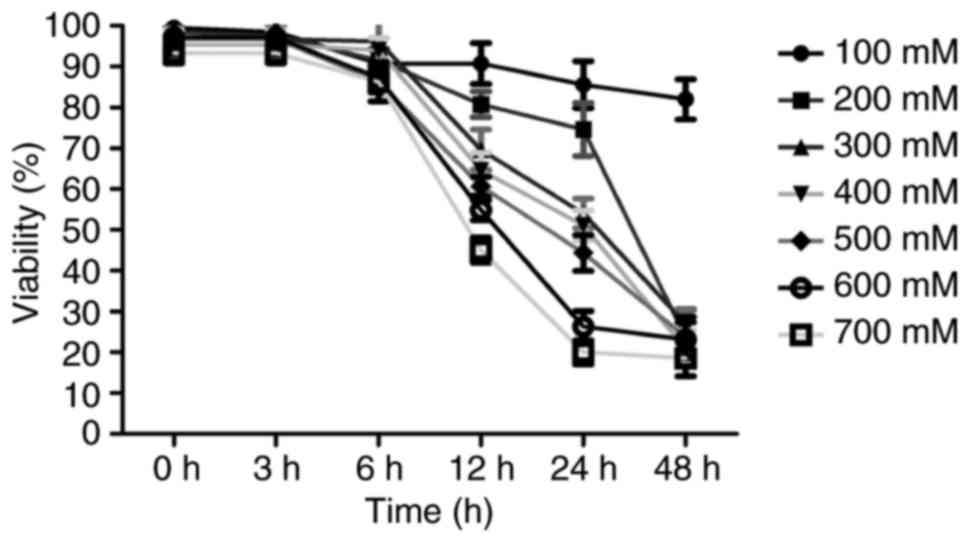
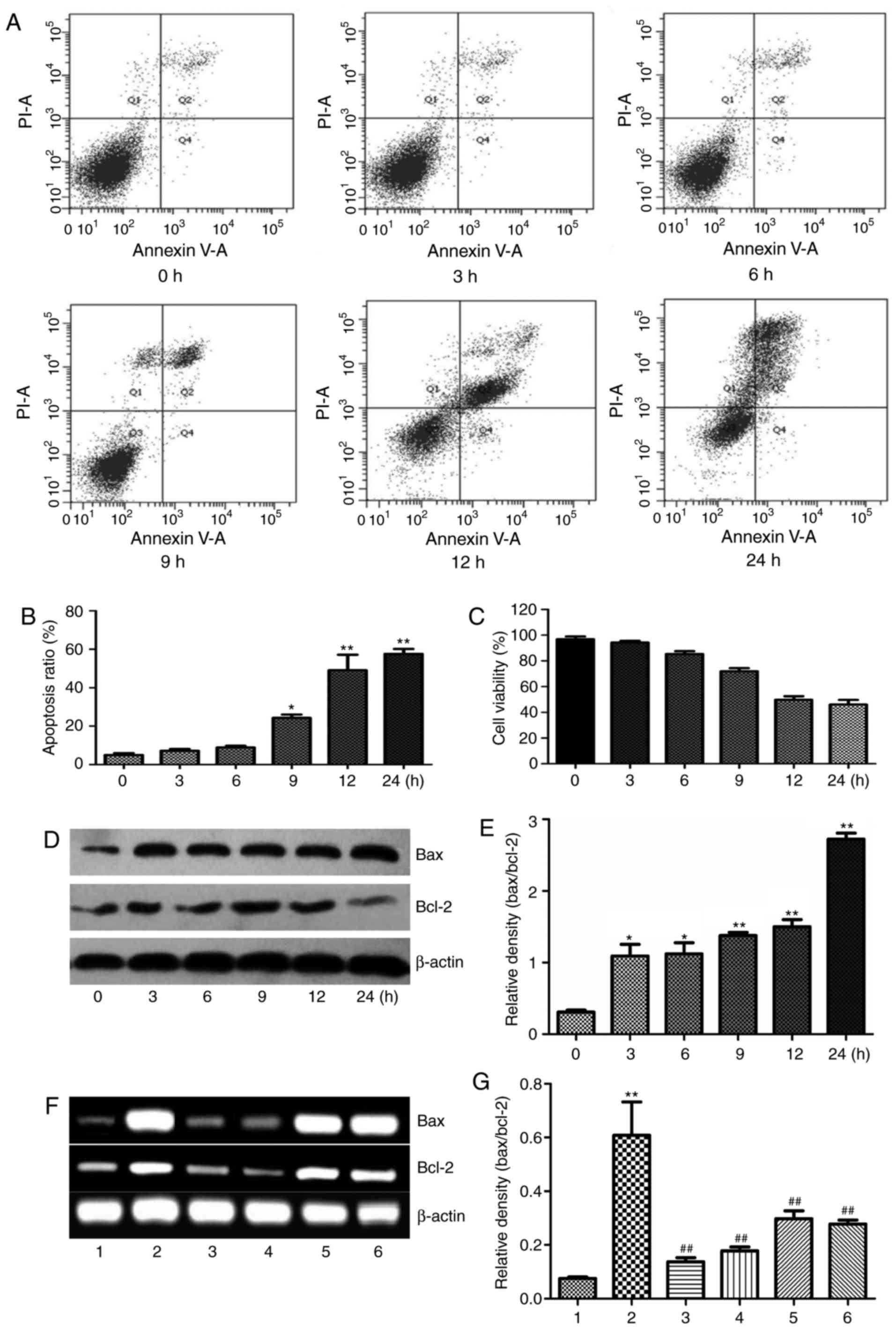
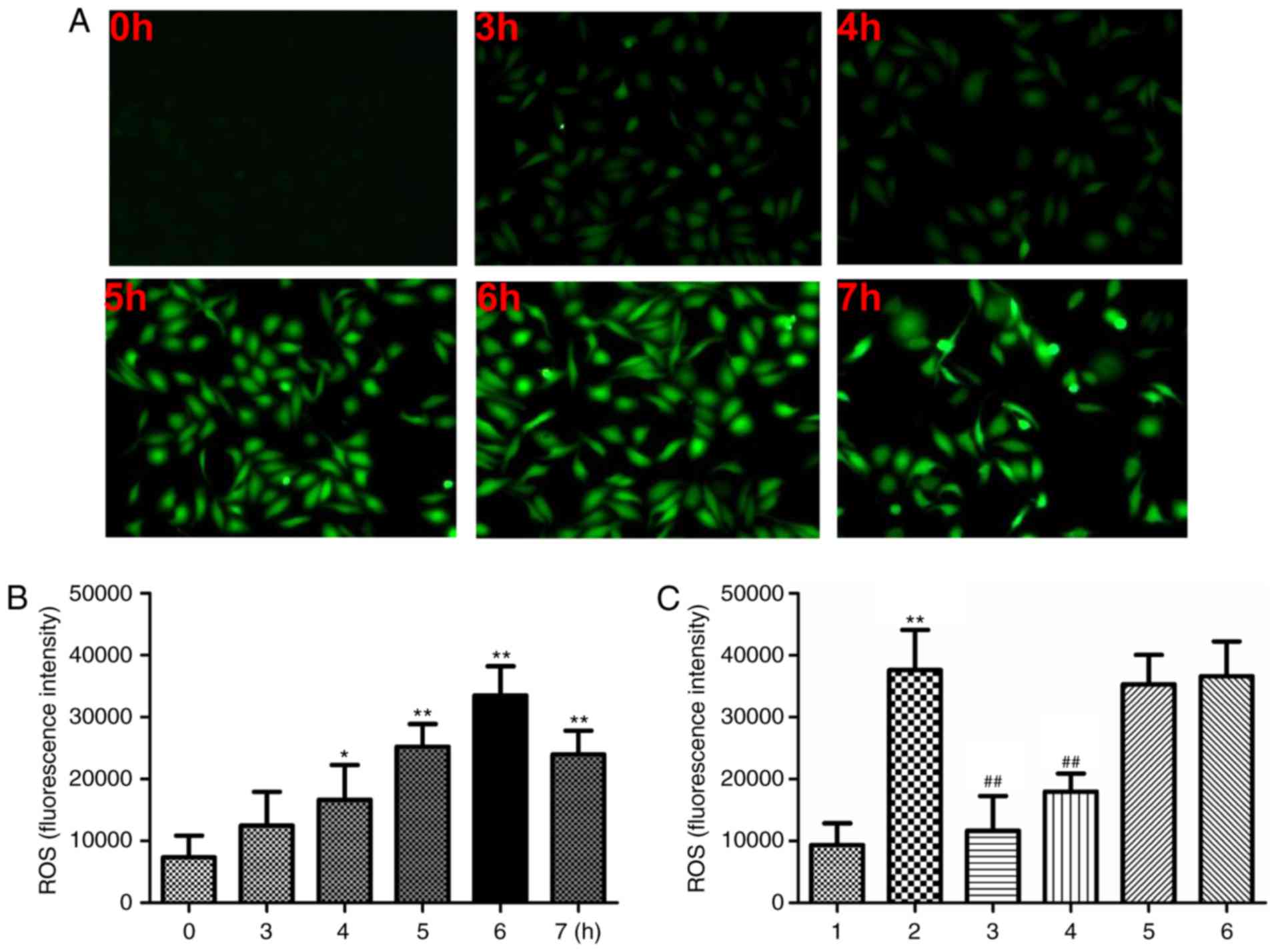
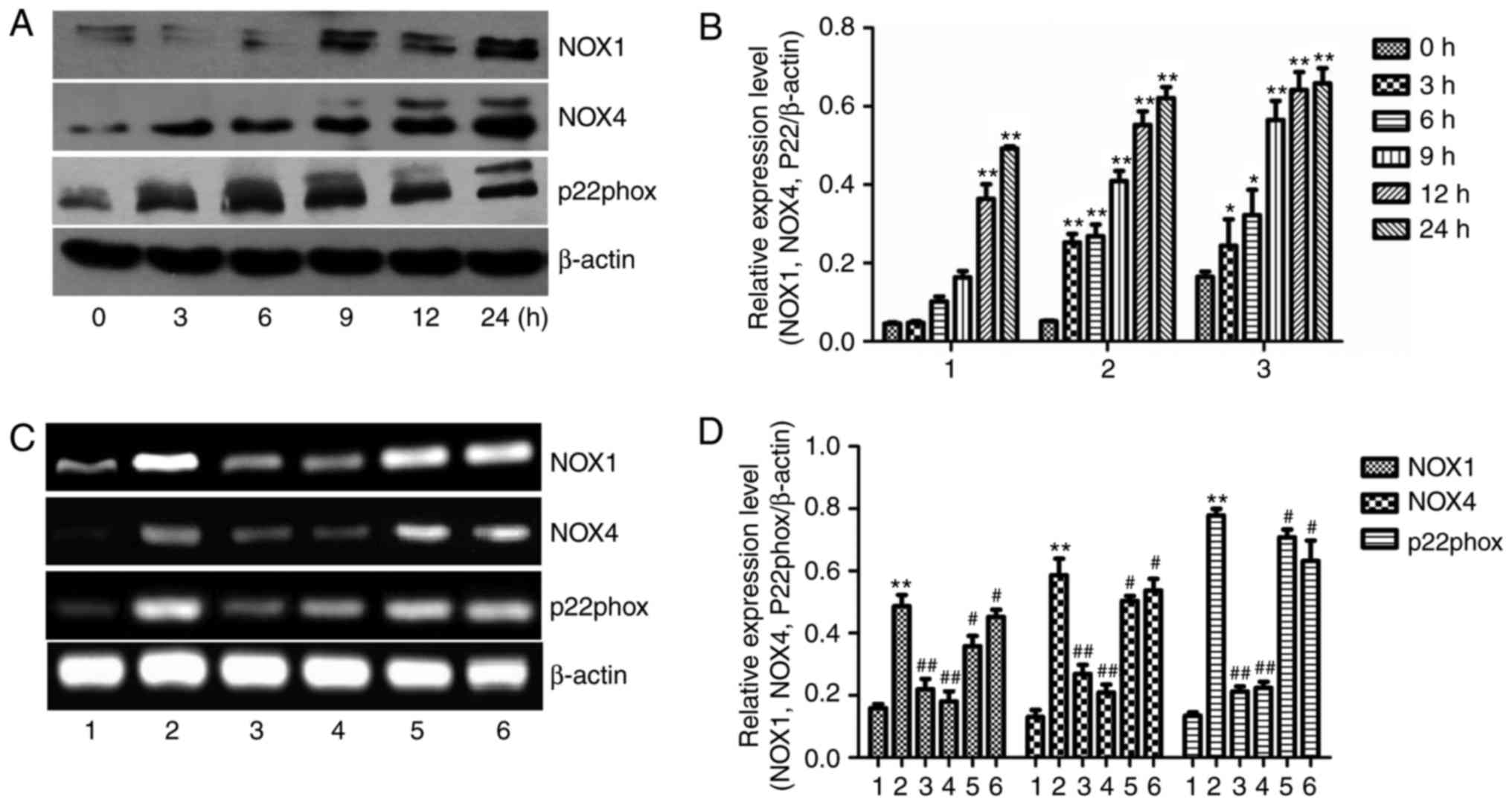
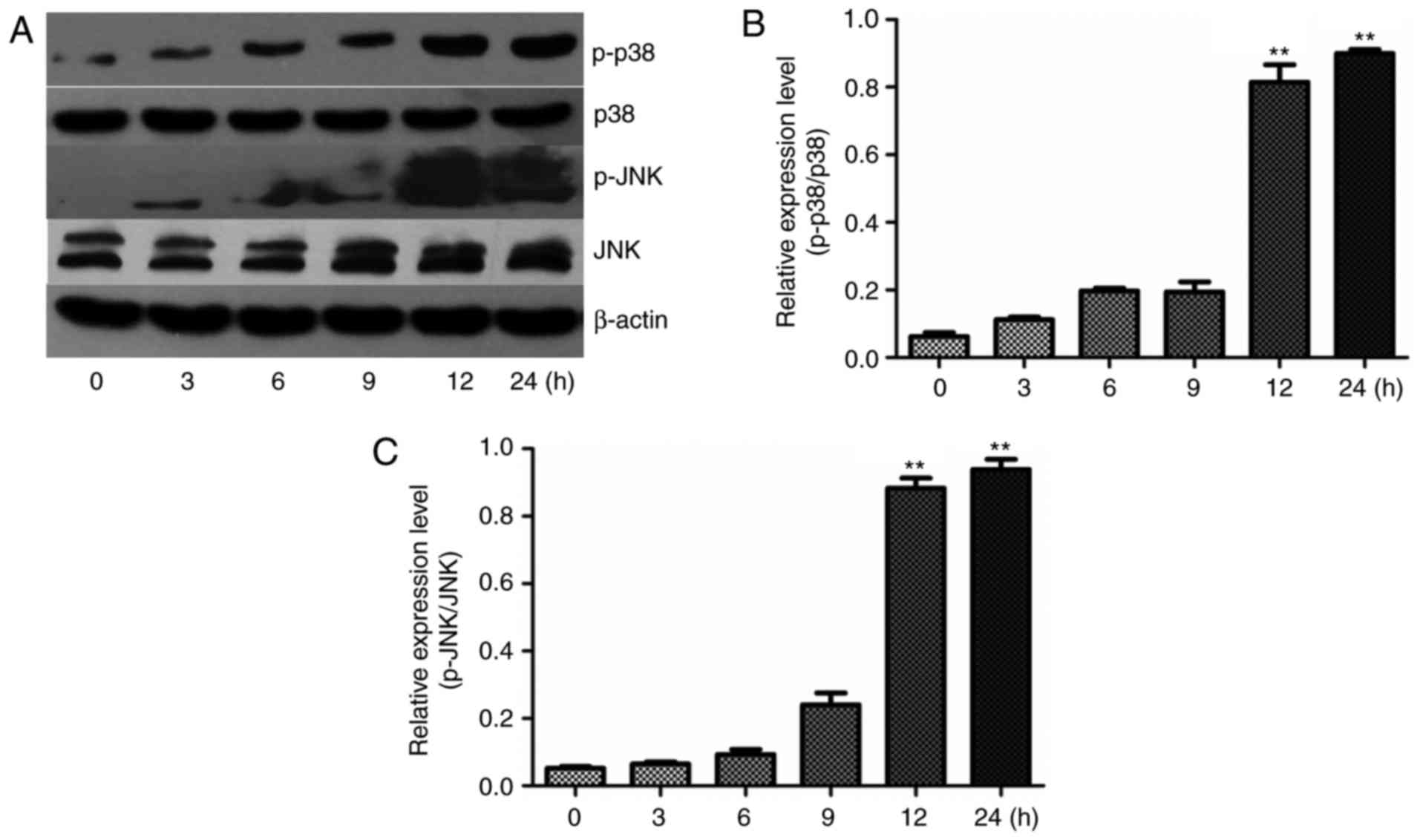
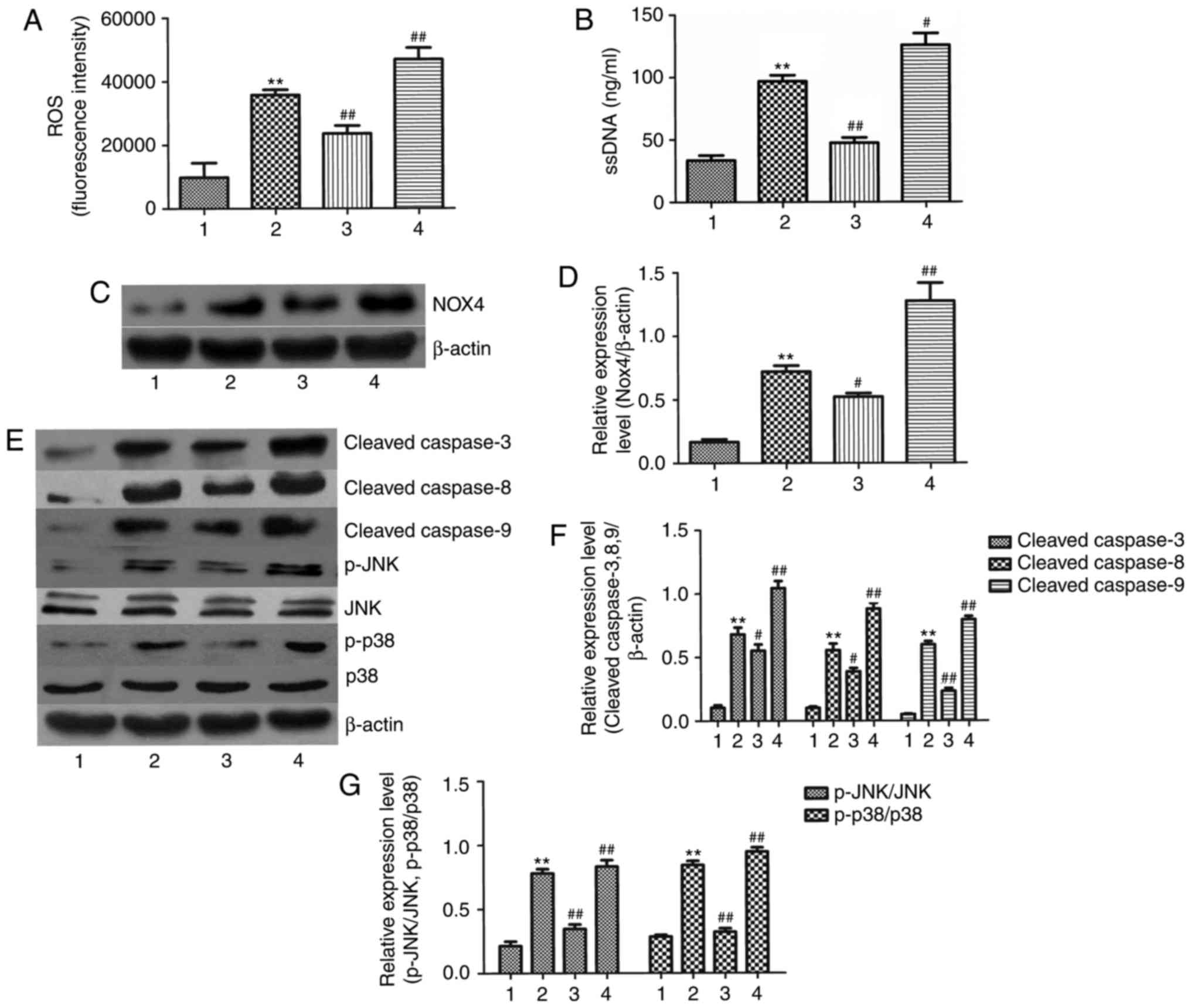
|
1
|
Duncan C: Rethinking excessive habits and
addictive behaviors. Alcohol Alcohol. 52:128–129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Owens RE, Snyder HS, Twilla JD and
Satapathy SK: Pharmacologic treatment of alcoholic hepatitis:
Examining outcomes based on disease severity stratification. J Clin
Exp Hepatol. 6:275–281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim JW, Yang H, Kim HW, Kim HP and Sung
SH: Lignans from Opuntia ficusindica seeds protect rat primary
hepatocytes and HepG2 cells against ethanol-induced oxidative
stress. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 81:181–183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sun Q, Zhang W, Zhong W, Sun X and Zhou Z:
Pharmacological inhibition of NOX4 ameliorates alcohol-induced
liver injury in mice through improving oxidative stress and
mitochondrial function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1861:2912–2921. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Zhang F, Wang X, Qiu X, Wang J, Fang H,
Wang Z, Sun Y and Xia Z: The protective effect of esculentoside a
on experimental acute liver injury in mice. PLoS One.
