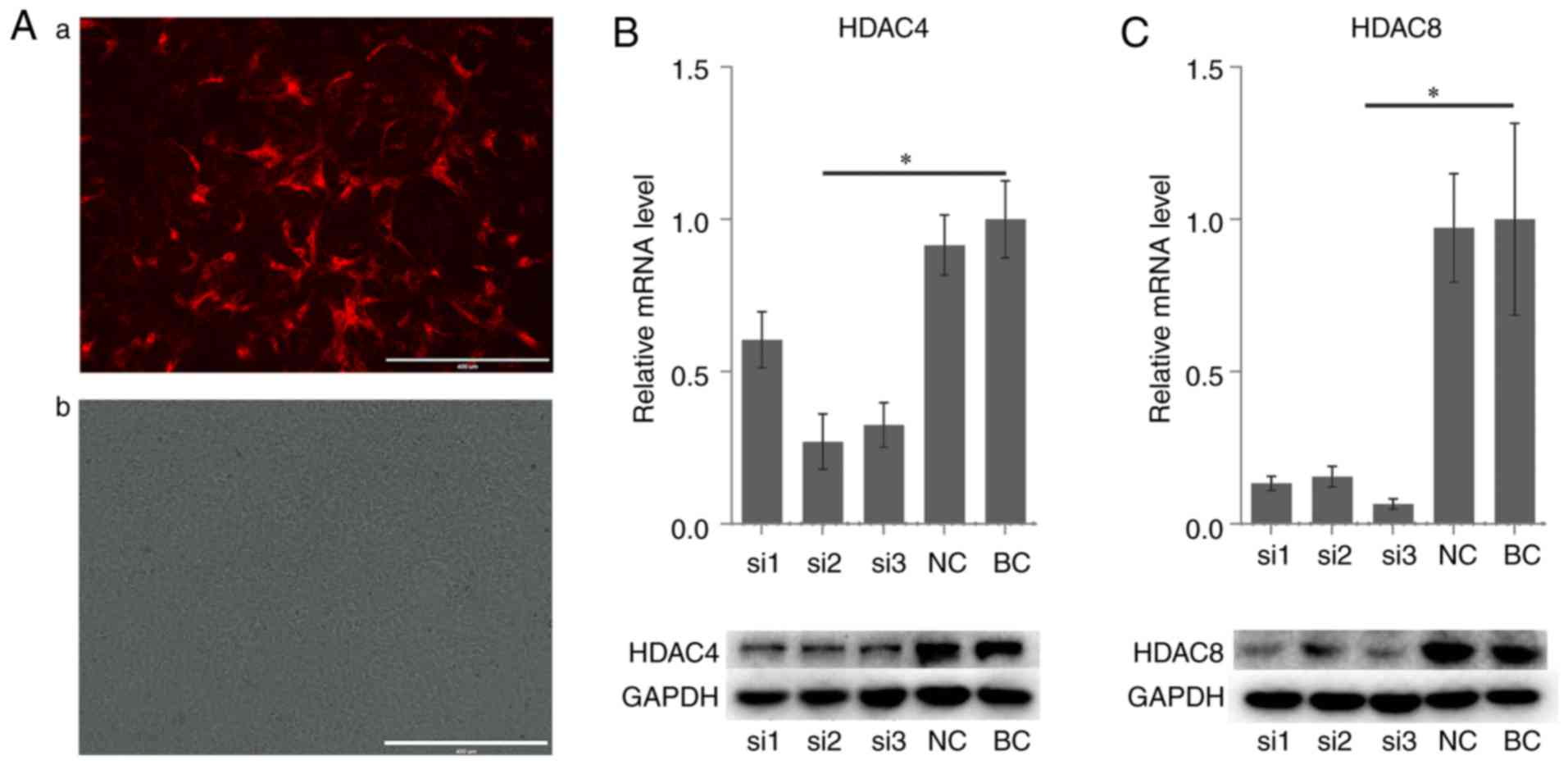
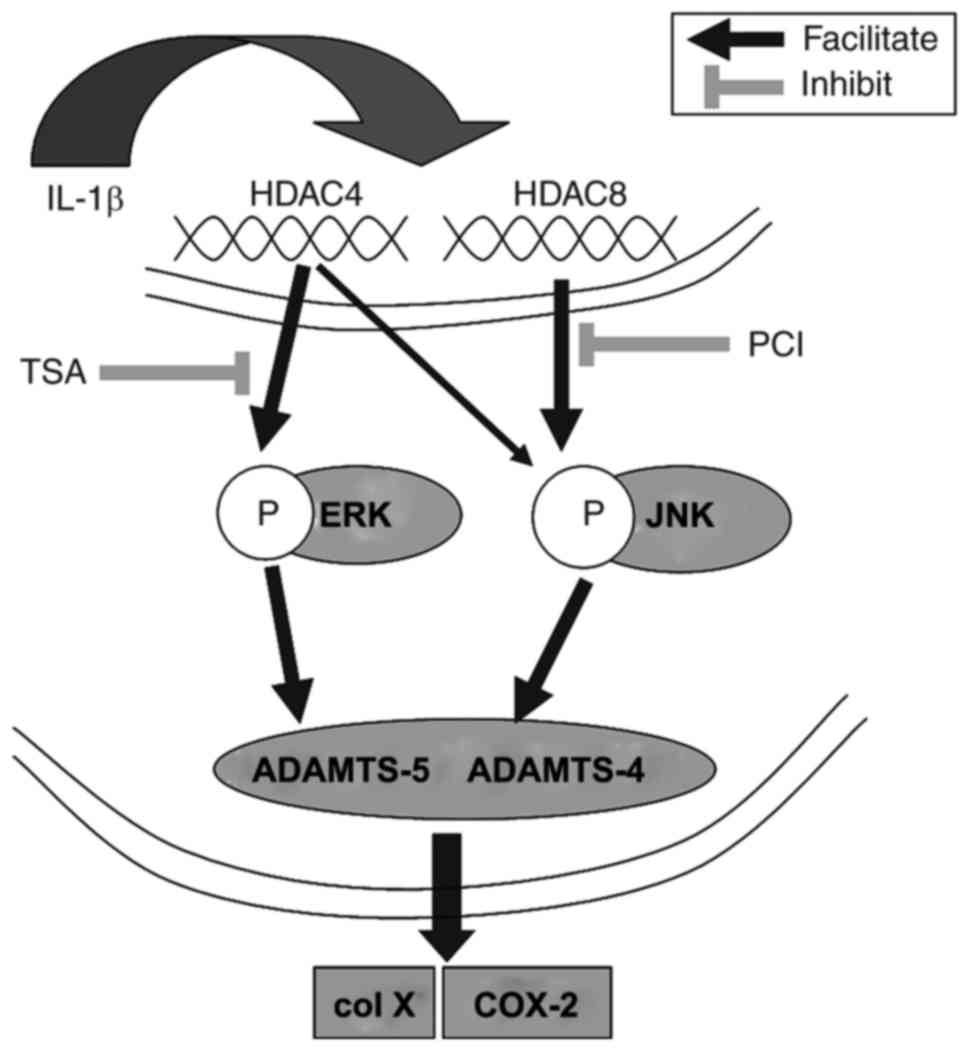
|
1
|
Hayami T, Pickarski M, Wesolowski GA,
McLane J, Bone A, Destefano J, Rodan GA and Duong LT: The role of
subchondral bone remodeling in osteoarthritis: Reduction of
cartilage degeneration and prevention of osteophyte formation by
alendronate in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection
model. Arthritis Rheum. 50:1193–1206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhong HM, Ding QH, Chen WP and Luo RB:
Vorinostat, a HDAC inhibitor, showed anti-osteoarthritic activities
through inhibition of iNOS and MMP expression, p38 and ERK
phosphorylation and blocking NF-κB nuclear translocation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 17:329–335. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tetsunaga T, Nishida K, Furumatsu T,
Naruse K, Hirohata S, Yoshida A, Saito T and Ozaki T: Regulation of
mechanical stress-induced MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 expression by RUNX-2
transcriptional factor in SW1353 chondrocyte-like cells.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:222–232. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Arden N and Nevitt MC: Osteoarthritis.
