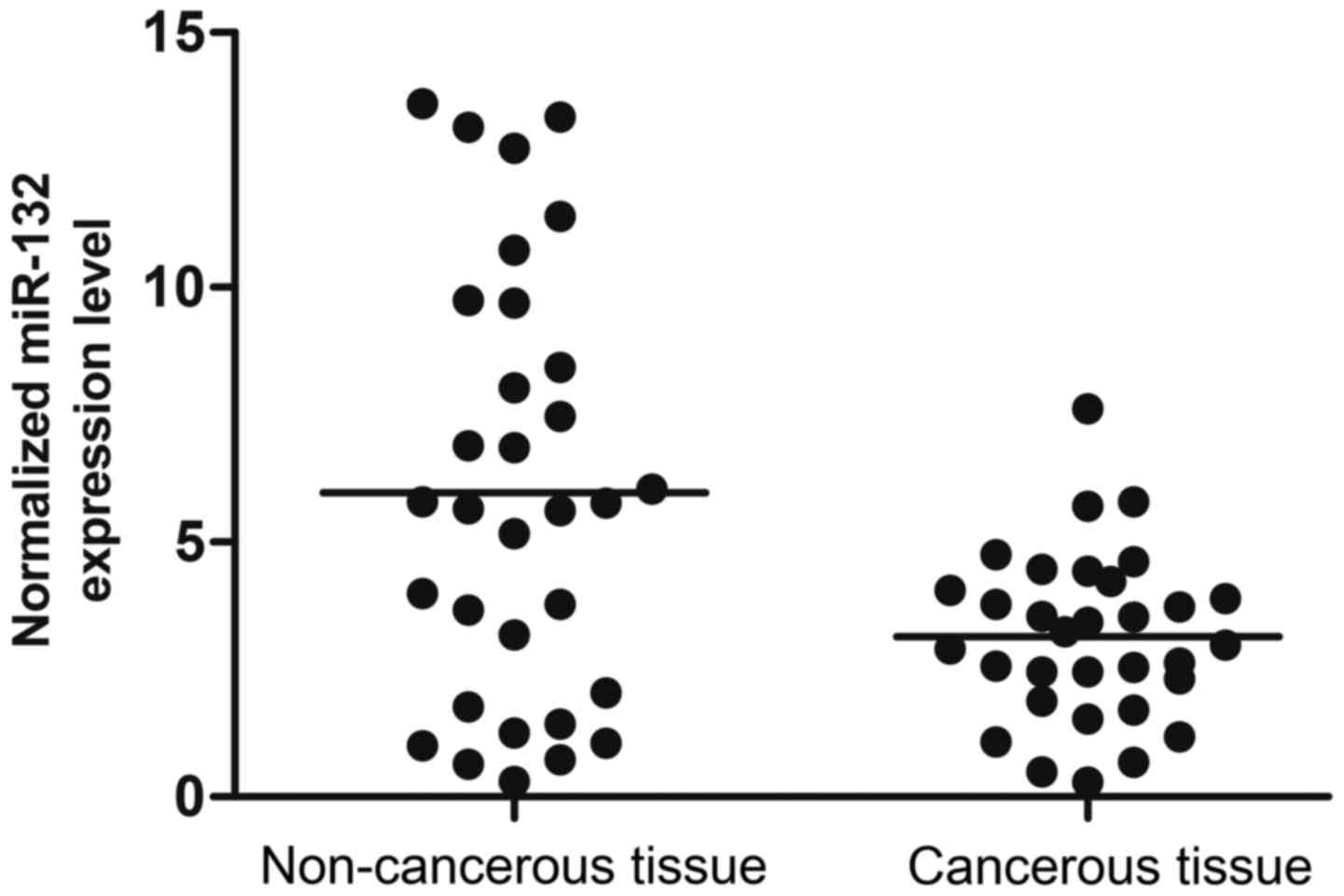
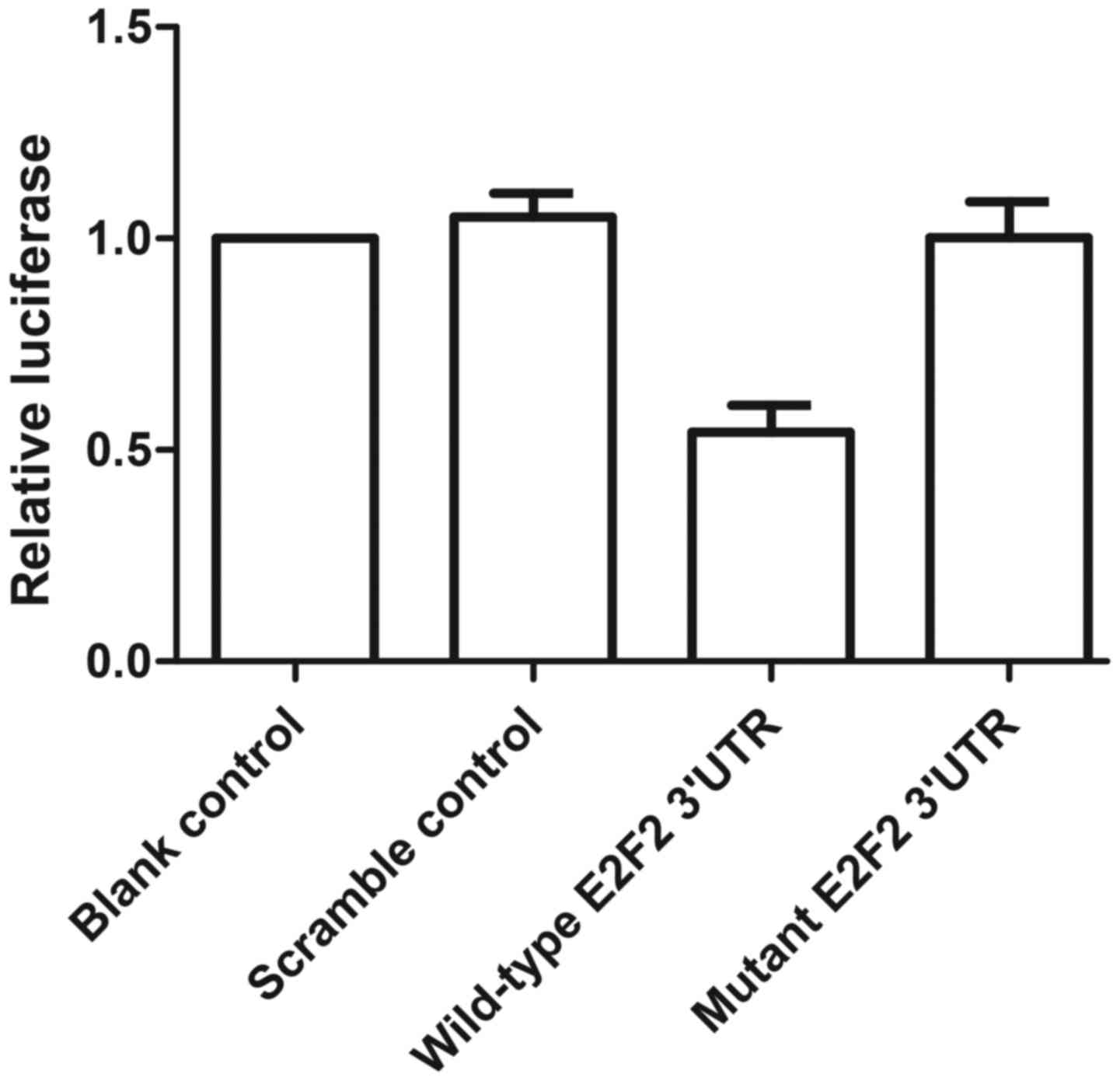
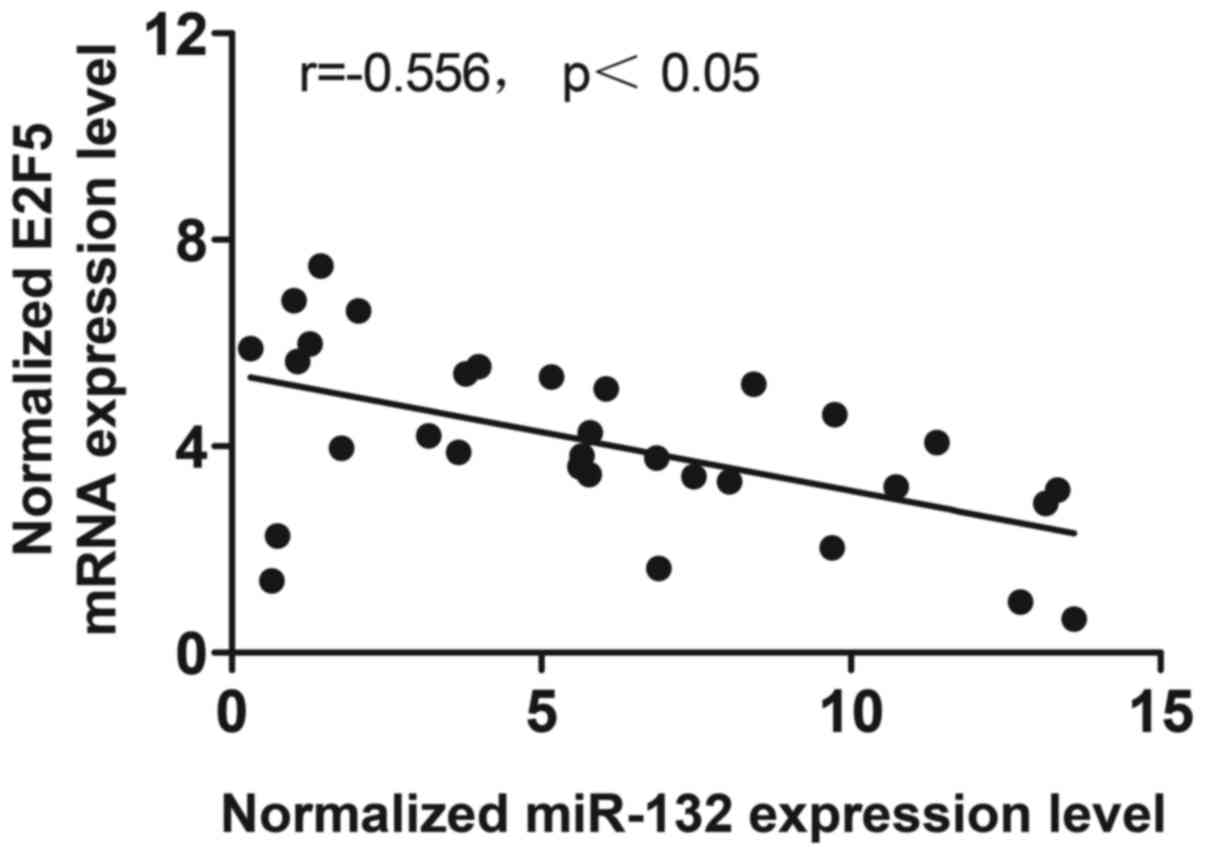
