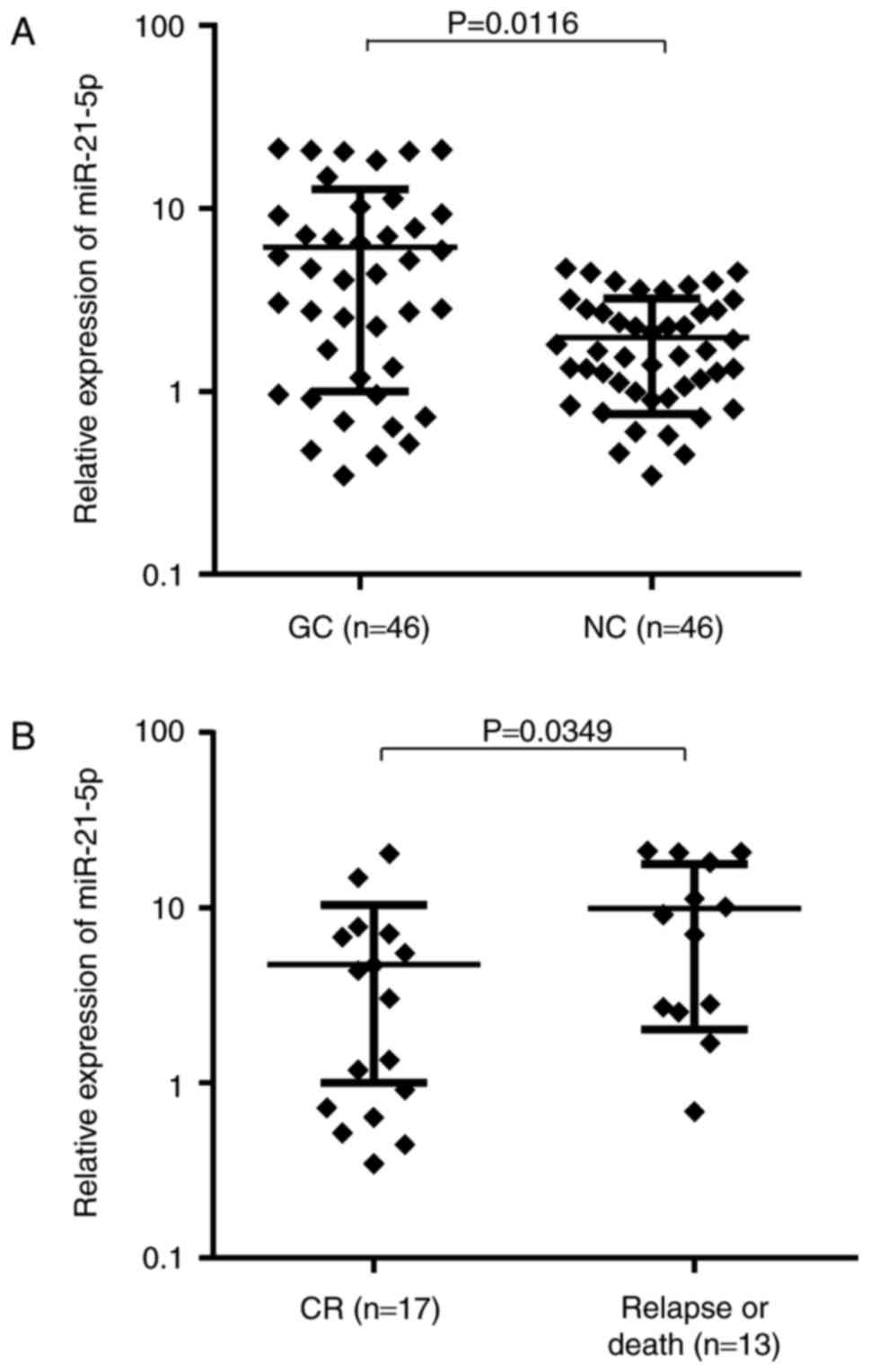
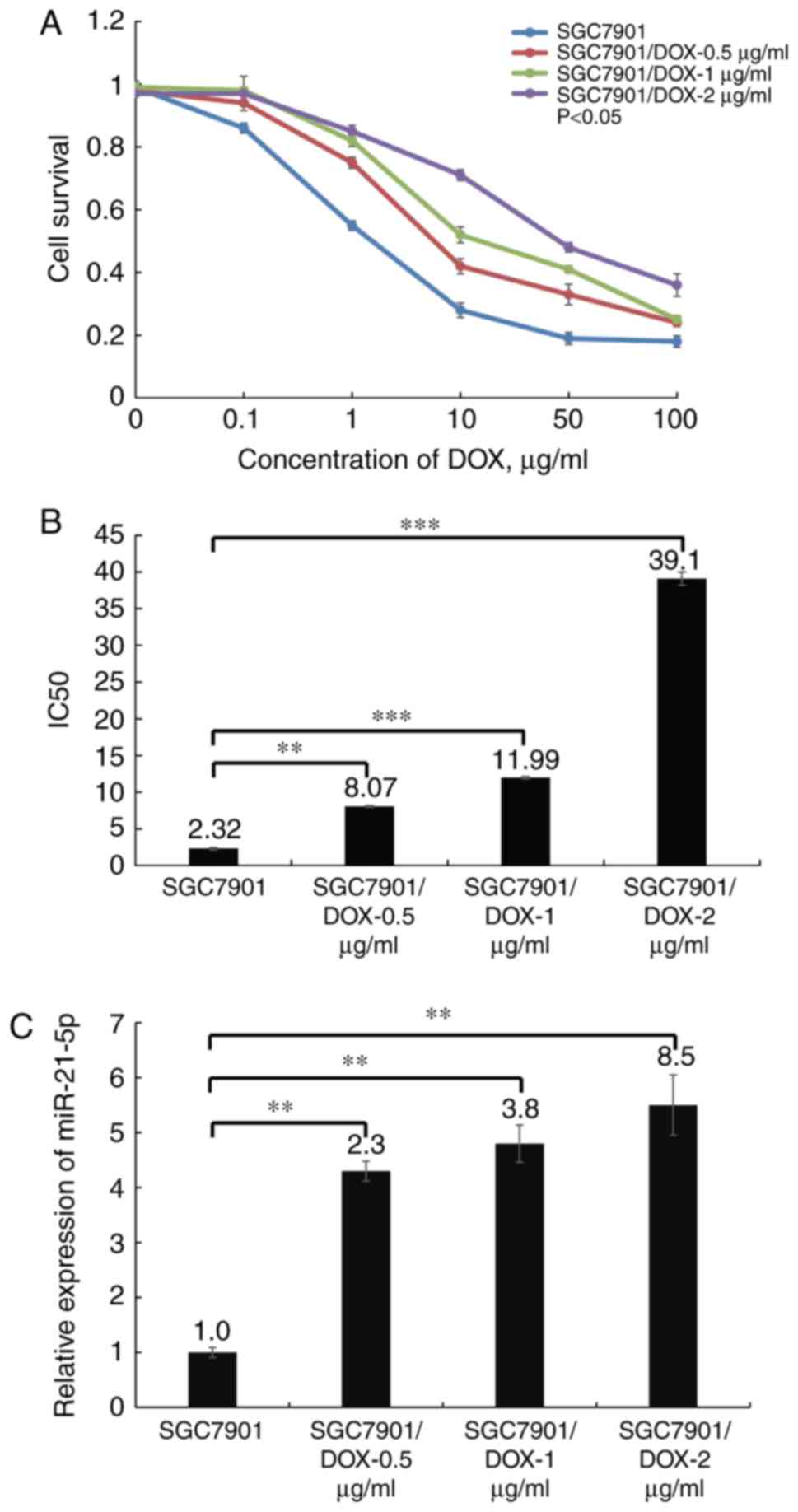
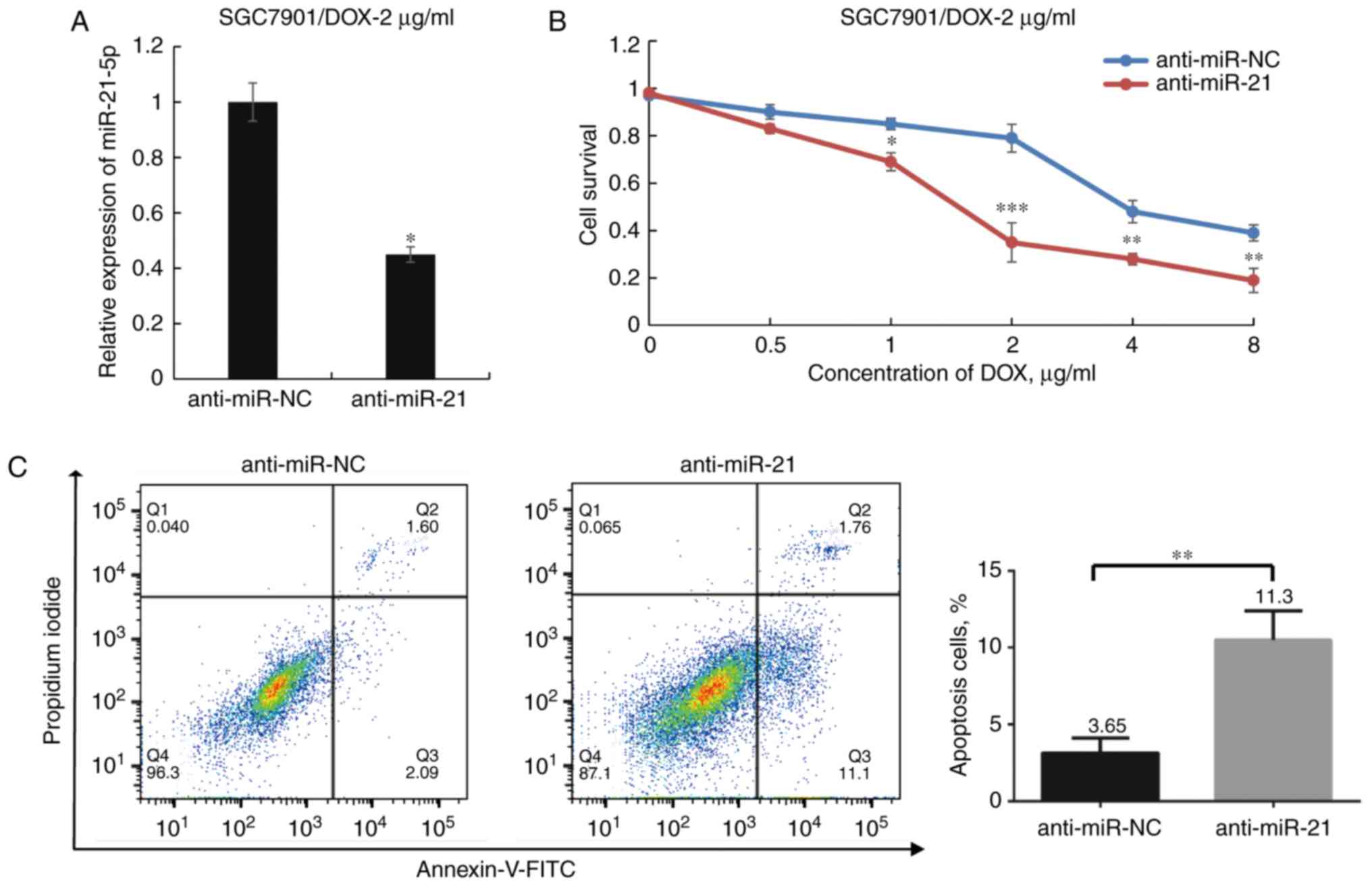
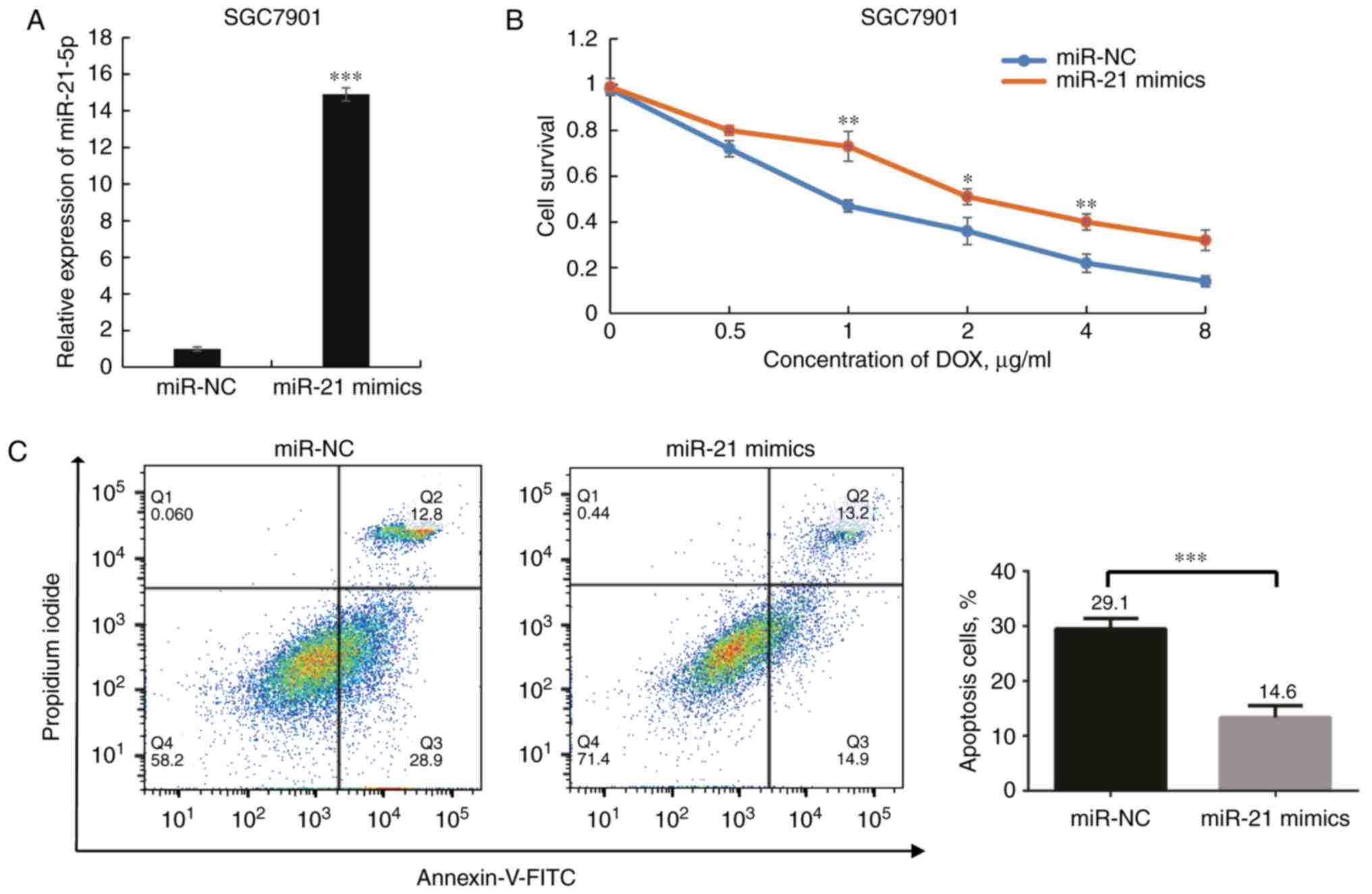
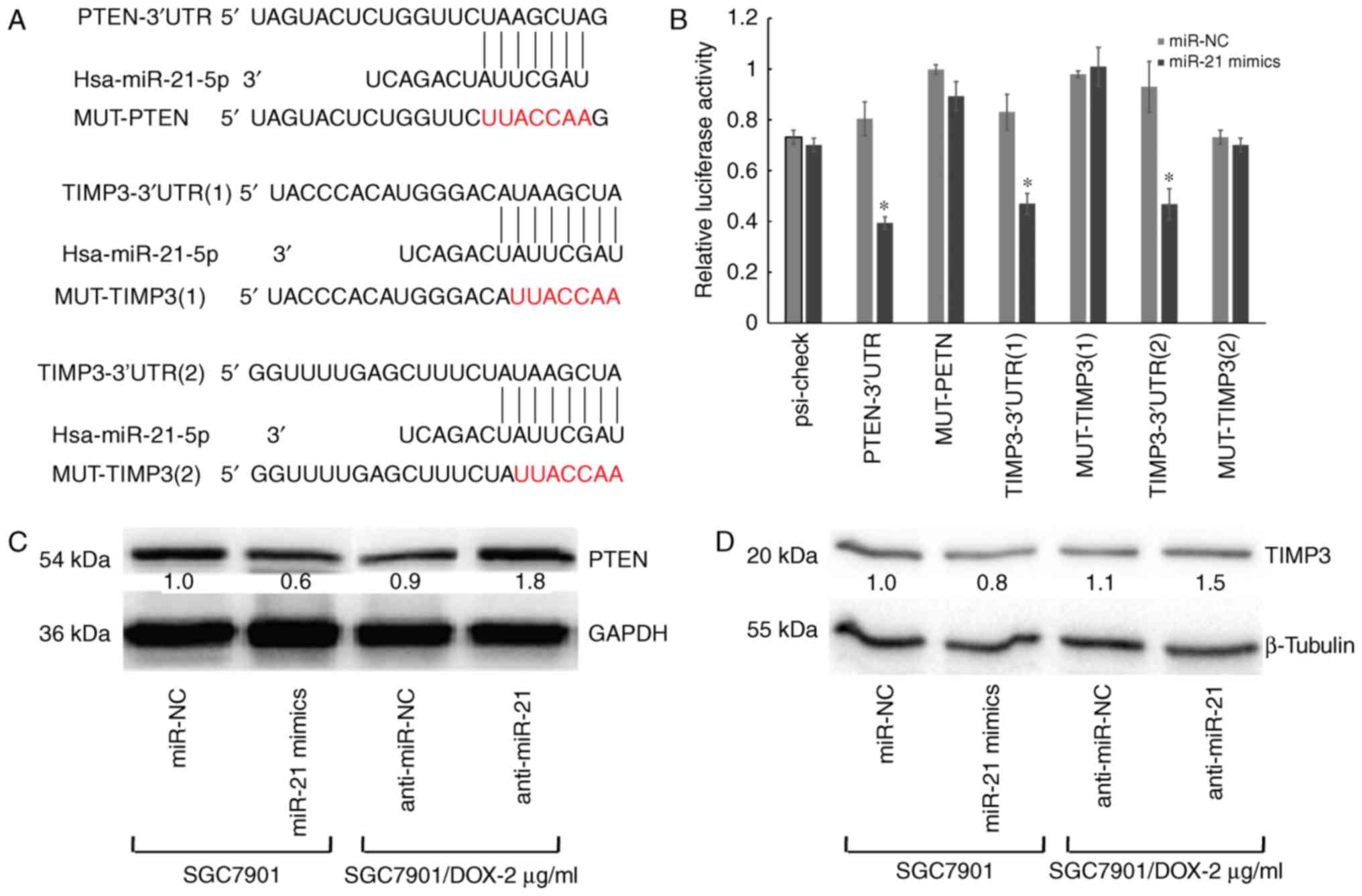
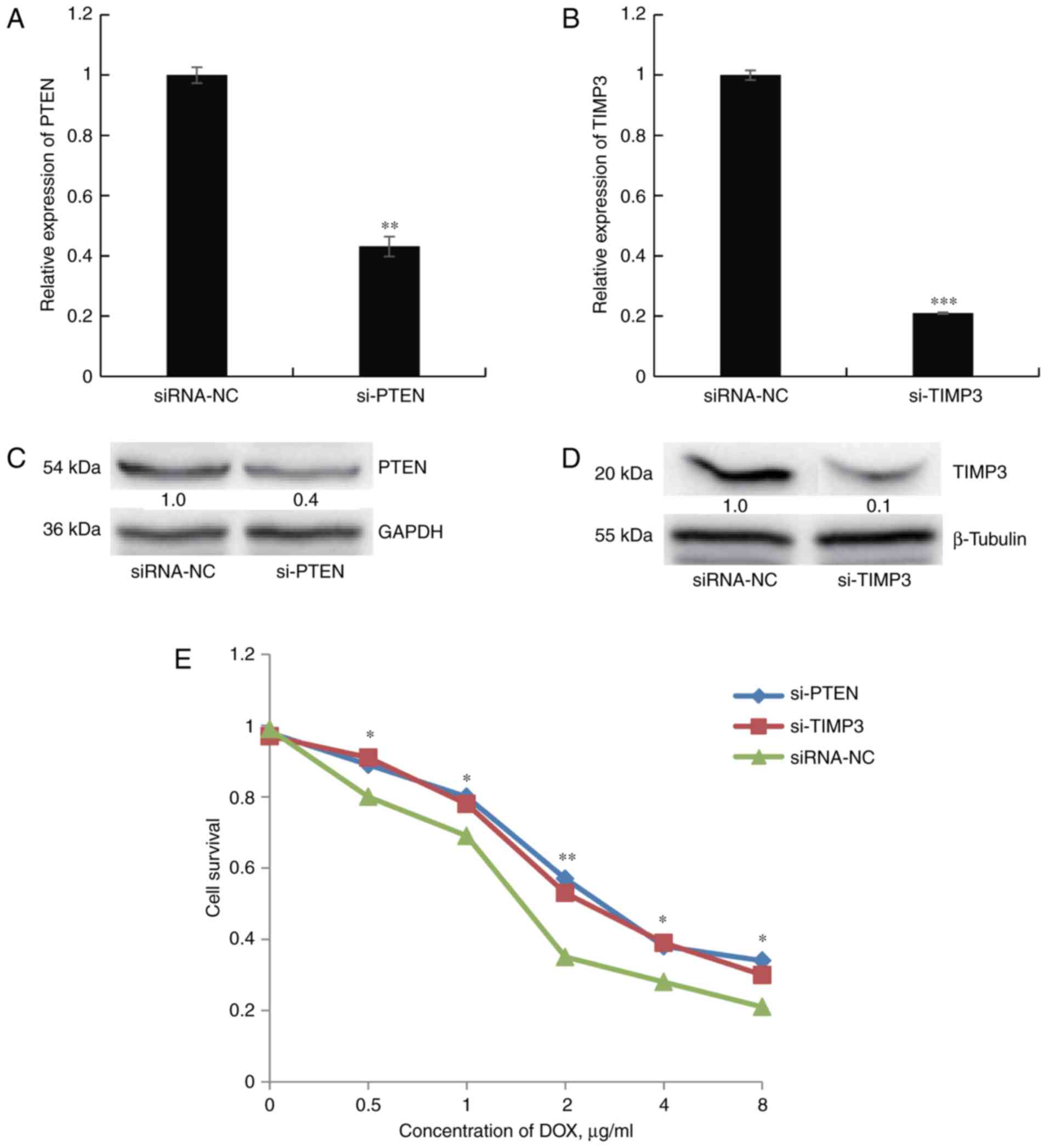
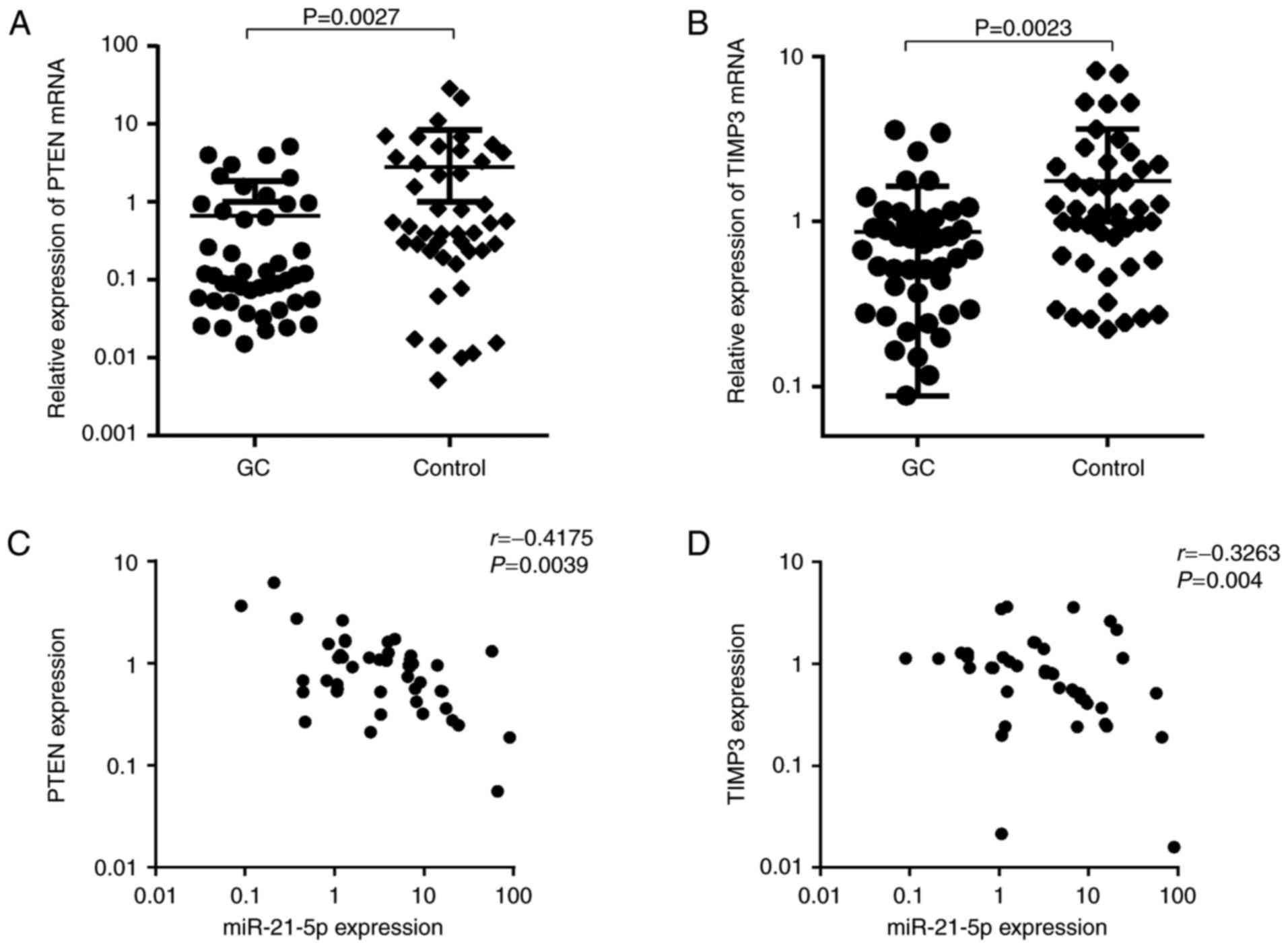
|
1
|
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S,
Freedman ND and Kamangar F: Gastric cancer: Descriptive
epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 23:700–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ali Z, Deng Y and Ma C: Progress of
