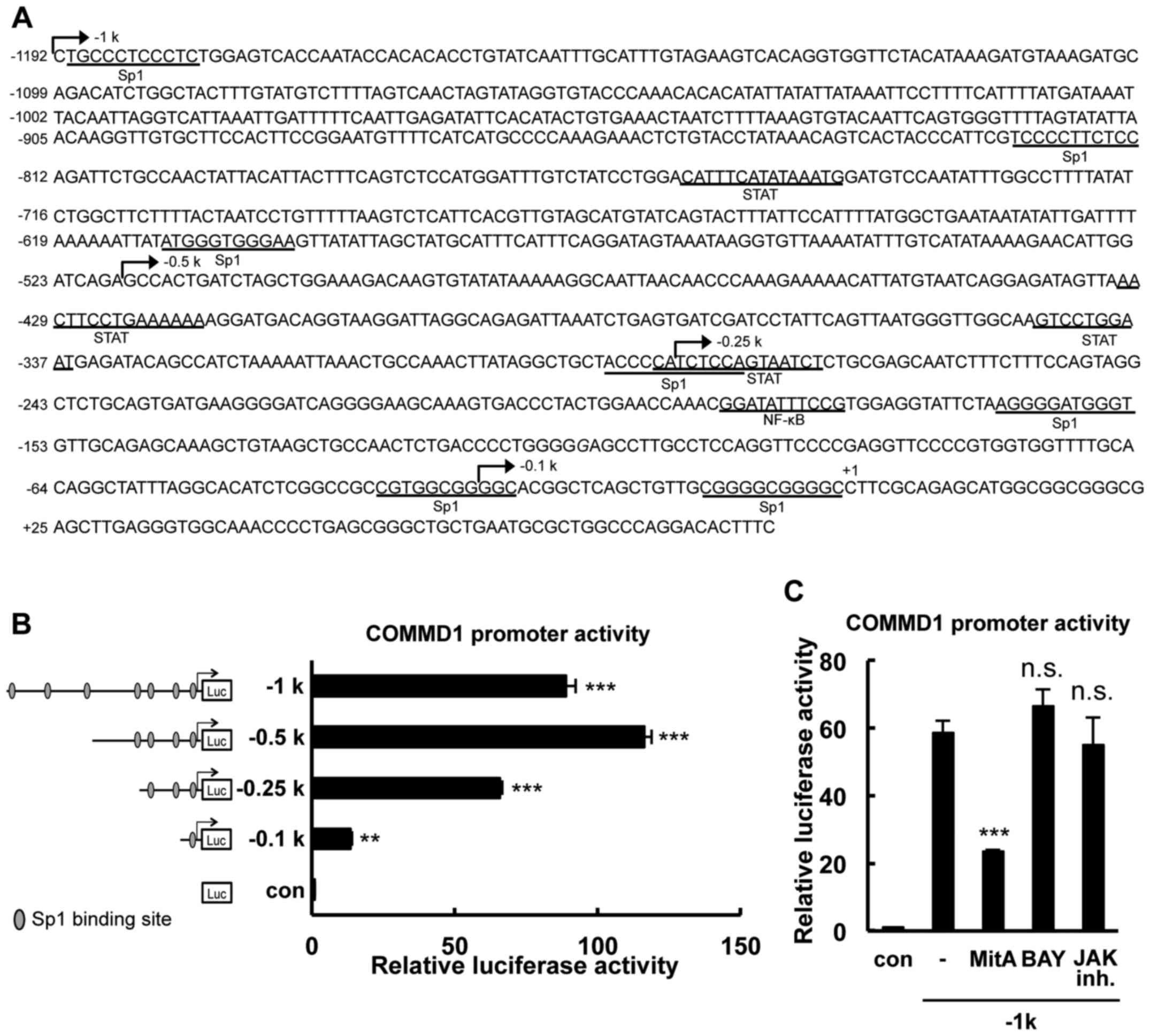
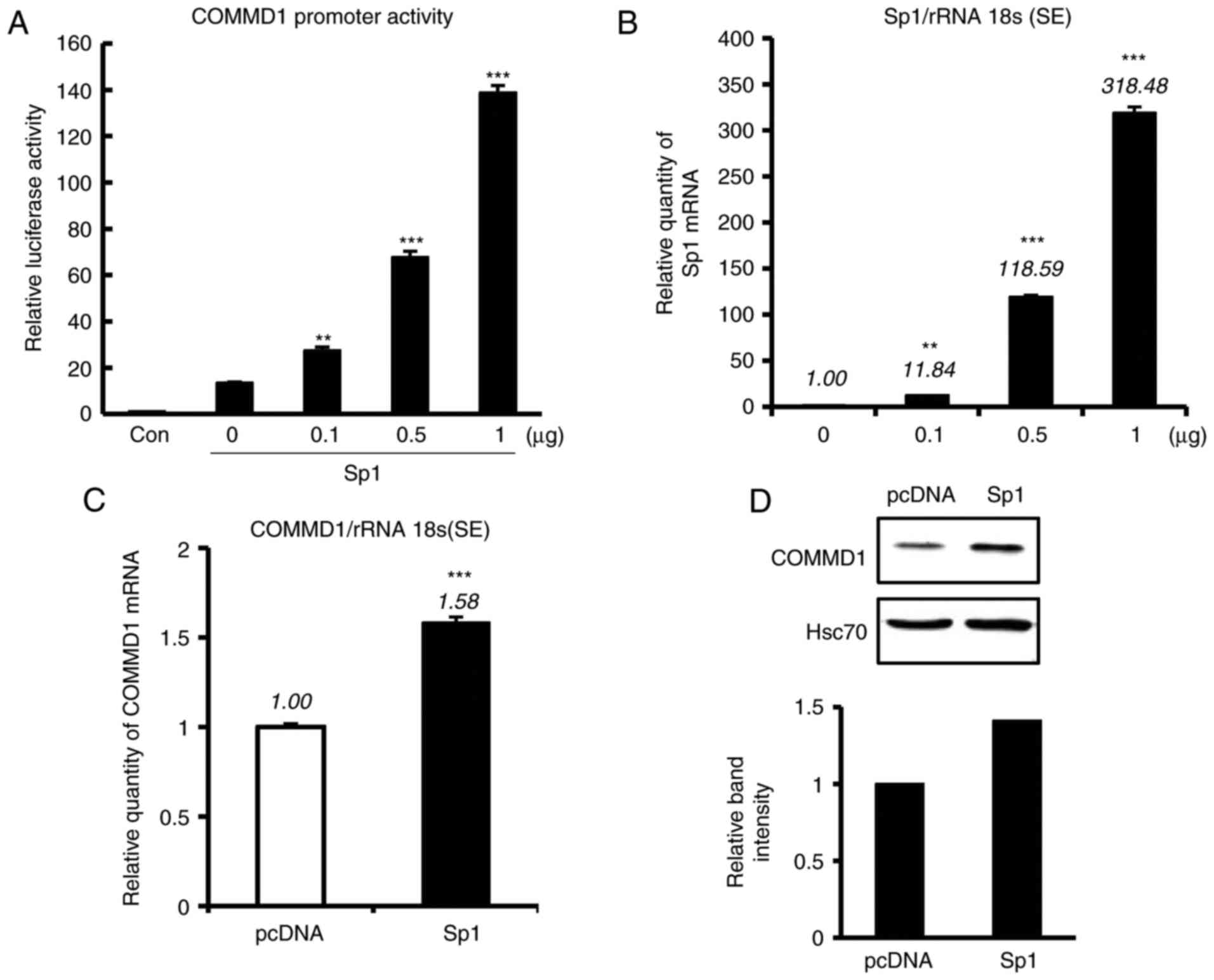
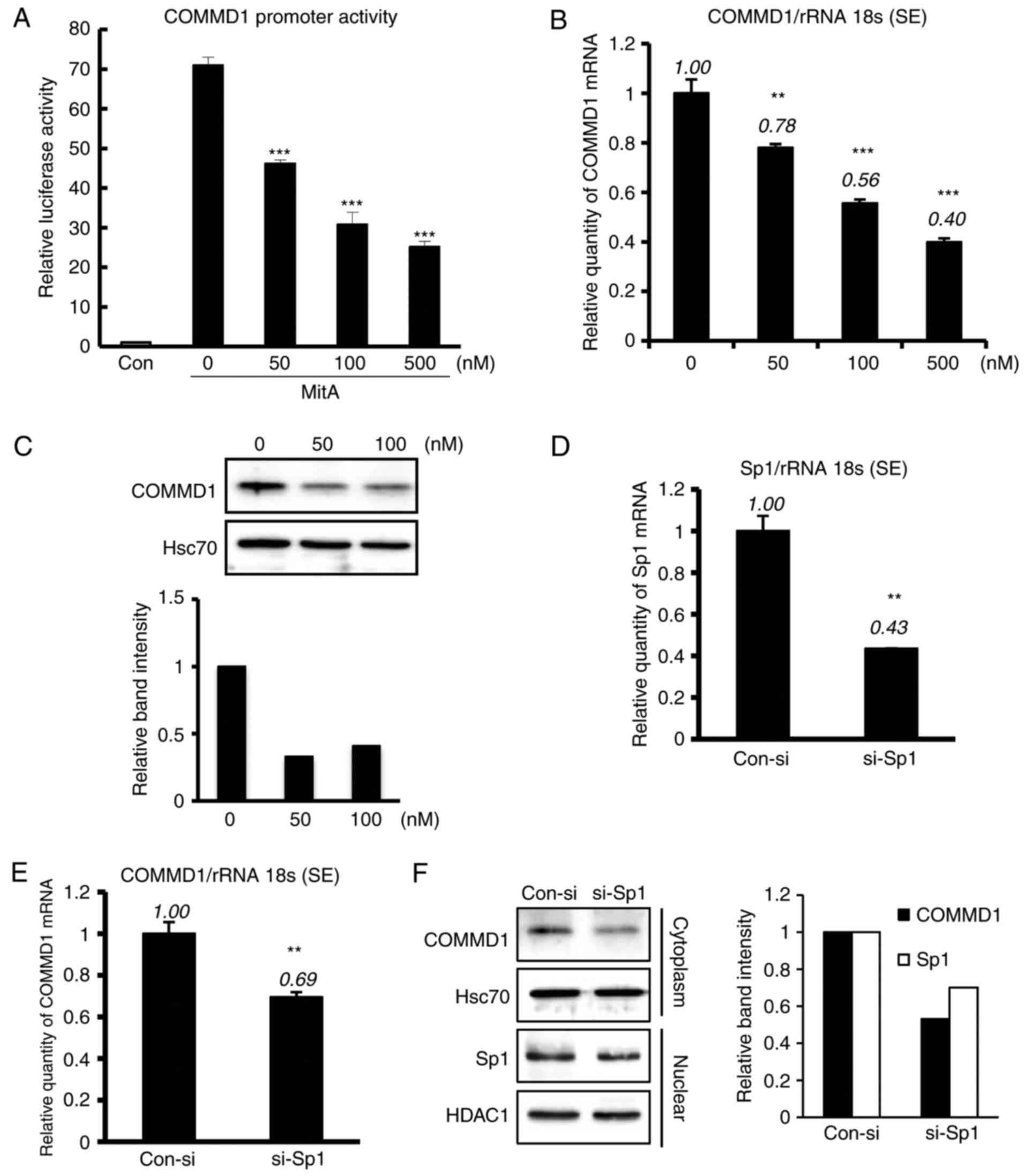
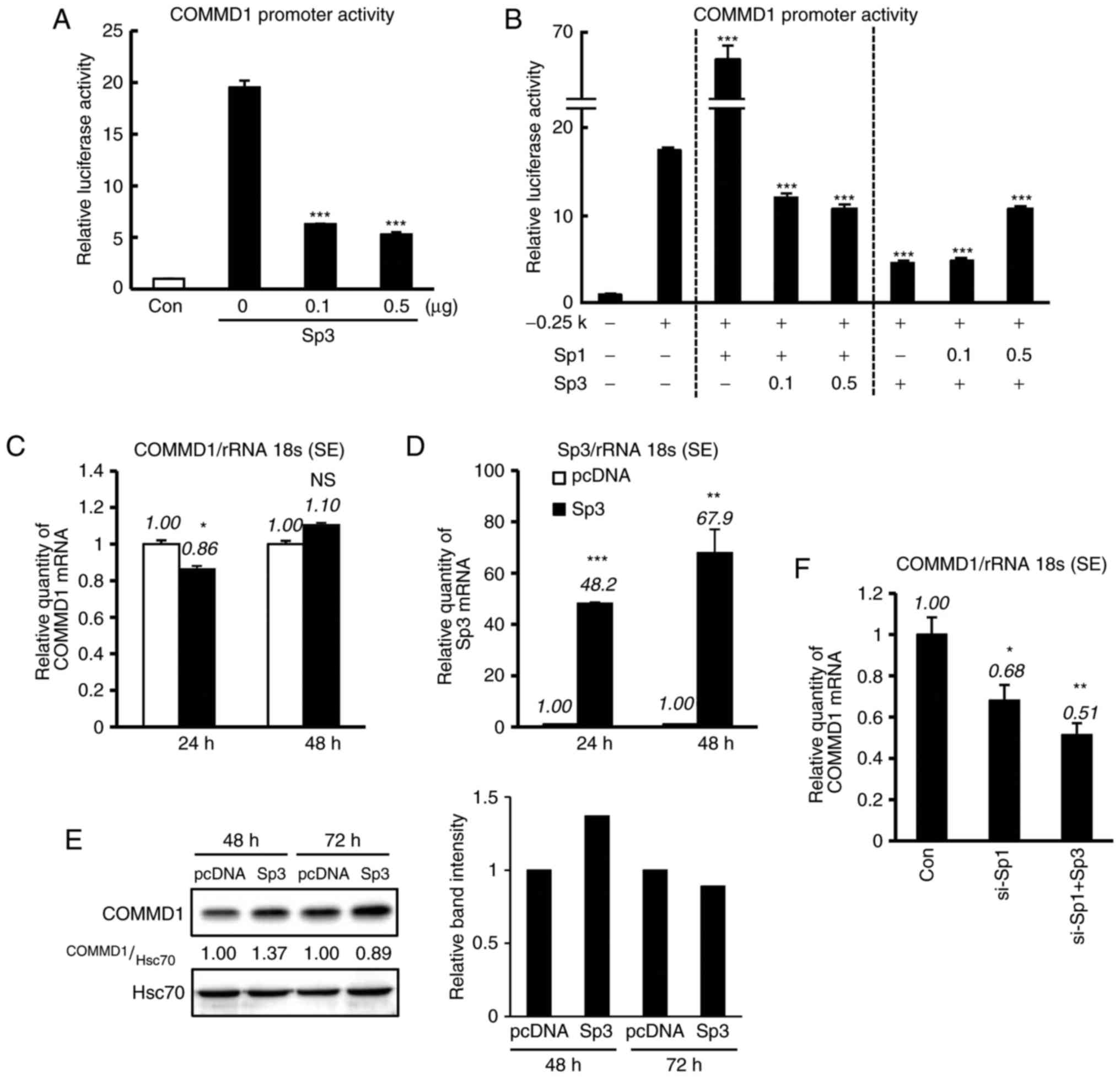
|
1
|
Burstein E, Hoberg JE, Wilkinson AS,
Rumble JM, Csomos RA, Komarck CM, Maine GN, Wilkinson JC, Mayo MW
and Duckett CS: COMMD proteins, a novel family of structural and
functional homologs of MURR1. J Biol Chem. 280:22222–22232. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tao TY, Liu F, Klomp L, Wijmenga C and
Gitlin JD: The copper toxicosis gene product Murr1 directly
interacts with the Wilson disease protein. J Biol Chem.
278:41593–41596. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Bie P, van de Sluis B, Burstein E, van
de Berghe PV, Muller P, Berger R, Gitlin JD, Wijmenga C and Klomp
