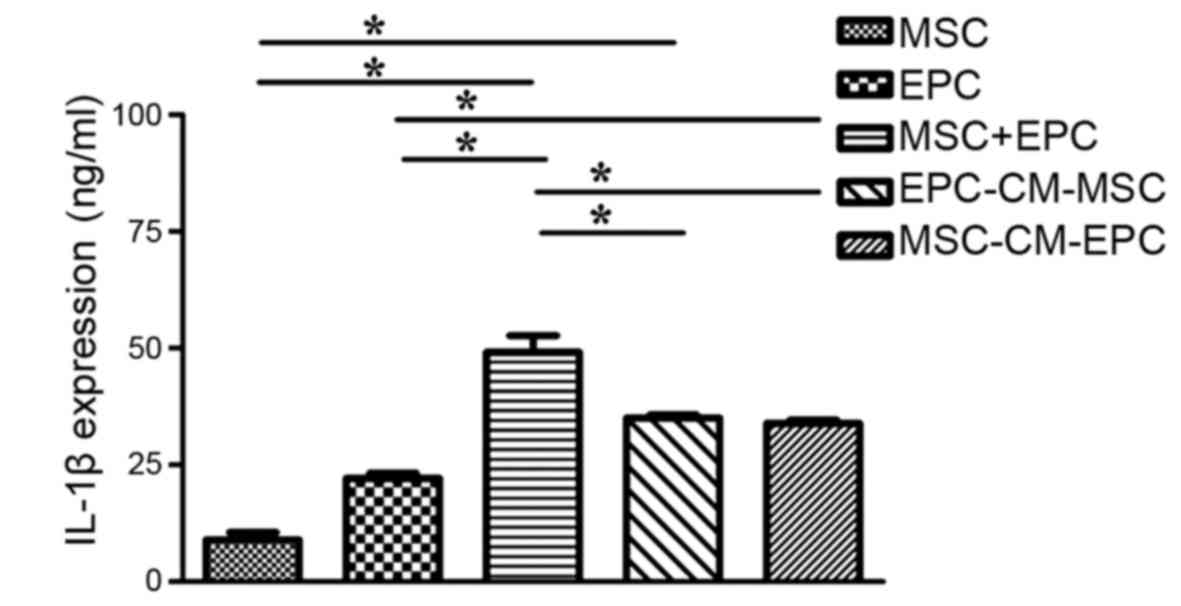
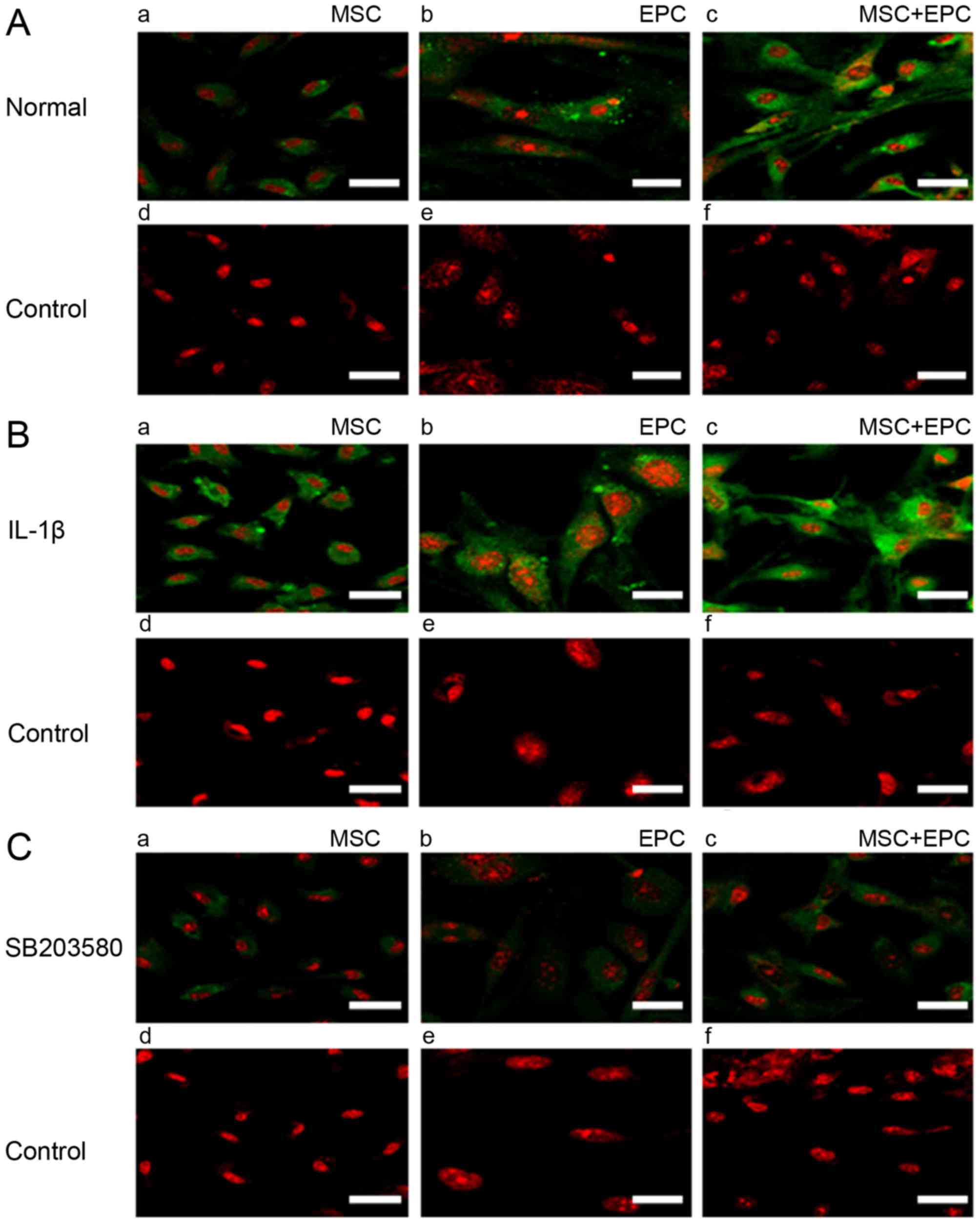
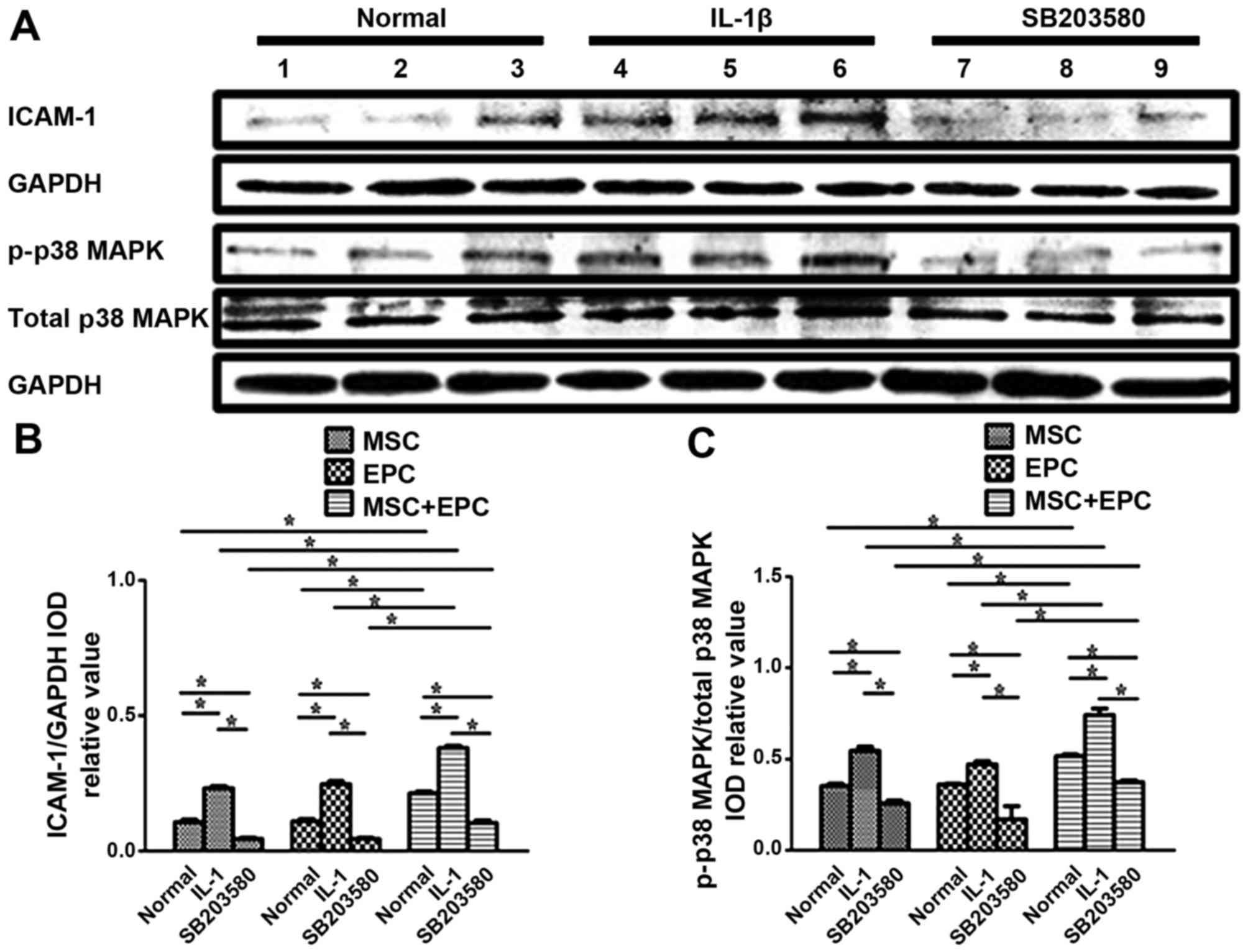
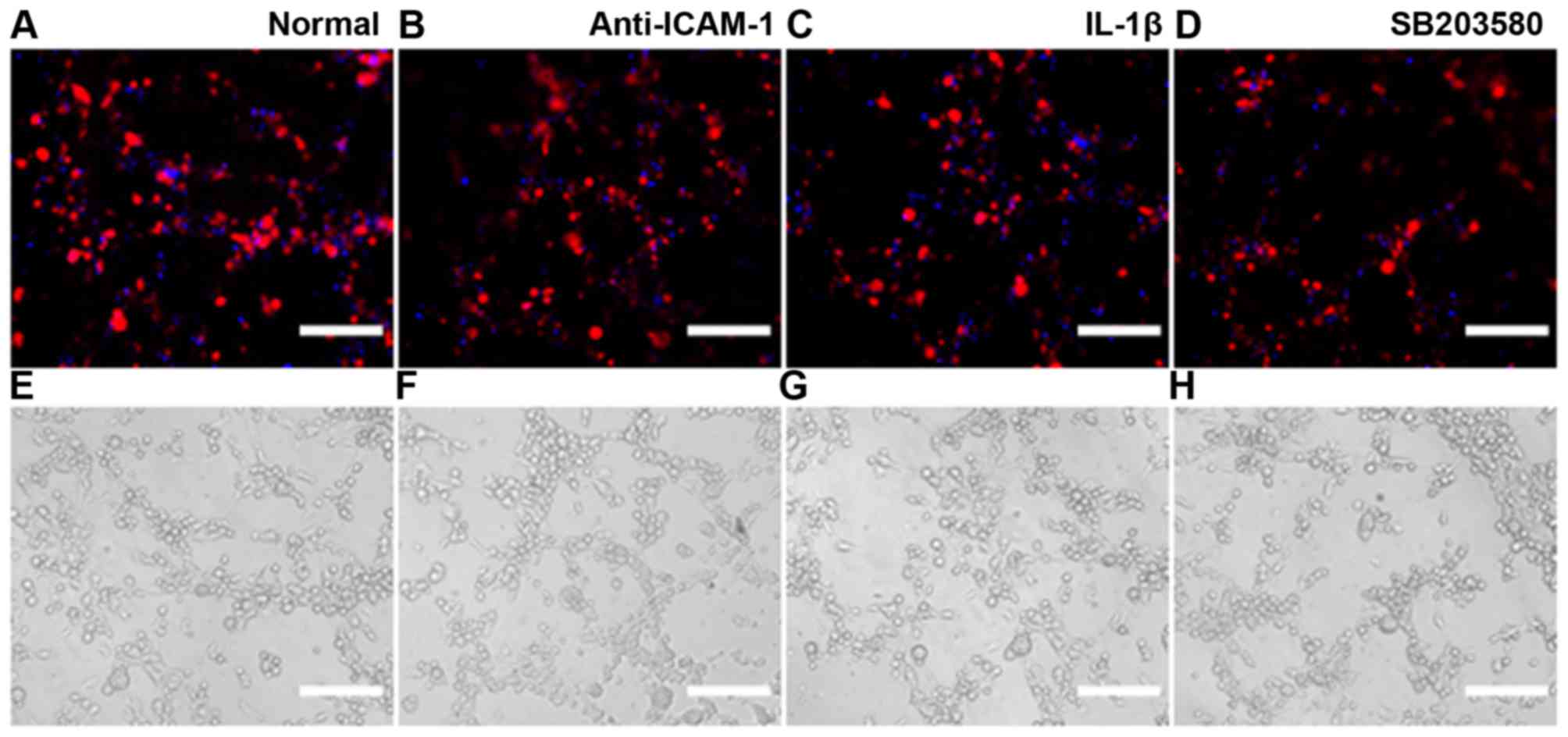
|
1
|
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK and
Lalykina KS: The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer
cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue
Kinet. 3:393–403. 1970.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,
Schwartz RE, Keene CD, Ortiz-Gonzalez XR, Reyes M, Lenvik T, Lund
T, Blackstad M, et al: Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells
derived from adult marrow. Nature. 418:41–49. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore KA and Elmendorf SC: Propagule vs.
