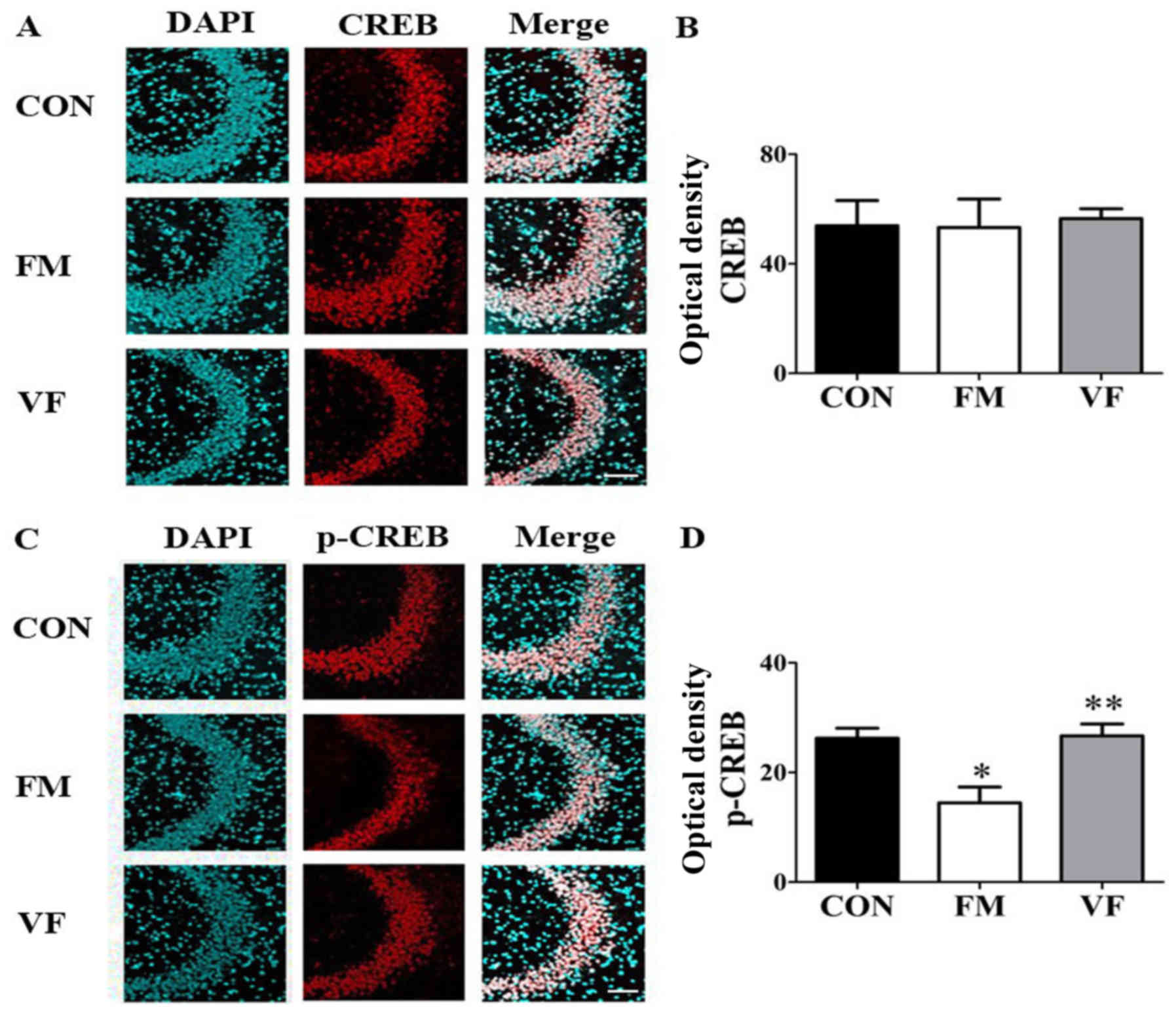
|
1
|
Lindell L, Bergman S, Petersson IF,
Jacobsson LT and Herrström P: Prevalence of fibromyalgia and
chronic widespread pain. Scand J Prim Health Care. 18:149–153.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM,
Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, Tugwell P, Campbell SM, Abeles M,
Clark P, et al: The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria
for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter
Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 33:160–172. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Montserrat-de la Paz S, García-Giménez MD,
Ángel-Martín M and Fernández-Arche A: Validation and additional
support for an experimental animal model of fibromyalgia. Mod
Rheumatol. 25:116–122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schmidt-Wilcke T and Clauw DJ:
Pharmacotherapy in fibromyalgia (FM) - implications for the
underlying pathophysiology. Pharmacol Ther. 127:283–294. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Green PG, Alvarez P, Gear RW, Mendoza D
and Levine JD: Further validation of a model of fibromyalgia
syndrome in the rat. J Pain. 12:811–818. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schur EA, Afari N, Furberg H, Olarte M,
Goldberg J, Sullivan PF and Buchwald D: Feeling bad in more ways
than one: Comorbidity patterns of medically unexplained and
psychiatric conditions. J Gen Intern Med. 22:818–821. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilson HD, Starz TW, Robinson JP and Turk
DC: Heterogeneity within the fibromyalgia population: Theoretical
implications of variable tender point severity ratings. J
Rheumatol. 36:2795–2801. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Anderson RJ, McCrae CS, Staud R, Berry RB
and Robinson ME: Predictors of clinical pain in fibromyalgia:
Examining the role of sleep. J Pain. 13:350–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Balasubramaniam R, de Leeuw R, Zhu H,
Nickerson RB, Okeson JP and Carlson CR: Prevalence of
temporomandibular disorders in fibromyalgia and failed back
syndrome patients: A blinded prospective comparison study. Oral
Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 104:204–216. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sluka KA, Kalra A and Moore SA: Unilateral
intramuscular injections of acidic saline produce a bilateral,
long-lasting hyperalgesia. Muscle Nerve. 24:37–46. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khasar SG, Miao JP, Jänig W and Levine JD:
Modulation of bradykinin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in the rat
by activity in abdominal vagal afferents. Eur J Neurosci.
10:435–444. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khasar SG, Dina OA, Green PG and Levine
JD: Sound stress-induced long-term enhancement of mechanical
hyperalgesia in rats is maintained by sympathoadrenal
catecholamines. J Pain. 10:1073–1077. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagakura Y, Oe T, Aoki T and Matsuoka N:
Biogenic amine depletion causes chronic muscular pain and tactile
allodynia accompanied by depression: A putative animal model of
fibromyalgia. Pain. 146:26–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishiyori M and Ueda H: Prolonged
gabapentin analgesia in an experimental mouse model of
fibromyalgia. Mol Pain. 4:522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nishiyori M, Uchida H, Nagai J, Araki K,
Mukae T, Kishioka S and Ueda H: Permanent relief from intermittent
cold stress-induced fibromyalgia-like abnormal pain by repeated
intrathecal administration of antidepressants. Mol Pain. 7:692011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Y, Lin D, Yu X, Xie X, Wang L, Lian L,
Fei N, Chen J, Zhu N, Wang G, et al: The antinociceptive effects of
ferulic acid on neuropathic pain: Involvement of descending
monoaminergic system and opioid receptors. Oncotarget.
7:20455–20468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uçar M, Sarp Ü, Karaaslan Ö, Gül AI, Tanik
N and Arik HO: Health anxiety and depression in patients with
fibromyalgia syndrome. J Int Med Res. 43:679–685. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Alok R, Das SK, Agarwal GG, Salwahan L and
Srivastava R: Relationship of severity of depression, anxiety and
stress with severity of fibromyalgia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 29(Suppl
69): S70–S72. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Marco EM, Granstrem O, Moreno E, Llorente
R, Adriani W, Laviola G and Viveros MP: Subchronic nicotine
exposure in adolescence induces long-term effects on hippocampal
and striatal cannabinoid-CB1 and mu-opioid receptors in rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 557:37–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kivinummi T, Kaste K, Rantamäki T, Castrén
E and Ahtee L: Alterations in BDNF and phospho-CREB levels
following chronic oral nicotine treatment and its withdrawal in
dopaminergic brain areas of mice. Neurosci Lett. 491:108–112. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geng SJ, Liao FF, Dang WH, Ding X, Liu XD,
Cai J, Han JS, Wan Y and Xing GG: Contribution of the spinal cord
BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the
NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation.
Exp Neurol. 222:256–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Masaki E, Mizuta K, Ohtani N and Kido K:
Early postoperative nociceptive threshold and production of
brain-derived neurotrophic factor induced by plantar incision are
not influenced with minocycline in a rat: Role of spinal microglia.
Neurosignals. 24:15–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuluğ B, Ozan E, Gönül AS and Kilic E:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, stress and depression: a
minireview. Brain Res Bull. 78:267–269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rybakowski JK: BDNF gene: Functional
Val66Met polymorphism in mood disorders and schizophrenia.