Epidemiology Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 20:3–25. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goldring MB and Goldring SR:
Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 213:626–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cooper C, Javaid MK and Arden N:
Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Atlas Osteoarthritis. 21–36.
2015.
|
|
7
|
Issa SN and Sharma L: Epidemiology of
osteoarthritis: An update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 8:7–15. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dancevic CM and McCulloch DR: Current and
emerging therapeutic strategies for preventing inflammation and
aggrecanase-mediated cartilage destruction in arthritis. Arthritis
Res Ther. 16:4292014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Krader CG: Guidance on non-surgical
management of knee osteoarthritis. Med Econ. 91:122014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McAlindon TE, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC,
Arden NK, Berenbaum F, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, Hawker GA, Henrotin Y,
Hunter DJ, Kawaguchi H, et al: OARSI guidelines for the
non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 22:363–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dodge GR and Poole AR: Immunohistochemical
detection and immunochemical analysis of type II collagen
degradation in human normal, rheumatoid, and osteoarthritic
articular cartilages and in explants of bovine articular cartilage
cultured with interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 83:647–661. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Farrajota K, Cheng S, Martel-Pelletier J,
Afif H, Pelletier JP, Li X, Ranger P and Fahmi H: Inhibition of
interleukin-1beta-induced cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human
synovial fibroblasts by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2
through a histone deacetylase-independent mechanism. Arthritis
Rheum. 52:94–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Attur M, Belitskaya-Lévy I, Oh C,
Krasnokutsky S, Greenberg J, Samuels J, Smiles S, Lee S, Patel J,
Al-Mussawir H, et al: Increased interleukin-1β gene expression in
peripheral blood leukocytes is associated with increased pain and
predicts risk for progression of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:1908–1917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chowdhury TT, Salter DM, Bader DL and Lee
DA: Signal transduction pathways involving p38 MAPK, JNK, NFkappaB
and AP-1 influences the response of chondrocytes cultured in
agarose constructs to IL-1beta and dynamic compression. Inflam Res.
57:306–313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lim H and Kim HP: Matrix
metalloproteinase-13 expression in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes by
activation of the p38 MAPK/c-Fos/AP-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. Arch
Pharm Res. 34:109–117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mitchell PG, Magna HA, Reeves LM,
Lopresti-Morrow LL, Yocum SA, Rosner PJ, Geoghegan KF and Hambor
JE: Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of
matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. J
Clin Invest. 97:761–768. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lauer-Fields JL, Juska D and Fields GB:
Matrix metalloproteinases and collagen catabolism. Biopolymers.
66:19–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qing C, Wei-ding C and Wei-min F:
Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular
matrix components. Braz J Med Biol Res. 44:303–310. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zuo Q, Cui W, Liu F, Wang Q, Chen Z and
Fan W: Co-cultivated mesenchymal stem cells support chondrocytic
differentiation of articular chondrocytes. Int Orthop. 37:747–752.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bolton M: Purification and cloning of
aggrecanase-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 3:667251999.