research in gastric cancer. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 12:8241–8248.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kikuchi S, Kaibe N, Morimoto K, Fukui H,
Niwa H, Maeyama Y, Takemura M, Matsumoto M, Nakamori S, Miwa H, et
al: Overexpression of Ephrin A2 receptors in cancer stromal cells
is a prognostic factor for the relapse of gastric cancer. Gastric
Cancer. 18:485–494. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Garrido M, Fonseca PJ, Vieitez JM, Frunza
M and Lacave AJ: Challenges in first line chemotherapy and targeted
therapy in advanced gastric cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.
14:887–900. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Lauro L, Vici P, Belli F, Tomao S,
Fattoruso SI, Arena MG, Pizzuti L, Giannarelli D, Paoletti G, Barba
M, et al: Docetaxel, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine combination
chemotherapy for metastatic gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer.
17:718–724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ruffell B and Coussens LM: Macrophages and
therapeutic resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell. 27:462–472. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zou HY, Friboulet L, Kodack DP, Engstrom
LD, Li Q, West M, Tang RW, Wang H, Tsaparikos K, Wang J, et al:
PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 inhibitor, overcomes resistance to first
and second generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Cancer
Cell. 28:70–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adams CM, Hiebert SW and Eischen CM: Myc
induces miRNA-mediated apoptosis in response to HDAC inhibition in
hematologic malignancies. Cancer Res. 76:736–748. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Palmbos PL, Wang L, Yang H, Wang Y,
Leflein J, Ahmet ML, Wilkinson JE, Kumar-Sinha C, Ney GM, Tomlins
SA, et al: ATDC/TRIM29 drives invasive bladder cancer formation
through miRNA-mediated and epigenetic mechanisms. Cancer Res.
75:5155–5166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang H, Pu J, Qi T, Qi M, Yang C, Li S,
Huang K, Zheng L and Tong Q: MicroRNA-145 inhibits the growth,
invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of neuroblastoma cells
through targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha. Oncogene.
33:387–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Henao-Mejia J, Williams A, Goff LA, Staron
M, Licona-Limón P, Kaech SM, Nakayama M, Rinn JL and Flavell RA:
The microRNA miR-181 is a critical cellular metabolic rheostat
essential for NKT cell ontogenesis and lymphocyte development and
homeostasis. Immunity. 38:984–997. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang E, Liu R and Chu Y: miRNA-15a/16: As
tumor suppressors and more. Future Oncol. 11:2351–2363. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie SY, Li YJ, Wang PY, Jiao F, Zhang S
and Zhang WJ: miRNA-regulated expression of oncogenes and tumor
suppressor genes in the cisplatin-inhibited growth of K562 cells.