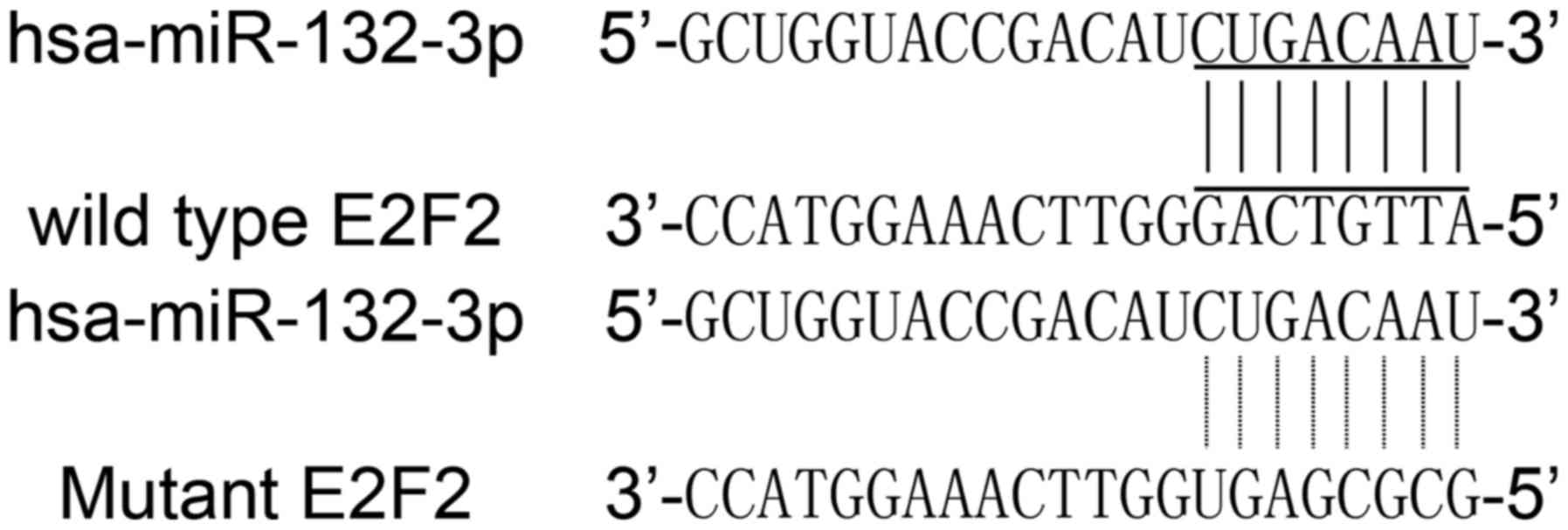|
1
|
Crawford ED: Epidemiology of prostate
cancer. Urology. 62(Suppl 1): 3–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Coughlin SS and Hall IJ: A review of
genetic polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk. Ann Epidemiol.
