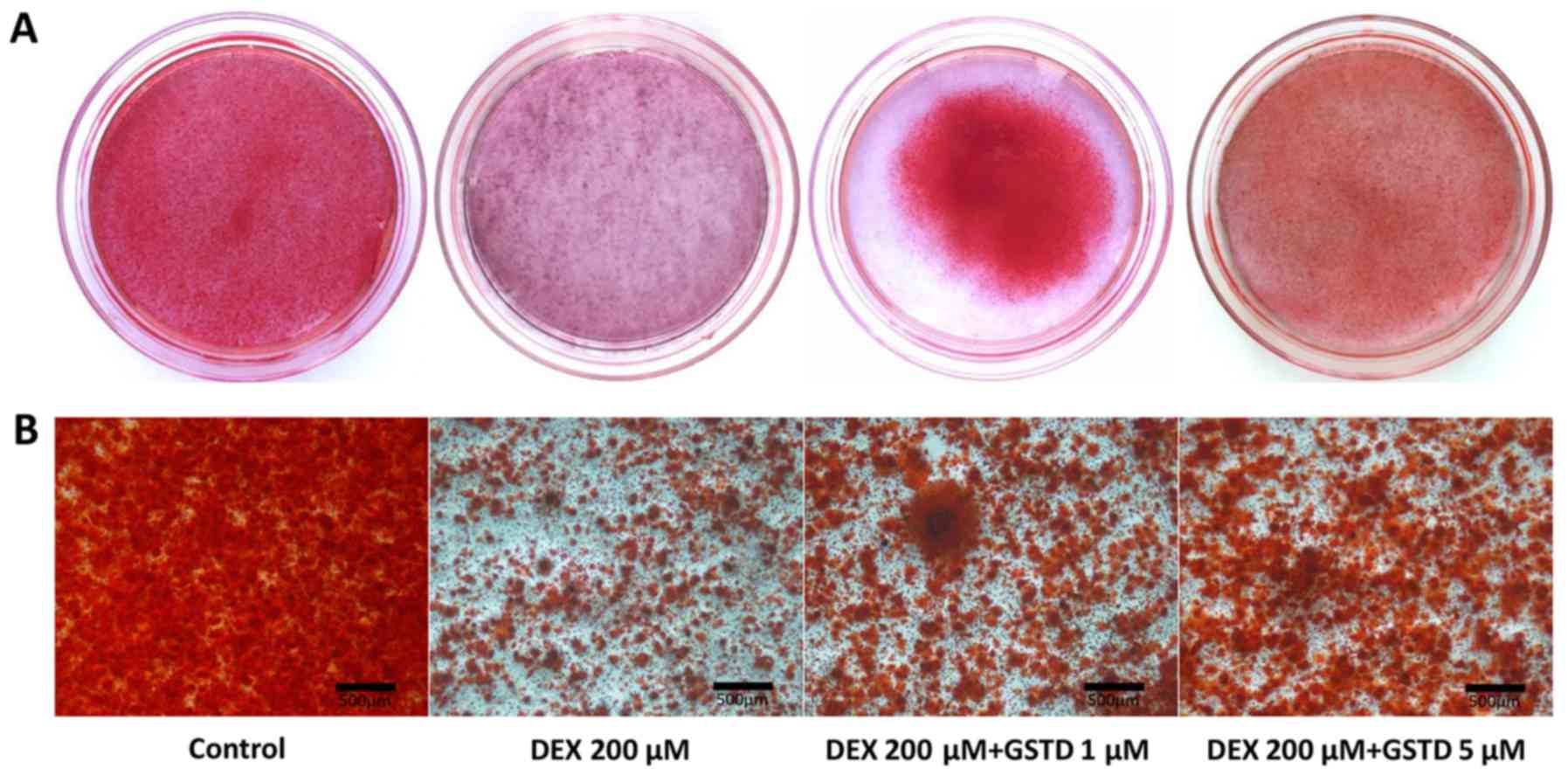
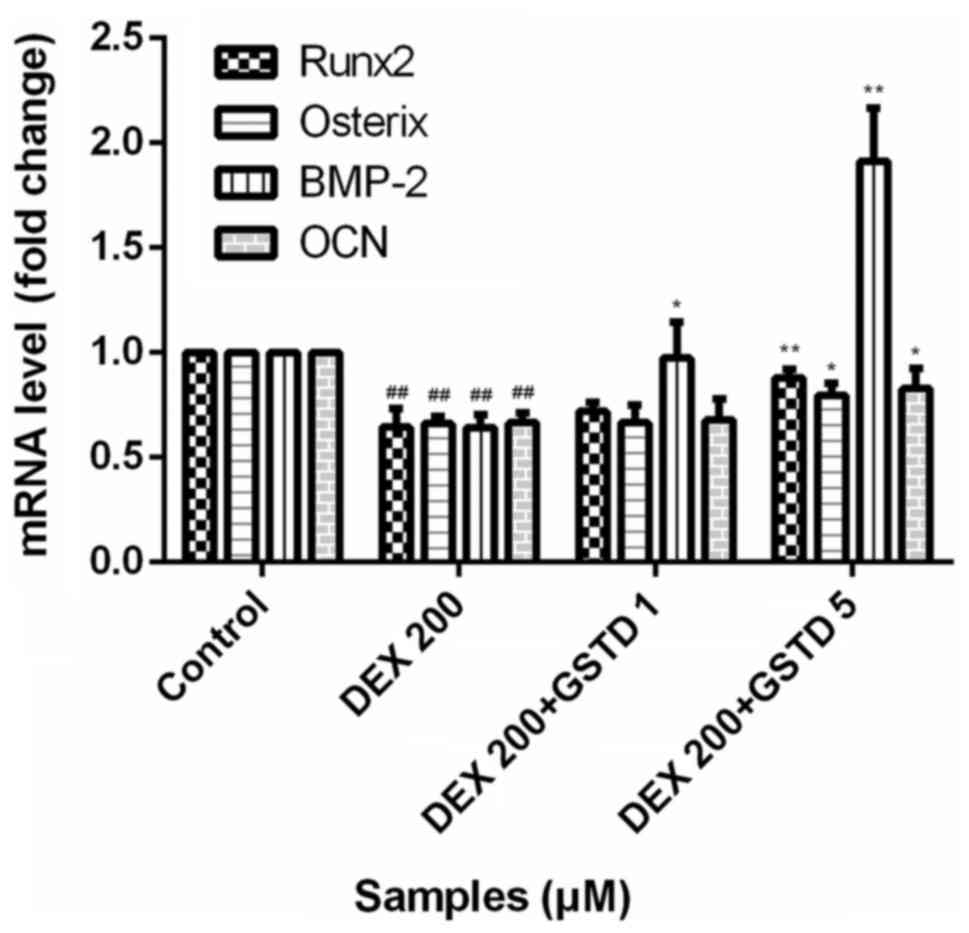
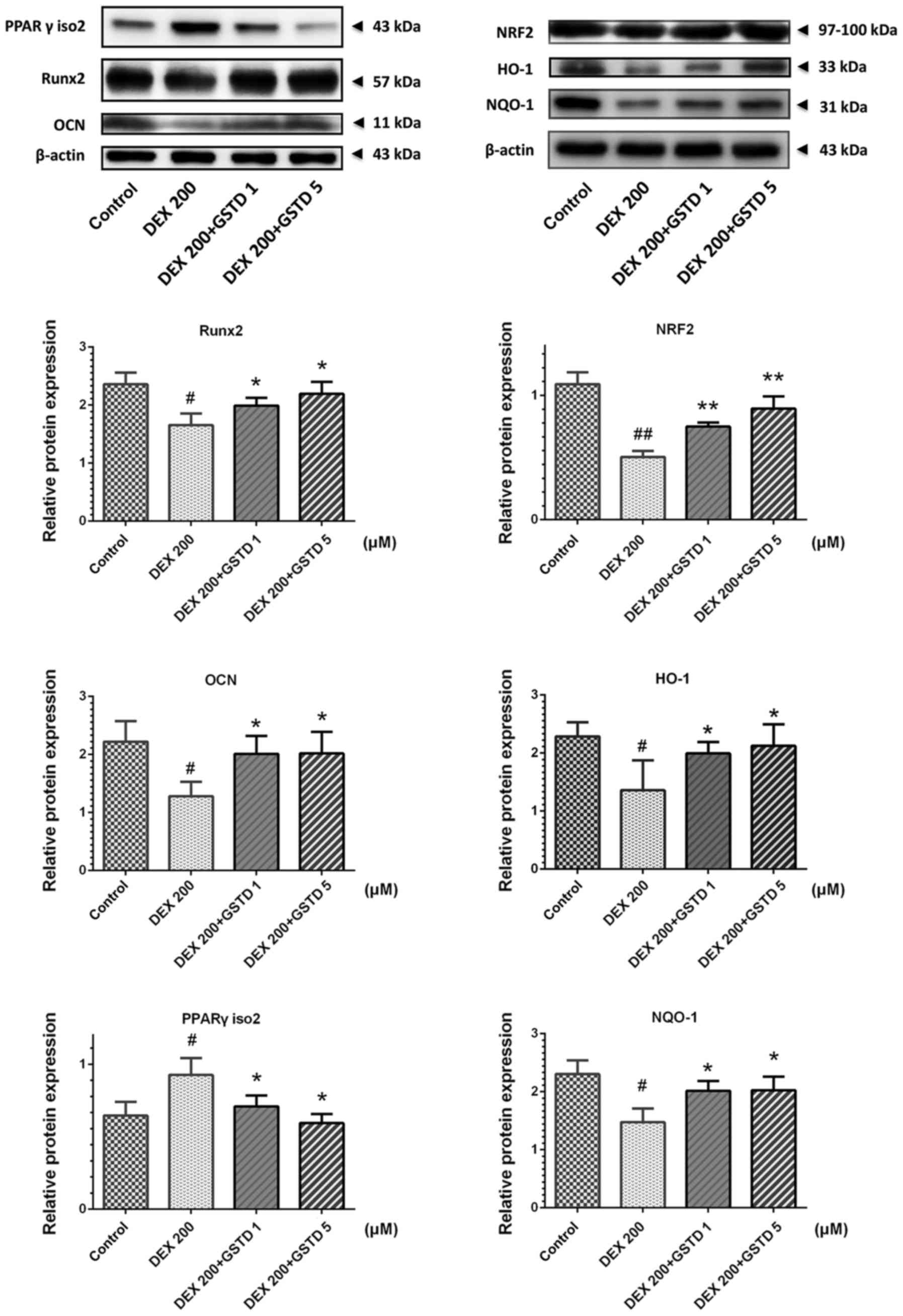
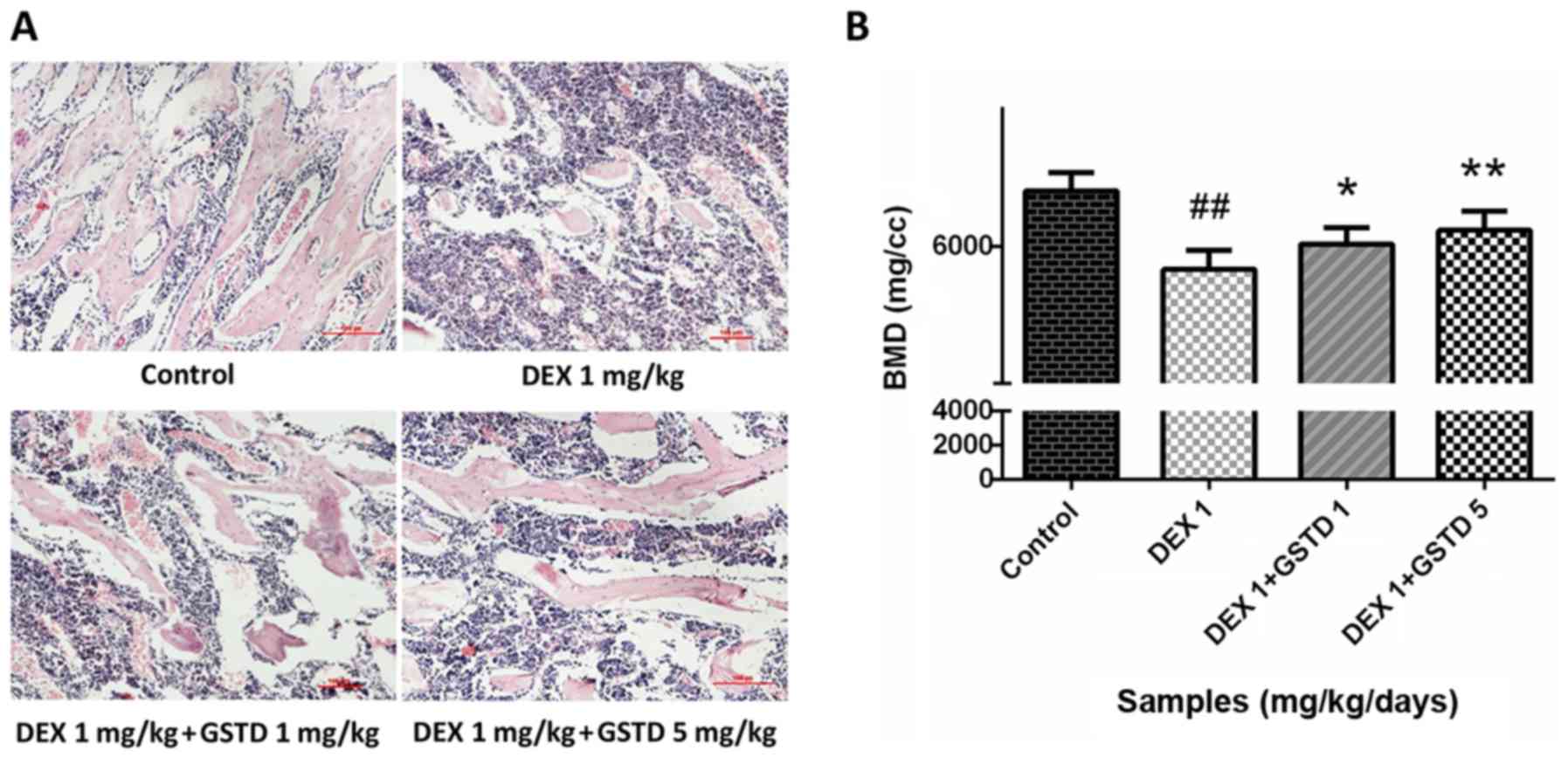
|
1
|
Drake MT, Clarke BL and Lewiecki EM: The
pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis. Clin Ther.
37:1837–1850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seibel MJ, Cooper MS and Zhou H:
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: Mechanisms, management, and
future perspectives. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 1:59–70. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Frenkel B, White W and Tuckermann J:
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 872:179–215.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henneicke H, Gasparini SJ,
Brennan-Speranza TC, Zhou H and Seibel MJ: Glucocorticoids and
bone: Local effects and systemic implications. Trends Endocrinol
Metab. 25:197–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Buehring B, Viswanathan R, Binkley N and
Busse W: Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: An update on effects
and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 132:1019–1030. 2013.
