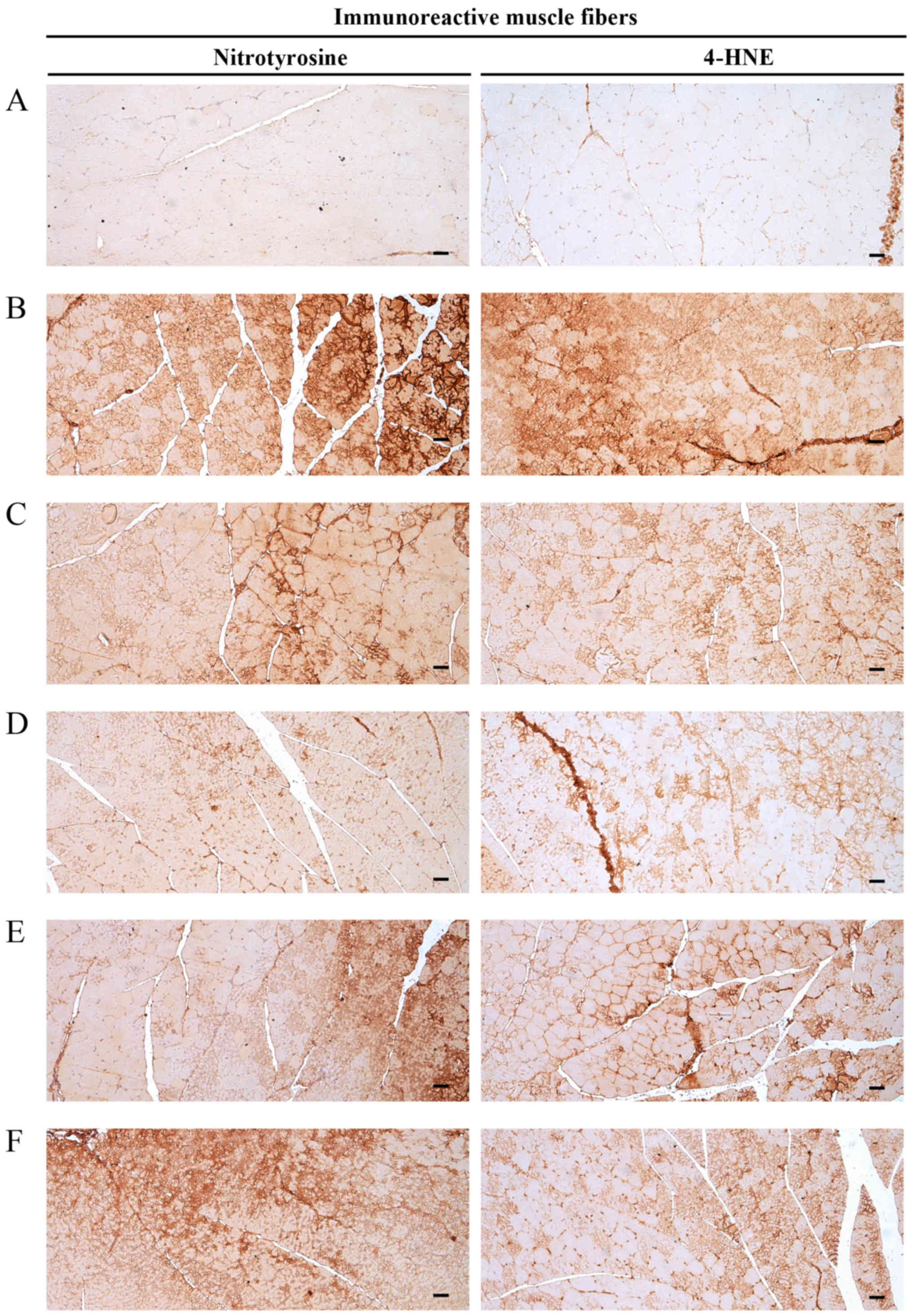
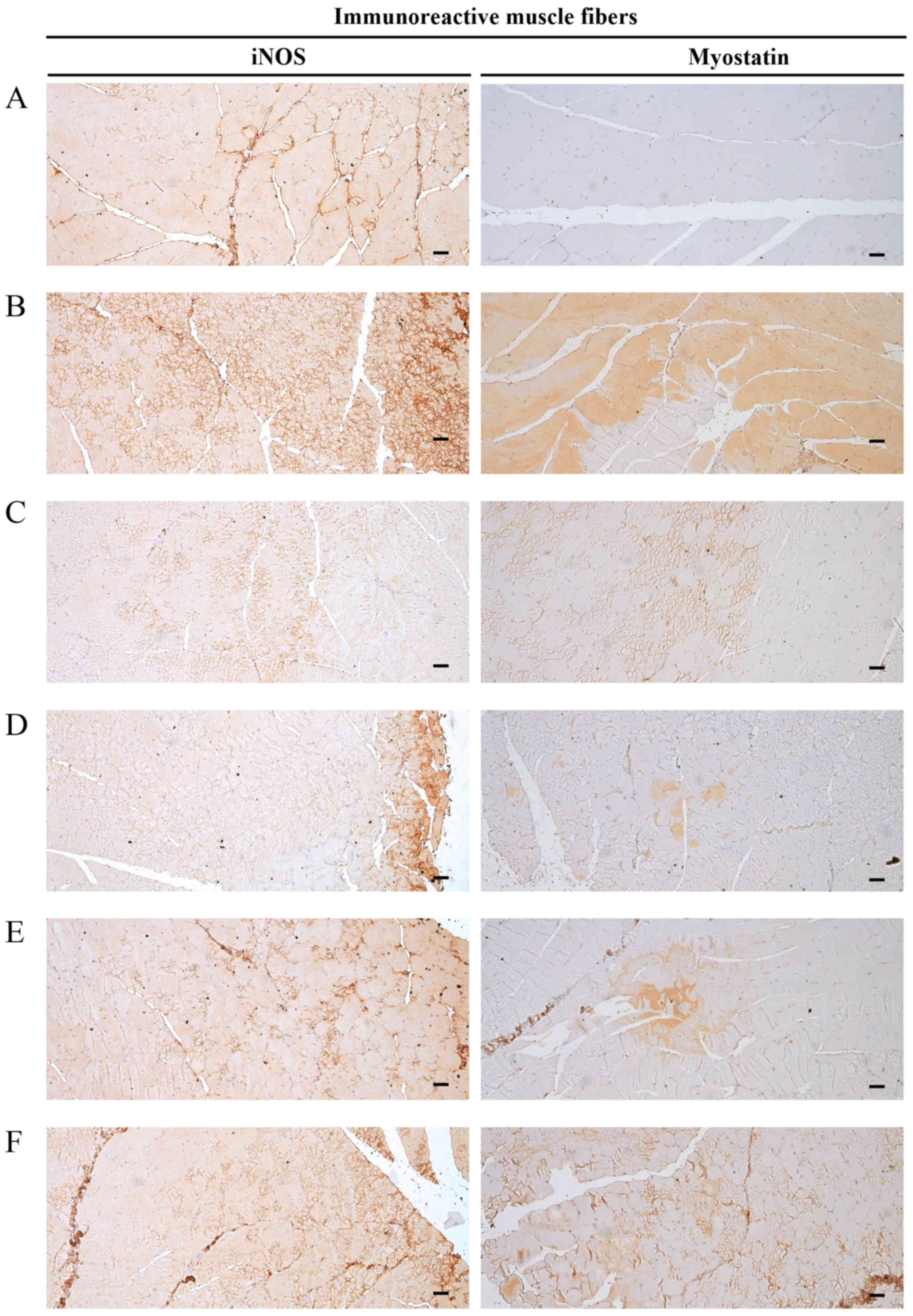
|
1
|
Brooks SV and Faulkner JA: Skeletal muscle
weakness in old age: Underlying mechanisms. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
26:432–439. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Frontera WR, Hughes VA, Fielding RA,
Fiatarone MA, Evans WJ and Roubenoff R: Aging of skeletal muscle: A
12-yr longitudinal study. J Appl Physiol. 88:1321–1326. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Metter EJ, Talbot LA, Schrager M and
Conwit R: Skeletal muscle strength as a predictor of all-cause
mortality in healthy men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
57:B359–B365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Glass DJ: Molecular mechanisms modulating
muscle mass. Trends Mol Med. 9:344–350. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glass DJ: Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and
atrophy signaling pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 37:1974–1984.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramírez C, Russo TL, Sandoval MC, Dentillo
AA, Couto MA, Durigan JL and Salvini TF: Joint inflammation alters
gene and protein expression and leads to atrophy in the tibialis
anterior muscle in rats. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 90:930–939. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hofer T, Marzetti E, Xu J, Seo AY, Gulec
S, Knutson MD, Leeuwenburgh C and Dupont-Versteegden EE: Increased
iron content and RNA oxidative damage in skeletal muscle with aging
and disuse atrophy. Exp Gerontol. 43:563–570. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Onda A, Jiao Q, Nagano Y, Akimoto T,
Miyamoto T, Minamisawa S and Fukubayashi T: Acupuncture ameliorated
skeletal muscle atrophy induced by hindlimb suspension in mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 410:434–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Booth FW: Physiologic and biochemical
effects of immobilization on muscle. Clin orthop Relat Res.
