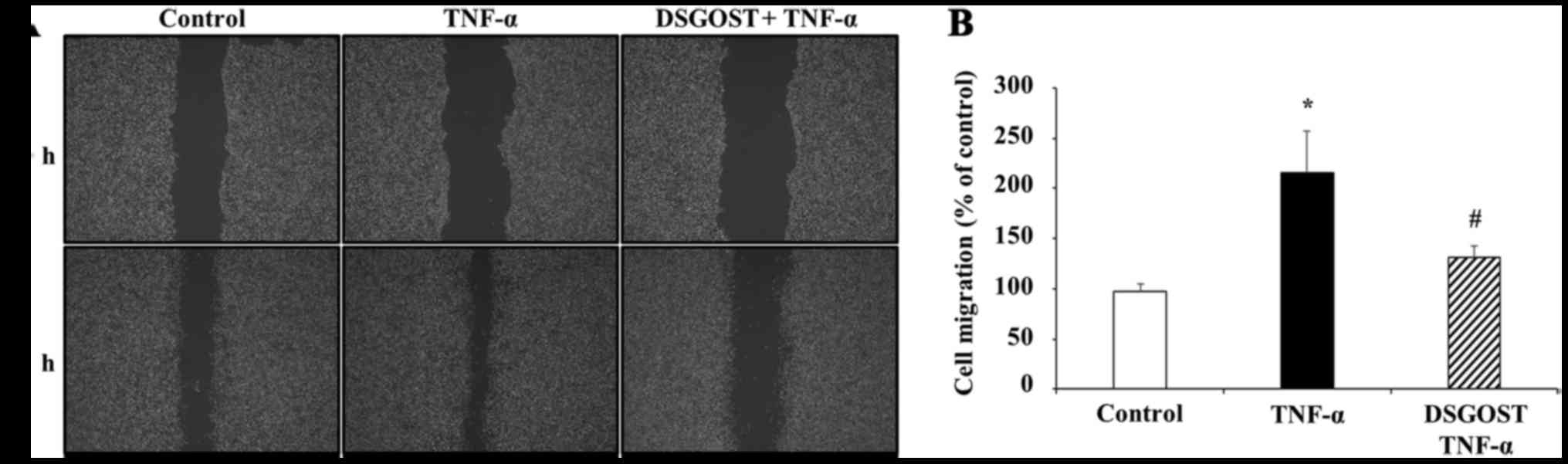
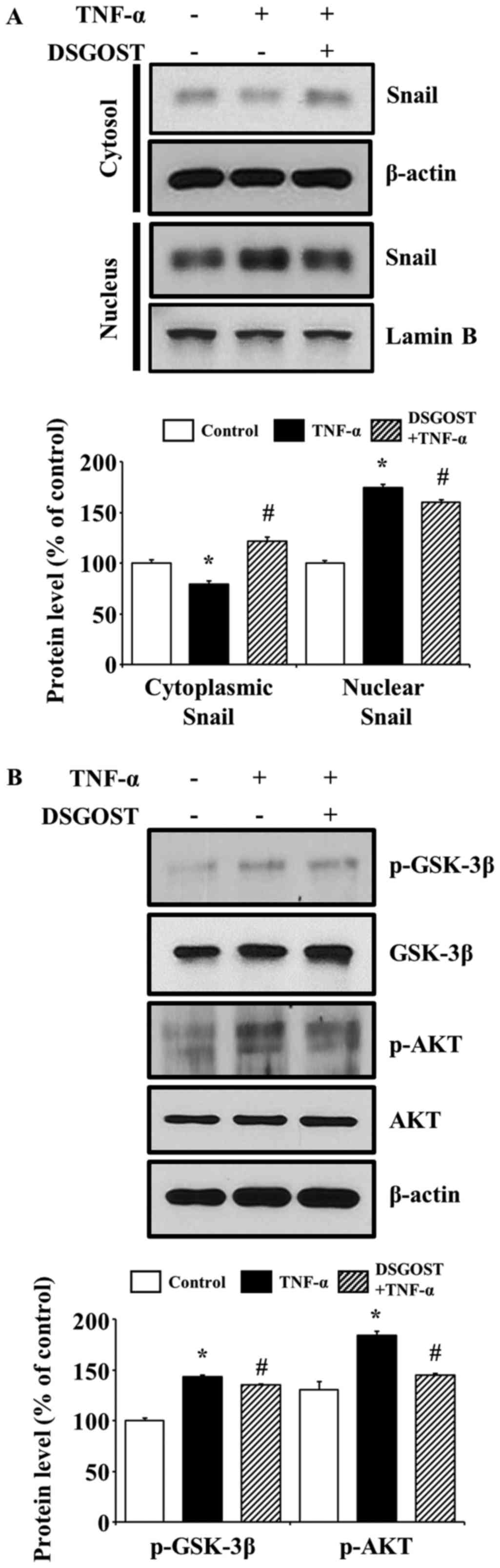
|
1
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pourhoseingholi MA: Increased burden of
colorectal cancer in Asia. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 4:68–70.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski
J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D'Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G,
et al: Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for
metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 360:1408–1417. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adam R, Avisar E, Ariche A, Giachetti S,
Azoulay D, Castaing D, Kunstlinger F, Levi F and Bismuth F:
Five-year survival following hepatic resection after neoadjuvant
therapy for nonresectable colorectal. Ann Surg Oncol. 8:347–353.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hamilton TD, Leugner D, Kopciuk K, Dixon
E, Sutherland FR and Bathe OF: Identification of prognostic
inflammatory factors in colorectal liver metastases. BMC Cancer.