niche limitation: Untangling the mechanisms behind plant species'
distributions. Ecol Lett. 9:797–804. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spradling A, Drummond-Barbosa D and Kai T:
Stem cells find their niche. Nature. 414:98–104. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moore KA and Lemischka IR: Stem cells and
their niches. Science. 311:1880–1885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang H, Xian L, Lin Z, Yang C, Zhang M,
Feng W, Peng X, Chen X and Wu X: Endothelial progenitor cells as a
possible component of stem cell niche to promote self-renewal of
mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 397:235–243. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver
M, van der Zee R, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G and Isner JM:
Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for
angiogenesis. Science. 275:964–967. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kalka C, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka-Moll
WM, Silver M, Kearney M, Li T, Isner JM and Asahara T:
Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells
for therapeutic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:3422–3427. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Minamino T, Miyauchi H, Yoshida T, Ishida
Y, Yoshida H and Komuro I: Endothelial cell senescence in human
atherosclerosis: Role of telomere in endothelial dysfunction.
Circulation. 105:1541–1544. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grellier M, Bordenave L and Amédée J:
Cell-to-cell communication between osteogenic and endothelial
lineages: Implications for tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol.
27:562–571. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu WL, Xiang Z, Huang FG, Gu ZP, Yu XX,
Cen SQ, Zhong G, Duan X and Liu M: Coculture of peripheral
blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor
cells on strontium-doped calcium polyphosphate scaffolds to
generate vascularized engineered bone. Tissue Eng Part A.
21:948–959. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Burlacu A, Grigorescu G, Rosca AM, Preda
MB and Simionescu M: Factors secreted by mesenchymal stem cells and
endothelial progenitor cells have complementary effects on
angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 22:643–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Zigdon-Giladi H, Bick T, Lewinson D and
Machtei EE: Co-transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells and
mesenchymal stem cells promote neovascularization and bone
regeneration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 17:353–359. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zuckerman LA, Pullen L and Miller J:
Functional consequences of costimulation by ICAM-1 on IL-2 gene
expression and T cell activation. J Immunol. 160:3259–3268.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Agarwal SK and Brenner MB: Role of
adhesion molecules in synovial inflammation. Curr Opin Rheumatol.
18:268–276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaw SK, Ma S, Kim MB, Rao RM, Hartman CU,
Froio RM, Yang L, Jones T, Liu Y, Nusrat A, et al: Coordinated
redistribution of leukocyte LFA-1 and endothelial cell ICAM-1
accompany neutrophil transmigration. J Exp Med. 200:1571–1580.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sumagin R and Sarelius IH: Intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 enrichment near tricellular endothelial
junctions is preferentially associated with leukocyte
transmigration and signals for reorganization of these junctions to
accommodate leukocyte passage. J Immunol. 184:5242–5252. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang MC, Hung HP, Lin LD, Shyu YC, Wang
TM, Lin HJ, Chan CP, Huang CC and Jeng JH: Effect of interleukin-1β
on ICAM-1 expression of dental pulp cells: Role of PI3K/Akt,
MEK/ERK, and cyclooxygenase. Clin Oral Investig. 19:117–126. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shikama Y, Aki N, Hata A, Nishimura M,
Oyadomari S and Funaki M: Palmitate-stimulated monocytes induce
adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells via IL-1
signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 230:732–742. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yamagami H, Yamagami S, Inoki T, Amano S
and Miyata K: The effects of proinflammatory cytokines on
cytokine-chemokine gene expression profiles in the human corneal
endothelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:514–520. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Horton JE, Raisz LG, Simmons HA, Oppenheim
JJ and Mergenhagen SE: Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid
from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science.