219:15–20. 1987.
|
|
11
|
Thomas DR: Loss of skeletal muscle mass in
aging: Examining the relationship of starvation, sarcopenia and
cachexia. Clin Nutr. 26:389–399. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Léger B, Senese R, Al-Khodairy AW, Dériaz
O, Gobelet C, Giacobino JP and Russell AP: Atrogin-1, MuRF1, and
FoXo, as well as phosphorylated GSK-3beta and 4EBP1 are reduced in
skeletal muscle of chronic spinal cord-injured patients. Muscle
Nerve. 40:69–78. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kawano F, Tanihata J, Sato S, Nomura S,
Shiraishi A, Tachiyashiki K and Imaizumi K: Effects of
dexamethasone on the expression of beta(1)-, beta (2)- and beta
(3)-adrenoceptor mRNAs in skeletal and left ventricle muscles in
rats. J Physiol Sci. 59:383–390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dardevet D, Sornet C, Savary I, Debras E,
Patureau-Mirand P and Grizard J: Glucocorticoid effects on insulin-
and IGF-I-regulated muscle protein metabolism during aging. J
Endocrinol. 156:83–89. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanda F, Takatani K, Okuda S, Matsushita T
and Chihara K: Preventive effects of insulinlike growth factor-I on
steroid-induced muscle atrophy. Muscle Nerve. 22:213–217. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gilson H, Schakman O, Combaret L, Lause P,
Grobet L, Attaix D, Ketelslegers JM and Thissen JP: Myostatin gene
deletion prevents glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy.
Endocrinology. 148:452–460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Auclair D, Garrel DR, Chaouki Zerouala A
and Ferland LH: Activation of the ubiquitin pathway in rat skeletal
muscle by catabolic doses of glucocorticoids. Am J Physiol.
272:C1007–C1016. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hasselgren PO: Glucocorticoids and muscle
catabolism. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2:201–205. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Komamura K, Shirotani-Ikejima H, Tatsumi
R, Tsujita-Kuroda Y, Kitakaze M, Miyatake K, Sunagawa K and Miyata
T: Differential gene expression in the rat skeletal and heart
muscle in glucocorticoid-induced myopathy: Analysis by microarray.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 17:303–310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McPherron AC, Lawler AM and Lee SJ:
Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-β
superfamily member. Nature. 387:83–90. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qin J, Du R, Yang YQ, Zhang HQ, Li Q, Liu
L, Guan H, Hou J and An XR: Dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle
atrophy was associated with upregulation of myostatin promoter
activity. Res Vet Sci. 94:84–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Allen DL, Bandstra ER, Harrison BC, Thorng
S, Stodieck LS, Kostenuik PJ, Morony S, Lacey DL, Hammond TG,
Leinwand LL, et al: Effects of spaceflight on murine skeletal
muscle gene expression. J Appl Physiol 1985. 106:582–595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Dirks-Naylor AJ and Griffiths CL:
Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and cellular mechanisms of
myopathy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 117:1–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Orzechowski A, Ostaszewski P, Wilczak J,
Jank M, Bałasińska B, Wareski P and Fuller J Jr: Rats with a
glucocorticoid-induced catabolic state show symptoms of oxidative
stress and spleen atrophy: The effects of age and recovery. J Vet
Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med. 49:256–263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alamdari N, Aversa Z, Castillero E, Gurav
A, Petkova V, Tizio S and Hasselgren PO: Resveratrol prevents
dexamethasone-induced expression of the muscle atrophy-related
ubiquitin ligases atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in cultured myotubes through