9:e1131072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Compromised MAPK
signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:867–882.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Wang R, Wang Y, Peng R, Wu Y and
Yuan Y: Ginkgo biloba extract mitigates liver fibrosis and
apoptosis by regulating p38 MAPK, NF-κB/IκBα, and Bcl-2/Bax
signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:6303–6317. 2015.
|
|
9
|
Crosas-Molist E and Fabregat I: Role of
NADPH oxidases in the redox biology of liver fibrosis. Redox Biol.
6:106–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L and Liu CM:
Hepatoprotective properties of sesamin against CCl4 induced
oxidative stress-mediatedapoptosisin mice via JNK pathway. Food
Chem Toxicol. 64:41–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Morio Y, Tsuji M, Inagaki M, Nakagawa M,
Asaka Y, Oyamada H, Furuya K and Oguchi K: Ethanol-induced
apoptosis in human liver adenocarcinoma cells (SK-Hep1): Fas- and
mitochondria-mediated pathways and interaction with MAPK signaling
system. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:1820–1829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo X, Cui R, Zhao J, Mo R, Peng L and Yan
M: Corosolic acid protects hepatocytes against ethanol-induced
damage by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and
activating autophagy. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:578–588. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang S, Su WW, Wang YG, Peng W, Nie YC
and Li PB: Effect of quercetin 7-rhamnoside on
glycochenodeoxycholic acid-induced L-02 human normal liver cell
apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. 32:323–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu LQ, Fan ZQ, Tang YF and Ke ZJ: The
resveratrol attenuates ethanol-induced hepatocyte apoptosis via
inhibiting ER-related caspase-12 activation and PDE activity in
vitro. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 38:683–693. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Andreu-Fernández V, Sancho M, Genovés A,
Lucendo E, Todt F, Lauterwasser J, Funk K, Jahreis G, Pérez-Payá E,
Mingarro I, et al: Bax transmembrane domain interacts with
prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 114:310–315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Farshori NN, Al-Sheddi ES, Al-Oqail MM,
Hassan WH, Al-Khedhairy AA, Musarrat J and Siddiqui MA:
Hepatoprotective potential of Lavandula coronopifolia extracts
against ethanol induced oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity in
HepG2 cells. Toxicol Ind Health. 31:727–737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liang S, Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: The
role of NADPH oxidases (NOXs) in liver fibrosis and the activation
of myofibro-blasts. Front Physiol. 7:172016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jiang JX and Török NJ: NADPH oxidases in
chronic liver diseases. Adv Hepatol. 2014:pii 7429312014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jiao Y, Ji L, Kuang Y and Yang Q:
Cytotoxic effect of oxaloacetate on HepG2-human hepatic carcinoma
cells via apoptosis and ROS accumulation. Neoplasma. 64:192–198.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bost ER, Frye GS, Ahn B and Ferreira LF:
Diaphragm dysfunction caused by sphingomyelinase requires the
p47(phox) subunit of NADPH oxidase. Respir Physiol Neurobiol.
205:47–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li YY, Shi ZM, Yu XY, Feng P and Wang XJ:
Urotensin II-induced insulin resistance is mediated by NADPH
oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species in HepG2 cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:5769–5779. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu J, Wei X, Wu Y, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Shi J,
Zhou H, Lu Z, Shao M, Yu L and Tong L: Giganteaside D induces
ROS-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through the MAPK pathway. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 39:333–342. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
He Y, Yang J, Li H, Shao H, Wei C, Wang Y,
Li M and Xu C: Exogenous spermine ameliorates high glucose-induced
cardiomyocytic apoptosis via decreasing reactive oxygen species
accumulation through inhibiting p38/JNK andJAK2 pathways. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:15537–15549. 2015.
|
|
24
|
Zhang C, Jia X, Bao J, Chen S, Wang K,
Zhang Y, Li P, Wan JB, Su H, Wang Y, et al: Polyphyllin VII induces
apoptosis in HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction and MAPK pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med.
