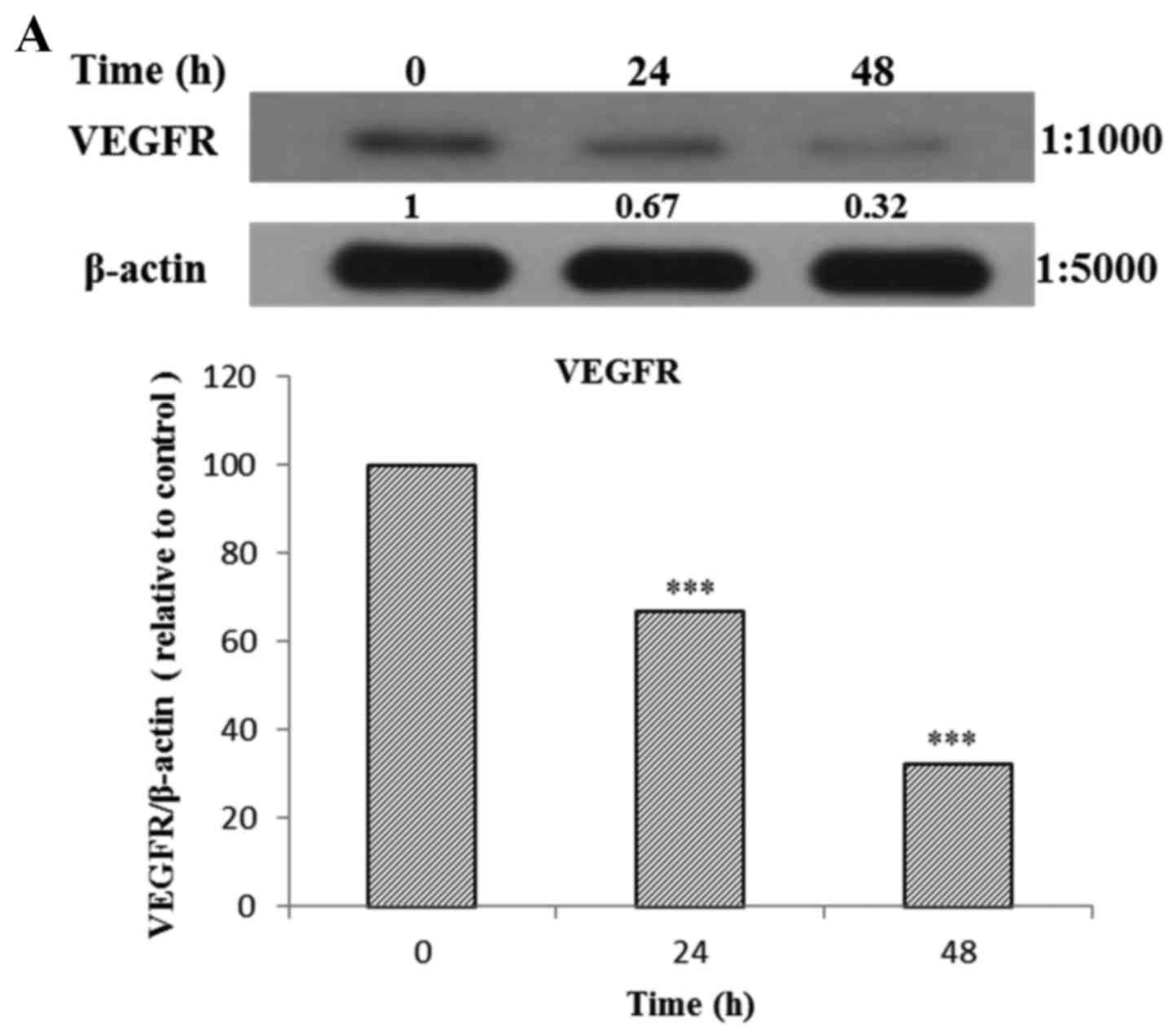
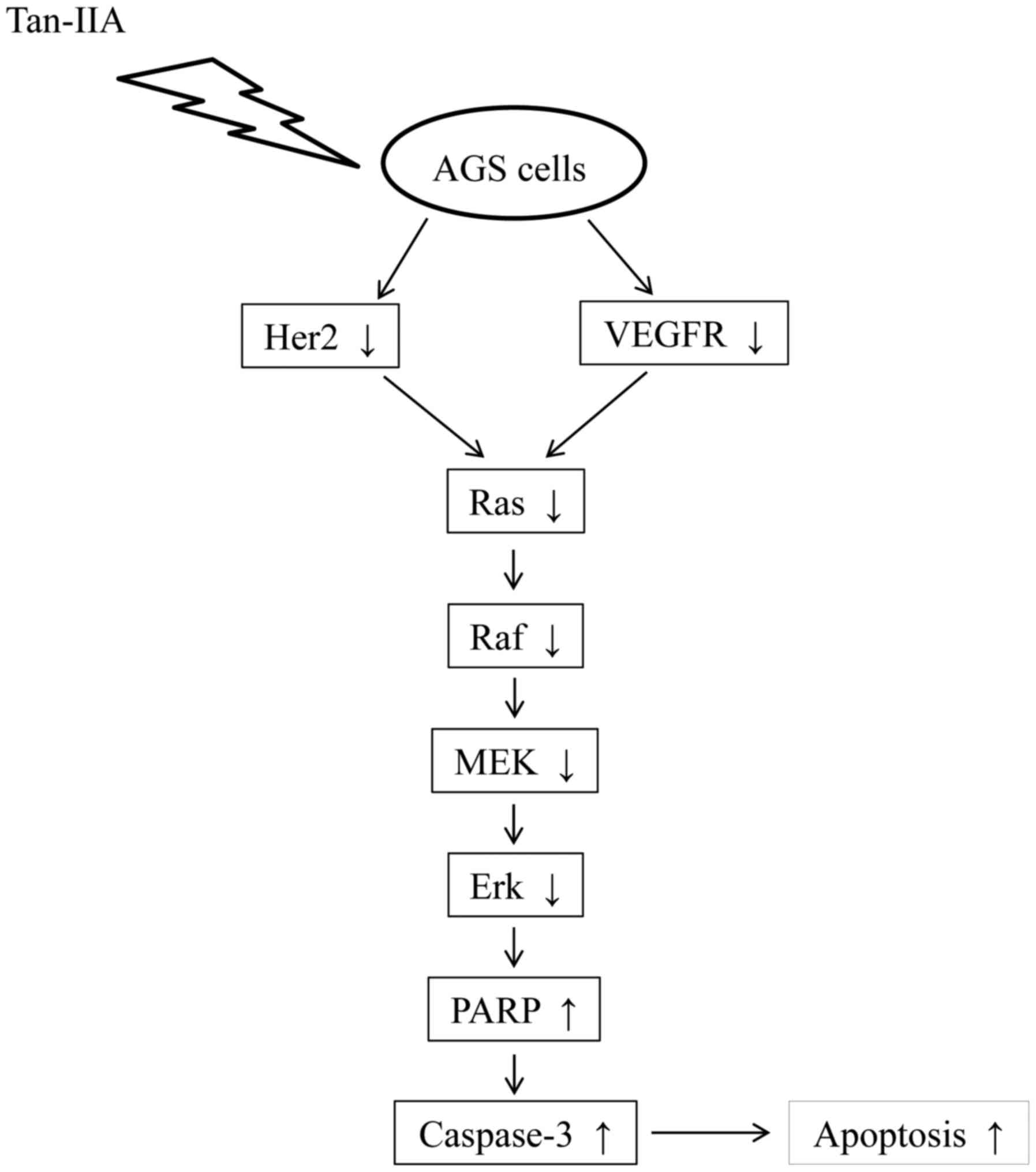
|
1
|
Che AJ, Zhang JY, Li CH, Chen XF, Hu ZD
and Chen XG: Separation and determination of active components in
Radix Salviae miltiorrhizae and its medicinal preparations by
nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis. J Sep Sci. 27:569–575. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou L, Zuo Z and Chow MS: Danshen: An
overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and
clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. 45:1345–1359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin R, Wang WR, Liu JT, Yang GD and Han
CJ: Protective effect of tanshinone IIA on human umbilical vein
endothelial cell injured by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism. J
Ethnopharmacol. 108:217–222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang AM, Sha SH, Lesniak W and Schacht J:
Tanshinone (Salviae miltiorrhizae extract) preparations attenuate
aminoglycoside-induced free radical formation in vitro and
ototoxicity in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 47:1836–1841.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jang SI, Kim HJ, Kim YJ, Jeong SI and You
YO: Tanshinone IIA inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in RAW
264.7 cells: Possible involvement of the NIK-IKK, ERK1/2, p38 and
JNK pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 542:1–7. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li W, Li J, Ashok M, Wu R, Chen D, Yang L,
Yang H, Tracey KJ, Wang P, Sama AE, et al: A cardiovascular drug
rescues mice from lethal sepsis by selectively attenuating a
late-acting proinflammatory mediator, high mobility group box 1. J
Immunol. 178:3856–3864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su CC and Lin YH: Tanshinone IIA
downregulates the protein expression of ErbB-2 and upregulates
TNF-α in colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med.