LW: Distinct Wilson's disease mutations in ATP7B are associated
with enhanced binding to COMMD1 and reduced stability of ATP7B.
Gastroenterology. 133:1316–1326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vonk WI, de Bie P, Wichers CG, van den
Berghe PV, van der Plaats R, Berger R, Wijmenga C, Klomp LW and van
de Sluis B: The copper-transporting capacity of ATP7A mutants
associated with Menkes disease is ameliorated by COMMD1 as a result
of improved protein expression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:149–163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Ke Y, Butt AG, Swart M, Liu YF and
McDonald FJ: COMMD1 downregulates the epithelial sodium channel
through Nedd4-2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F1445–F1456. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maine GN, Mao X, Komarck CM and Burstein
E: COMMD1 promotes the ubiquitination of NF-kappaB subunits through
a cullin-containing ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J. 26:436–447. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Drevillon L, Tanguy G, Hinzpeter A, Arous
N, de Becdelièvre A, Aissat A, Tarze A, Goossens M and Fanen P:
COMMD1-mediated ubiquitination regulates CFTR trafficking. PLoS
One. 6:e183342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van de Sluis B, Mao X, Zhai Y, Groot AJ,
Vermeulen JF, van der Wall E, van Diest PJ, Hofker MH, Wijmenga C,
Klomp LW, et al: COMMD1 disrupts HIF-1alpha/beta dimerization and
inhibits human tumor cell invasion. J Clin Invest. 120:2119–2130.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ganesh L, Burstein E, Guha-Nijogi A,
Louder MK, Mascola JR, Klomp LW, Wijmenga C, Duckett CS and Nabel
GJ: The gene product Murr1 restricts HIV-1 replication in resting
CD4+ lymphocytes. Nature. 426:853–857. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Taura M, Kudo E, Kariya R, Goto H, Matsuda
K, Hattori S, Vaeteewoottacharn K, McDonald F, Suico MA, Shuto T,
et al: COMMD1/Murr1 reinforces HIV-1 latent infection through IκB-α
stabilization. J Virol. 89:2643–2658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Beishline K and Azizkhan-Clifford J: Sp1
and the 'hallmarks of cancer'. FEBS J. 282:224–258. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Resendes KK and Rosmarin AG: Sp1 control
of gene expression in myeloid cells. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.
