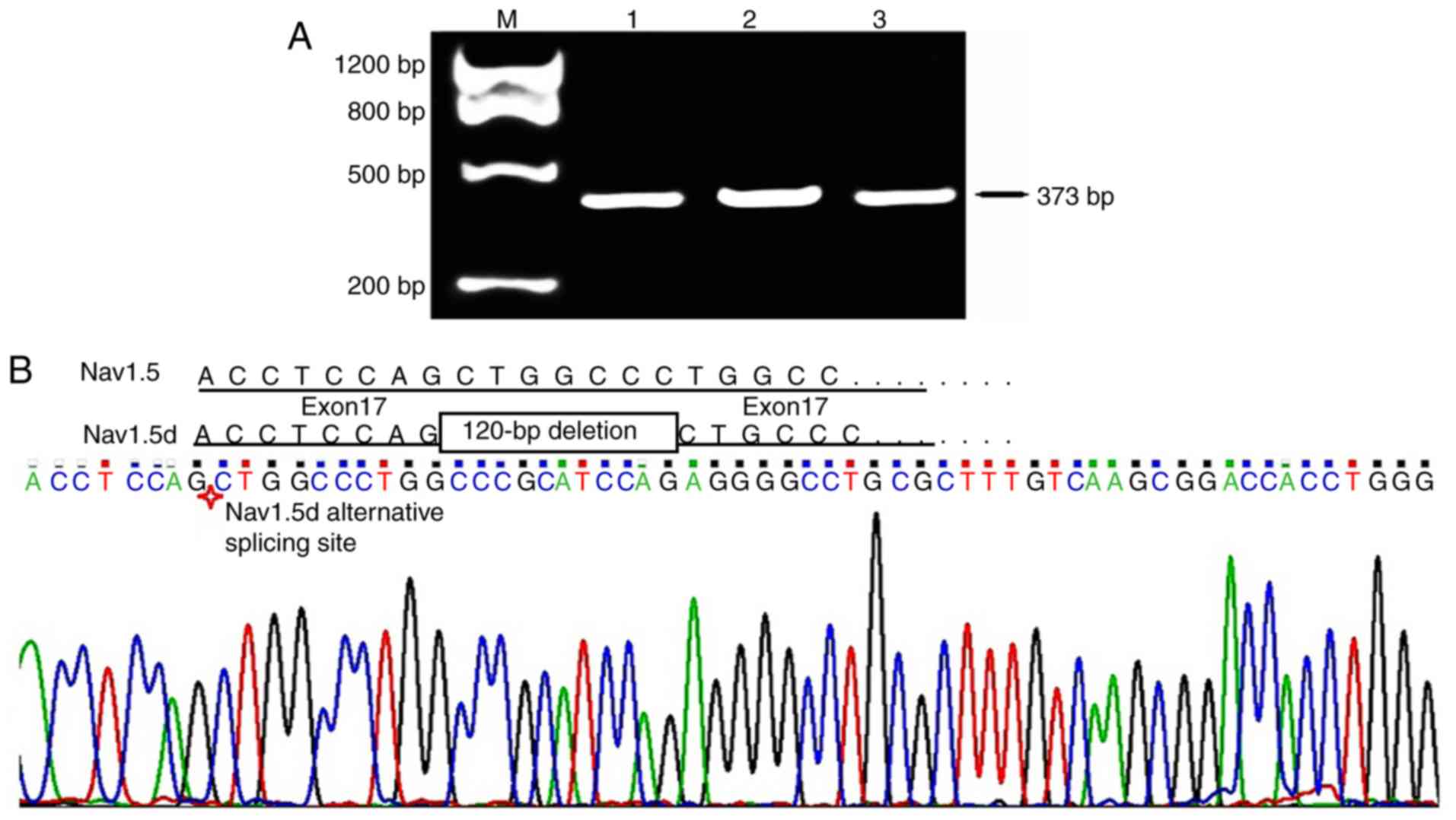
|
1
|
Eijkelkamp N, Linley JE, Baker MD, Minett
MS, Cregg R, Werdehausen R, Rugiero F and Wood JN: Neurological
perspectives on voltage-gated sodium channels. Brain.
135:2585–2612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu W, Tian C, Li T, Yang M, Hou H and Shu
Y: Distinct contributions of Na(v)1.6 and Na(v)1.2 in action
potential initiation and backpropagation. Nat Neurosci.