Oncol Rep. 23:1693–1700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xue J, Chi Y, Chen Y, Huang S, Ye X, Niu
J, Wang W, Pfeffer LM, Shao ZM, Wu ZH and Wu J: MiRNA-621
sensitizes breast cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing FBXO11 and
enhancing p53 activity. Oncogene. 35:448–458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu C, Xie S, Song C, Huang L and Jiang Z:
Lin28 mediates cancer chemotherapy resistance via Regulation of
miRNA signaling. Hepatogastroenterology. 61:1138–1141. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Massoner P, Thomm T, Mack B, Untergasser
G, Martowicz A, Bobowski K, Klocker H, Gires O and Puhr M: EpCAM is
overexpressed in local and metastatic prostate cancer, suppressed
by chemotherapy and modulated by MET-associated miRNA-200c/205. Br
J Cancer. 111:955–964. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Liu C, Luo M, Zhang Z, Gong J, Li
J, You L, Dong L, Su R, Lin H, et al: Chemotherapy-induced
miRNA-29c/Catenin-δ signaling suppresses metastasis in gastric
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:1332–1344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar S, Keerthana R, Pazhanimuthu A and
Perumal P: Overexpression of circulating miRNA-21 and miRNA-146a in
plasma samples of breast cancer patients. Indian J Biochem Biophys.
50:210–214. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HL, Yang LF, Zhu Y, Yao XD, Zhang
SL, Dai B, Zhu YP, Shen YJ, Shi GH and Ye DW: Serum miRNA-21:
Elevated levels in patients with metastatic hormone-refractory
prostate cancer and potential predictive factor for the efficacy of
docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Prostate. 71:326–331. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang XC, Wang W, Zhang ZB, Zhao J, Tan XG
and Luo JC: Overexpression of miRNA-21 promotes
radiation-resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol.
8:1462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao W, Lu X, Liu L, Xu J, Feng D and Shu
Y: MiRNA-21: A biomarker predictive for platinum-based adjuvant
chemotherapy response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Biol Ther. 13:330–340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song J, Bai Z, Zhang J, Meng H, Cai J,
Deng W, Bi J, Ma X and Zhang Z: Serum microRNA-21 levels are
related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict
prognosis. Oncol Lett. 6:1733–1737. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C and
Bloomston M: MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and
a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg.
12:2171–2176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mydlarz W, Uemura M, Ahn S, Hennessey P,
Chang S, Demokan S, Sun W, Shao C, Bishop J, Krosting J, et al:
Clusterin is a gene-specific target of microRNA-21 in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:868–877. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Goldoni M, Azzalin
G, Carucci N, Tavolaro S, Castellano L, Magrelli A, Citarella F,
Messina M, et al: Quantitative technologies establish a novel
microRNA profile of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood.
109:4944–4951. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paik WH, Kim HR, Park JK, Song BJ, Lee SH
and Hwang JH: Chemosensitivity induced by down-regulation of
microRNA-21 in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells by
indole-3-carbinol. Anticancer Res. 33:1473–1481. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei X, Wang W, Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhang X,
Chen M, Wang F, Yu J, Ma Y and Sun G: MicroRNA-21 induces
5-fluorouracil resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells by
regulating PTEN and PDCD4. Cancer Med. 5:693–702. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Valeri N, Gasparini P, Braconi C, Paone A,
Lovat F, Fabbri M, Sumani KM, Alder H, Amadori D, Patel T, et al:
MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating
human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:21098–21103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davies GF, Juurlink BH and Harkness TA:
Troglitazone reverses the multiple drug resistance phenotype in
cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 3:79–88. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Clément T, Salone V and Rederstorff M:
Dual luciferase gene reporter assays to study miRNA function.
Methods Mol Biol. 1296:187–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li SC, Liao YL, Ho MR, Tsai KW, Lai CH and
Lin WC: miRNA arm selection and isomiR distribution in gastric
cancer. BMC Genomics 1. 3(Suppl 1): S132012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Oddo D, Sennott EM, Barault L, Valtorta E,
Arena S, Cassingena A, Filiciotto G, Marzolla G, Elez E, van Geel
RM, et al: Molecular landscape of acquired resistance to targeted
therapy combinations in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
76:4504–4515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Khanal P, Savage P, She YM, Cyr TD
and Yang X: YAP-induced resistance of cancer cells to antitubulin
drugs is modulated by a Hippo-independent pathway. Cancer Res.
74:4493–4503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mueller T, Voigt W, Simon H, Fruehauf A,
Bulankin A, Grothey A and Schmoll HJ: Failure of activation of
caspase-9 induces a higher threshold for apoptosis and cisplatin
resistance in testicular cancer. Cancer Res. 63:513–521.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chauhan D, Tian Z, Nicholson B, Kumar KG,
Zhou B, Carrasco R, McDermott JL, Leach CA, Fulcinniti M, Kodrasov
MP, et al: A small molecule inhibitor of ubiquitin-specific
protease-7 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells and
overcomes bortezomib resistance. Cancer Cell. 22:345–358. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio
I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S, Deng X, Zhai D, Shi YX, Sneed T, et al:
Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3
mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 10:375–388.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, Huang MY, Deng
L, Wu QL, Zeng YX and Shao JY: MicroRNA miR-21 overexpression in
human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage,
lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA.