14:171–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li L, He S, Sun J and Davie J: Gene
regulation by Sp1 and Sp3. Biochem Cell Biol. 82:460–471. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Majello B, De Luca P and Lania L: Sp3 is a
bifunctional transcription regulator with modular independent
activation and repression domains. J Biol Chem. 272:4021–4026.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taura M, Kariya R, Kudo E, Goto H, Iwawaki
T, Amano M, Suico MA, Kai H, Mitsuya H and Okada S: Comparative
analysis of ER stress response into HIV protease inhibitors:
Lopinavir but not darunavir induces potent ER stress response via
ROS/JNK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:778–788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suico MA, Taura M, Kudo E, Gotoh K, Shuto
T, Okada S and Kai H: The ETS factor myeloid Elf-1-like factor
(MEF)/Elf4 is transcriptionally and functionally activated by
hypoxia. Biol Pharm Bull. 39:641–647. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kudo E, Taura M, Matsuda K, Shimamoto M,
Kariya R, Goto H, Hattori S, Kimura S and Okada S: Inhibition of
HIV-1 replication by a tricyclic coumarin GUT-70 in acutely and
chronically infected cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:606–609. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taura M, Eguma A, Suico MA, Shuto T, Koga
T, Komatsu K, Komune T, Sato T, Saya H, Li JD and Kai H: p53
regulates Toll-like receptor 3 expression and function in human
epithelial cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 28:6557–6567. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greenwel P, Inagaki Y, Hu W, Walsh M and
Ramirez F: Sp1 is required for the early response of alpha2(I)
collagen to transforming growth factor-beta1. J Biol Chem.
272:19738–19745. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Chan L, Bartuzi P, Melton SD, Weber
A, Ben-Shlomo S, Varol C, Raetz M, Mao X, Starokadomskyy P, et al:
Copper metabolism domain-containing 1 represses genes that promote
inflammation and protects mice from colitis and colitis-associated
cancer. Gastroenterology. 147:184–195.e3. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yeh DW, Chen YS, Lai CY, Liu YL, Lu CH, Lo
JF, Chen L, Hsu LC, Luo Y, Xiang R and Chuang TH: Downregulation of
COMMD1 by miR-205 promotes a positive feedback loop for amplifying
inflammatory- and stemness-associated properties of cancer cells.
Cell Death Differ. 23:841–852. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
O'Connor L, Gilmour J and Bonifer C: The
role of the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor Sp1 in
tissue-specific transcriptional regulation and in disease. Yale J
Biol Med. 89:513–525. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang DE, Hetherington CJ, Tan S, Dziennis
SE, Gonzalez DA, Chen HM and Tenen DG: Sp1 is a critical factor for
the monocytic specific expression of human CD14. J Biol Chem.
269:11425–11434. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tone M, Powell MJ, Tone Y, Thompson SA and
Waldmann H: IL-10 gene expression is controlled by the
transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. J Immunol. 165:286–291. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Le Goff W, Guerin M, Petit L, Chapman MJ
and Thillet J: Regulation of human CETP gene expression: Role of
SP1 and SP3 transcription factors at promoter sites-690, -629, and
-37. J Lipid Res. 44:1322–1331. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Apt D, Watts RM, Suske G and Bernard HU:
High Sp1/Sp3 ratios in epithelial cells during epithelial
differentiation and cellular transformation correlate with the
activation of the HPV-16 promoter. Virology. 224:281–291. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Encarnacao PC, Ramirez VP, Zhang C and
Aneskievich BJ: Sp sites contribute to basal and inducible
expression of the human TNIP1 (TNFα-inducible protein 3-interacting
protein 1) promoter. Biochem J. 452:519–529. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li R, Hodny Z, Luciakova K, Barath P and
Nelson BD: Sp1 activates and inhibits transcription from separate
elements in the proximal promoter of the human adenine nucleotide
translocase 2 (ANT2) gene. J Biol Chem. 271:18925–18930. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|