a SIRT1-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
417:528–533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Kim JW, Ku SK, Han MH, Kim KY, Kim SG, Kim
GY, Hwang HJ, Kim BW, Kim CM and Choi YH: The administration of
Fructus Schisandrae attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy
in mice. Int J Mol Med. 36:29–42. 2015a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Benveniste O, Jacobson L, Farrugia ME,
Clover L and Vincent A: MuSK antibody positive myasthenia gravis
plasma modifies MURF-1 expression in C2C12 cultures and mouse
muscle in vivo. J Neuroimmunol. 170:41–48. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jones A, Hwang DJ, Narayanan R, Miller DD
and Dalton JT: Effects of a novel selective androgen receptor
modulator on dexa-methasone-induced and hypogonadism-induced muscle
atrophy. Endocrinology. 151:3706–3719. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Nakagawa K, Sarkar A, Maruyama J,
Iwasa H, Bao Y, Ishigami-Yuasa M, Ito S, Kagechika H, Hata S, et
al: Screening with a novel cell-based assay for TAZ activators
identifies a compound that enhances myogenesis in C2C12 cells and
facilitates muscle repair in a muscle injury model. Mol Cell Biol.
34:1607–1621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ringold HJ, Batres E, Halpern O and
Necoechea E: Steroids. CV. 12-Methyl and
2-hydroxymethylene-androstane derivatives. J Am Chem Soc.
81:427–432. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lennon HD: Effects of various
17-alpha-alkyl substitutions and structural modifications of
steroids on sulfobromophthalein (BSP) retention in rabbits.
Steroids. 7:157–170. 1966. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dorfman RI and Kincl FA: Relative potency
of steroids in an anabolic-androgenic assay using the castrated
rat. Endocrinology. 72:259–266. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Pavlatos AM, Fultz O, Monberg MJ and
Vootkur A: Review of oxymetholone: A 17alpha-alkylated
anabolic-androgenic steroid. Clin Ther. 23:789–801; discussion 771.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Isaacs J, Loveland K, Mallu S, Adams S and
Wodicka R: The use of anabolic steroids as a strategy in reversing
denervation atrophy after delayed nerve repair. Hand (NY).
6:142–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim JW, Ku SK, Kim KY, Kim SG, Han MH, Kim
GY, Hwang HJ, Kim BW, Kim CM and Choi YH: Schisandrae Fructus
supplementation ameliorates sciatic neurectomy-induced muscle
atrophy in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:8724282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Young GP, Bhathal PS, Sullivan JR, Wall
AJ, Fone DJ and Hurley TH: Fatal hepatic coma complicating
oxymetholone therapy in multiple myeloma. Aust N Z J Med. 7:47–51.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wood P and Yin JA: Oxymetholone
hepatotoxicity enhanced by concomitant use of cyclosporin A in a
bone marrow transplant patient. Clin Lab Haematol. 16:201–204.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Walker ID, Davidson JF, Young P and Conkie
JA: Plasma fibrinolytic activity following oral anabolic steroid
therapy. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 34:236–245. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tzianabos AO: Polysaccharide
immunomodulators as therapeutic agents: Structural aspects and
biologic function. Clin Microbiol Rev. 13:523–533. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Estrada A, Yun CH, Van Kessel A, Li B,
Hauta S and Laarveld B: Immunomodulatory activities of oat
beta-glucan in vitro and in vivo. Microbiol Immunol. 41:991–998.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lotzová E and Gutterman JU: Effect of
glucan on natural killer (NK) cells: Further comparison between NK
cell and bone marrow effector cell activities. J Immunol.