14:5422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weiss L, Grundmann E, Torhorst J, Hartveit
F, Moberg I, Eder M, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Napier J, Horne CH, Lopez
MJ, et al: Haematogenous metastatic patterns in colonic carcinoma:
An analysis of 1541 necropsies. J Pathol. 150:195–203. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noura S, Ohue M, Shingai T, Fujiwara A,
Imada S, Sueda T, Yamada T, Fujiwara Y, Ohigashi H, Yano M, et al:
Brain metastasis from colorectal cancer: Prognostic factors and
survival. J Surg Oncol. 106:144–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jimi S, Yasui T, Hotokezaka M, Shimada K,
Shinagawa Y, Shiozaki H, Tsutsumi N and Takeda S: Clinical features
and prognostic factors of bone metastases from colorectal cancer.
Surg Today. 43:751–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Terzic J, Grivennikov S, Karin E and Karin
M: Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 138:2101–2114
e2105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balkwill FR and Mantovani A:
Cancer-related inflammation: Common themes and therapeutic
opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:33–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klampfer L: Cytokines, inflammation and
colon cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:451–464. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Balkwill F: Tumour necrosis factor and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:361–371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Balkwill F: TNF-alpha in promotion and
progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:409–416. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Wang HS, Zhou BH, Li CL, Zhang F,
Wang XF, Zhang G, Bu XZ, Cai SH and Du J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) induced by TNF-α requires AKT/GSK-3β-mediated
stabilization of snail in colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
8:e566642013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dong C, Wu Y, Yao J, Wang Y, Yu Y,
Rychahou PG, Evers BM and Zhou BP: G9a interacts with Snail and is
critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in human breast
cancer. J Clin Invest. 122:1469–1486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pon YL, Zhou HY, Cheung AN, Ngan HY and
Wong AS: p70 S6 kinase promotes epithelial to mesenchymal
transition through snail induction in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 68:6524–6532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Zhu X, Hu J, He G, Li X, Wu P, Ren
X, Wang F, Liao W, Liang L, et al: The positive feedback between
Snail and DAB2IP regulates EMT, invasion and metastasis in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:27427–27439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bates RC and Mercurio AM: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer
progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:365–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kroepil F, Fluegen G, Vallböhmer D, Baldus
SE, Dizdar L, Raffel AM, Hafner D, Stoecklein NH and Knoefel WT:
Snail1 expression in colorectal cancer and its correlation with
clinical and pathological parameters. BMC Cancer. 13:1452013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kwon CH, Park HJ, Choi JH, Lee JR, Kim HK,
Jo HJ, Kim HS, Oh N, Song GA and Park DY: Snail and serpinA1
promote tumor progression and predict prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:20312–20326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Bertrand FE,
Davis NM, Sokolosky M, Abrams SL, Montalto G, D'Assoro AB, Libra M,
Nicoletti F, et al: GSK-3 as potential target for therapeutic
intervention in cancer. Oncotarget. 5:2881–2911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pappalardo F, Russo G, Candido S, Pennisi
M, Cavalieri S, Motta S, McCubrey JA, Nicoletti F and Libra M:
Computational modeling of PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in
melanoma cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01521042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ciuffreda L, McCubrey JA and Milella M:
Signaling intermediates (PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK
pathways) as therapeutic targets for anticancer and
anti-angiogenesis treatments. Curr Signal Transduct Ther.
