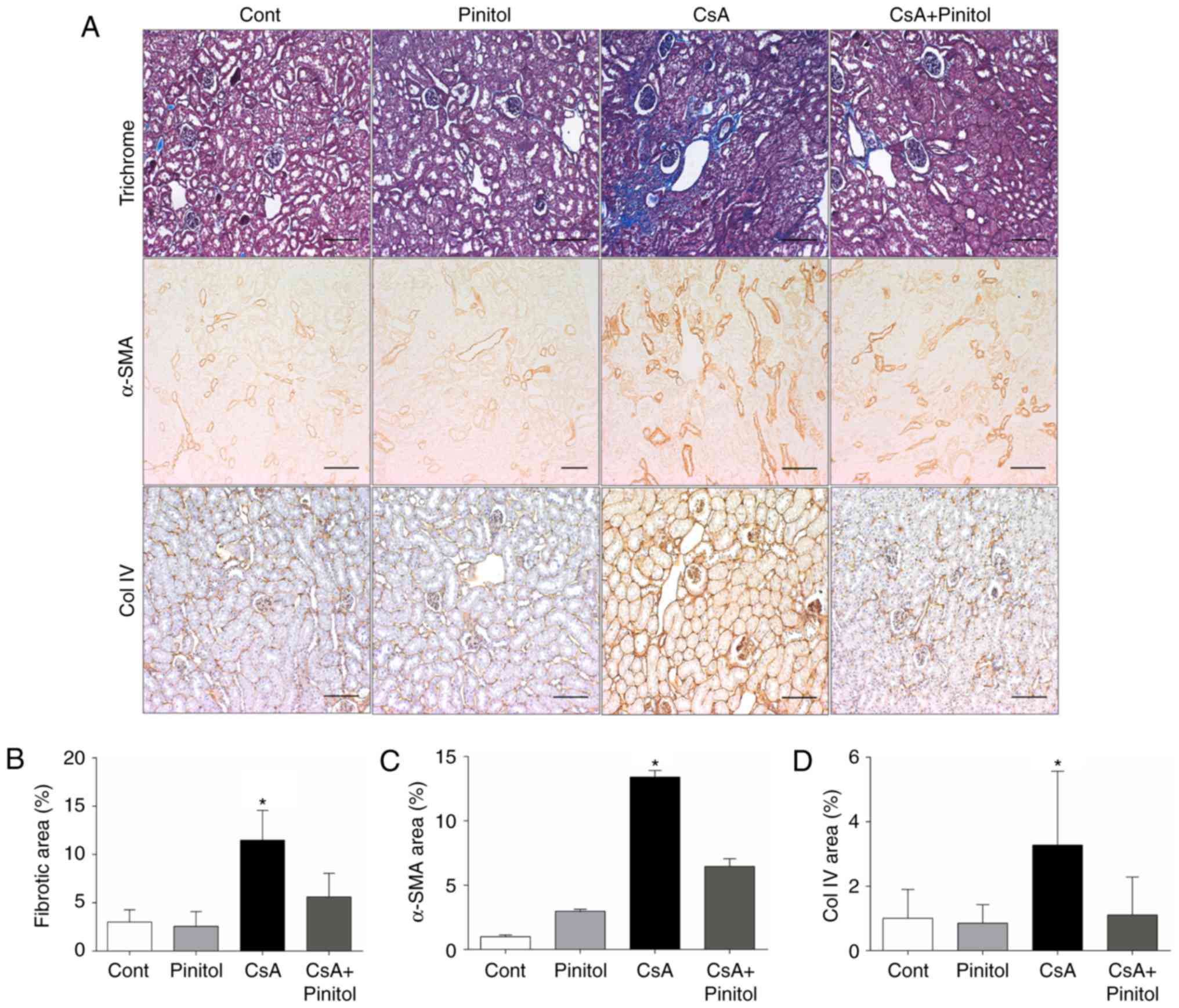
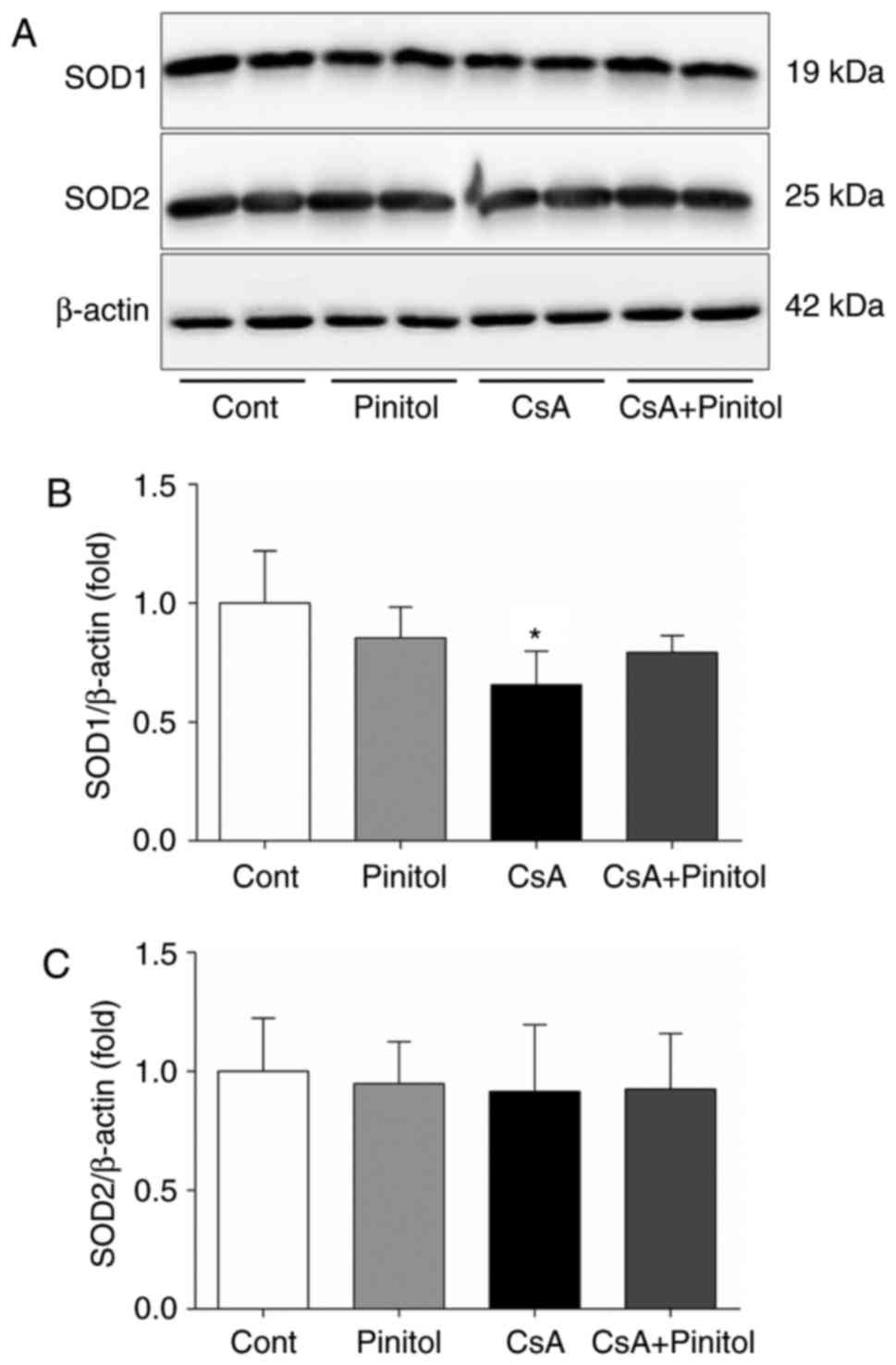
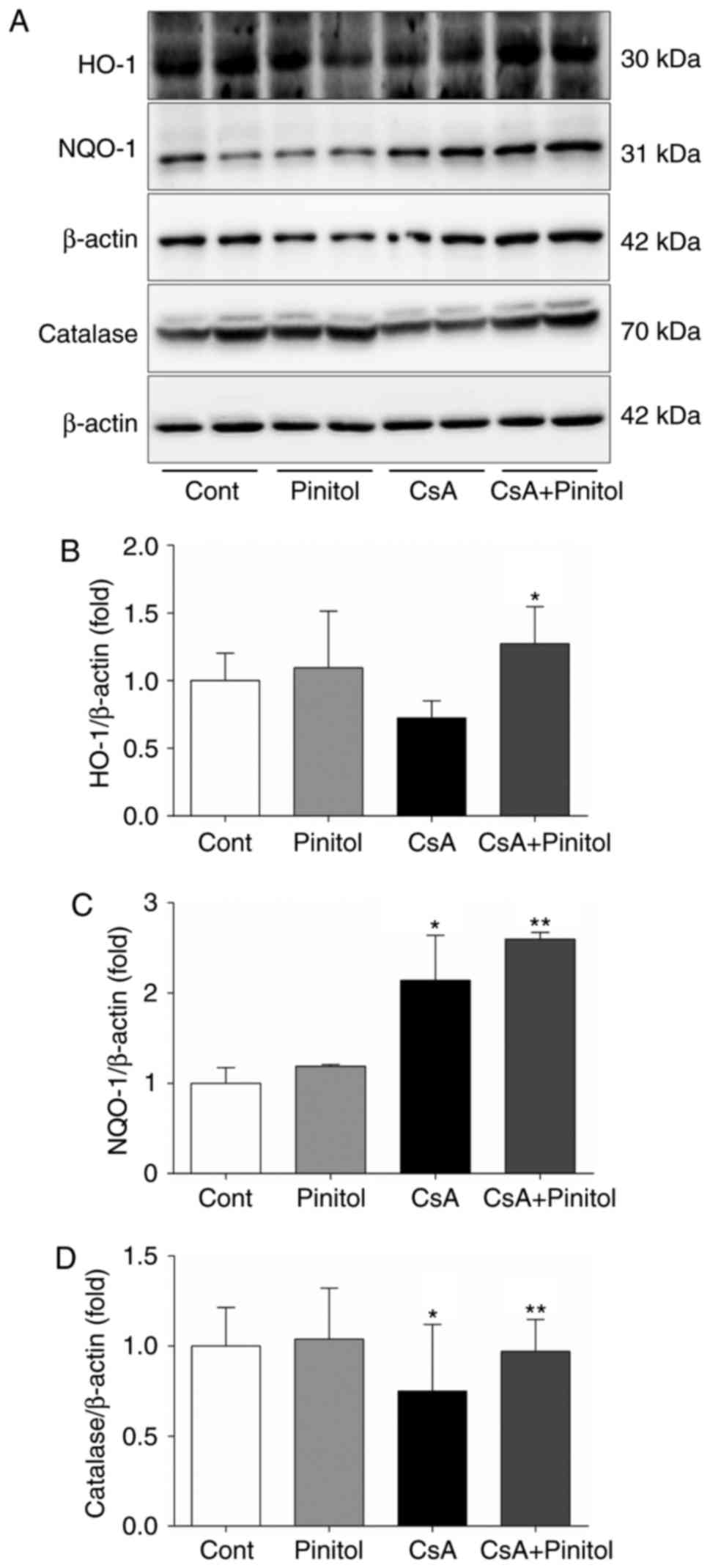
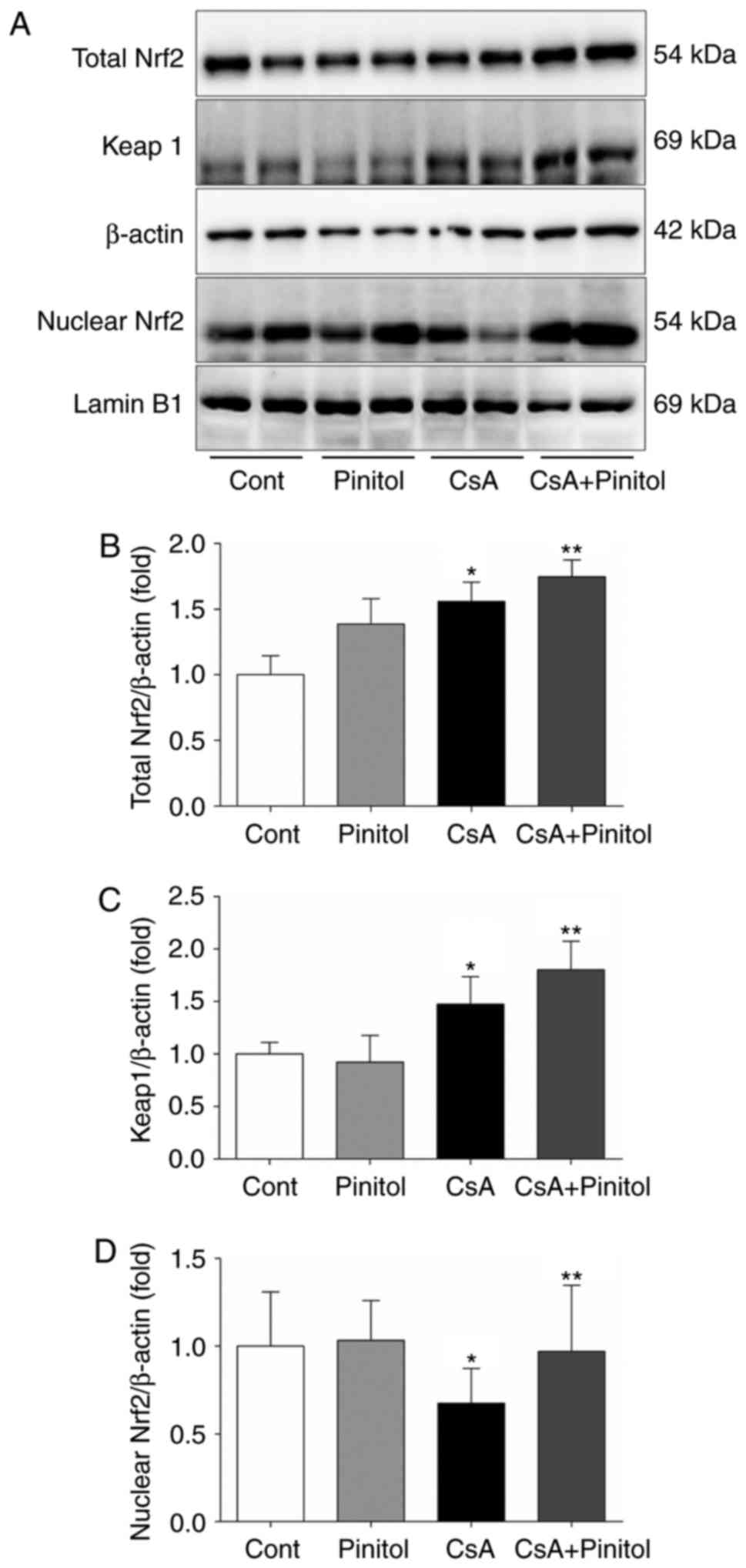