177:793–795. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dewhirst FE, Stashenko PP, Mole JE and
Tsurumachi T: Purification and partial sequence of human
osteoclast-activating factor: Identity with interleukin 1 beta. J
Immunol. 135:2562–2568. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stashenko P, Dewhirst FE, Peros WJ, Kent
RL and Ago JM: Synergistic interactions between interleukin 1,
tumor necrosis factor, and lymphotoxin in bone resorption. J
Immunol. 138:1464–1468. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiong Y, Donovan KA, Kline MP, Gornet MK,
Moon-Tasson LL, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Greipp PR and
Lust JA: Identification of two groups of smoldering multiple
myeloma patients who are either high or low producers of
interleukin-1. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 26:83–95. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang R, Jiang F, Chen CS, Wang T, Feng J,
Tao T and Qin X: Serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β, and MMP-9 in
patients undergoing carotid artery stenting and regulation of MMP-9
in a new in vitro model of THP-1 cells activated by stenting.
Mediators Inflamm. 2015:9560822015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Alfaidi M, Wilson H, Daigneault M, Burnett
A, Ridger V, Chamberlain J and Francis S: Neutrophil elastase
promotes interleukin-1β secretion from human coronary endothelium.
J Biol Chem. 290:24067–24078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wuyts WA, Vanaudenaerde BM, Dupont LJ,
Demedts MG and Verleden GM: Involvement of p38 MAPK, JNK, p42/p44
ERK and NF-kappaB in IL-1β-induced chemokine release in human
airway smooth muscle cells. Respir Med. 97:811–817. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hsu WY, Chao YW, Tsai YL, Lien CC, Chang
CF, Deng MC, Ho LT, Kwok CF and Juan CC: Resistin induces
monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion by increasing ICAM-1 and VCAM-1
expression in endothelial cells via p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. J
Cell Physiol. 226:2181–2188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang B, Wang X, Zhang N, Yang H, Bai R,
Liu M, Bian Y, Xiao C and Yang Z: Angiotensin-(1-7) attenuates
angiotensin II-induced ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and MCP-1 expression via the
MAS Receptor through suppression of P38 and NF-κB pathways in
HUVECs. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:2472–2482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee SJ, Drabik K, Van Wagoner NJ, Lee S,
Choi C, Dong Y and Benveniste EN: ICAM-1-induced expression of
proinflammatory cytokines in astrocytes: Involvement of
extracellular signal-regulated kinase and P38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathways. J Immunol. 165:4658–4666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park JS, Kim KM, Kim MH, Chang HJ, Baek
MK, Kim SM and Jung YD: Resveratrol inhibits tumor cell adhesion to
endothelial cells by blocking ICAM-1 expression. Anticancer Res.
29:355–362. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Deane JA, Abeynaike LD, Norman MU, Wee JL,
Kitching AR, Kubes P and Hickey MJ: Endogenous regulatory T cells
adhere in inflamed dermal vessels via ICAM-1: Association with
regulation of effector leukocyte adhesion. J Immunol.
188:2179–2188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lacal PM, Petrillo MG, Ruffini F, Muzi A,
Bianchini R, Ronchetti S, Migliorati G, Riccardi C, Graziani G and
Nocentini G: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor
family-related ligand triggering upregulates vascular cell adhesion
molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and promotes
leukocyte adhesion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 347:164–172. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim KH, Lee EN, Park JK, Lee JR, Kim JH,
Choi HJ, Kim BS, Lee HW, Lee KS and Yoon S: Curcumin attenuates
TNF-α-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1,
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and proinflammatory cytokines in
human endometriotic stromal cells. Phytother Res. 26:1037–1047.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Park GS and Kim JH: LPS Up-regulates
ICAM-1 expression in breast cancer cells by stimulating a
MyD88-BLT2-ERK-linked cascade, which promotes adhesion to
monocytes. Mol Cells. 38:821–828. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang M, Zhang H, Feng W, Wang Y, Yin S,
Chen X and Wu X: Endothelial progenitor cells promote osteogenic
differentiation of marrow stromal cells in a paracrine manner.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 95:1253–1257. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ern C, Krump-Konvalinkova V, Docheva D,
Schindler S, Rossmann O, Böcker W, Mutschler W and Schieker M:
Interactions of human endothelial and multipotent mesenchymal stem
cells in cocultures. Open Biomed Eng J. 4:190–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|