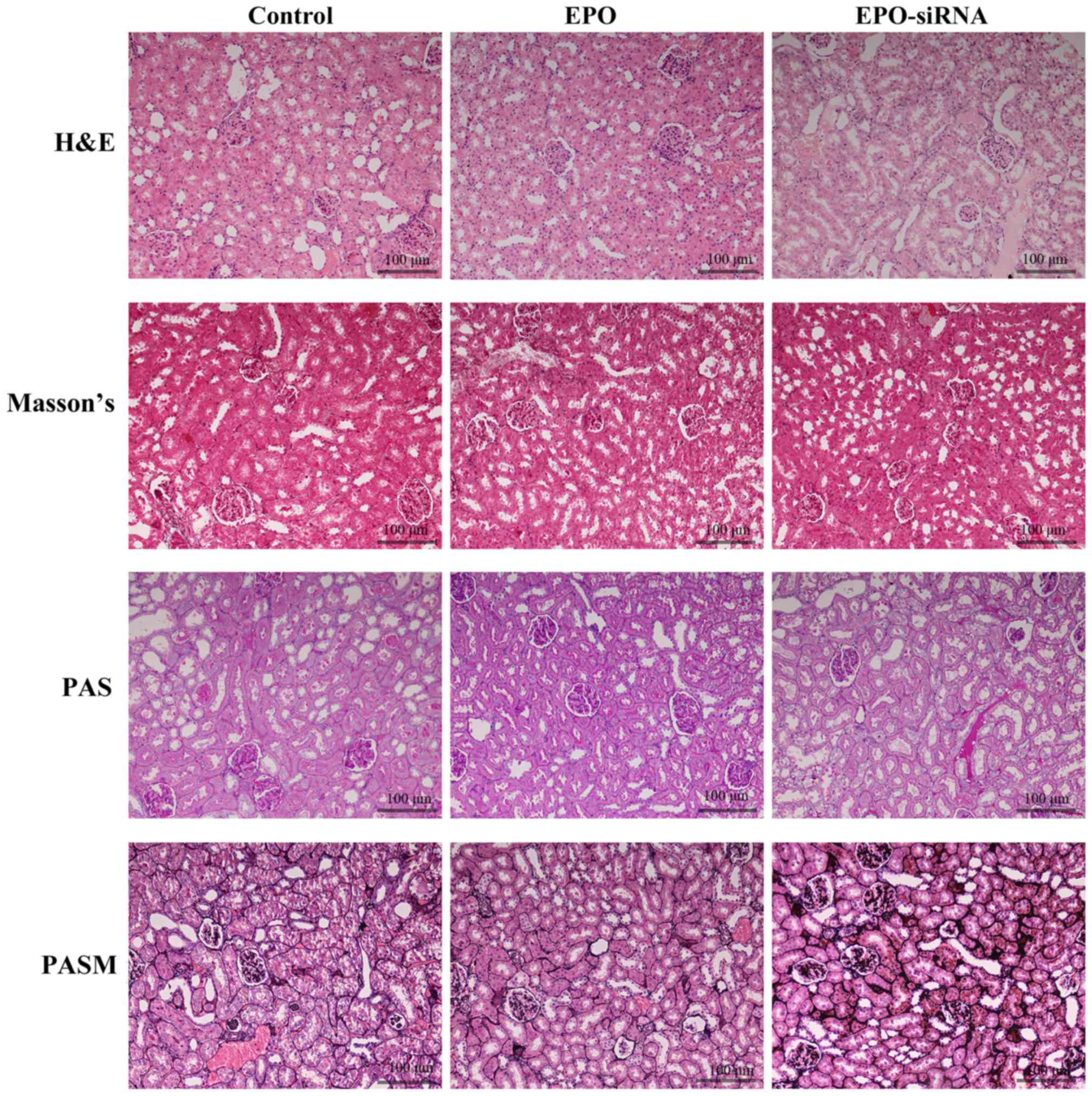
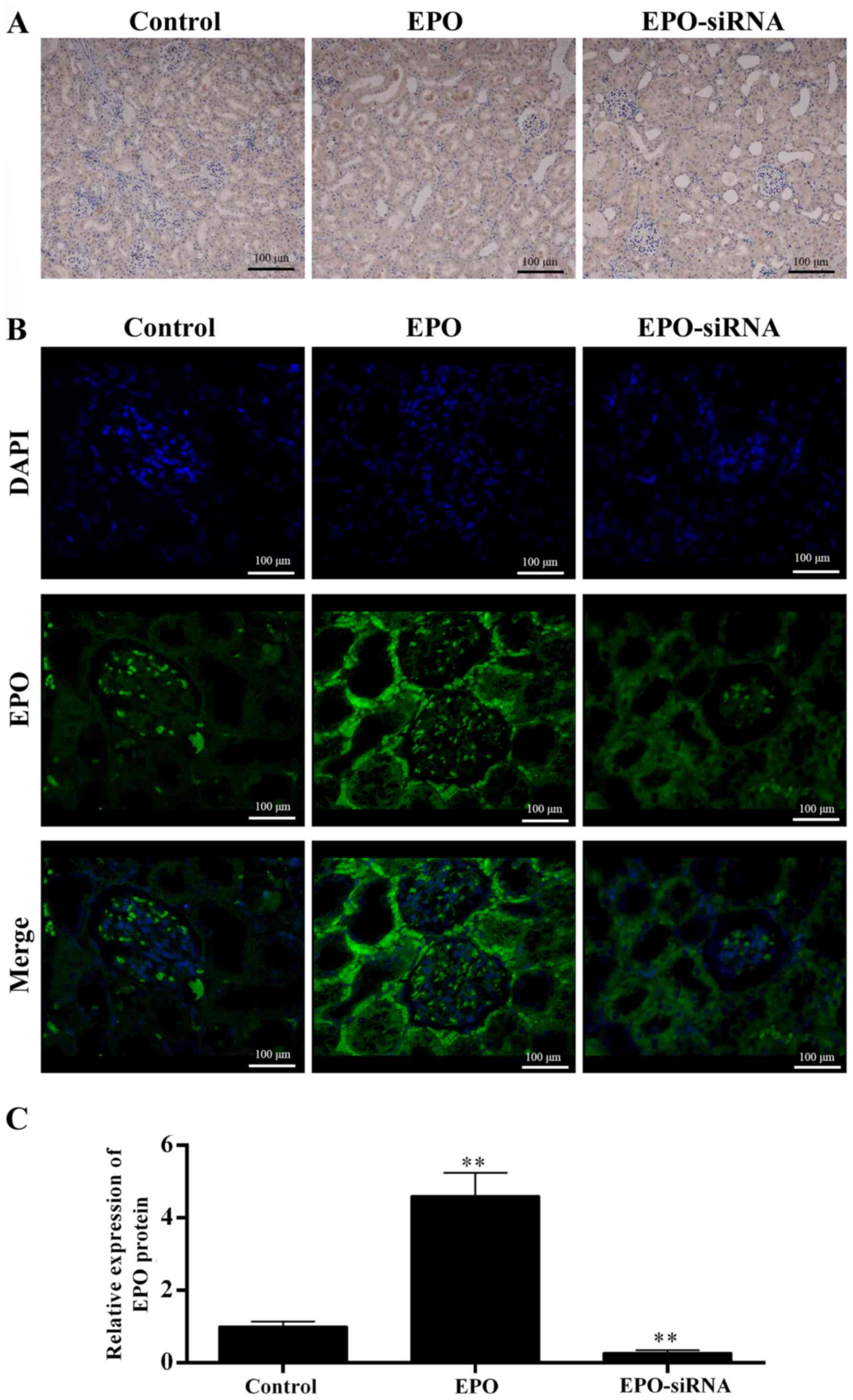
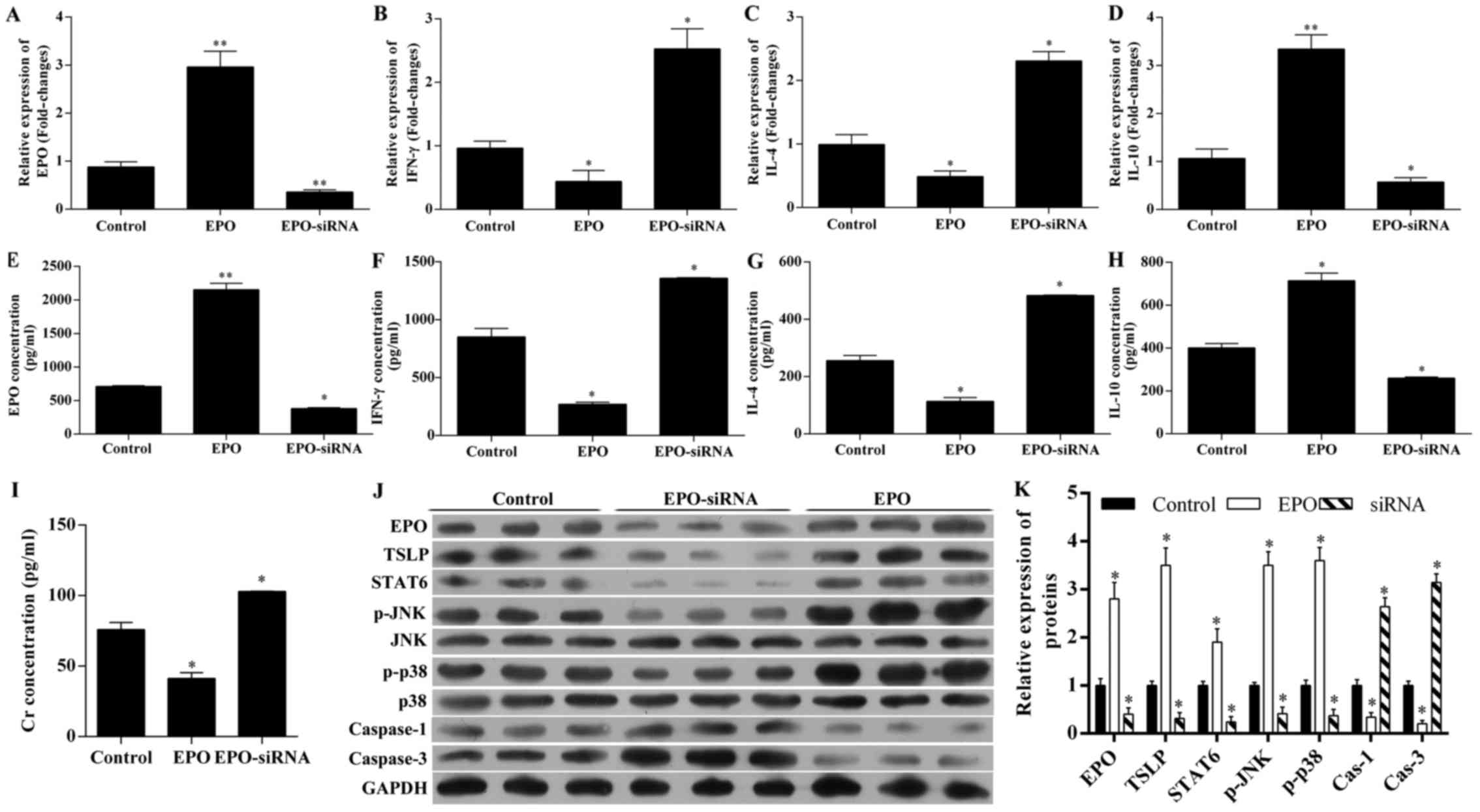
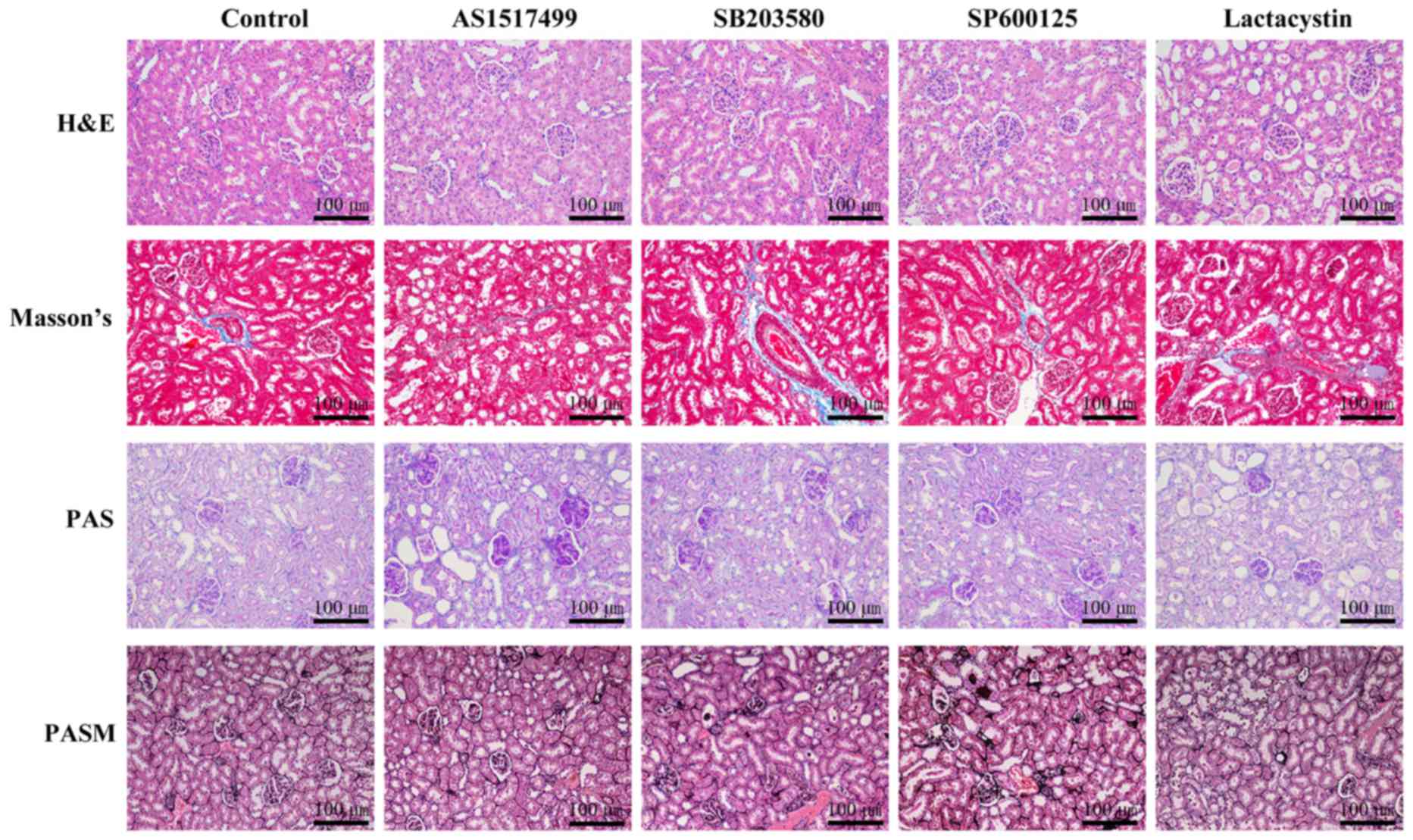
|
1
|
Naylor KL, Zou G, Leslie WD, Hodsman AB,
Lam NN, McArthur E, Fraser LA, Knoll GA, Adachi JD, Kim SJ, et al:
Risk factors for fracture in adult kidney transplant recipients.
World J Transplant. 6:370–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO,
Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, Held PJ and Port FK: Comparison of
mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis
awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric