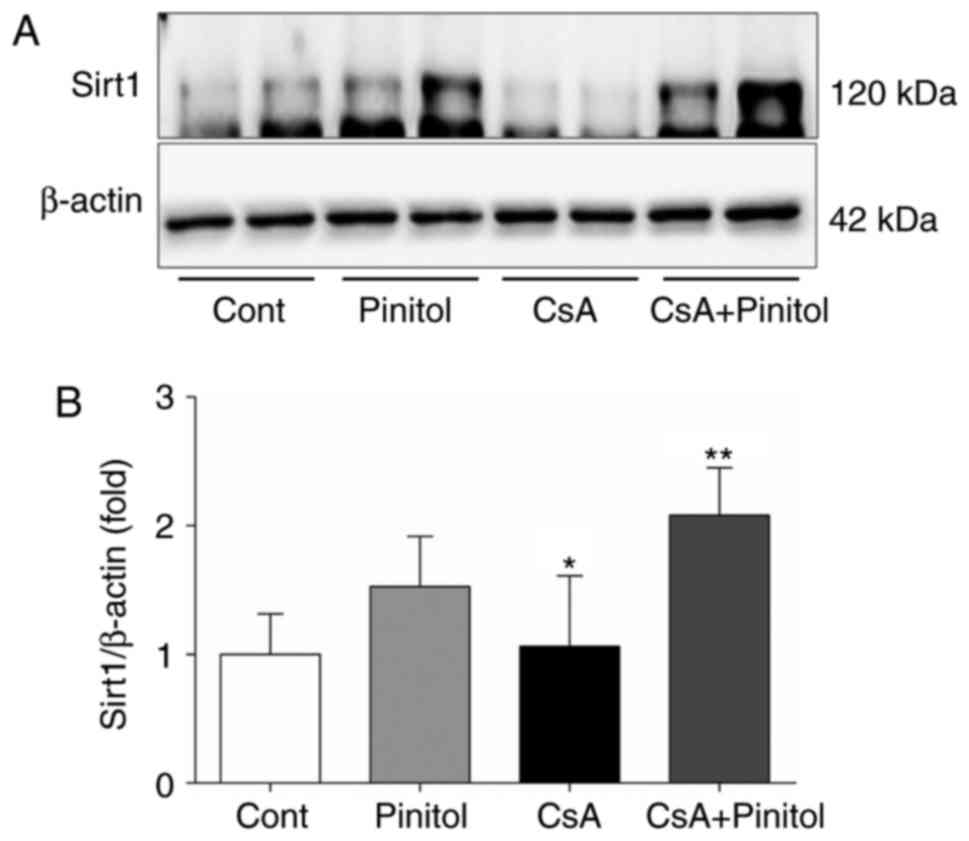
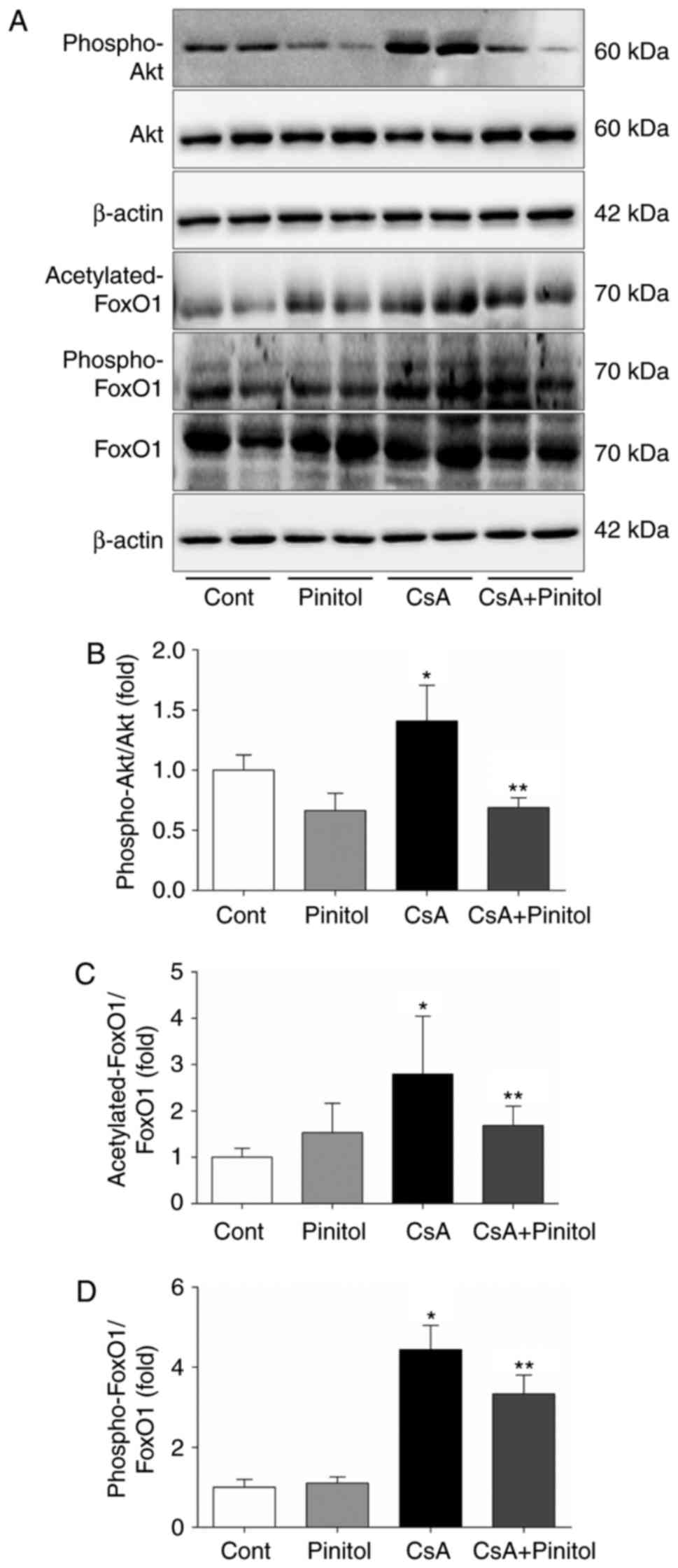
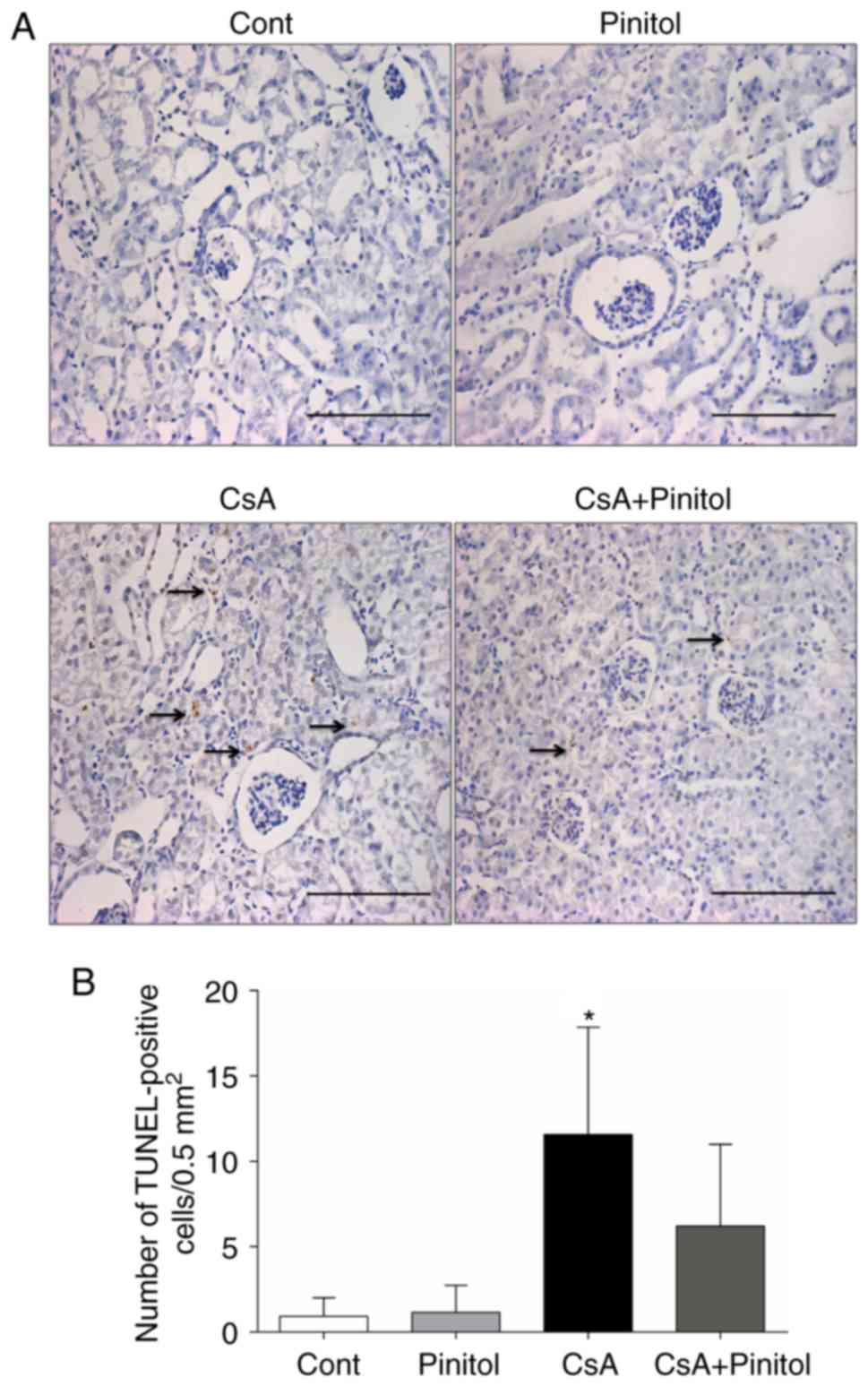
|
1
|
Lin TH, Tan TW, Tsai TH, Chen CC, Hsieh
TF, Lee SS, Liu HH, Chen WC and Tang CH: D-pinitol inhibits
prostate cancer metastasis through inhibition of alphaVbeta3
integrin by modulating FAK, c-Src and NF-κB pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:9790–9802. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao Y, Zhang M, Wu T, Xu M, Cai H and
Zhang Z: Effects of D-pinitol on insulin resistance through the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. J
Agric Food Chem. 63:6019–6026. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi MS, Lee MK, Jung UJ, Kim HJ, Do GM,
Park YB and Jeon SM: Metabolic response of soy pinitol on
lipid-lowering, antioxidant and hepatoprotective action in hamsters
fed-high fat and high cholesterol diet. Mol Nutr Food Res.