12:996–1002. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kole MH, Ilschner SU, Kampa BM, Williams
SR, Ruben PC and Stuart GJ: Action potential generation requires a
high sodium channel density in the axon initial segment. Nat
Neurosci. 11:178–186. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Catterall WA: From ionic currents to
molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated
sodium channels. Neuron. 26:13–25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu FH, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Gutman GA and
Catterall WA: Overview of molecular relationships in the
voltage-gated ion channel superfamily. Pharmacol Rev. 57:387–395.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Catterall WA: Voltage-gated sodium
channels at 60: Structure, function and pathophysiology. J Physiol.
590:2577–2589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cummins TR, Aglieco F, Renganathan M,
Herzog RI, Dib-Hajj SD and Waxman SG: Nav1.3 sodium channels: Rapid
repriming and slow closed-state inactivation display quantitative
differences after expression in a mammalian cell line and in spinal
sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 21:5952–5961. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noda M, Ikeda T, Kayano T, Suzuki H,
Takeshima H, Kurasaki M, Takahashi H and Numa S: Existence of
distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature.
320:188–192. 1986. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schaller KL, Krzemien DM, Yarowsky PJ,
Krueger BK and Caldwell JH: A novel, abundant sodium channel
expressed in neurons and glia. J Neurosci. 15:3231–3242.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yarowsky PJ, Krueger BK, Olson CE,
Clevinger EC and Koos RD: Brain and heart sodium channel subtype
mRNA expression in rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:9453–9457. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
White JA, Alonso A and Kay AR: A
heart-like Na+ current in the medial entorhinal cortex.
Neuron. 11:1037–1047. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoehn K, Watson TW and MacVicar BA: A
novel tetrodotoxin-insensitive, slow sodium current in striatal and
hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 10:543–552. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng D, Kyle JW, Martin RL, Ambler KS and
Hanck DA: Cardiac sodium channels expressed in a peripheral
neurotumor-derived cell line, RT4-B8. Am J Physiol.
270:C1522–C1531. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deisz RA: A tetrodotoxin-insensitive
[corrected] sodium current initiates burst firing of neocortical
neurons. Neuroscience. 70:341–351. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu XQ, Dib-Hajj S, Rizzo MA and Waxman SG:
TTX-sensitive and -resistant Na+ currents, and mRNA for
the TTX-resistant rH1 channel, are expressed in B104 neuroblastoma
cells. J Neurophysiol. 77:236–246. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hartmann HA, Colom LV, Sutherland ML and
Noebels JL: Selective localization of cardiac SCN5A sodium channels
in limbic regions of rat brain. Nat Neurosci. 2:593–595. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Donahue LM, Coates PW, Lee VH, Ippensen
DC, Arze SE and Poduslo SE: The cardiac sodium channel mRNA is
expressed in the developing and adult rat and human brain. Brain
Res. 887:335–343. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gersdorff Korsgaard MP, Christophersen P,
Ahring PK and Olesen SP: Identification of a novel voltage-gated
Na+ channel rNa(v)1.5a in the rat hippocampal progenitor
stem cell line HiB5. Pflugers Arch. 443:18–30. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu L, Nishiyama K, Hollyfield JG and Wang
Q: Localization of Nav1.5 sodium channel protein in the mouse
brain. Neuroreport. 13:2547–2551. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ou SW, Kameyama A, Hao LY, Horiuchi M,
Minobe E, Wang WY, Makita N and Kameyama M: Tetrodotoxin-resistant
Na+ channels in human neuroblastoma cells are encoded by
new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A. Eur J Neurosci. 22:793–801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chioni AM, Fraser SP, Pani F, Foran P,
Wilkin GP, Diss JK and Djamgoz MB: A novel polyclonal antibody
specific for the Na(v)1.5 voltage-gated Na(+) channel ʻneonatalʼ
splice form. J Neurosci Methods. 147:88–98. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Frenz CT, Hansen A, Dupuis ND, Shultz N,
Levinson SR, Finger TE and Dionne VE: NaV1.5 sodium channel window
currents contribute to spontaneous firing in olfactory sensory
neurons. J Neurophysiol. 112:1091–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Zong ZH, Lin L,
Kameyama M and Kameyama A: New variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A encode
Na+ channels in the brain. J Neurogenet. 22:57–75. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Kameyama M,
Kameyama A and Zong ZH: Analysis of four novel variants of
Nav1.5/SCN5A cloned from the brain. Neurosci Res. 64:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schroeter A, Walzik S, Blechschmidt S,
Haufe V, Benndorf K and Zimmer T: Structure and function of splice
variants of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.5. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:16–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Onkal R, Mattis JH, Fraser SP, Diss JK,
Shao D, Okuse K and Djamgoz MB: Alternative splicing of Nav1.5: An
electrophysiological comparison of ʻneonatalʼ and ʻadultʼ isoforms
and critical involvement of a lysine residue. J Cell Physiol.