4:130–143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
El Touny LH and Banerjee PP: Akt GSK-3
pathway as a target in genistein-induced inhibition of TRAMP
prostate cancer progression toward a poorly differentiated
phenotype. Carcinogenesis. 28:1710–1717. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Bassignana A and
Miglietta A: Antiproliferative effects of COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib
on human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem. 350:59–70.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Firdous AB, Sharmila G, Balakrishnan S,
RajaSingh P, Suganya S, Srinivasan N and Arunakaran J: Quercetin, a
natural dietary flavonoid, acts as a chemopreventive agent against
prostate cancer in an in vivo model by inhibiting the EGFR
signaling pathway. Food Funct. 5:2632–2645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yim NH, Jung YP, Kim A, Ma CJ, Cho WK and
Ma JY: Oyaksungisan, a traditional herbal formula, inhibits cell
proliferation by induction of autophagy via JNK activation in human
colon cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2318742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hou F, Li W, Shi Q, Li H, Liu S, Zong S,
Ren J, Chai J and Xu J: Yi Ai Fang, a traditional Chinese herbal
formula, impacts the vasculogenic mimicry formation of human
colorectal cancer through HIF-1α and epithelial mesenchymal
transition. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:4282016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ohnishi Y, Fujii H, Hayakawa Y, Sakukawa
R, Yamaura T, Sakamoto T, Tsukada K, Fujimaki M, Nunome S, Komatsu
Y, et al: Oral administration of a Kampo (Japanese herbal) medicine
Juzen-taiho-to inhibits liver metastasis of colon 26-L5 carcinoma
cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 89:206–213. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leung WK, Wu JC, Liang SM, Chan LS, Chan
FK, Xie H, Fung SS, Hui AJ, Wong VW, Che CT, et al: Treatment of
diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome with traditional
Chinese herbal medicine: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am
J Gastroenterol. 101:1574–1580. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hosokawa A, Ogawa K, Ando T, Suzuki N,
Ueda A, Kajiura S, Kobayashi Y, Tsukioka Y, Horikawa N, Yabushita
K, et al: Preventive effect of traditional Japanese medicine on
neurotoxicity of FOLFOX for metastatic colorectal cancer: A
multicenter retrospective study. Anticancer Res. 32:2545–2550.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yoshikawa K, Shimada M, Nishioka M, Kurita
N, Iwata T, Morimoto S, Miyatani T, Komatsu M, Kashihara H and
Mikami C: The effects of the Kampo medicine (Japanese herbal
medicine) 'Daikenchuto' on the surgical inflammatory response
following laparoscopic colorectal resection. Surg Today.
42:646–651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tsukada R, Yamaguchi T, Hang L, Iseki M,
Kobayashi H and Inada E: Effect of a traditional Japanese medicine
goshajinkigan, tokishigyakukagoshuyushokyoto on the warm and cold
sense threshold and peripheral blood flow. Health (NY). 6:757–763.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yoko K, Akira T and Hiroshi S: Efficacy of
Kampo formula Tokishigyakukagoshuyushokyoto for cold syndrome
evaluated with a novel clinical method using a patient-based
questionnaire database. Kampo Med. 63:299–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Oya A, Oikawa T, Nakai A, Takeshita T and
Hanawa T: Clinical efficacy of Kampo medicine (Japanese traditional
herbal medicine) in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. J Obstet
Gynaecol Res. 34:898–908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hiromi K, Hisashi T, Shigeto Y, Takeshi N,
Nobuyuki M, Daisuke T and Masamitsu I: Usefulness of Kampo formulas
in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Tradit Medicines.
29:93–96. 2012.
|
|
42
|
Choi HS, Lee K, Kim MK, Lee KM, Shin YC,
Cho SG and Ko SG: DSGOST inhibits tumor growth by blocking
VEGF/VEGFR2-activated angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 7:21775–21785.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nagata T, Toume K, Long LX, Hirano K,
Watanabe T, Sekine S, Okumura T, Komatsu K and Tsukada K:
Anticancer effect of a Kampo preparation Daikenchuto. J Nat Med.