12:182–196. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Witte JS: Prostate cancer genomics:
towards a new under-standing. Nat Rev Genet. 10:77–82. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kim TM, Yim SH, Shin SH, Xu HD, Jung YC,
Park CK, Choi JY, Park WS, Kwon MS, Fiegler H, et al: Clinical
implication of recurrent copy number alterations in hepatocellular
carcinoma and putative oncogenes in recurrent gains on 1q. Int J
Cancer. 123:2808–2815. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen HZ, Tsai SY and Leone G: Emerging
roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:785–797. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T,
Terragni J, Young RA and Dynlacht BD: E2F integrates cell cycle
progression with DNA repair, replication, and G(2)/M checkpoints.
Genes Dev. 16:245–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kim
YD and Kim HY: E2F1 expression is related with the poor survival of
lymph node-positive breast cancer patients treated with
fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 82:11–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reimer D, Sadr S, Wiedemair A, Stadlmann
S, Concin N, Hofstetter G, Müller-Holzner E, Marth C and Zeimet AG:
Clinical relevance of E2F family members in ovarian cancer - an
evaluation in a training set of 77 patients. Clin Cancer Res.
13:144–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eymin B, Gazzeri S, Brambilla C and
Brambilla E: Distinct pattern of E2F1 expression in human lung
tumours: E2F1 is upregulated in small cell lung carcinoma.
Oncogene. 20:1678–1687. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee J, Park CK, Park JO, Lim T, Park YS,
Lim HY, Lee I, Sohn TS, Noh JH, Heo JS, et al: Impact of E2F-1
expression on clinical outcome of gastric adenocarcinoma patients
with adjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:82–88.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saugstad JA: MicroRNAs as effectors of
brain function with roles in ischemia and injury, neuroprotection,
and neurodegeneration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1564–1576.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Coppola V, De Maria R and Bonci D:
MicroRNAs and prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F1–F17.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fang YX and Gao WQ: Roles of microRNAs
during prostatic tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Oncogene.
33:135–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Casanova-Salas I, Rubio-Briones J,