123:607–611. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hofer M and Pospísil M: Glucan as
stimulator of hematopoiesis in normal and gamma-irradiated mice. A
survey of the authors’ results. Int J Immunopharmacol. 19:607–609.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lee JN, Lee DY, Ji IH, Kim GE, Kim HN,
Sohn J, Kim S and Kim CW: Purification of soluble beta-glucan with
immune-enhancing activity from the cell wall of yeast. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 65:837–841. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Benach JL, Habicht GS, Holbrook TW and
Cook JA: Glucan as an adjuvant for a murine Babesia microti
immunization trial. Infect Immun. 35:947–951. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoon HS, Kim JW, Cho HR, Moon SB, Shin HD,
Yang KJ, Lee HS, Kwon YS and Ku SK: Immunomodulatory effects of
Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001 exopolymers on the
cyclo-phosphamide-treated mice. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 20:438–445.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jung MY, Kim JW, Kim KY, Choi SH and Ku
SK: Polycan, a β-glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans SM-2001,
mitigates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Exp Ther Med.
12:1251–1262. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim HD, Cho HR, Moon SB, Shin HD, Yang KJ,
Park BR, Jang HJ, Kim LS, Lee HS and Ku SK: Effects of β-glucan
from Aureobasidium pullulans on acute inflammation in mice. Arch
Pharm Res. 30:323–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim HD, Cho HR, Moon SB, Shin HD, Yang KJ,
Park BR, Jang HJ, Kim LS, Lee HS and Ku SK: Effect of Exopolymers
from Aureobasidum pullulans on formalin-induced chronic paw
inflammation in mice. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 16:1954–1960.
2006.
|
|
49
|
Ku SK, Lee YJ, Lee SD, Cho HR, Moon SB,
Kim KY, Kwon YS and Kim JW: Nephroprotective effect of Polycan on
acute renal failure induced by cisplatin in rats. ISRN Vet Sci.
2012:8621042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ku SK, Kim JW, Cho HR, Kim KY, Min YH,
Park JH, Kim JS, Park JH, Seo BI and Roh SS: Effect of β-glucan
originated from Aureobasidium pullulans on asthma induced by
ovalbumin in mouse. Arch Pharm Res. 35:1073–1081. 2012a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kim JW, Cho HR and Ku SK: Efficacy test of
Polycan, a beta-glucan originated from Aureobasidium pullulans
SM-2001, on anterior cruciate ligament transection and partial
medial meniscectomy-induced-osteoarthritis rats. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 22:274–282. 2012a. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kim YS, Kang SJ, Kim JW, Cho HR, Moon SB,
Kim KY, Lee HS, Han CH, Ku SK and Lee YJ: Effects of Polycan, a
β-glucan, on experimental periodontitis and alveolar bone loss in
Sprague-Dawley rats. J Periodontal Res. 47:800–810. 2012b.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Seo HP, Kim JM, Shin HD, Kim TK, Chang HJ,
Park BR and Lee JW: Production of β-1,3/1,6-glucan by Aureobasidium
pullulans SM-2001. Korean J Bitechnol Bioeng. 17:376–380. 2002.
|
|
54
|
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ and Pellegrini N: A
review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and
biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
15:316–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jamall IS and Smith JC: Effects of cadmium
on glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and lipid
peroxidation in the rat heart: A possible mechanism of cadmium
cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 80:33–42. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He HJ, Wang GY, Gao Y, Ling WH, Yu ZW and
Jin TR: Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress
in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice. World
J Diabetes. 3:94–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sedlak J and Lindsay RH: Estimation of
total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue
with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem. 25:192–205. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Aebi H: Catalase. Methods in Enzymatic
Analysis. Bergmeyer HU: Academic Press; New York, NY: pp. 673–686.
1974, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Sun Y, Oberley LW and Li Y: A simple
method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem.
34:497–500. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yokoyama U, Minamisawa S, Quan H, Akaike
T, Suzuki S, Jin M, Jiao Q, Watanabe M, Otsu K, Iwasaki S, et al:
Prostaglandin E2-activated Epac promotes neointimal formation of
the rat ductus arteriosus by a process distinct from that of
cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 283:28702–28709.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ogawa T, Nikawa T, Furochi H, Kosyoji M,
Hirasaka K, Suzue N, Sairyo K, Nakano S, Yamaoka T, Itakura M, et
al: Osteoactivin upregulates expression of MMP-3 and MMP-9 in
fibroblasts infiltrated into denervated skeletal muscle in mice. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 289:C697–C707. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Tipoe GL, Leung TM, Liong EC, Lau TY, Fung
ML and Nanji AA: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces liver
inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride
(CCl4)-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicology. 273:45–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shi SR, Chaiwun B, Young L, Cote RJ and
Taylor CR: Antigen retrieval technique utilizing citrate buffer or
urea solution for immunohistochemical demonstration of androgen
receptor in formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Histochem Cytochem.