53:751–759. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sung B and Aggarwal BB:
Pinitol targets nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway leading to
inhibition of gene products associated with proliferation,
apoptosis, invasion, and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:1604–1614. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rengarajan T, Nandakumar N, Rajendran P,
Ganesh MK, Balasubramanian MP and Nishigaki I: D-pinitol mitigates
tumor growth by modulating interleukins and hormones and induces
apoptosis in rat breast carcinogenesis through inhibition of
NF-kappaB. J Physiol Biochem. 71:191–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dang NT, Mukai R, Yoshida K and Ashida H:
D-pinitol and myo-inositol stimulate translocation of glucose
transporter 4 in skeletal muscle of C57BL/6 mice. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 74:1062–1067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hernández-Mijares A, Bañuls C, Peris JE,
Monzó N, Jover A, Bellod L, Victor VM and Rocha M: A single acute
dose of pinitol from a naturally-occurring food ingredient
decreases hyperglycaemia and circulating insulin levels in healthy
subjects. Food Chem. 141:1267–1272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stull AJ, Wood KV, Thyfault JP and
Campbell WW: Effects of acute pinitol supplementation on plasma
pinitol concentration, whole body glucose tolerance, and activation
of the skeletal muscle insulin receptor in older humans. Horm Metab
Res. 41:381–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sivakumar S, Palsamy P and Subramanian SP:
Impact of D-pinitol on the attenuation of proinflammatory
cytokines, hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and protection
of kidney tissue ultrastructure in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. Chem Biol Interact. 188:237–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nankivell BJ, P'Ng CH, O'Connell PJ and
Chapman JR: Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity through the lens
of longitudinal histology: Comparison of cyclosporine and
tacrolimus eras. Transplantation. 100:1723–1731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Büscher AK, Beck BB, Melk A, Hoefele J,
Kranz B, Bamborschke D, Baig S, Lange-Sperandio B, Jungraithmayr T,
Weber LT, et al: Rapid response to cyclosporin A and favorable
renal outcome in nongenetic versus genetic steroid-resistant
nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:245–253. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gooch JL, King C, Francis CE, Garcia PS
and Bai Y: Cyclosporine A alters expression of renal microRNAs: New
insights into calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. PLoS One.
12:e01752422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hošková L, Málek I, Kopkan L and Kautzner
J: Pathophysiological mechanisms of calcineurin inhibitor-induced
nephrotoxicity and arterial hypertension. Physiol Res. 66:167–180.
2017.
|
|
14
|
Lim SW, Doh KC, Jin L, Jin J, Piao SG, Heo
SB, Chung BH and Yang CW: Ginseng treatment attenuates autophagic
cell death in chronic cyclosporine nephropathy. Nephrology
(Carlton). 19:490–499. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA and Vaziri
ND: Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative
stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int.
83:1029–1241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang CW, Ahn HJ, Kim WY, Shin MJ, Kim SK,
Park JH, Kim YO, Kim YS, Kim J and Bang BK: Influence of the
renin-angiotensin system on epidermal growth factor expression in
normal and cyclosporine-treated rat kidney. Kidney Int. 60:847–857.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong YA, Lim JH, Kim MY, Kim EN, Koh ES,
Shin SJ, Choi BS, Park CW, Chang YS and Chung S: Delayed treatment
with oleanolic acid attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in
chronic cyclosporine nephropathy through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. J
Transl Med. 12:502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reisman SA, Aleksunes LM and Klaassen CD:
Oleanolic acid activates Nrf2 and protects from acetaminophen
hepatotoxicity via Nrf2-dependent and Nrf2-independent processes.
Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1273–1282. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chung S, Kim S, Kim M, Koh ES, Yoon HE,
Kim HS, Park CW, Chang YS and Shin SJ: T-type calcium channel
blocker attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal
interstitial fibrosis by activating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway.
