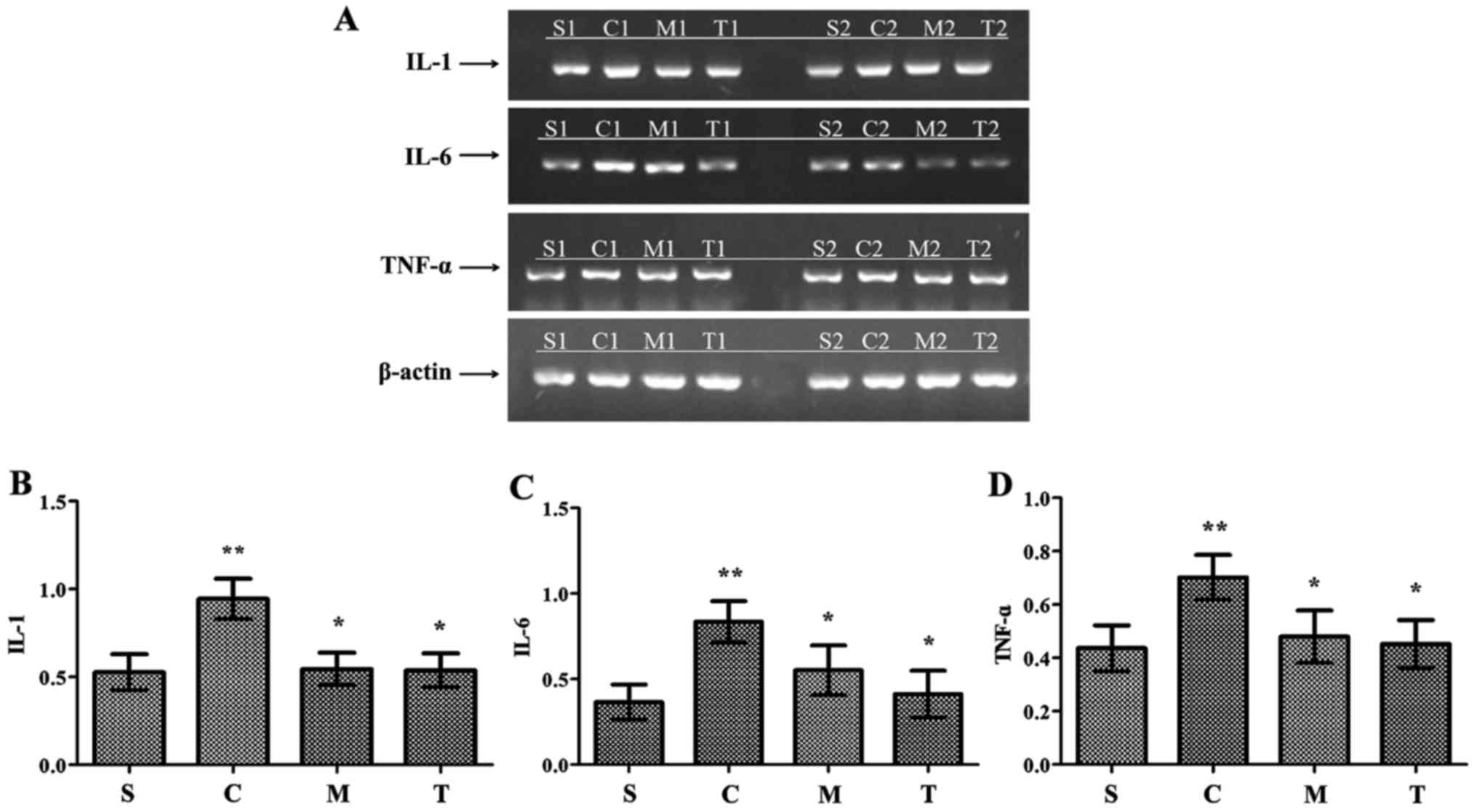
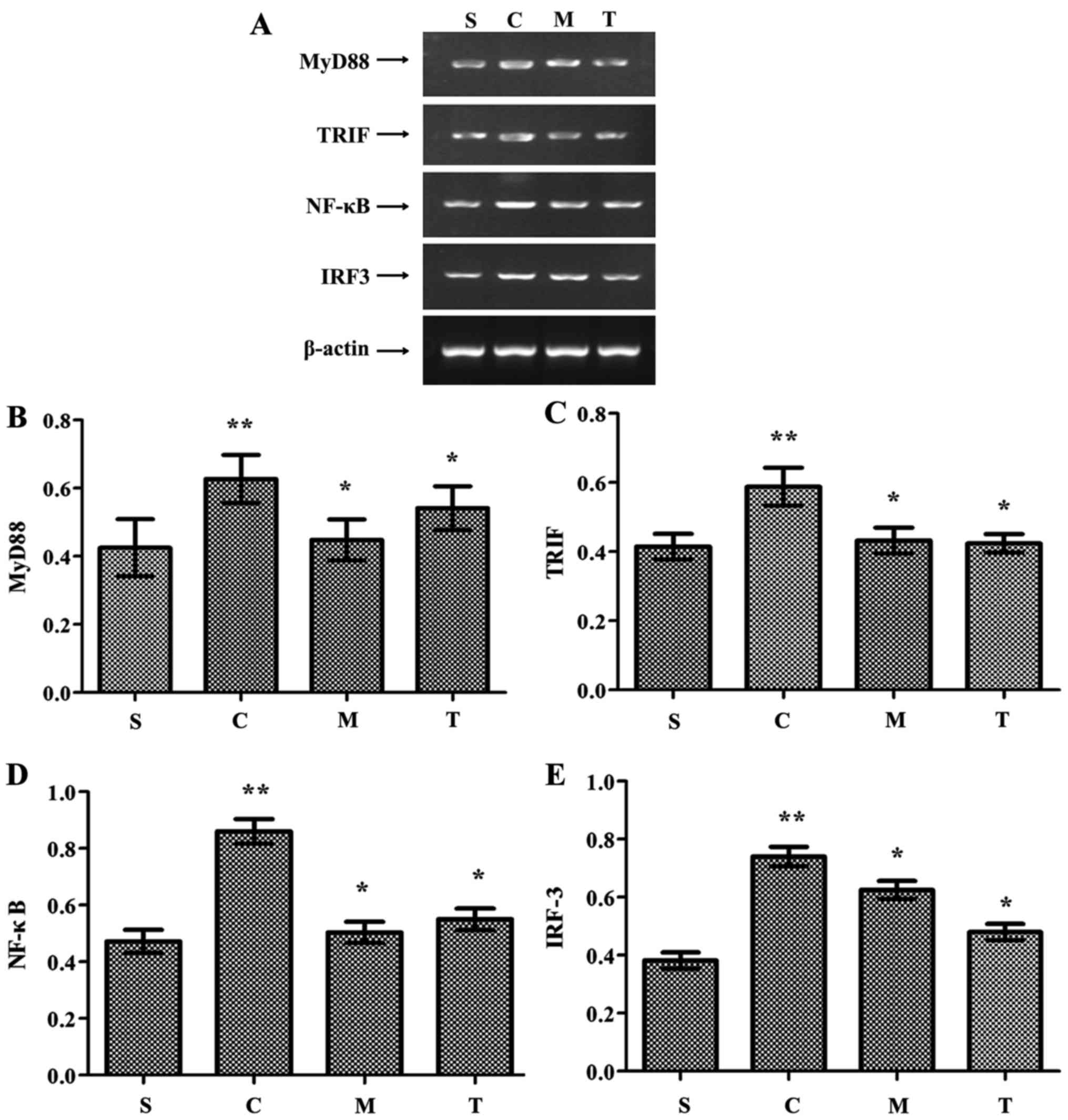
|
1
|
Schefold JC, Bierbrauer J and
Weber-Carstens S: Intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICUAW) and
muscle wasting in critically ill patients with severe sepsis and
septic shock. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 1:147–157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
No authors listed. American College of
Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus
Conference: Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines
for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med.
20:864–874. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J,
Clermont G, Carcillo J and Pinsky MR: Epidemiology of severe sepsis
in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and
associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 29:1303–1310. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parrillo JE, Parker MM, Natanson C,
Suffredini AF, Danner RL, Cunnion RE and Ognibene FP: Septic shock
in humans. Advances in the understanding of pathogenesis,
cardiovascular dysfunction, and therapy. Ann Intern Med.
113:227–242. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Niu J, Azfer A and Kolattukudy PE:
Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial
dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of soluble Fas.
J Mol Cell Cardiol. 44:160–169. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fauvel H, Marchetti P, Chopin C,
Formstecher P and Nevière R: Differential effects of caspase
inhibitors on endotoxin-induced myocardial dysfunction and heart
apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 280:H1608–H1614. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O'Neill LA, Golenbock D and Bowie AG: The
history of Toll-like receptors - redefining innate immunity. Nat
Rev Immunol. 13:453–460. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mann DL: The emerging role of innate
immunity in the heart and vascular system: For whom the cell tolls.