16:582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Sun Z, Chen S, Jiao Y and Bai C:
ROS-mediated activation of JNK/p38 contributes partially to the
pro-apoptotic effect of ajoene on cells of lung adenocarcinoma.
Tumour Biol. 37:3727–3738. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang Q, Cui C, Chen CQ, Hu XL, Liu YH,
Fan YH, Meng WH and Zhao QC: Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic
activities of Alpinia oxyphylla on HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated
signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 169:99–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liang B, Liu Z, Cao Y, Zhu C, Zuo Y, Huang
L, Wen G, Shang N, Chen Y, Yue X, et al: MC37, a new mono-carbonyl
curcumin analog, induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 796:139–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen J, Wang Y, Hui C, Xi Y, Liu X, Qi F,
Liu H, Wang Z and Niu S: Mechanisms of Heshouwuyin in regulating
apoptosis of testicular cells in aging rats through mitochondrial
pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:3372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan X, Jiang Z, Bi L, Yang Y and Chen W:
Salvianolic acid A attenuates TNF-α- and D-GalN-induced ER
stress-mediated and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis by modulating
Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and calcium release in hepatocyte LO2 cells. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 388:817–830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang Y, Zong M, Xu W, Zhang Y, Wang B,
Yang M and Tao L: Natural pyrethrins induces apoptosis in human
hepatocyte cells via Bax- and Bcl-2-mediated mitochondrial pathway.
Chem Biol Interact. 262:38–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen LY, Chen Q, Zhu XJ, Kong DS, Wu L,
Shao JJ and Zheng SZ: Diallyl trisulfide protects against
ethanol-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via a hydrogen
sulfide-mediated mechanism. Int Immunopharmacol. 36:23–30. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sumegi K, Fekete K, Antus C, Debreceni B,
Hocsak E, Gallyas F Jr, Sumegi B and Szabo A: BGP-15 protects
against oxidative stress- or lipopolysaccharide-induced
mitochondrial destabilization and reduces mitochondrial production
of reactive oxygen species. PLoS One. 12:e01693722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan F, Wang Y, Wu X, Peshavariya HM,
Dusting GJ, Zhang M and Jiang F: Nox4 and redox signaling mediate
TGF-β-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and phenotypic switch.
Cell Death Dis. 5:e10102014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Amatore D, Sgarbanti R, Aquilano K,
Baldelli S, Limongi D, Civitelli L, Nencioni L, Garaci E, Ciriolo
MR and Palamara AT: Influenza virus replication in lung epithelial
cells depends on redox-sensitive pathways activated by NOX4-derived
ROS. Cell Microbiol. 17:131–145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Chuang WL, Lin PY, Lin HC and Chen YL: The
apoptotic effect of ursolic acid on SK-Hep-1 cells is regulated by
the I3K/Akt, p38 and JNK mapk signaling pathways. Molecules.
21:4602016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Paik YH, Kim J, Aoyama T, De Minicis S,
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Role of NADPH oxidases in liver
fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:2854–2872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Nguyen KC, Willmore WG and Tayabali AF:
Cadmium telluride quantum dots cause oxidative stress leading to
extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2
cells. Toxicology. 306:114–123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao WX, Tang SS, Jin X, Zhang CM, Zhang
T, Wang CC, Sun Y and Xiao XL: Olaquindox-induced apoptosis is
suppressed through p38 MAPK and ROS-mediated JNK pathways in HepG2
cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 29:229–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoon J, Ham H, Sung J, Kim Y, Choi Y, Lee
JS, Jeong HS, Lee J and Kim D: Black rice extract protected HepG2
cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death via ERK1/2 and Akt
activation. Nutr Res Pract. 8:125–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Stiuso P, Bagarolo ML, Ilisso CP, Vanacore
D, Martino E, Caraglia M, Porcelli M and Cacciapuoti G: Protective
effect of tyrosol and S-Adenosylmethionine against ethanol-induced
oxidative stress of Hepg2 cells involves sirtuin 1, P53 and Erk1/2
Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 17:pii: E6222016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Szuster-Ciesielska A, Plewka K, Daniluk J
and Kandefer-Szerszeń M: Zinc inhibits ethanol-induced HepG2 cell
apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 229:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Abid MD, Chen J, Xiang M, Zhou J, Chen X
and Gong F: Khat (Catha edulis) generates reactive oxygen species
and promotes hepatic cell apoptosis via MAPK activation. Int J Mol
Med. 32:389–395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|