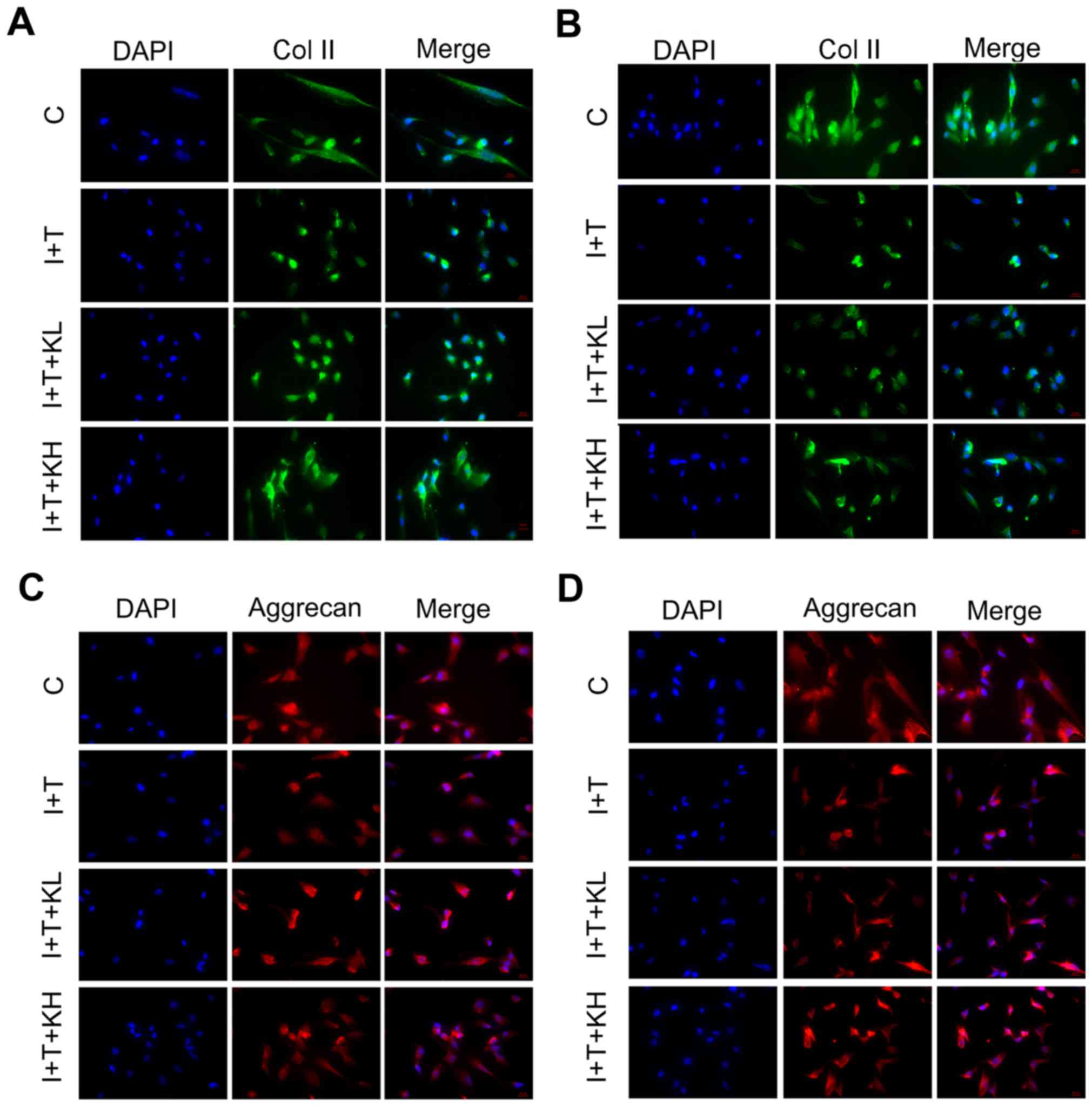
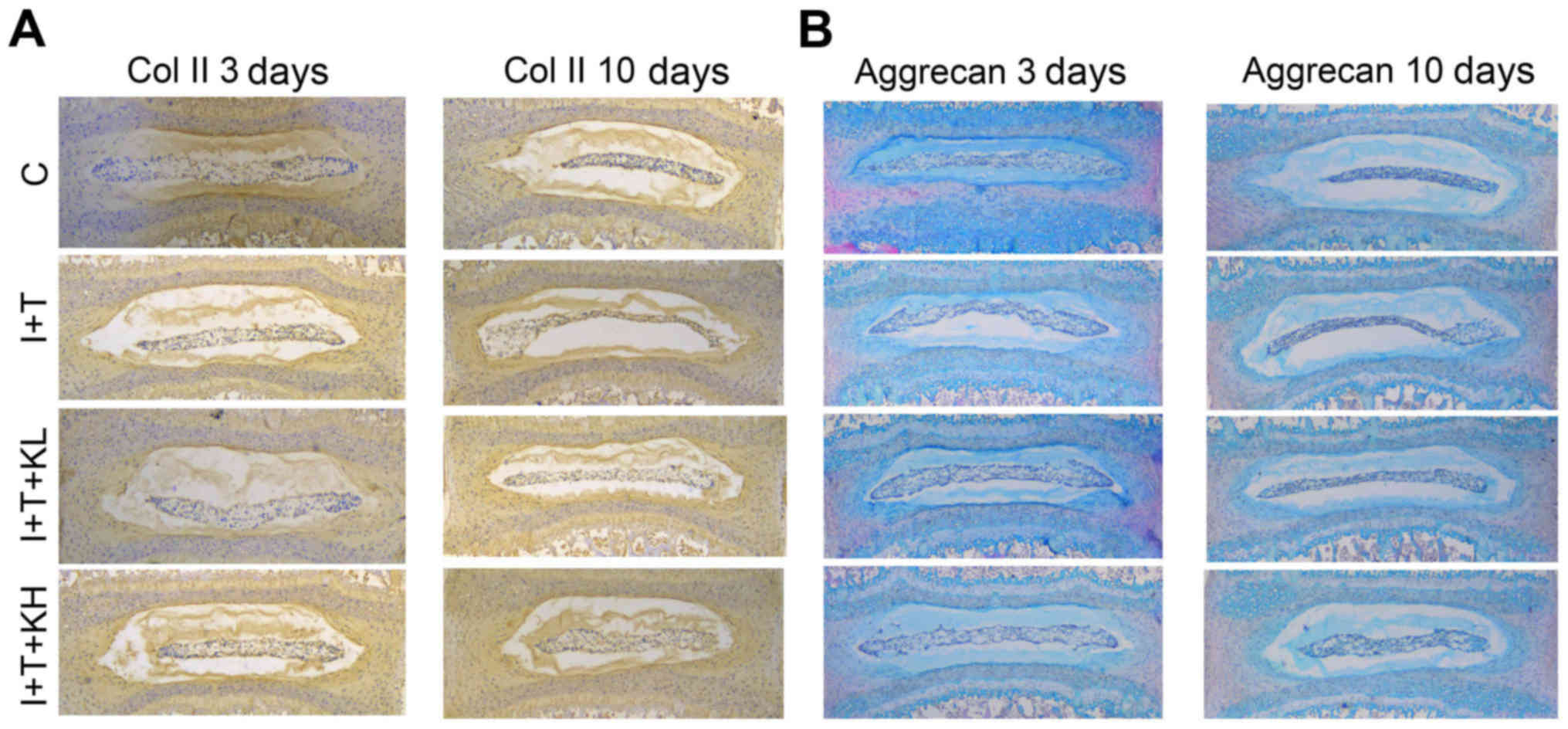
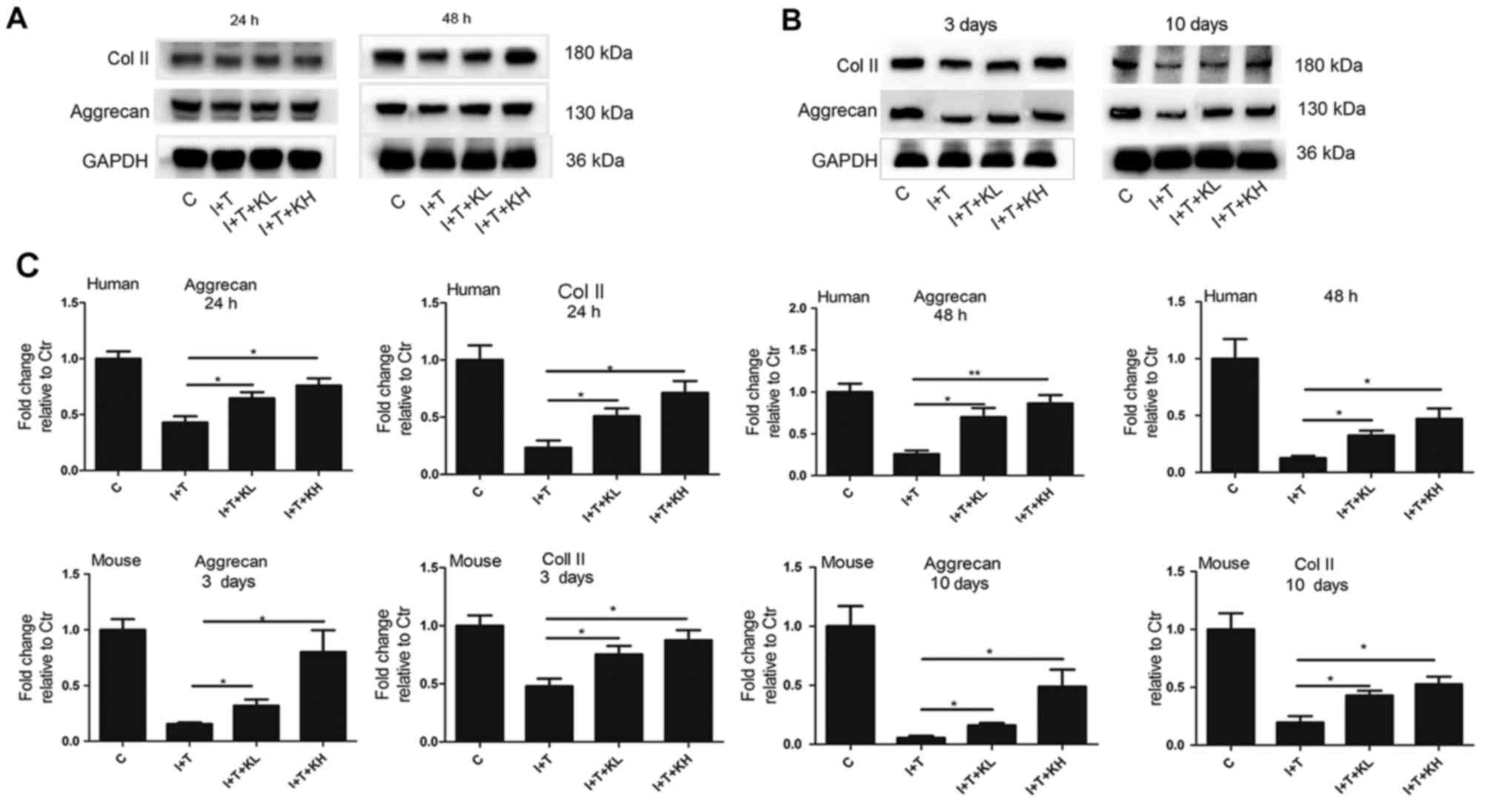
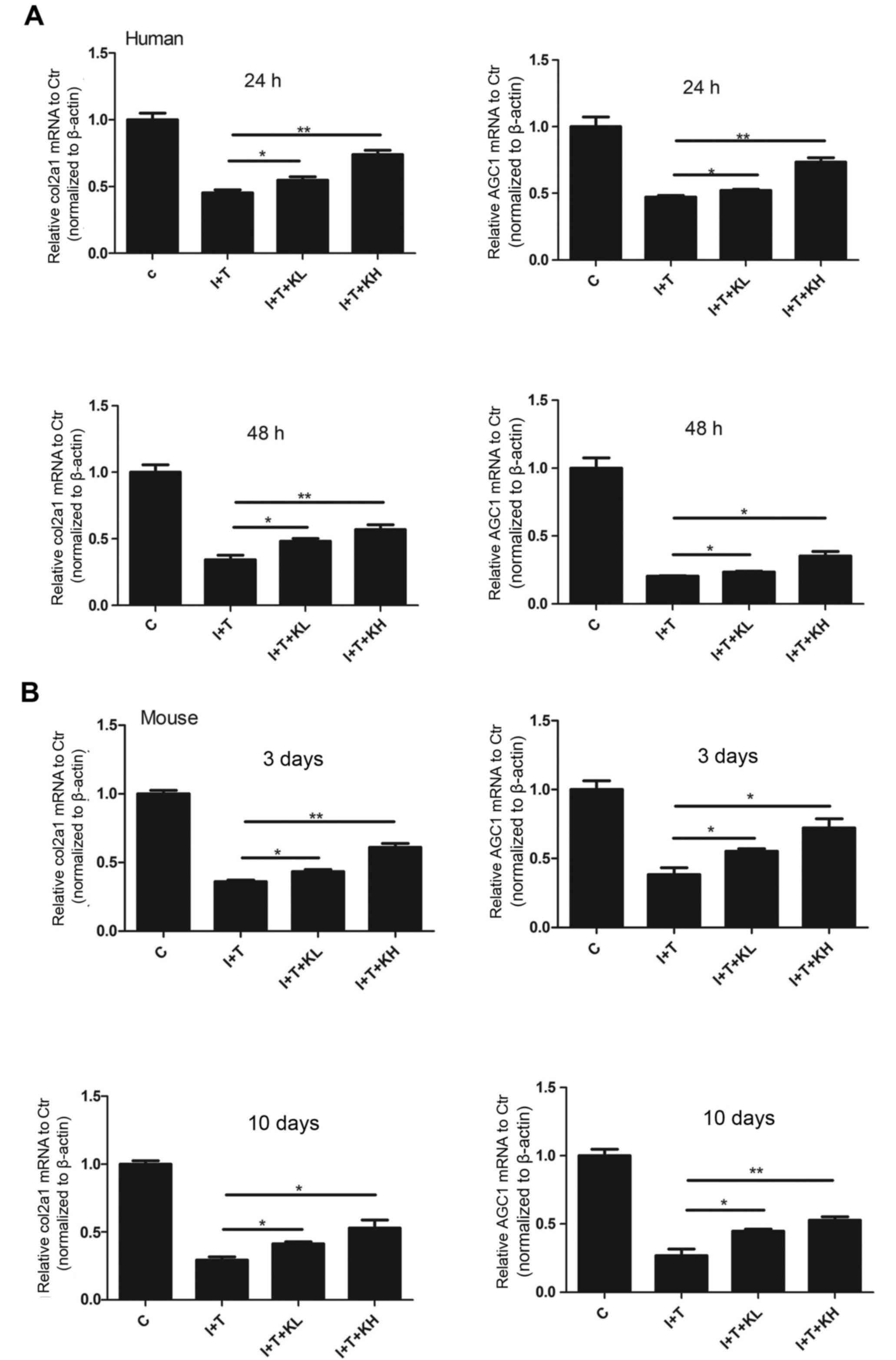
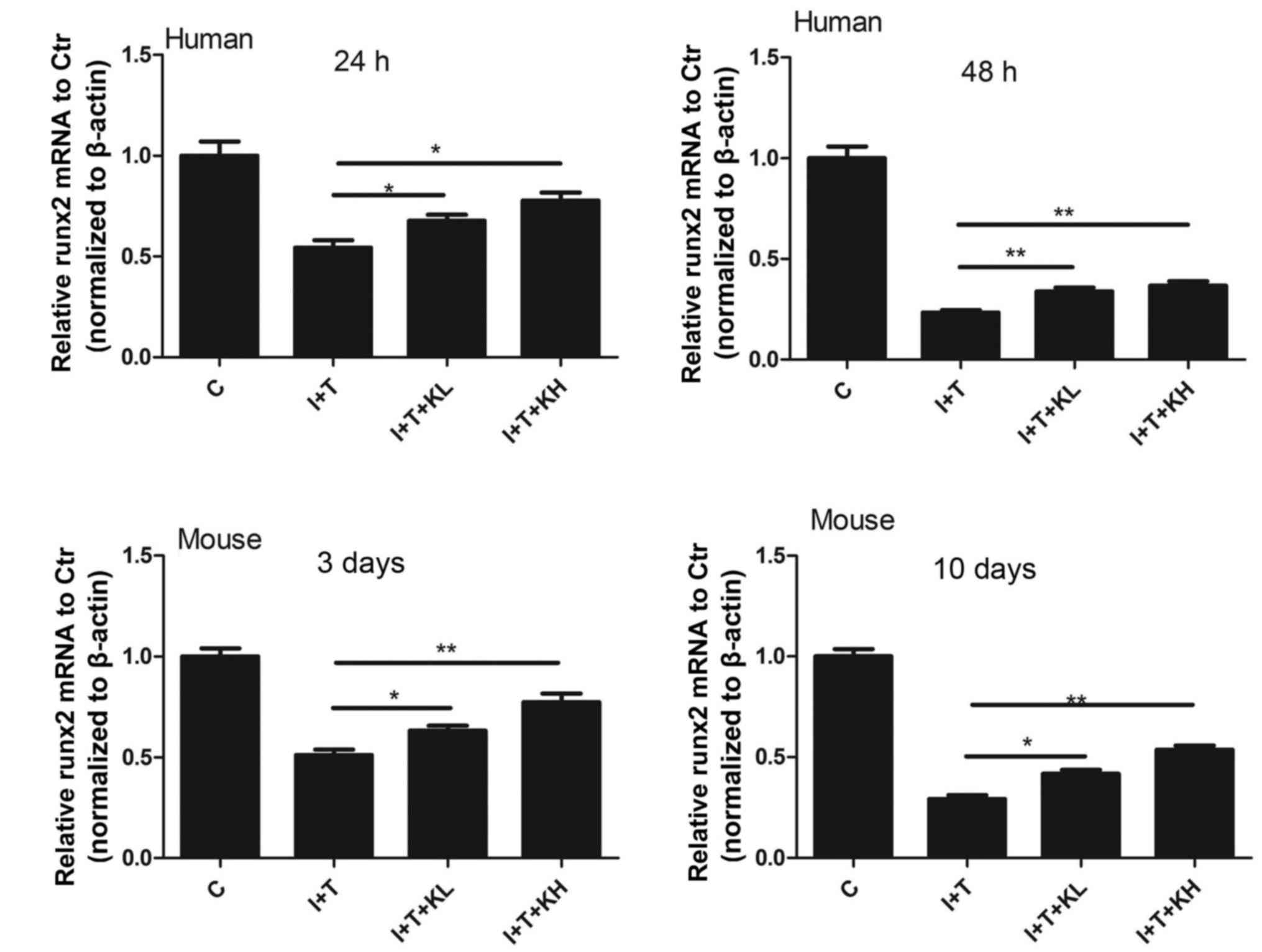
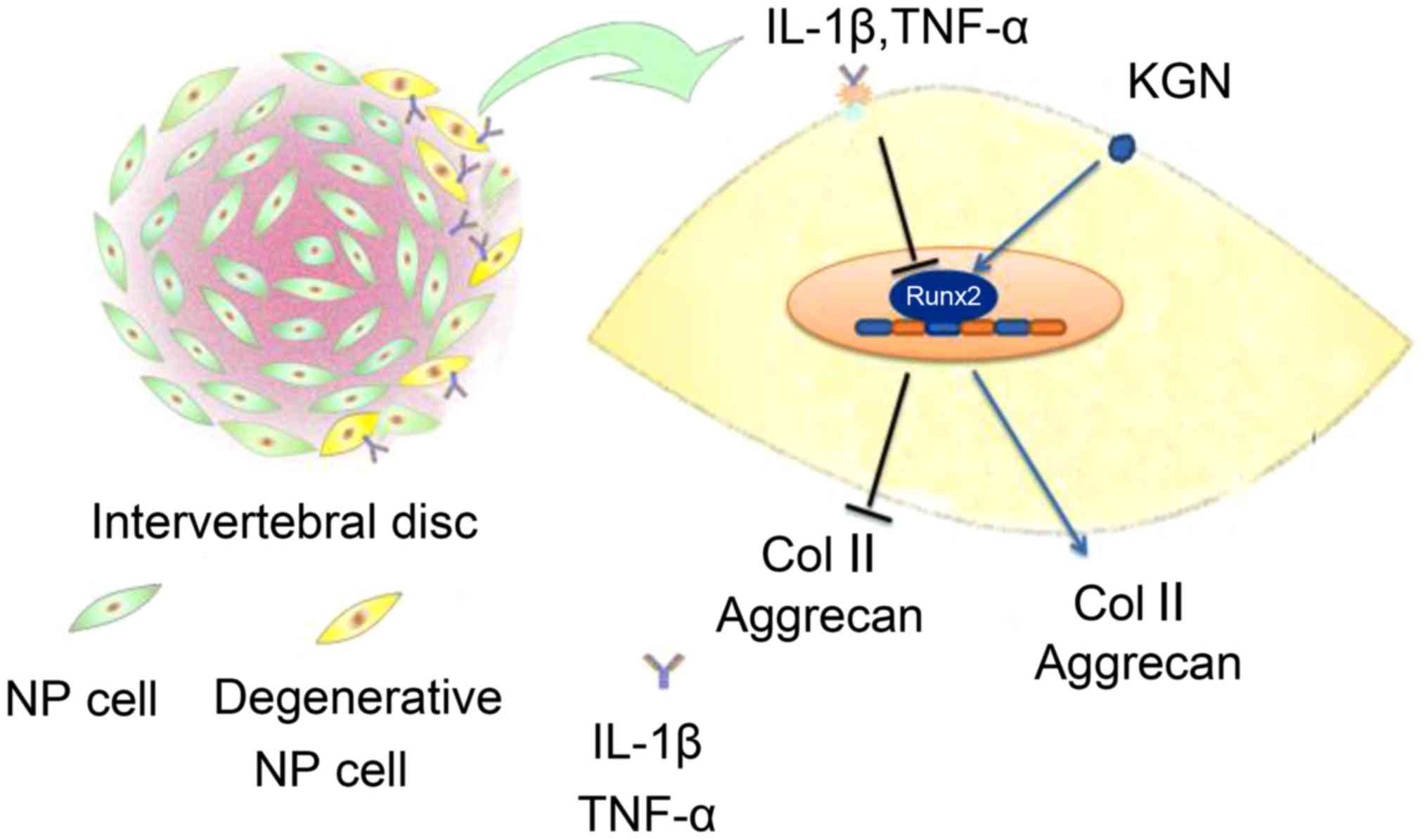
|
1
|
Andersson GB: Epidemiological features of
chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 354:581–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katz