|
|
21
|
Abbaszade I, Liu RQ, Yang F, Rosenfeld SA,
Ross OH, Link JR, Ellis DM, Tortorella MD, Pratta MA, Hollis JM, et
al: Cloning and characterization of ADAMTS11, an aggrecanase from
the ADAMTS family. J Biol Chem. 274:23443–23450. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, Carito B,
Blanchet T, Ma HL, Flannery CR, Peluso D, Kanki K, Yang Z, et al:
Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a
murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature. 434:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, Carito
BA, Blanchet T, Ma HL, Flannery CR, Kanki K, Wang E, Peluso D, et
al: Characterization of and osteoarthritis susceptibility in
ADAMTS-4-knockout mice. Arthritis Rheum. 50:2547–2558. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodríguez-Manzaneque JC, Westling J, Thai
SN, Luque A, Knauper V, Murphy G, Sandy JD and Iruela-Arispe ML:
ADAMTS1 cleaves aggrecan at multiple sites and is differentially
inhibited by metalloproteinase inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 293:501–508. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Collins-Racie LA, Flannery CR, Zeng W,
Corcoran C, Annis-Freeman B, Agostino MJ, Arai M, DiBlasio-Smith E,
Dorner AJ, Georgiadis KE, et al: ADAMTS-8 exhibits aggrecanase
activity and is expressed in human articular cartilage. Matrix
Biol. 23:219–230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dancevic CM, Fraser FW, Smith AD, Stupka
N, Ward AC and Mcculloch DR: Biosynthesis and expression of a
disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase domain with thrombospondin-1
repeats-15: A novel versican-cleaving proteoglycanase. J Biol Chem.
288:37267–37276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chu X, You H, Yuan X, Zhao W, Li W and Guo
X: Protective effect of lentivirus-mediated siRNA targeting
ADAMTS-5 on cartilage degradation in a rat model of osteoarthritis.
Int J Mol Med. 31:1222–1228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan HW, Liu GY, Zhao CF, Li XF and Yang
XY: Differential expression of COX-2 in osteoarthritis and
rheumatoid arthritis. Genet Mol Res. 14:12872–12879. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Su SC, Tanimoto K, Tanne Y, Kunimatsu R,
Hirose N, Mitsuyoshi T, Okamoto Y and Tanne K: Celecoxib exerts
protective effects on extracellular matrix metabolism of mandibular
condylar chondrocytes under excessive mechanical stress.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:845–851. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Herold C, Ganslmayer M, Ocker M, Hermann
M, Geerts A, Hahn EG and Schuppan D: The histone-deacetylase
inhibitor Trichostatin A blocks proliferation and triggers
apoptotic programs in hepatoma cells. J Hepatol. 36:233–240. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen J, Lai J, Yang L, Ruan G, Chaugai S,
Ning Q, Chen C and Wang DW: Trimetazidine prevents
macrophage-mediated septic myocardial dysfunction via activation of
the histone deacetylase sirtuin 1. Br J Pharmacol. 173:545–561.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan M, Chen C, Gong W, Yin Z, Zhou L,
Chaugai S and Wang DW: miR-21-3p regulates cardiac hypertrophic
response by targeting histone deacetylase-8. Cardiovasc Res.
105:340–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Adcock IM: HDAC inhibitors as
anti-inflammatory agents. Brit J Pharmacol. 150:829–831. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Halili MA, Andrews MR, Labzin LI, Schroder
K, Matthias G, Cao C, Lovelace E, Reid RC, Le GT, Hume DA, et al:
Differential effects of selective HDAC inhibitors on macrophage
inflammatory responses to the Toll-like receptor 4 agonist LPS. J
Leukocyte Biol. 87:1103–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sweet MJ, Shakespear MR, Kamal NA and
Fairlie DP: HDAC inhibitors: Modulating leukocyte differentiation,
survival, proliferation and inflammation. Immunol Cell Biol.
90:14–22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shuttleworth SJ, Bailey SG and Townsend
PA: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: New promise in the treatment of
immune and inflammatory diseases. Curr Drug Targets. 11:1430–1438.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song C, Zhu S, Wu C and Kang J: Histone
deacetylase (HDAC) 10 Suppresses cervical cancer metastasis through
inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and 9 Expression. J
Biol Chem. 288:28021–28033. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Young DA, Lakey RL, Pennington CJ, Jones
D, Kevorkian L, Edwards DR, Cawston TE and Clark IM: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors modulate metalloproteinase gene expression
in chondrocytes and block cartilage resorption. Arthritis Res Ther.