Pharmacogenomics. 9:1589–1593. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Licinio J, Dong C and wong ML: Novel
sequence variations in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene
and association with major depression and antidepressant treatment
response. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 66:488–497. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Russell IJ, Mease PJ, Smith TR, Kajdasz
DK, Wohlreich MM, Detke MJ, Walker DJ, Chappell AS and Arnold LM:
Efficacy and safety of duloxetine for treatment of fibromyalgia in
patients with or without major depressive disorder: Results from a
6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose
trial. Pain. 136:432–444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hobbs C: Valerian: A literature review.
HerbalGram. 21:19–34. 1989.
|
|
28
|
Liu XG, Gao PY, Wang GS, Song SJ, Li LZ,
Li X, Yao XS and Zhang ZX: In vivo antidepressant activity of
sesquiterpenes from the roots of Valeriana fauriei Briq.
Fitoterapia. 83:599–603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang BS, Kang SS, Kang SK, Kang CK, Ko WC
and Ko HG: Dictionary of traditional Chinese medicines. Jungdam
Publ Korea. 10:5171–5174. 1985.
|
|
30
|
Yao M, Ritchie HE and Brown-Woodman PD: A
developmental toxicity-screening test of valerian. J
Ethnopharmacol. 113:204–209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ortiz JG, Nieves-Natal J and Chavez P:
Effects of Valeriana officinalis extracts on [3H]flunitrazepam
binding, synaptosomal [3H]GABA uptake, and hippocampal [3H]GABA
release. Neurochem Res. 24:1373–1378. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sudati JH, Vieira FA, Pavin SS, Dias GR,
Seeger RL, Golombieski R, Athayde ML, Soares FA, Rocha JB and
Barbosa NV: Valeriana officinalis attenuates the rotenone-induced
toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurotoxicology. 37:118–126.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Oliveria DM, Barreto G, De Andrade DV,
Saraceno E, Aon-Bertolino L, Capani F, Dos Santos El Bachá R and
Giraldez LD: Cytoprotective effect of Valeriana officinalis extract
on an in vitro experimental model of Parkinson disease. Neurochem
Res. 34:215–220. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Malva JO, Santos S and Macedo T:
Neuroprotective properties of Valeriana officinalis extracts.
Neurotox Res. 6:131–140. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pereira RP, Fachinetto R, de Souza Prestes
A, Wagner C, Sudati JH, Boligon AA, Athayde ML, Morsch VM and Rocha
JB: Valeriana officinalis ameliorates vacuous chewing movements
induced by reserpine in rats. J Neural Transm Vienna.
118:1547–1557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barnes J, Anderson LA and Phillipson JD:
Herbal Medicines. A Guide for Heathcare Professionals. 2nd edition.
Pharmaceutical Press; London: 2002
|
|
37
|
Pizzorno JE and Murray MT: Textbook of
Natural Medicine. 2nd edition. Churchill Livingstone; London:
1999
|
|
38
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies Press;
washington, DC: 1996
|
|
39
|
Lee H, Won H, Im J, Kim YO, Lee S, Cho IH,
Kim HK, Kwon JT and Kim HJ: Effect of Valeriana fauriei extract on
the offspring of adult rats exposed to prenatal stress. Int J Mol
Med. 38:251–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ejchel-Cohen TF, Wood GE, Wang JF, Barlow
K, Nobrega JN, S McEwen B and Trevor Young L: Chronic restraint
stress decreases the expression of glutathione S-transferase pi2 in
the mouse hippocampus. Brain Res. 1090:156–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Magariños AM, Li CJ, Gal Toth J, Bath KG,
Jing D, Lee FS and McEwen BS: Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic
factor haploinsufficiency on stress-induced remodeling of
hippocampal neurons. Hippocampus. 21:253–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Keyhanfar F, Shamsi Meymandi M, Sepehri G,
Rastegaryanzadeh R and Heravi G: Evaluation of antinociceptive
effect of pregabalin in mice and its combination with tramadol
using Tail Flick test. Iran J Pharm Res. 12:483–493.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meymandi MS, Sepehri G and Mobasher M:
Gabapentin enhances the analgesic response to morphine in acute
model of pain in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 85:185–189.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B and Simon P:
The tail suspension test: A new method for screening
antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 85:367–370.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C
and Joris J: A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal
nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 32:77–88. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Inoue M, Rashid MH, Fujita R, Contos JJ,
Chun J and Ueda H: Initiation of neuropathic pain requires
lysophosphatidic acid receptor signaling. Nat Med. 10:712–718.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rashid MH, Inoue M, Toda K and Ueda H:
Loss of peripheral morphine analgesia contributes to the reduced
effectiveness of systemic morphine in neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 309:380–387. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Morley-Fletcher S, Darnaudery M, Koehl M,
Casolini P, Van Reeth O and Maccari S: Prenatal stress in rats
predicts immobility behavior in the forced swim test. Effects of a
chronic treatment with tianeptine. Brain Res. 989:246–251. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Joo J, Lee S, Nah SS, Kim YO, Kim DS, Shim
SH, Hwangbo Y, Kim HK, Kwon JT, Kim JW, et al: Lasp1 is
down-regulated in NMDA receptor antagonist-treated mice and
implicated in human schizophrenia susceptibility. J Psychiatr Res.