JN: Lumbar disc disorders and
low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint
Surg A. 88(Suppl 2): 21–24. 2006.
|
|
3
|
Jenkins H: Classification of low back
pain. Australas Chiropr Osteopathy. 10:91–97. 2002.
|
|
4
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human
intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 7:R732–R745.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Séguin CA, Pilliar RM, Roughley PJ and
Kandel RA: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates matrix production
and catabolism in nucleus pulposus tissue. Spine. 30:1940–1948.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA and Freemont AJ:
Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human
intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.
Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R772007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tian Y, Yuan W, Fujita N, Wang J, Wang H,
Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Inflammatory cytokines associated with
degenerative disc disease control aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS-4)
expression in nucleus pulposus cells through MAPK and NF-κB. Am J
Pathol. 182:2310–2321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Tian Y, Wang J, Phillips KL, Binch
AL, Dunn S, Cross A, Chiverton N, Zheng Z, Shapiro IM, et al:
Inflammatory cytokines induce NOTCH signaling in nucleus pulposus
cells: implications in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Biol
Chem. 288:16761–16774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu H, Pan H, Yang H, Wang J, Zhang K, Li
X, Wang H, Ding W, Li B and Zheng Z: LIM mineralization protein-1
suppresses TNF-alpha induced intervertebral disc degeneration by
maintaining nucleus pulposus extracellular matrix production and
inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases expression. J Orthop Res.