Circ Res. 108:1133–1145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chao W: Toll-like receptor signaling: A
critical modulator of cell survival and ischemic injury in the
heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H1–H12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol.
5:987–995. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takeda K, Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like
receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 21:335–376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weighardt H, Kaiser-Moore S, Vabulas RM,
Kirschning CJ, Wagner H and Holzmann B: Cutting edge: Myeloid
differentiation factor 88 deficiency improves resistance against
sepsis caused by polymicrobial infection. J Immunol. 169:2823–2827.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guidotti LG and Chisari FV: Noncytolytic
control of viral infections by the innate and adaptive immune
response. Annu Rev Immunol. 19:65–91. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Feng Y, Zou L, Wang L, Chen HH,
Cai JY, Xu JM, Sosnovik DE and Chao W: Role of extracellular RNA
and TLR3-Trif signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
J Am Heart Assoc. 3:e0006832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaczorowski DJ, Nakao A, Vallabhaneni R,
Mollen KP, Sugimoto R, Kohmoto J, Zuckerbraun BS, McCurry KR and
Billiar TR: Mechanisms of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated
inflammation after cold ischemia/reperfusion in the heart.
Transplantation. 87:1455–1463. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Si R, Feng Y, Chen HH, Zou L, Wang
E, Zhang M, Warren HS, Sosnovik DE and Chao W: Myocardial ischemia
activates an injurious innate immune signaling via cardiac heat
shock protein 60 and Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem.
286:31308–31319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Urheim S, Edvardsen T, Torp H, Angelsen B
and Smiseth OA: Myocardial strain by Doppler echocardiography.
Validation of a new method to quantify regional myocardial
function. Circulation. 102:1158–1164. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heimdal A, Støylen A, Torp H and Skjaerpe
T: Real-time strain rate imaging of the left ventricle by
ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 11:1013–1019. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cimolai MC, Alvarez S, Bode C and Bugger
H: Mitochondrial mechanisms in septic cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:17763–17778. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vinten-Johansen J: Involvement of
neutrophils in the pathogenesis of lethal myocardial reperfusion
injury. Cardiovasc Res. 61:481–497. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Castoldi A, Braga TT, Correa-Costa M,
Aguiar CF, Bassi EJ, Correa-Silva R, Elias RM, Salvador F,
Moraes-Vieira PM, Cenedeze MA, et al: TLR2, TLR4 and the MYD88
signaling pathway are crucial for neutrophil migration in acute
kidney injury induced by sepsis. PLoS One. 7:e375842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu X, Zhao H, Graveline AR, Buys ES,
Schmidt U, Bloch KD, Rosenzweig A and Chao W: MyD88 and NOS2 are
essential for Toll-like receptor 4-mediated survival effect in
cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H1900–H1909.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alves-Filho JC, de Freitas A, Spiller F,
Souto FO and Cunha FQ: The role of neutrophils in severe sepsis.
Shock. 30(Suppl 1): 3–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng Y, Zou L, Zhang M, Li Y, Chen C and
Chao W: MyD88 and Trif signaling play distinct roles in cardiac
dysfunction and mortality during endotoxin shock and polymicrobial
sepsis. Anesthesiology. 115:555–567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng X, Moore TA, Newstead MW, Deng JC,
Kunkel SL, Luster AD and Standiford TJ: Interferon-inducible
protein 10, but not monokine induced by gamma interferon, promotes
protective type 1 immunity in murine Klebsiella pneumoniae
pneumonia. Infect Immun. 73:8226–8236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Soraya H, Rameshrad M, Mokarizadeh A and
Garjani A: Metformin attenuates myocardial remodeling and
neutrophil recruitment after myocardial infarction in rat.
Bioimpacts. 5:3–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McDonald TE, Grinman MN, Carthy CM and
Walley KR: Endotoxin infusion in rats induces apoptotic and
survival pathways in hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H2053–H2061. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cavassani KA, Ishii M, Wen H, Schaller MA,
Lincoln PM, Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM and Kunkel SL: TLR3 is an
endogenous sensor of tissue necrosis during acute inflammatory
events. J Exp Med. 205:2609–2621. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun R, Zhang Y, Lv Q, Liu B, Jin M, Zhang
W, He Q, Deng M, Liu X, Li G, et al: Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3)
induces apoptosis via death receptors and mitochondria by
up-regulating the trans-activating p63 isoform alpha (TAP63alpha).
J Biol Chem. 286:15918–15928. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Delhalle S, Blasius R, Dicato M and
Diederich M: A beginner's guide to NF-kappaB signaling pathways.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1030:1–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|