47:105–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hindmarch I: Expanding the horizons of
depression: Beyond the monoamine hypothesis. Hum Psychopharmacol.
16:203–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Raison CL, Capuron L and Miller AH:
Cytokines sing the blues: Inflammation and the pathogenesis of
depression. Trends Immunol. 27:24–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sebastião AM, Assaife-Lopes N, Diógenes
MJ, Vaz SH and Ribeiro JA: Modulation of brain-derived neurotrophic
factor (BDNF) actions in the nervous system by adenosine A(2A)
receptors and the role of lipid rafts. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1808:1340–1349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Pillai A: Brain-derived neurotropic
factor/TrkB signaling in the pathogenesis and novel pharmacotherapy
of schizophrenia. Neurosignals. 16:183–193. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Laske C, Stransky E, Eschweiler GW, Klein
R, Wittorf A, Leyhe T, Richartz E, Köhler N, Bartels M, Buchkremer
G, et al: Increased BDNF serum concentration in fibromyalgia with
or without depression or antidepressants. J Psychiatr Res.
41:600–605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Groth R and Aanonsen L: Spinal
brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) produces hyperalgesia in
normal mice while antisense directed against either BDNF or trkB,
prevent inflammation-induced hyperalgesia. Pain. 100:171–181. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xu Y, Ku B, Tie L, Yao H, Jiang W, Ma X
and Li X: Curcumin reverses the effects of chronic stress on
behavior, the HPA axis, BDNF expression and phosphorylation of
CREB. Brain Res. 1122:56–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu L, Liu C, Wang Y, Wang P, Li Y and Li
B: Herbal medicine for anxiety, depression and insomnia. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 13:481–493. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Liu L, Li B, Zhou Y, Wang L, Tang F, Shao
D, Jiang X, Zhao H, Cui R and Li Y: Antidepressant-like effect of
Fuzi total alkaloid on ovariectomized mice. J Pharmacol Sci.
120:280–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Deng S, West BJ, Palu AK, Zhou BN and
Jensen CJ: Noni as an anxiolytic and sedative: A mechanism
involving its gamma-aminobutyric acidergic effects. Phytomedicine.
14:517–522. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sarris J: Herbal medicines in the
treatment of psychiatric disorders: A systematic review. Phytother
Res. 21:703–716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sarris J and Byrne GJ: A systematic review
of insomnia and complementary medicine. Sleep Med Rev. 15:99–106.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Murphy K, Kubin ZJ, Shepherd JN and
Ettinger RH: Valeriana officinalis root extracts have potent
anxiolytic effects in laboratory rats. Phytomedicine. 17:674–678.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Dietz BM, Mahady GB, Pauli GF and
Farnsworth NR: Valerian extract and valerenic acid are partial
agonists of the 5-HT5a receptor in vitro. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
138:191–197. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
No authors listed. Classification of
chronic pain. Descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and
definitions of pain terms Prepared by the International Association
for the study of pain, subcommittee on taxonomy. Pain Suppl.
3:S1–S226. 1986.
|
|
65
|
Livingston G, Watkin V, Milne B, Manela MV
and Katona C: Who becomes depressed? The Islington community study
of older people. J Affect Disord. 58:125–133. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
McBeth J and Silman AJ: Role Psychiatr
Disord Fibromyalgia. 3:157–166. 2001.
|
|
67
|
Ammer K and Melnizky P: Medicinal baths
for treatment of generalized fibromyalgia. Forsch Komplementarmed.
6:80–85. 1999.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|