70:627–633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lee K, Cho SG, Woo SM, Kim AJ, Lee KM, Go
HY, Sun SH, Kim TH, Jung KY, Choi YK, et al: Danggui Sayuk Ga Osuyu
Senggang Tang ameliorates cold induced vasoconstriction in vitro
and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 14:4723–4728. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bates RC and Mercurio AM: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha stimulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of
human colonic organoids. Mol Biol Cell. 14:1790–1800. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Christiansen JJ and Rajasekaran AK:
Reassessing epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a prerequisite
for carcinoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 66:8319–8326.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM,
Gunduz M and Hung MC: Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3
beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Green S, Dobrjansky A and Chiasson MA:
Murine tumor necrosis-inducing factor: Purification and effects on
myelomonocytic leukemia cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 68:997–1003.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Carswell EA, Old LJ, Kassel RL, Green S,
Fiore N and Williamson B: An endotoxin-induced serum factor that
causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 72:3666–3670.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP:
TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and
invasion. Br J Cancer. 102:639–644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zins K, Abraham D, Sioud M and Aharinejad
S: Colon cancer cell-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates
the tumor growth-promoting response in macrophages by upregulating
the colony-stimulating factor-1 pathway. Cancer Res. 67:1038–1045.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ferrajoli A, Keating MJ, Manshouri T,
Giles FJ, Dey A, Estrov Z, Koller CA, Kurzrock R, Thomas DA, Faderl
S, et al: The clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha
plasma level in patients having chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Blood. 100:1215–1219. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Csiszár A, Szentes T, Haraszti B, Balázs
A, Petrányi GG and Pócsik E: The pattern of cytokine gene
expression in human colorectal carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res.
10:109–116. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grimm M, Lazariotou M, Kircher S,
Höfelmayr A, Germer CT, von Rahden BH, Waaga-Gasser AM and Gasser
M: Tumor necrosis factor-α is associated with positive lymph node
status in patients with recurrence of colorectal cancer-indications
for anti-TNF-α agents in cancer treatment. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
34:315–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Al Obeed OA, Alkhayal KA, Al Sheikh A,
Zubaidi AM, Vaali-Mohammed MA, Boushey R, Mckerrow JH and Abdulla
MH: Increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-α is associated
with advanced colorectal cancer stages. World J Gastroenterol.
20:18390–18396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Petrelli A and Giordano S: From single- to
multi-target drugs in cancer therapy: When aspecificity becomes an
advantage. Curr Med Chem. 15:422–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Attele AS, Wu JA and Yuan CS: Ginseng
pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem
Pharmacol. 58:1685–1693. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Banerjee S, Li Y, Wang Z and Sarkar FH:
Multi-targeted therapy of cancer by genistein. Cancer Lett.
269:226–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nandakumar V, Singh T and Katiyar SK:
Multi-targeted prevention and therapy of cancer by
proanthocyanidins. Cancer Lett. 269:378–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gao JL, He TC, Li YB and Wang YT: A
traditional Chinese medicine formulation consisting of Rhizoma
Corydalis and Rhizoma Curcumae exerts synergistic antitumor
activity. Oncol Rep. 22:1077–1083. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Di Maio M, Costanzo R, Giordano P,
Piccirillo MC, Sandomenico C, Montanino A, Carillio G, Muto P,
Jones DR, Daniele G, et al: Integrated therapeutic approaches in
the treatment of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:844–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Choi YJ, Choi YK, Lee KM, Cho SG, Kang SY
and Ko SG: SH003 induces apoptosis of DU145 prostate cancer cells
by inhibiting ERK-involved pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
16:5072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Choi EK, Kim SM, Hong SW, Moon JH, Shin
JS, Kim JH, Hwang IY, Jung SA, Lee DH, Lee EY, et al: SH003
selectively induces p73 dependent apoptosis in triple negative
breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:3955–3960. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Choi YK, Cho SG, Choi YJ, Yun YJ, Lee KM,
Lee K, Yoo HH, Shin YC and Ko SG: SH003 suppresses breast cancer
growth by accumulating p62 in autolysosomes. Oncotarget. Aug
19–2016.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
65
|
Choi HS, Kim MK, Lee K, Lee KM, Choi YK,
Shin YC, Cho SG and Ko SG: SH003 represses tumor angiogenesis by
blocking VEGF binding to VEGFR2. Oncotarget. 7:32969–32979. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Choi YK, Cho SG, Woo SM, Yun YJ, Park S,
Shin YC and Ko SG: Herbal extract SH003 suppresses tumor growth and
metastasis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by inhibiting
STAT3-IL-6 signaling. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:4921732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|