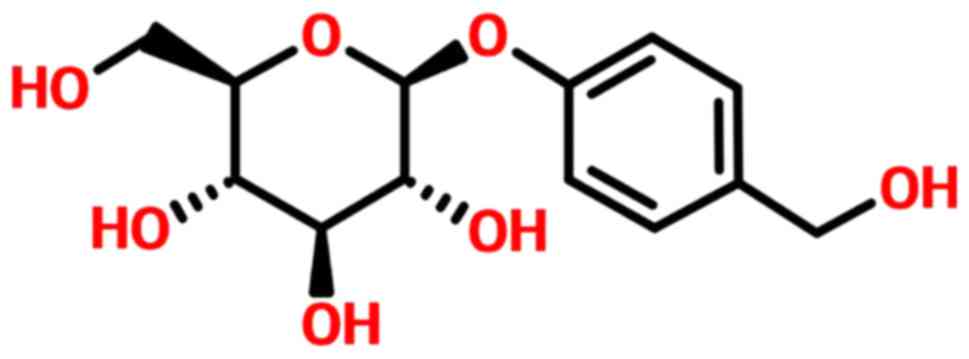
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang Q, Shi J, Gao B, Zhang HY, Fan J, Li
XJ, Fan JZ, Han YH, Zhang JK, Yang L, et al: Gastrodin: An ancient
Chinese herbal medicine as a source for anti-osteoporosis agents
via reducing reactive oxygen species. Bone. 73:132–144. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng H, Yang E, Peng H, Li J, Chen S,
Zhou J, Fang H, Qiu B and Wang Z: Gastrodin prevents
steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats by
anti-apoptosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 127:3926–3931. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Qu LL, Yu B, Li Z, Jiang WX, Jiang JD and
Kong WJ: Gastrodin ameliorates oxidative stress and proinflammatory
response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through the AMPK/Nrf2
pathway. Phytother Res. 30:402–411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Peng Z, Wang S, Chen G, Cai M, Liu R, Deng
J, Liu J, Zhang T, Tan Q and Hai C: Gastrodin alleviates cerebral
ischemic damage in mice by improving anti-oxidant and
anti-inflammation activities and inhibiting apoptosis pathway.
Neurochem Res. 40:661–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun YX, Xu AH, Yang Y and Li J: Role of
Nrf2 in bone metabolism. J Biomed Sci. 22:1012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz
A and Dulak J: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative
stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved
mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3221–3247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun YX, Li L, Corry KA, Zhang P, Yang Y,
Himes E, Mihuti CL, Nelson C, Dai G and Li J: Deletion of Nrf2
reduces skeletal mechanical properties and decreases load-driven
bone formation. Bone. 74:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin H, Wei B, Li G, Zheng J, Sun J, Chu J,
Zeng R and Niu Y: Sulforaphane reverses glucocorticoid-induced
apoptosis in osteoblastic cells through regulation of the Nrf2
pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:973–982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pellegrini GG, Morales CC, Wallace TC,
Plotkin LI and Bellido T: Avenanthramides prevent osteoblast and
osteocyte apoptosis and induce osteoclast apoptosis in vitro in an
Nrf2-independent manner. Nutrients. 8:4232016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Choi EM: Magnolol protects osteoblastic
MC3T3-E1 cells against antimycin A-induced cytotoxicity through
activation of mitochondrial function. Inflammation. 35:1204–1212.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan Z, Li Q, Luo S, Liu Z, Luo D, Zhang
B, Zhang D, Rao P and Xiao J: PPARγ and Wnt signaling in adipogenic
and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Stem
Cell Res Ther. 11:216–225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rauch A, Seitz S, Baschant U, Schilling
AF, Illing A, Stride B, Kirilov M, Mandic V, Takacz A,
Schmidt-Ullrich R, et al: Glucocorticoids suppress bone formation
by attenuating osteoblast differentiation via the monomeric
glucocorticoid receptor. Cell Metab. 11:517–531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hartmann K, Koenen M, Schauer S,
Wittig-Blaich S, Ahmad M, Baschant U and Tuckermann JP: Molecular
actions of glucocor-ticoids in cartilage and bone during health,
disease, and steroid therapy. Physiol Rev. 96:409–447. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu S, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Chu Y, Zmuda JM
and Zhang Y: E2F1 effects on osteoblast differentiation and
mineralization are mediated through upregulation of frizzled-1.