7:R503–R512. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chabane N, Zayed N, Afif H, Mfuna-Endam L,
Benderdour M, Boileau C, Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Duval N
and Fahmi H: Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress
interleukin-1beta-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
production in human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
16:1267–1274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nasu Y, Nishida K, Miyazawa S, Komiyama T,
Kadota Y, Abe N, Yoshida A, Hirohata S, Ohtsuka A and Ozaki T:
Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses
synovial inflammation and subsequent cartilage destruction in a
collagen antibody-induced arthritis mouse model. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 16:723–732. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Song Y, Jacobi JL and Tuan RS:
Inhibition of histone deacetylases antagonized FGF2 and IL-1beta
effects on MMP expression in human articular chondrocytes. Growth
Factors. 27:40–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Saito T, Nishida K, Furumatsu T, Yoshida
A, Ozawa M and Ozaki T: Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress
mechanical stress-induced expression of RUNX-2 and ADAMTS-5 through
the inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway in cultured human
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:165–174. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Koshy PJ, Lundy CJ, Rowan AD, Porter S,
Edwards DR, Hogan A, Clark IM and Cawston TE: The modulation of
matrix metalloproteinase and ADAM gene expression in human
chondrocytes by interleukin-1 and oncostatin M: A time-course study
using real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain
reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 46:961–967. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tian Y, Yuan W, Fujita N, Wang J, Wang H,
Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Inflammatory cytokines associated with
degenerative disc disease control aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS-4)
expression in nucleus pulposus cells through MAPK and NF-κB. Am J
Pathol. 182:2310–2321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pan T, Chen R, Wu D, Cai N, Shi X, Li B
and Pan J: Alpha-Mangostin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced
apoptosis in rat chondrocytes by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling
pathway and delays the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat
model. Int Immunopharmacol. 52:156–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Feng Z, Zheng W, Li X, Lin J, Xie C, Li H,
Cheng L, Wu A and Ni W: Cryptotanshinone protects against
IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and
ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 50:161–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tang Q, Zheng G, Feng Z, Tong M, Xu J, Hu
Z, Shang P, Chen Y, Wang C, Lou Y, et al: Wogonoside inhibits IL-1β
induced catabolism and hypertrophy in mouse chondrocyte and
ameliorates murine osteoarthritis. Oncotarget. 8:61440–61456.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Guo X, Chu X, Li W, Pan Q and You H:
Chondrogenic effect of precartilaginous stem cells following
NLS-TAT cell penetrating peptide-assisted transfection of
eukaryotic hTGFβ3. J Cell Biochem. 114:2588–2594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim YI, Ryu JS, Yeo JE, Choi YJ, Kim YS,
Ko K and Koh YG: Overexpression of TGF-β1 enhances chondrogenic
differentiation and proliferation of human synovium-derived stem
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:1593–1599. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pan Q, Li W, Yuan X, Rakhmanov Y, Wang P,
Lu R, Mao Z, Shang X and You H: Chondrogenic effect of cell-based
scaffold of self-assembling peptides/PLGA-PLL loading the hTGFβ3
plasmid DNA. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 27:192016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
You H, Chen A, Liu T, Wang M and Zhang G:
Construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid of hTGF-β3 and its
inducing effect on differentiation of precartilaginous stem cells
into chondroblasts. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci.
31:524–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bouffi C, Thomas O, Bony C, Giteau A,
Venier-Julienne MC, Jorgensen C, Montero-Menei C and Noël D: The
role of pharmacologically active microcarriers releasing TGF-beta3
in cartilage formation in vivo by mesenchymal stem cells.