216:716–726. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Walzik S, Schroeter A, Benndorf K and
Zimmer T: Alternative splicing of the cardiac sodium channel
creates multiple variants of mutant T1620K channels. PLoS One.
6:e191882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rook MB, Evers MM, Vos MA and Bierhuizen
MF: Biology of cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 expression. Cardiovasc
Res. 93:12–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Black JA, Newcombe J and Waxman SG:
Astrocytes within multiple sclerosis lesions upregulate sodium
channel Nav1.5. Brain. 133:835–846. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aurlien D, Leren TP, Tauboll E and
Gjerstad L: New SCN5A mutation in a SUDEP victim with idiopathic
epilepsy. Seizure. 18:158–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Parisi P, Oliva A, Coll Vidal M, Partemi
S, Campuzano O, Iglesias A, Pisani D, Pascali VL, Paolino MC, Villa
MP, et al: Coexistence of epilepsy and Brugada syndrome in a family
with SCN5A mutation. Epilepsy Res. 105:415–418. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kerr NC, Gao Z, Holmes FE, Hobson SA,
Hancox JC, Wynick D and James AF: The sodium channel Nav1.5a is the
predominant isoform expressed in adult mouse dorsal root ganglia
and exhibits distinct inactivation properties from the full-length
Nav1.5 channel. Mol Cell Neurosci. 35:283–291. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zimmer T, Bollensdorff C, Haufe V,
Birch-Hirschfeld E and Benndorf K: Mouse heart Na+
channels: Primary structure and function of two isoforms and
alternatively spliced variants. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
282:H1007–H1017. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kerr NC, Holmes FE and Wynick D: Novel
isoforms of the sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.5 are produced by a
conserved mechanism in mouse and rat. J Biol Chem. 279:24826–24833.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wasner U, Geist B, Battefeld A, Bauer P,
Müller J, Rolfs A and Strauss U: Specific properties of sodium
currents in multipotent striatal progenitor cells. Eur J Neurosci.
28:1068–1079. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ren CT, Li DM, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Lin Y, Zong
ZH, Kameyama M and Kameyama A: Cloning and expression of the two
new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A in rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem.
365:139–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Blechschmidt S, Haufe V, Benndorf K and
Zimmer T: Voltage-gated Na+ channel transcript patterns
in the mammalian heart are species-dependent. Prog Biophys Mol
Biol. 98:309–318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Makielski JC, Ye B, Valdivia CR, Pagel MD,
Pu J, Tester DJ and Ackerman MJ: A ubiquitous splice variant and a
common polymorphism affect heterologous expression of recombinant
human SCN5A heart sodium channels. Circ Res. 93:821–828. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tan BH, Valdivia CR, Rok BA, Ye B, Ruwaldt
KM, Tester DJ, Ackerman MJ and Makielski JC: Common human SCN5A
polymorphisms have altered electrophysiology when expressed in
Q1077 splice variants. Heart Rhythm. 2:741–747. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tan BH, Valdivia CR, Song C and Makielski
JC: Partial expression defect for the SCN5A missense mutation
G1406R depends on splice variant background Q1077 and rescue by
mexiletine. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H1822–H1828. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang DW, Desai RR, Crotti L, Arnestad M,
Insolia R, Pedrazzini M, Ferrandi C, Vege A, Rognum T, Schwartz PJ
and George AL Jr: Cardiac sodium channel dysfunction in sudden
infant death syndrome. Circulation. 115:368–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Camacho JA, Hensellek S, Rougier JS,
Blechschmidt S, Abriel H, Benndorf K and Zimmer T: Modulation of
Nav1.5 channel function by an alternatively spliced sequence in the
DII/DIII linker region. J Biol Chem. 281:9498–9506. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xing D, Wang J, Ou S, Wang Y, Qiu B, Ding
D, Guo F and Gao Q: Expression of neonatal Nav1.5 in human brain
astrocytoma and its effect on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis
of astrocytoma cells. Oncol Rep. 31:2692–2700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brackenbury WJ, Chioni AM, Diss JK and
Djamgoz MB: The neonatal splice variant of Nav1.5 potentiates in
vitro invasive behaviour of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 101:149–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Chioni AM, Mycielska
ME, Pan H, Yamaci RF, Pani F, Siwy Z, Krasowska M, Grzywna Z, et
al: Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of
human breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5381–5389.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
House CD, Vaske CJ, Schwartz AM, Obias V,
Frank B, Luu T, Sarvazyan N, Irby R, Strausberg RL, Hales TG, et
al: Voltage-gated Na+ channel SCN5A is a key regulator
of a gene transcriptional network that controls colon cancer
invasion. Cancer Res. 70:6957–6967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|