transplant. N Engl J Med. 341:1725–1730. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kosieradzki M and Rowiński W:
Ischemia/reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: mechanisms
and prevention. Transplant Proc. 40:3279–3288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hoshinaga K, Shiroki R, Fujita T, Kanno T
and Naide Y: The fate of 359 renal allografts harvested from
non-heart beating cadaver donors at a single center. Clin Transpl.
213–220. 1998.
|
|
5
|
Perico N, Cattaneo D, Sayegh MH and
Remuzzi G: Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation.
Lancet. 364:1814–1827. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gueler F, Gwinner W, Schwarz A and Haller
H: Long-term effects of acute ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Kidney Int. 66:523–527. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bonventre JV and Yang L: Cellular
pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest.
121:4210–4221. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Devarajan P: Update on mechanisms of
ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1503–1520. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bajwa A, Kinsey GR and Okusa MD: Immune
mechanisms and novel pharmacological therapies of acute kidney
injury. Curr Drug Targets. 10:1196–1204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Silver SA, Cardinal H, Colwell K, Burger D
and Dickhout JG: Acute kidney injury: preclinical innovations,
challenges, and opportunities for translation. Can J Kidney Health
Dis. 2:302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu QS, Cheng ZW, Xiong JG, Cheng S, He XF
and Li XC: Erythropoietin pretreatment exerts anti-inflammatory
effects in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-injured rats via
suppression of the TLR2/NF-κB pathway. Transplant Proc. 47:283–289.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McCook O, Georgieff M, Scheuerle A, Möller
P, Thiemermann C and Radermacher P: Erythropoietin in the
critically ill: do we ask the right questions. Crit Care.