41:1599–1604. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Levene A: Pathological factors influencing
excision of tumours in the head and neck. Part I. Clin Otolaryngol
Allied Sci. 6:145–151. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ludbrook J: Update: Microcomputer
statistics packages. A personal view. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
24:294–296. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Jackman RW and Kandarian SC: The molecular
basis of skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
287:C834–C843. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sandri M: Signaling in muscle atrophy and
hypertrophy. Physiology (Bethesda). 23:160–170. 2008.
|
|
70
|
Glass DJ: Signaling pathways perturbing
muscle mass. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 13:225–229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Powers SK, Kavazis AN and McClung JM:
Oxidative stress and disuse muscle atrophy. J Appl Physiol 1985.
102:2389–2397. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Arakawa T, Katada A, Shigyo H, Kishibe K,
Adachi M, Nonaka S and Harabuchi Y: Electrical stimulation prevents
apoptosis in denervated skeletal muscle. NeuroRehabilitation.
27:147–154. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lim JY and Han TR: Effect of
electromyostimulation on apoptosis-related factors in denervation
and reinnervation of rat skeletal muscles. Muscle Nerve.
42:422–430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Mastagllia FL: Drug induced myopathies.
Pract Neurol. 6:4–13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Seale JP and Compton MR: Side-effects of
corticosteroid agents. Med J Aust. 144:139–142. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zoorob RJ and Cender D: A different look
at corticosteroids. Am Fam Physician. 58:443–450. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bowyer SL, LaMothe MP and Hollister JR:
Steroid myopathy: Incidence and detection in a population with
asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 76:234–242. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Covar RA, Leung DY, McCormick D, Steelman
J, Zeitler P and Spahn JD: Risk factors associated with
glucocorticoid-induced adverse effects in children with severe
asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 106:651–659. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Owczarek J, Jasińska M and
Orszulak-Michalak D: Drug-induced myopathies. An overview of the
possible mechanisms. Pharmacol Rep. 57:23–34. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fox JG, Cohen BJ and Loew FM: Laboratory
animal medicine. Academic Press Inc.; Orlando, Fl: 1984
|
|
81
|
Tajima Y: Biological reference data book
on experimental animals. Soft Science Inc.; Tokyo: 1989
|
|
82
|
Gupta AK and Chow M: Prednicarbate
(Dermatop): Profile of a corticosteroid. J Cutan Med Surg.
8:244–247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Cho YH, Chung IK, Cheon WH, Lee HS and Ku
SK: Effect of DHU001, a polyherbal formula on formalin-induced paw
chronic inflammation of mice. Toxicol Res. 27:95–102. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lee HS, Yang KJ, Shin HD, Park BR, Son CW,
Jang HJ, Park DC, Jung YM and Ku SK: Single oral dose toxicity
studies of Polycan, β-glucan originated from Aureobasidium in mice.
Toxicol Res. 21:361–365. 2005.
|
|
85
|
Duarte CG, dos Santos GL, Azzolini AE and
de Assis Pandochi AI: The effect of the antithyroid drug
propylthiouracil on the alternative pathway of complement in rats.
Int J Immunopharmacol. 22:25–33. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pinzone JJ, Fox ML, Sastry MK, Parenti DM
and Simon GL: Plasma leptin concentration increases early during
highly active antiretroviral therapy for acquired immunodeficiency
syndrome, independent of body weight. J Endocrinol Invest.
28:RC1–RC3. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hengge UR, Baumann M, Maleba R, Brockmeyer
NH and Goos M: Oxymetholone promotes weight gain in patients with
advanced human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection. Br J Nutr.