Fernández-Serra A and López-Guerrero JA: miRNAs as biomarkers in
prostate cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 14:803–811. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Howe
TM, Petrocca F, Wallace TA, Liu CG, Volinia S, Calin GA, et al:
Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated
microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6162–6170.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Theodore SC, Davis M, Zhao F, Wang H, Chen
D, Rhim J, Dean-Colomb W, Turner T, Ji W, Zeng G, et al: MicroRNA
profiling of novel African American and Caucasian prostate cancer
cell lines reveals a reciprocal regulatory relationship of miR-152
and DNA methyltranferase 1. Oncotarget. 5:3512–3525. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao J, Wu XY, Ling XH, Lin ZY, Fu X, Deng
YH, He HC and Zhong W: Analysis of genetic aberrations on
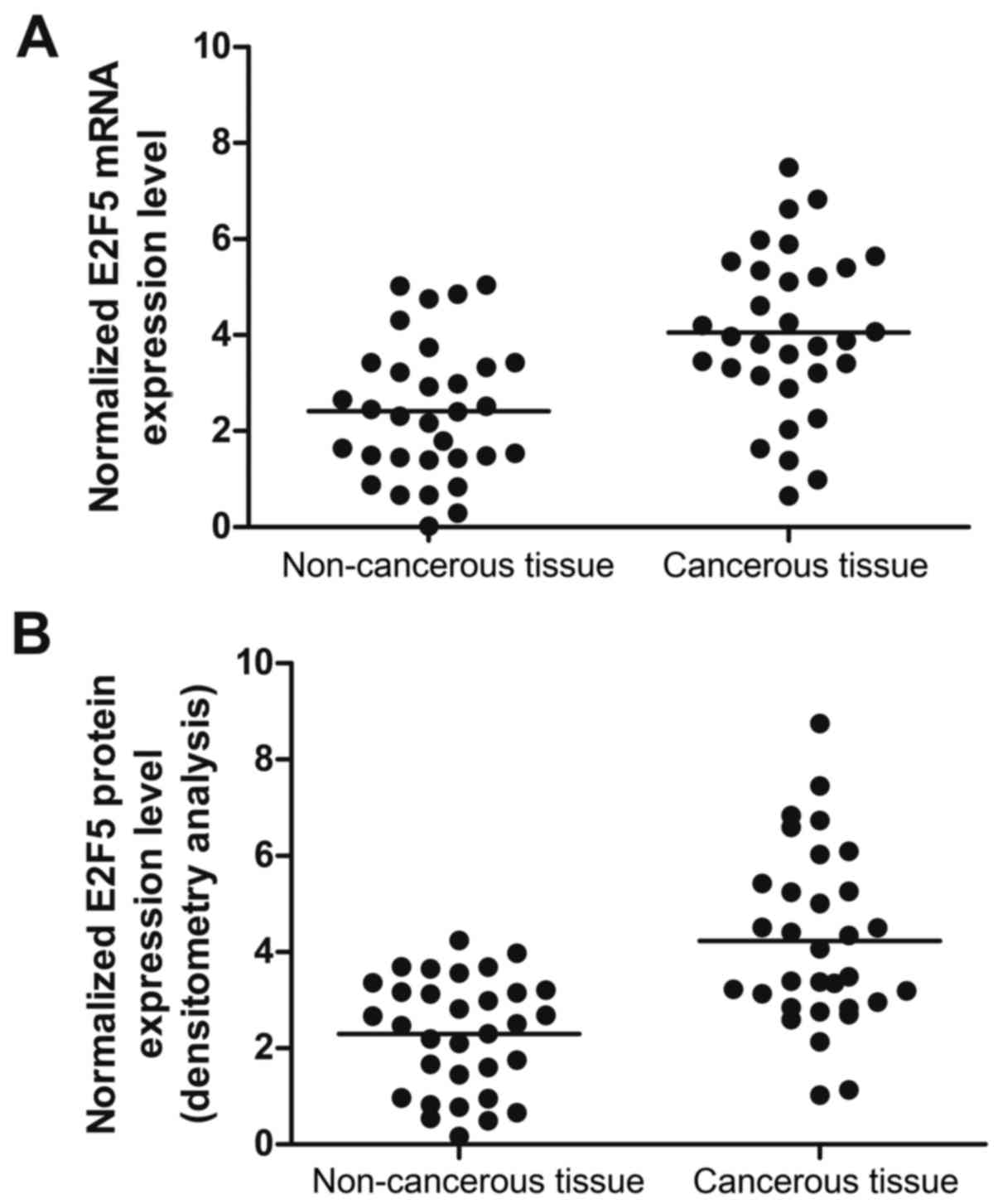
chromosomal region 8q21-24 identifies E2F5 as an oncogene with copy
number gain in prostate cancer. Med Oncol. 30:4652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Agarwal C, Dhanalakshmi S, Singh RP and
Agarwal R: Inositol hexaphosphate inhibits growth and induces G1
arrest and apoptotic death of androgen-dependent human prostate
carcinoma LNCaP cells. Neoplasia. 6:646–659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lau P, Bossers K, Janky R, Salta E,
Frigerio CS, Barbash S, Rothman R, Sierksma AS, Thathiah A,
Greenberg D, et al: Alteration of the microRNA network during the
progression of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO Mol Med. 5:1613–1634.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jin W, Reddy MA, Chen Z, Putta S, Lanting
L, Kato M, Park JT, Chandra M, Wang C, Tangirala RK, et al: Small
RNA sequencing reveals microRNAs that modulate angiotensin II
effects in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem.
287:15672–15683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang ZG, Chen WX, Wu YH, Liang HF and
Zhang BX: miR-132 prohibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and
metastasis in breast cancer by targeting HN1. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 454:109–114. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng YB, Luo HP, Shi Q, Hao ZN, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB, Xiao GC and Tong SL: miR-132 inhibits colorectal
cancer invasion and metastasis via directly targeting ZEB2. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:6515–6522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|