33:294–303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang X and Li X: Nucleus pulposus tissue
engineering: a brief review. Eur Spine J. 18:1564–1572. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang SZ, Rui YF, Lu J and Wang C: Cell and
molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration: current
understanding and implications for potential therapeutic
strategies. Cell Prolif. 47:381–390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vasiliadis ES, Pneumaticos SG,
Evangelopoulos DS and Papavassiliou AG: Biologic treatment of mild
and moderate intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med. 20:400–409.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sakai D and Grad S: Advancing the cellular
and molecular therapy for intervertebral disc disease. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 84:159–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Masuda K: Biological repair of the
degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors.
Eur Spine. 17(Suppl 4): 441–451. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Marini JC and Forlino A: Replenishing
cartilage from endogenous stem cells. N Engl J Med. 366:2522–2524.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Johnson K, Zhu S, Tremblay MS, Payette JN,
Wang J, Bouchez LC, Meeusen S, Althage A, Cho CY, Wu X, et al: A
stem cell-based approach to cartilage repair. Science. 336:717–721.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang ML, Ko JY, Kim JE and Im GI:
Intra-articular delivery of kartogenin-conjugated chitosan
nano/microparticles for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials.
35:9984–9994. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Johnson ZI, Schoepflin ZR, Choi H, Shapiro
IM and Risbud MV: Disc in flames: roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 30:104–116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Patel KP, Sandy JD, Akeda K, Miyamoto K,
Chujo T, An HS and Masuda K: Aggrecanases and aggrecanase-generated
fragments in the human intervertebral disc at early and advanced
stages of disc degeneration. Spine. 32:2596–2603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Videman T, Saarela J, Kaprio J, Näkki A,
Levälahti E, Gill K, Peltonen L and Battié MC: Associations of 25
structural, degra-dative, and inflammatory candidate genes with
lumbar disc desiccation, bulging, and height narrowing. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:470–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V and
Myers RR: 2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies:
exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus
pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and
behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine. 25:2975–2980. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Beierfuss A, Dietrich H, Kremser C,
Hunjadi M, Ritsch A, Rulicke T, Thome C and Mern DS: Knockout of
Apolipoprotein E in rabbit promotes premature intervertebral disc
degeneration: A new in vivo model for therapeutic approaches of
spinal disc disorders. PloS One. 12:pp. e01875642017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pelle DW, Peacock JD, Schmidt CL,
Kampfschulte K, Scholten DJ II, Russo SS, Easton KJ and Steensma
MR: Genetic and functional studies of the intervertebral disc: a
novel murine intervertebral disc model. PLoS One. 9:pp.
e1124542014, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeda S, Bonnamy JP, Owen MJ, Ducy P and
Karsenty G: Continuous expression of Cbfa1 in nonhypertrophic
chondrocytes uncovers its ability to induce hypertrophic
chondrocyte differentiation and partially rescues Cbfa1-deficient
mice. Genes Dev. 15:467–481. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Studer D, Millan C, Öztürk E,
Maniura-Weber K and Zenobi-Wong M: Molecular and biophysical
mechanisms regulating hypertrophic differentiation in chondrocytes
and mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 24:118–135. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Zhou J, Zhang N, Zhang X and Li Q:
A heterocyclic molecule kartogenin induces collagen synthesis of
human dermal fibroblasts by activating the smad4/smad5 pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:568–574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu X, Shi D, Shen Y, Xu Z, Dai J, Chen D,
Teng H and Jiang Q: Full-thickness cartilage defects are repaired
via a microfracture technique and intraarticular injection of the
small-molecule compound kartogenin. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA,
Risbud MV and Anderson DG: The molecular basis of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:318–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|