75:129–138. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hengge UR, Stocks K, Faulkner S, Wiehler
H, Lorenz C, Jentzen W, Hengge D and Ringham G: Oxymetholone for
the treatment of HIV-wasting: A double-blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled phase III trial in eugonadal men and women. HIV
Clin Trials. 4:150–163. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Hengge UR, Stocks K, Wiehler H, Faulkner
S, Esser S, Lorenz C, Jentzen W, Hengge D, Goos M, Dudley RE, et
al: Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial of
oxymetholone for the treatment of HIV wasting. AIDS. 17:699–710.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wyss M and Kaddurah-Daouk R: Creatine and
creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. 80:1107–1213. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hunter A: The biological distribution of
creatine and creatinine. Creatine and Creatinine. Longmans; Green,
London: pp. 73–113. 1928
|
|
92
|
Balsom PD, Söderlund K and Ekblom B:
Creatine in humans with special reference to creatine
supplementation. Sports Med. 18:268–280. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Fitch CD, Lucy DD, Bornhofen JH and
Dalrymple GV: Creatine metabolism in skeletal muscle. II. Creatine
kinetics in man. Neurology. 18:32–42. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bloch K and Schoenheimer R: Studies in
protein metabolism. XI. The metabolic relation of creatine and
creatinine studies with isotopic nitrogen. J Biol Chem.
131:111–119. 1939.
|
|
95
|
Heymsfield SB, Arteaga C, McManus C, Smith
J and Moffitt S: Measurement of muscle mass in humans: Validity of
the 24-hour urinary creatinine method. Am J Clin Nutr. 37:478–494.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sala A, Tarnopolsky M, Webber C, Norman G
and Barr R: Serum creatinine: A surrogate measurement of lean body
mass in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 45:16–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Stimpson SA, Turner SM, Clifton LG, Poole
JC, Mohammed HA, Shearer TW, Waitt GM, Hagerty LL, Remlinger KS,
Hellerstein MK, et al: Total-body creatine pool size and skeletal
muscle mass determination by creatine-(methyl-D3) dilution in rats.
J Appl Physiol 1985. 112:1940–1948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhang Y, Huang JJ, Wang ZQ, Wang N and Wu
ZY: Value of muscle enzyme measurement in evaluating different
neuro-muscular diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 413:520–524. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Choi M, Park H, Cho S and Lee M: Vitamin
D3 supplementation modulates inflammatory responses from the muscle
damage induced by high-intensity exercise in SD rats. Cytokine.
63:27–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Cohen I, Bogin E, Chechick A and Rzetelny
V: Biochemical alterations secondary to disuse atrophy in the rat’s
serum and limb tissues. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 119:410–417. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Pellegrino MA, D’Antona G, Bortolotto S,
Boschi F, Pastoris O, Bottinelli R, Polla B and Reggiani C:
Clenbuterol antagonizes glucocorticoid-induced atrophy and fibre
type transformation in mice. Exp Physiol. 89:89–100. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Comporti M: Lipid peroxidation and
cellular damage in toxic liver injury. Lab Invest. 53:599–623.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Gore M, Fiebig R, Hollander J,
Leeuwenburgh C, Ohno H and Ji LL: Endurance training alters
antioxidant enzyme gene expression in rat skeletal muscle. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 76:1139–1145. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Süleyman H, Cadirci E, Albayrak A, Polat
B, Halici Z, Koc F, Hacimuftuoglu A and Bayir Y: Comparative study
on the gastroprotective potential of some antidepressants in
indomethacin-induced ulcer in rats. Chem Biol Interact.
180:318–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Chen JH, Tipoe GL, Liong EC, So HS, Leung
KM, Tom WM, Fung PC and Nanji AA: Green tea polyphenols prevent
toxin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by down-regulating inducible
nitric oxide-derived prooxidants. Am J Clin Nutr. 80:742–751. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Mohiuddin I, Chai H, Lin PH, Lumsden AB,
Yao Q and Chen C: Nitrotyrosine and chlorotyrosine: Clinical
significance and biological functions in the vascular system. J
Surg Res. 133:143–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Pacher P, Beckman JS and Liaudet L: Nitric
oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
87:315–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Salvini TF, Durigan JL, Peviani SM and
Russo TL: Effects of electrical stimulation and stretching on the
adaptation of denervated skeletal muscle: Implications for physical
therapy. Rev Bras Fisioter. 16:175–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Delgado J, Saborido A and Megías A:
Prolonged treatment with the anabolic-androgenic steroid stanozolol
increases antioxidant defences in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol
Biochem. 66:63–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yoo YE and Ko CP: Dihydrotestosterone
ameliorates degeneration in muscle, axons and motoneurons and
improves motor function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis model
mice. PLoS One. 7:e372582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Nuñez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y and Inohara N:
Caspases: The proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene.