Bone. 56:234–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Z, Xue J, Shen T, Ba G, Yu D and Fu
Q: Curcumin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by
protecting osteoblasts from apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:268–276. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fang J, Yamaza H, Uchiumi T, Hoshino Y,
Masuda K, Hirofuji Y, Wagener FA, Kang D and Nonaka K:
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase depletion hampers mitochondrial
function and osteogenic differentiation in osteoblasts. Eur J Oral
Sci. 124:241–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan CK, Mason A, Cooper C and Dennison E:
Novel advances in the treatment of osteoporosis. Br Med Bull.
119:129–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kalak R, Zhou H, Street J, Day RE,
Modzelewski JR, Spies CM, Liu PY, Li G, Dunstan CR and Seibel MJ:
Endogenous glucocorticoid signalling in osteoblasts is necessary to
maintain normal bone structure in mice. Bone. 45:61–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Xue J, Shen T, Mu S and Fu Q:
Curcumin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through the
regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:329–338.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Kim J, Lee H, Kang KS, Chun KH and Hwang
GS: Protective effect of Korean Red Ginseng against
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in vitro and in vivo. J Ginseng
Res. 39:46–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liang W, Lin M, Li X, Li C, Gao B, Gan H,
Yang Z, Lin X, Liao L and Yang M: Icariin promotes bone formation
via the BMP-2/Smad4 signal transduction pathway in the hFOB 1.19
human osteoblastic cell line. Int J Mol Med. 30:889–895. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cao H, Ke Y, Zhang Y, Zhang CJ, Qian W and
Zhang GL: Icariin stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and
differentiation through upregulation of bone morphogenetic
protein-2. Int J Mol Med. 29:435–439. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Zhuang H, Zhang X, Zhu C, Tang X, Yu F,
Shang GW and Cai X: Molecular mechanisms of PPAR-γ governing MSC
osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
11:255–264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gómez-Puerto MC, Verhagen LP, Braat AK,
Lam EW, Coffer PJ and Lorenowicz MJ: Activation of autophagy by
FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic
differentiation. Autophagy. 12:1804–1816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Choi EM, Suh KS, Kim YJ, Hong SM, Park SY
and Chon S: Glabridin alleviates the toxic effects of methylglyoxal
on osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by increasing expression of the
glyoxalase system and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and protecting
mitochondrial function. J Agric Food Chem. 64:226–235. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Angelova PR and Abramov AY: Functional
role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in physiology. Free
Radic Biol Med. 100:81–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhen YF, Wang GD, Zhu LQ, Tan SP, Zhang
FY, Zhou XZ and Wang XD: P53 dependent mitochondrial permeability
transition pore opening is required for dexamethasone-induced death
of osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 229:1475–1483. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
O’Brien CA, Jia D, Plotkin LI, Bellido T,
Powers CC, Stewart SA, Manolagas SC and Weinstein RS:
Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to
induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength.
Endocrinology. 145:1835–1841. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
de Vries F, Pouwels S, Lammers JW,
Leufkens HG, Bracke M, Cooper C and van Staa TP: Use of inhaled and
oral glucocorticoids, severity of inflammatory disease and risk of
hip/femur fracture: A population-based case-control study. J Intern
Med. 261:170–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Giusti A, Hamdy NA and Papapoulos SE:
Atypical fractures of the femur and bisphosphonate therapy: A
systematic review of case/case series studies. Bone. 47:169–180.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang ZC, Su G, Li J, Wu H and Xie XD: Two
new neuroprotective phenolic compounds from Gastrodia elata. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 15:619–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu W, Wang L, Yu J, Asare PF and Zhao YQ:
GSTD reduces blood pressure by intervening with RAAS and PPARγ in
SHRs. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:8284272015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang XL, Xing GH, Hong B, Li XM, Zou Y,
Zhang XJ and Dong MX: Gastrodin prevents motor deficits and
oxidative stress in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease:
Involvement of ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 114:77–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|