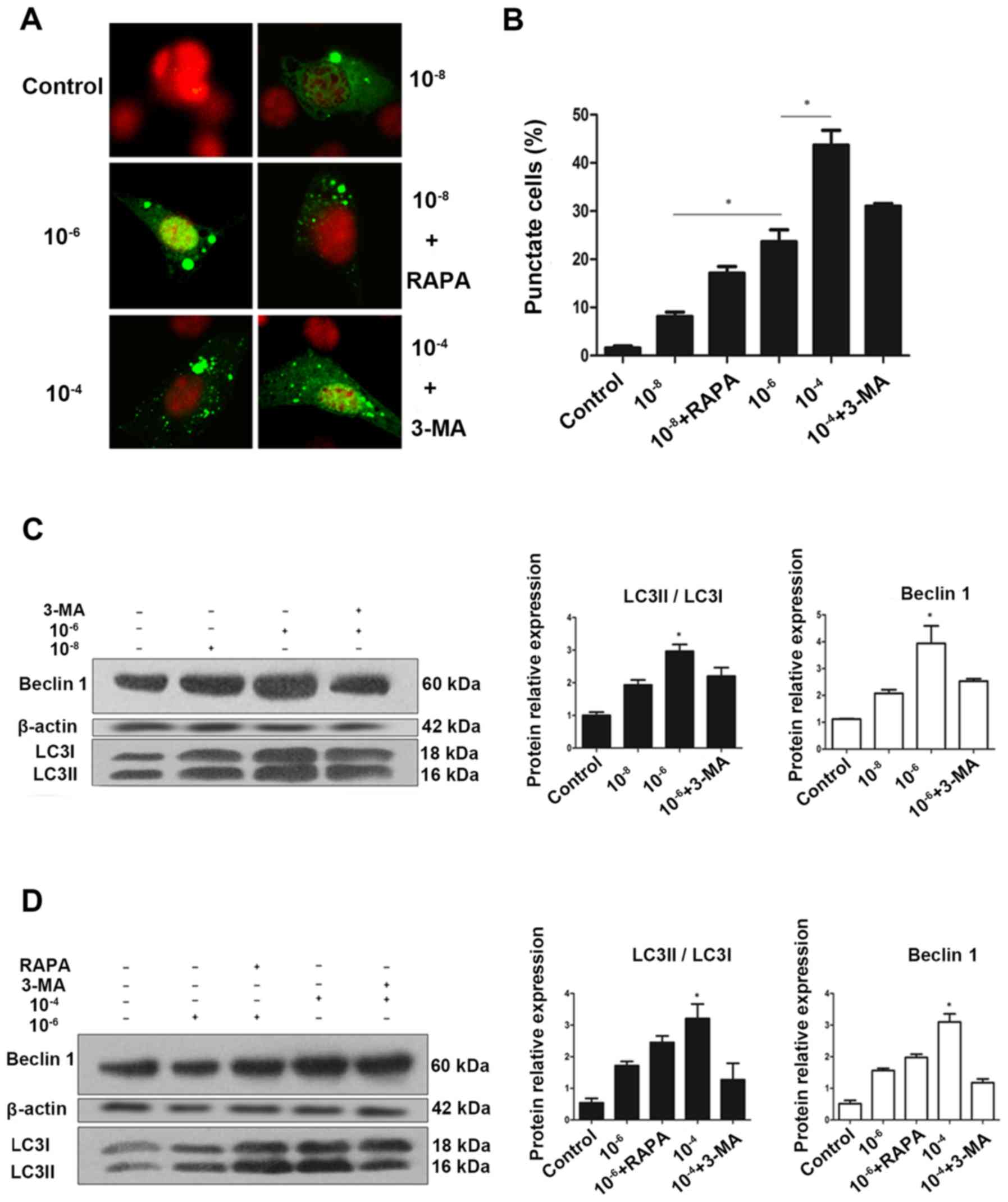
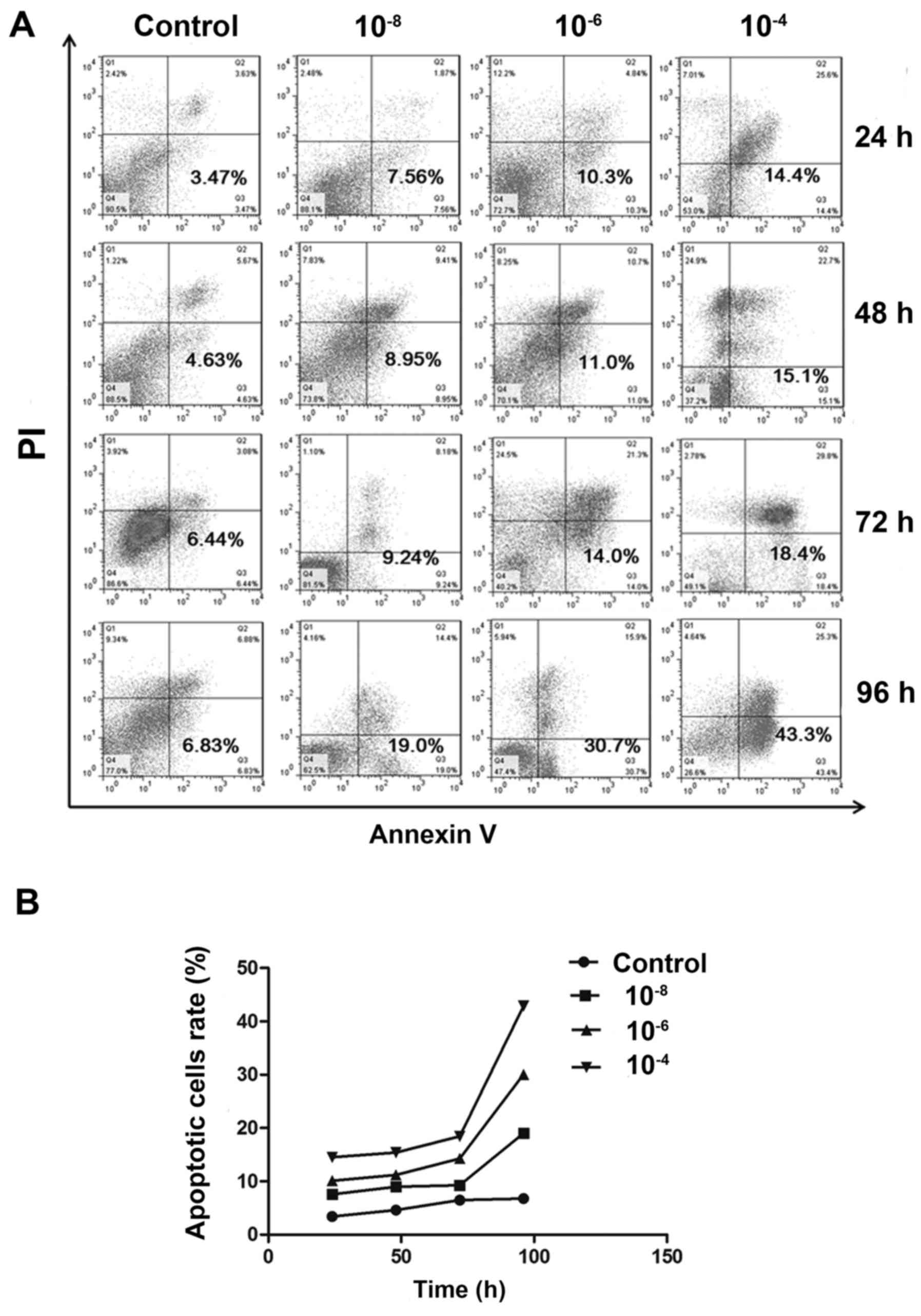
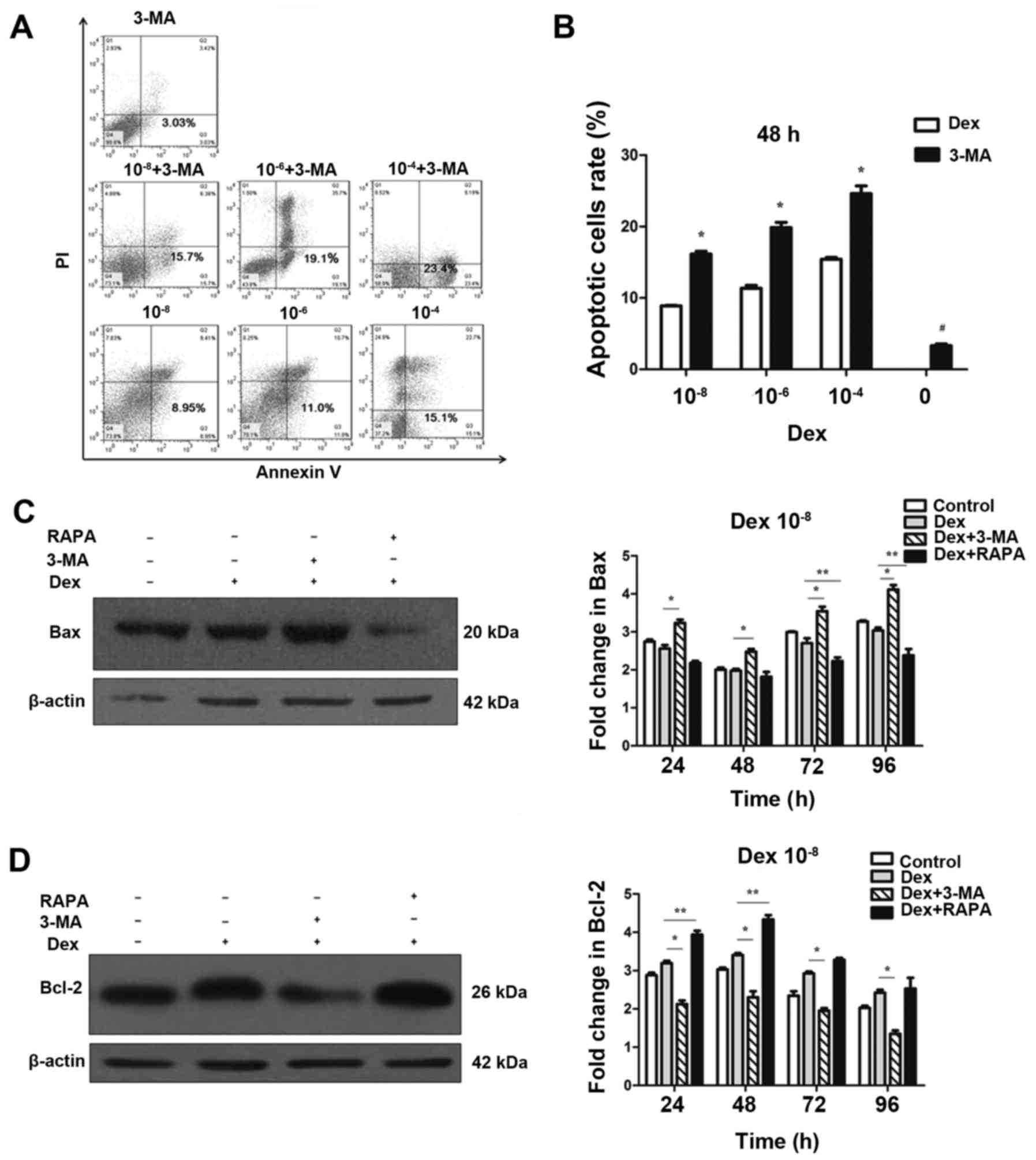
|
1
|
Kanis JA, Johansson H, Oden A, Johnell O,
de Laet C, Melton LJ III, Tenenhouse A, Reeve J, Silman AJ, Pols
HA, et al: A meta-analysis of prior corticosteroid use and fracture
risk. J Bone Miner Res. 19:893–899. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Van Staa TP, Laan RF, Barton IP, Cohen S,
Reid DM and Cooper C: Bone density threshold and other predictors
of vertebral fracture in patients receiving oral glucocorticoid
therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 48:3224–3229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weinstein RS: Clinical practice.