16:3192012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Akcay A, Nguyen Q and Edelstein CL:
Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury. Mediators
Inflamm. 137072:2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kono H, Nakagawa K, Morita S, Shinoda K,
Mizuno R, Kikuchi E, Miyajima A, Umezawa K and Oya M: Effect of a
novel nuclear factor-κB activation inhibitor on renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplantation. 96:863–870. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Latanich CA and Toledo-Pereyra LH:
Searching for NF-kappaB-based treatments of ischemia reperfusion
injury. J Invest Surg. 22:301–315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bennett BL, Cruz R, Lacson RG and Manning
AM: Interleukin-4 suppression of tumor necrosis factor
alpha-stimulated E-selectin gene transcription is mediated by STAT6
antagonism of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 272:10212–10219. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato A, Yoshidome H, Edwards MJ and
Lentsch AB: Reduced hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by IL-4:
potential anti-inflammatory role of STAT6. Inflamm Res. 49:275–279.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang Z, Zhong Z, Li M, Xiong Y, Wang Y,
Peng G and Ye Q: Hypothermic machine perfusion increases A20
expression which protects renal cells against ischemia/reperfusion
injury by suppressing inflammation, apoptosis and necroptosis. Int
J Mol Med. 38:161–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Toronyi E: Role of apoptosis in the kidney
after reperfusion. Orv Hetil. 149:305–315. 2008.In Hungarian.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu H, Jiang W, Xi X, Zou C and Ye Z:
MicroRNA-21 attenuates renal ischemia reperfusion injury via
targeting caspase signaling in mice. Am J Nephrol. 40:215–223.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haylor JL, Harris KP, Nicholson ML, Waller
HL, Huang Q and Yang B: Atorvastatin improving renal ischemia
reperfusion injury via direct inhibition of active caspase-3 in
rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 236:755–763. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fisher JW: Erythropoietin: physiology and
pharmacology update. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:1–14. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pellegrini L, Bennis Y, Velly L,
Grandvuillemin I, Pisano P, Bruder N and Guillet B: Erythropoietin
protects newborn rat against sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity.
Paediatr Anaesth. 24:749–759. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu L, Liu C, Hou L, Lv J, Wu F, Yang X,
Ren S, Ji W, Wang M and Chen L: Protection against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury by co treatment with
erythropoietin and sodium selenite. Mol Med Rep. 12:7933–7940.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Zou YR, Zhong X, Deng HD, Pu L,
Peng K and Wang L: Erythropoietin pretreatment ameliorates renal
ischaemia-reperfusion injury by activating I3K/Akt signalling.
Nephrology (Carlton). 20:266–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kwon MS, Kim MH, Kim SH, Park KD, Yoo SH,
Oh IU, Pak S and Seo YJ: Erythropoietin exerts cell protective
effect by activating I3K/Akt and MAPK pathways in C6 cells. Neurol
Res. 36:215–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li XJ, Zhang GX, Sun N, Sun Y, Yang LZ and
Du YJ: Protective effects of erythropoietin on endotoxin-related
organ injury in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
33:680–686. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cugini D, Azzollini N, Gagliardini E,
Cassis P, Bertini R, Colotta F, Noris M, Remuzzi G and Benigni A:
Inhibition of the chemokine receptor CXCR2 prevents kidney graft
function deterioration due to ischemia/reperfusion. Kidney Int.
67:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Y, Adamson RH, Curry FR and Tarbell
JM: Sphin-gosine-1-phosphate protects endothelial glycocalyx by
inhibiting syndecan-1 shedding. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
306:H363–H372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zeng Y, Liu XH, Tarbell J and Fu B:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate induced synthesis of glycocalyx on
endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 339:90–95. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ratilal BO, Arroja MM, Rocha JP, Fernandes
AM, Barateiro AP, Brites DM, Pinto RM, Sepodes BM and Mota-Filipe
HD: Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin pretreatment in a
rodent model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. J
Neurosurg. 121:55–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jun JH, Jun NH, Shim JK, Shin EJ and Kwak
YL: Erythropoietin protects myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion
injury under moderate hyperglycemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 745:1–9.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu MJ, Chen YS, Huang HS and Ma MC:
Erythropoietin alleviates post-ischemic injury of rat hearts by
attenuating nitrosative stress. Life Sci. 90:776–784. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu X, Cao Z, Cao B, Li J, Guo L, Que L, Ha
T, Chen Q, Li C and Li Y: Carbamylated erythropoietin protects the
myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury through a
I3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Surgery. 146:506–514. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Soranno DE, Rodell CB, Altmann C,
Duplantis J, Andres-Hernando A, Burdick JA and Faubel S: Delivery
of interleukin-10 via injectable hydrogels improves renal outcomes
and reduces systemic inflammation following ischemic acute kidney
injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 311:F362–F372. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun P, Liu J, Li W, Xu X, Gu X, Li H, Han
H, Du C and Wang H: Human endometrial regenerative cells attenuate
renal ischemia reperfusion injury in mice. J Transl Med. 14:282016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Segawa R, Mizuno N, Hatayama T, Jiangxu D,
Hiratsuka M, Endo Y and Hirasawa N: Lipopolysaccharide-activated
leukocytes enhance thymic stromal lymphopoietin production in a
mouse air-pouch-type inflammation model. Inflammation.
39:1527–1537. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takai T: TSLP expression: cellular
sources, triggers, and regulatory mechanisms. Allergol Int.
61:3–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|