14:2348–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu CW, Ng SS, Dong YJ, Ng SC, Leung WW,
Lee CW, Wong YN, Chan FK, Yu J and Sung JJ: Detection of miR-92a
and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for
colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut. 61:739–745. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lee HW, Lee EH, Ha SY, Lee CH, Chang HK,
Chang S, Kwon KY, Hwang IS, Roh MS and Seo JW: Altered expression
of microRNA miR-21, miR-155, and let-7a and their roles in
pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. Pathol Int. 62:583–591. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park SK, Park YS, Ahn JY, Do EJ, Kim D,
Kim JE, Jung K, Byeon JS, Ye BD, Yang DH, et al: MiR 21-5p as a
predictor of recurrence in young gastric cancer patients. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:1429–1435. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yin C, Zhou X, Dang Y, Yan J and Zhang G:
Potential role of circulating MiR-21 in the diagnosis and prognosis
of digestive system cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e21232015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gong C, Yao Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Wu W, Chen
J, Su F, Yao H and Song E: Up-regulation of miR-21 mediates
resistance to trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J Biol Chem.
286:19127–19137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H,
Tomokuni A, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Takeda Y, Tanemura M,
Umeshita K, et al: MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to the
anti-tumour effect of interferon-alpha/5-fluorouracil in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 103:1617–1626. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y and
Li J: miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells
by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. 306:162–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jin B, Liu Y and Wang H: Antagonism of
miRNA-21 Sensitizes Human Gastric Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 72:275–282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zheng P, Chen L, Yuan X, Luo Q, Liu Y, Xie
G, Ma Y and Shen L: Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated
macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric
cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang S, Wang A, Shao M, Lin L, Li P and
Wang Y: Schisandrin B reverses doxorubicin resistance through
inhibiting P-glycoprotein and promoting proteasome-mediated
degradation of survivin. Sci Rep. 7:84192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cao Z, Liang N, Yang H and Li S: Visfatin
mediates doxorubicin resistance in human non-small-cell lung cancer
via Akt-mediated up-regulation of ABCC1. Cell Prolif. 50:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Papagiannakopoulos T, Shapiro A and Kosik
KS: MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways
in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 68:8164–8172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H and Mo YY: MicroRNA-21
targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol
Chem. 282:14328–14336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sayed D, He M, Hong C, Gao S, Rane S, Yang
Z and Abdellatif M: MicroRNA-21 is a downstream effector of AKT
that mediates its antiapoptotic effects via suppression of Fas
ligand. J Biol Chem. 285:20281–20290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Blumenthal GM and Dennis PA: Pten
hamartoma tumor syndromes. Eur J Hum Genet. 16:1289–1300. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kennedy SG, Wagner AJ, Conzen SD, Jordán
J, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis PN and Hay N: The pi3-kinase/akt signaling
pathway delivers an anti-apoptotic signal. Genes Dev. 11:701–713.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yea SS and Fruman DA: Achieving cancer
cell death with PI3K/mtor-targeted therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1280:15–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Westhoff MA, Faham N, Marx D, Nonnenmacher
L, Jennewein C, Enzenmuller S, Gonzalez P, Fulda S and Debatin KM:
Sequential dosing in chemo-sensitization: Targeting the
PI3K/akt/mtor pathway in neuroblastoma. PLoS One. 8:e831282013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Defamie V, Sanchez O, Murthy A and Khokha
R: TIMP3 controls cell fate to confer hepatocellular carcinoma
resistance. Oncogene. 34:4098–4108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Han J and Sun P: The pathways to tumor
suppression via route p38. Trends Biochem Sci. 32:364–371. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bulavin DV and Fornace AJ Jr: p38 MAP
kinase's emerging role as a tumor suppressor. Adv Cancer Res.
92:95–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Rangarajan A, Talora C, Okuyama R, Nicolas
M, Mammucari C, Oh H, Aster JC, Krishna S, Metzger D, Chambon P, et
al: Notch signaling is a direct determinant of keratinocyte growth
arrest and entry into differentiation. EMBO J. 20:3427–3436. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shibata T, Watari K, Izumi H, Kawahara A,
Hattori S, Fukumitsu C, Murakami Y, Takahashi R, Toh U, Ito KI,
Ohdo S, et al: Breast cancer resistance to antiestrogens is
enhanced by increased ER degradation and ERBB2 expression. Cancer
Res. 77:545–556. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Schneider C, Oellerich T, Baldauf HM,
Schwarz SM, Thomas D, Flick R, Bohnenberger H, Kaderali L, Stegmann
L, Cremer A, et al: SAMHD1 is a biomarker for cytarabine response
and a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med.
23:250–255. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Feng DD, Zhang H, Zhang P, Zheng YS, Zhang
XJ, Han BW, Luo XQ, Xu L, Zhou H, Qu LH and Chen YQ: Down-regulated
miR-331-5p and miR-27a are associated with chemotherapy resistance
and relapse in leukaemia. J Cell Mol Med. 15:2164–2175. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kimura A, Ogata K, Altan B, Yokobori T,
Ide M, Mochiki E, Toyomasu Y, Kogure N, Yanoma T, Suzuki M, et al:
Nuclear heat shock protein 110 expression is associated with poor
prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:18415–18423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|