Glucocorticoid-induced bone disease. N Engl J Med. 365:62–70. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mankin HJ: Nontraumatic necrosis of bone
(osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med. 326:1473–1479. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
LoCascio V, Bonucci E, Imbimbo B, Ballanti
P, Adami S, Milani S, Tartarotti D and DellaRocca C: Bone loss in
response to long-term glucocorticoid therapy. Bone Miner. 8:39–51.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jia D, O'Brien CA, Stewart SA, Manolagas
SC and Weinstein RS: Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoclasts to
increase their life span and reduce bone density. Endocrinology.
147:5592–5599. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hong JM, Teitelbaum SL, Kim TH, Ross FP,
Kim SY and Kim HJ: Calpain-6, a target molecule of glucocorticoids,
regulates osteoclastic bone resorption via cytoskeletal
organization and microtubule acetylation. J Bone Miner Res.
26:657–665. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li H, Qian W, Weng X, Wu Z, Li H, Zhuang
Q, Feng B and Bian Y: Glucocorticoid receptor and sequential 53
activation by dexamethasone mediates apoptosis and cell cycle
arrest of osteoblastic MC3T3E1 cells. PLoS One. 7:e370302012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Naves MA, Pereira RM, Comodo AN, de
Alvarenga EL, Caparbo VF and Teixeira VP: Effect of dexamethasone
on human osteoblasts in culture: involvement of β1 integrin and
integrin-linked kinase. Cell Biol Int. 35:1147–1151. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mizushima N: Physiological functions of
autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 335:71–84. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Xia X, Kar R, Gluhak-Heinrich J, Yao W,
Lane NE, Bonewald LF, Biswas SK, Lo WK and Jiang JX:
Glucocorticoid-induced autophagy in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res.
25:2479–2488. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Martinet W, Agostinis P, Vanhoecke B,
Dewaele M and De Meyer GR: Autophagy in disease: a double-edged
sword with therapeutic potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:697–712.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Another way to
die: autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Diffe. 12(Suppl
2): 1528–1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Czaja MJ: Autophagy in health and disease.
2. Regulation of lipid metabolism and storage by autophagy:
pathophysiological implications. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C973–C978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laane E, Tamm KP, Buentke E, Ito K,
Kharaziha P, Oscarsson J, Corcoran M, Björklund AC, Hultenby K,
Lundin J, et al: Cell death induced by dexamethasone in lymphoid
leukemia is mediated through initiation of autophagy. Cell Death
Differ. 16:1018–1029. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nollet M, Santucci-Darmanin S, Breuil V,
Al-Sahlanee R, Cros C, Topi M, Momier D, Samson M, Pagnotta S,
Cailleteau L, et al: Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in
mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy. 10:1965–1977. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kimura S, Noda T and Yoshimori T:
Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel
reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy.