22:847–851. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su CC and Lin YH: Tanshinone IIA inhibits
human breast cancer cells through increased Bax to Bcl-xL ratios.
Int J Mol Med. 22:357–361. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiu TL and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA induces
apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through the induction of
reactive oxygen species and decreasing the mitochondrial membrane
potential. Int J Mol Med. 25:231–236. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng CY and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA may
inhibit the growth of small cell lung cancer H146 cells by
up-regulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and decreasing mitochondrial
membrane potential. Mol Med Rep. 3:645–650. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Cheng CY and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA
inhibits Hep-J5 cells by increasing calreticulin, caspase 12 and
GADD153 protein expression. Int J Mol Med. 26:379–385.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan MY, Chien SY, Kuo SJ, Chen DR and Su
CC: Tanshinone IIA inhibits BT-20 human breast cancer cell
proliferation through increasing caspase 12, GADD153 and
phospho-p38 protein expression. Int J Mol Med. 29:855–863.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang CY, Chiu TL, Kuo SJ, Chien SY, Chen
DR and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA inhibits the growth of pancreatic
cancer BxPC3 cells by decreasing protein expression of TCTP, MCL1
and Bcl-xL. Mol Med Rep. 7:1045–1049. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su CC: Tanshinone IIA could inhibit
pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells through increasing PERK, ATF6,
caspase-12 and CHOP expression to induce apoptosis. J Biomed Sci
Eng. 8:149–159. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yuen JS and Macaulay VM: Targeting the
type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor as a treatment for
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:589–603. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chitnis MM, Yuen JS, Protheroe AS, Pollak
M and Macaulay VM: The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor
pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6364–6370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Santarpia L, Lippman SM and El-Naggar AK:
Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:103–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Kempf CR,
Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Stivala F, Malaponte G, Nicoletti F, Libra
M, Bäsecke J, et al: Therapeutic resistance resulting from
mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and I3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.
J Cell Physiol. 226:2762–2781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su CC: Tanshinone IIA inhibits human
gastric carcinoma AGS cell growth by decreasing BiP, TCTP, Mcl 1
and Bcl xL and increasing Bax and CHOP protein expression. Int J
Mol Med. 34:1661–1668. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su CC: Tanshinone IIA inhibits gastric
carcinoma AGS cells through increasing p-p38, p-JNK and p53 but
reducing p-ERK, CDC2 and cyclin B1 expression. Anticancer Res.
34:7097–7110. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou J, He J, Jin X, Hu T and Zhang Y:
Study on optimisation of extraction process of tanshinone IIA and
its mechanism of induction of gastric cancer SGC7901 cell
apoptosis. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Medicines. 10:456–458.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu M, Cao FL, Li NY, Liu YQ, Li YP and Lv
CL: Tanshinone IIA reverses the malignant phenotype of SGC7901
gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:173–177. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong X, Dong J, Peng G, Hou X and Wu G:
Growth-inhibiting and apoptosis-inducing effects of Tanshinone II A
on human gastric carcinoma cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 27:706–709. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kranenburg O, Gebbink MF and Voest EE:
Stimulation of angiogenesis by Ras proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1654:23–37. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stacey DW: Cyclin D1 serves as a cell
cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 15:158–163. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boonstra J, Rijken P, Humbel B, Cremers F,
Verkleij A and van Bergen en Henegouwen P: The epidermal growth
factor. Cell Biol Int. 19:413–430. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cary LA, Han DC and Guan JL:
Integrin-mediated signal transduction pathways. Histol Histopathol.
14:1001–1009. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schlesinger TK, Fanger GR, Yujiri T and
Johnson GL: The TAO of MEKK. Front Biosci. 3:D1181–D1186. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ
and Greenberg ME: Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases
on apoptosis. Science. 270:1326–1331. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rubinfeld H and Seger R: The ERK cascade:
A prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 31:151–174. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|