Am J Transl Res. 8:4574–4585. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kitada M and Koya D: Role of sirtuins in
kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 23:75–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang K, Huang J, Xie X, Wang S, Chen C,
Shen X, Liu P and Huang H: Sirt1 resists advanced glycation end
products-induced expressions of fibronectin and TGF-β1 by
activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway in glomerular mesangial cells. Free
Radic Biol Med. 65:528–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Parra Cid T, Conejo Garcia JR, Carballo
Alvarez F and de Arriba G: Antioxidant nutrients protect against
cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity. Toxicology. 189:99–111. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yoon HE, Ghee JY, Piao S, Song JH, Han DH,
Kim S, Ohashi N, Kobori H, Kuro-o M and Yang CW: Angiotensin II
blockade upregulates the expression of klotho, the anti-ageing
gene, in an experimental model of chronic cyclosporine nephropathy.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:800–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Kim HJ and Vaziri ND: Contribution of
impaired Nrf2-Keap1 pathway to oxidative stress and inflammation in
chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F662–F671.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chung S, Yoon HE, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, Koh ES,
Hong YA, Park CW, Chang YS and Shin SJ: Oleanolic acid attenuates
renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction via
facilitating nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Nutr Metab (Lond).
11:22014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim S, Kim SJ, Yoon HE, Chung S, Choi BS,
Park CW and Shin SJ: Fimasartan, a novel angiotensin-receptor
blocker, protects against renal inflammation and fibrosis in mice
with unilateral ureteral obstruction: The possible role of nrf2.
Int J Med Sci. 12:891–904. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Piao SG, Kang SH, Lim SW, Chung BH, Doh
KC, Heo SB, Jin L, Li C and Yang CW: Influence of N-acetylcysteine
on klotho expression and its signaling pathway in experimental
model of chronic cyclosporine nephropathy in mice. Transplantation.
96:146–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Doh KC, Lim SW, Piao SG, Jin L, Heo SB,
Zheng YF, Bae SK, Hwang GH, Min KI, Chung BH and Yang CW: Ginseng
treatment attenuates chronic cyclosporine nephropathy via reducing
oxidative stress in an experimental mouse model. Am J Nephrol.
37:421–433. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gęgotek A and Skrzydlewska E: The role of
transcription factor Nrf2 in skin cells metabolism. Arch Dermatol
Res. 307:385–396. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sivakumar S, Palsamy P and Subramanian SP:
Attenuation of oxidative stress and alteration of hepatic tissue
ultrastructure by D-pinitol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. Free Radic Res. 44:668–678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim MJ, Yoo KH, Kim JH, Seo YT, Ha BW, Kho
JH, Shin YG and Chung CH: Effect of pinitol on glucose metabolism
and adipocytokines in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 77(Suppl 1): S247–S251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F,
Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A and
Altucci L: Sirtuin functions and modulation: From chemistry to the
clinic. Clin Epigenetics. 8:612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wakino S, Hasegawa K and Itoh H: Sirtuin
and metabolic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 88:691–698. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Medema RH and Jäättelä M: Cytosolic FoxO1:
Alive and killing. Nat Cell Biol. 12:642–643. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Yang J, Liao W, Liu X, Zhang H,
Wang S, Wang D, Feng J, Yu L and Zhu WG: Cytosolic FoxO1 is
essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 12:665–675. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szydłowski M, Jabłońska E and Juszczyński
P: FOXO1 transcription factor: A critical effector of the PI3K-AKT
axis in B-cell development. Int Rev Immunol. 33:146–157. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Aoyama H,
Yoshimochi K and Fukamizu A: Acetylation of Foxo1 alters its
DNA-binding ability and sensitivity to phosphorylation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:11278–11283. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim DH, Park CH, Park D, Choi YJ, Park MH,
Chung KW, Kim SR, Lee JS and Chung HY: Ginsenoside Rc modulates
Akt/FoxO1 pathways and suppresses oxidative stress. Arch Pharm Res.
37:813–820. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kulkarni SR, Donepudi AC, Xu J, Wei W,
Cheng QC, Driscoll MV, Johnson DA, Johnson JA, Li X and Slitt AL:
Fasting induces nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 and ATP-binding
cassette transporters via protein kinase A and sirtuin-1 in mouse
and human. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:15–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Huang K, Chen C, Hao J, Huang J, Wang S,
Liu P and Huang H: Polydatin promotes Nrf2-ARE anti-oxidative
pathway through activating Sirt1 to resist AGEs-induced
upregulation of fibronetin and transforming growth factor-β1 in rat
glomerular messangial cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 399:178–189.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|