17:3237–3245. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Barrett KL, Willingham JM, Garvin AJ and
Willingham MC: Advances in cytochemical methods for detection of
apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 49:821–832. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Dam AD, Mitchell AS, Rush JW and
Quadrilatero J: Elevated skeletal muscle apoptotic signaling
following glutathione depletion. Apoptosis. 17:48–60. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Yen YP, Tsai KS, Chen YW, Huang CF, Yang
RS and Liu SH: Arsenic induces apoptosis in myoblasts through a
reactive oxygen species-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondrial dysfunction pathway. Arch Toxicol. 86:923–933. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A and
Goldberg AL: Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly
expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:14440–14445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Cohen S, Brault JJ, Gygi SP, Glass DJ,
Valenzuela DM, Gartner C, Latres E and Goldberg AL: During muscle
atrophy, thick, but not thin, filament components are degraded by
MuRF1-dependent ubiquitylation. J Cell Biol. 185:1083–1095. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Berne RM, Knabb RM, Ely SW and Rubio R:
Adenosine in the local regulation of blood flow: A brief overview.
Fed Proc. 42:3136–3142. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Segal SS and Kurjiaka DT: Coordination of
blood flow control in the resistance vasculature of skeletal
muscle. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 27:1158–1164. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Hespel P and Richter EA: Role of adenosine
in regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in contracting muscle.
Skeletal Muscle Metabolism in Exercise and Diabetes. Richter EA,
Kiens B, Galbo H and Saltin B: Plenum Press; New York, NY: pp.
97–106. 1998, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Dobson JG Jr, Rubio R and Berne RM: Role
of adenine nucleotides, adenosine, and inorganic phosphate in the
regulation of skeletal muscle blood flow. Circ Res. 29:375–384.
1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Vergauwen L, Hespel P and Richter EA:
Adenosine receptors mediate synergistic stimulation of glucose
uptake and transport by insulin and by contractions in rat skeletal
muscle. J Clin Invest. 93:974–981. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Lynge J and Hellsten Y: Distribution of
adenosine A1, A2A and A2B receptors in human skeletal muscle. Acta
Physiol Scand. 169:283–290. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M,
Rosen TA, Levine JD and Julius D: The capsaicin receptor: A
heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature.
389:816–824. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Guilak F, Leddy HA and Liedtke W:
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4: The sixth sense of the
musculoskeletal system? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1192:404–409. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Mizoguchi F, Mizuno A, Hayata T, Nakashima
K, Heller S, Ushida T, Sokabe M, Miyasaka N, Suzuki M, Ezura Y, et
al: Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 deficiency suppresses
unloading-induced bone loss. J Cell Physiol. 216:47–53. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM,
Barrett JC and Horikawa I: Evolutionarily conserved and
nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT
proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 16:4623–4635. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Haigis MC and Guarente LP: Mammalian
sirtuins - emerging roles in physiology, aging, and calorie
restriction. Genes Dev. 20:2913–2921. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Amat R, Planavila A, Chen SL, Iglesias R,
Giralt M and Villarroya F: SIRT1 controls the transcription of the
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
Co-activator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) gene in skeletal muscle through
the PGC-1alpha autoregulatory loop and interaction with MyoD. J
Biol Chem. 284:21872–21880. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Toledo M, Busquets S, Ametller E,
López-Soriano FJ and Argilés JM: Sirtuin 1 in skeletal muscle of
cachectic tumour-bearing rats: A role in impaired regeneration? J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2:57–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Amat R, Solanes G, Giralt M and Villarroya
F: SIRT1 is involved in glucocorticoid-mediated control of
uncoupling protein-3 gene transcription. J Biol Chem.
282:34066–34076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|