3:452–460. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Liu Y, Wang Z, Liu K, Wang Y, Liu J,
Ding H and Yuan Z: Subversion of cellular autophagy machinery by
hepatitis B virus for viral envelopment. J Virol. 85:6319–6333.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang YH, Chen K, Li B, Chen JW, Zheng XF,
Wang YR, Jiang SD and Jiang LS: Estradiol inhibits osteoblast
apoptosis via promotion of autophagy through the ER-ERK-mTOR
pathway. Apoptosis. 18:1363–1375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang YH, Li B, Zheng XF, Chen JW, Chen K,
Jiang SD and Jiang LS: Oxidative damage to osteoblasts can be
alleviated by early autophagy through the endoplasmic reticulum
stress pathway - implications for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Free Radic Biol Med. 77:10–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsunaga K, Saitoh T, Tabata K, Omori H,
Satoh T, Kurotori N, Maejima I, Shirahama-Noda K, Ichimura T, Isobe
T, et al: Two Beclin 1-binding proteins, Atg14L and Rubicon,
reciprocally regulate autophagy at different stages. Nat Cell Biol.
11:385–396. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Itakura E, Kishi C, Inoue K and Mizushima
N: Beclin 1 forms two distinct phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
complexes with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG. Mol Biol Cell.
19:5360–5372. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Alm JJ, Heino TJ, Hentunen TA, Väänänen HK
and Aro HT: Transient 100 nM dexamethasone treatment reduces inter-
and intraindividual variations in osteoblastic differentiation of
bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C
Methods. 18:658–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dalle Carbonare L, Arlot ME, Chavassieux
PM, Roux JP, Portero NR and Meunier PJ: Comparison of trabecular
bone microarchitecture and remodeling in glucocorticoid-induced and
postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 16:97–103. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mazziotti G, Angeli A, Bilezikian JP,
Canalis E and Giustina A: Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: an
update. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 17:144–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Canalis E, Bilezikian JP, Angeli A and
Giustina A: Perspectives on glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
Bone. 34:593–598. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weinstein RS: Glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2:65–73. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Parfitt AM and
Manolagas SC: Inhibition of osteoblastogenesis and promotion of
apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by glucocorticoids.
Potential mechanisms of their deleterious effects on bone. J Clin
Invest. 102:274–282. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chipuk JE, McStay GP, Bharti A, Kuwana T,
Clarke CJ, Siskind LJ, Obeid LM and Green DR: Sphingolipid
metabolism cooperates with BAK and BAX to promote the mitochondrial
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 148:988–1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jilka RL, O'Brien CA, Roberson PK,
Bonewald LF, Weinstein RS and Manolagas SC: Dysapoptosis of
osteoblasts and osteocytes increases cancellous bone formation but
exaggerates cortical porosity with age. J Bone Miner Res.
29:103–117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang T, Li Y, Park KA, Byun HS, Won M,
Jeon J, Lee Y, Seok JH, Choi SW, Lee SH, et al: Cucurbitacin
induces autophagy through mitochondrial ROS production which
counteracts to limit caspase-dependent apoptosis. Autophagy.
8:559–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rangaraju S, Verrier JD, Madorsky I, Nicks
J, Dunn WA Jr and Notterpek L: Rapamycin activates autophagy and
improves myelination in explant cultures from neuropathic mice. J
Neurosci. 30:11388–11397. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang M, Wei Q, Dong G, Komatsu M, Su Y
and Dong Z: Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute
kidney injury. Kidney Int. 82:1271–1283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Warr MR, Binnewies M, Flach J, Reynaud D,
Garg T, Malhotra R, Debnath J and Passegué E: FOXO3A directs a
protective autophagy program in haematopoietic stem cells. Nature.
494:323–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jung HS, Chung KW, Won Kim J, Kim J,
Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Nguyen YH, Kang TM, Yoon KH, Kim JW, et al:
Loss of autophagy diminishes pancreatic beta cell mass and function
with resultant hyperglycemia. Cell Metab. 8:318–324. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jia J, Yao W, Guan M, Dai W, Shahnazari M,
Kar R, Bonewald L, Jiang JX and Lane NE: Glucocorticoid dose
determines osteocyte cell fate. FASEB J. 25:3366–3376. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xia HF, Jin XH, Cao ZF, Shi T and Ma X:
miR-98 is involved in rat embryo implantation by targeting Bcl-xl.
FEBS Lett. 588:574–583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|