Biomaterials. 31:6485–6493. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ding R, Zhang Y, You HB, Li F and Sun K:
Transfecting human transformation growth factor beta 3 gene into
precartilaginous stem cells cultured in three-dimensional
self-assembled peptide nanofiber scaffold of KLD-12. J Clin
Rehabilitative Tissue Eng Res. 14:5339–5343. 2010.
|
|
55
|
Qi J, Chen A, You H, Li K, Zhang D and Guo
F: Proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of CD105-positive
enriched rat synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells in
three-dimensional porous scaffolds. Biomed Mater. 6:0150062011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Danišovič L, Varga I and Polák S: Growth
factors and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Tissue Cell. 44:69–73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Osterman C, McCarthy MB, Cote MP, Beitzel
K, Bradley J, Polkowski G and Mazzocca AD: Platelet-rich plasma
increases anti-inflammatory markers in a human coculture model for
osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 43:1474–1484. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ying X, Chen X, Cheng S, Shen Y, Peng L
and Xu HZ: Piperine inhibits IL-β induced expression of
inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocyte. Int
Immunopharmacol. 17:293–299. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Seki S, Asanuma-Abe Y, Masuda K, Kawaguchi
Y, Asanuma K, Muehleman C, Iwai A and Kimura T: Effect of small
interference RNA (siRNA) for ADAMTS5 on intervertebral disc
degeneration in the rabbit anular needle-puncture model. Arthritis
Res Ther. 11:R1662009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Song RH, Tortorella MD, Malfait AM, Alston
JT, Yang Z, Arner EC and Griggs DW: Aggrecan degradation in human
articular cartilage explants is mediated by both ADAMTS-4 and
ADAMTS-5. Arthritis Rheum. 56:575–585. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fliedner SM, Engel T, Lendvai NK,
Shankavaram U, Nölting S, Wesley R, Elkahloun AG, Ungefroren H,
Oldoerp A, Lampert G, et al: Anti-cancer potential of MAPK pathway
inhibition in paragangliomas-effect of different statins on mouse
pheochromocytoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e977122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ge C, Yang Q, Zhao G, Yu H, Kirkwood KL
and Franceschi RT: Interactions between extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 MAP kinase pathways in the
control of RUNX2 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. J
Bone Miner Res. 27:538–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Li W, Li G, Zhang Y, Wei S, Song M, Wang
W, Yuan X, Wu H and Yang Y: Role of 2 × 7 receptor in the
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells into osteoblasts and
adipocytes. Exp Cell Res. 339:367–379. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li W, Wei S, Liu C, Song M, Wu H and Yang
Y: Regulation of the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of
bone marrow-derived stromal cells by extracellular uridine
triphosphate: The role of P2Y2 receptor and ERK1/2 signaling. Int J
Mol Med. 37:63–73. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
66
|
Ismail HM, Yamamoto K, Vincent TL, Nagase
H, Troeberg L and Saklatvala J: Interleukin-1 Acts via the JNK-2
signaling pathway to induce aggrecan degradation by human
chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:1826–1836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang JH, Shih KS, Wu YW, Wang AW and Yang
CR: Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase microRNA-146a
expression and enhance negative regulation of interleukin-1β
signaling in osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1987–1996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lu J, Sun Y, Ge Q, Teng H and Jiang Q:
Histone deacetylase 4 alters cartilage homeostasis in human
osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 15:4382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Higashiyama R, Miyaki S, Yamashita S,
Yoshitaka T, Lindman G, Ito Y, Sasho T, Takahashi K, Lotz M and
Asahara H: Correlation between MMP-13 and HDAC7 expression in human
knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 20:11–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
70
|
Song J, Jin EH, Kim D, Kim KY, Chun CH and
Jin EJ: MicroRNA-222 regulates MMP-13 via targeting HDAC-4 during
osteoarthritis pathogenesis. BBA Clin. 3:79–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|