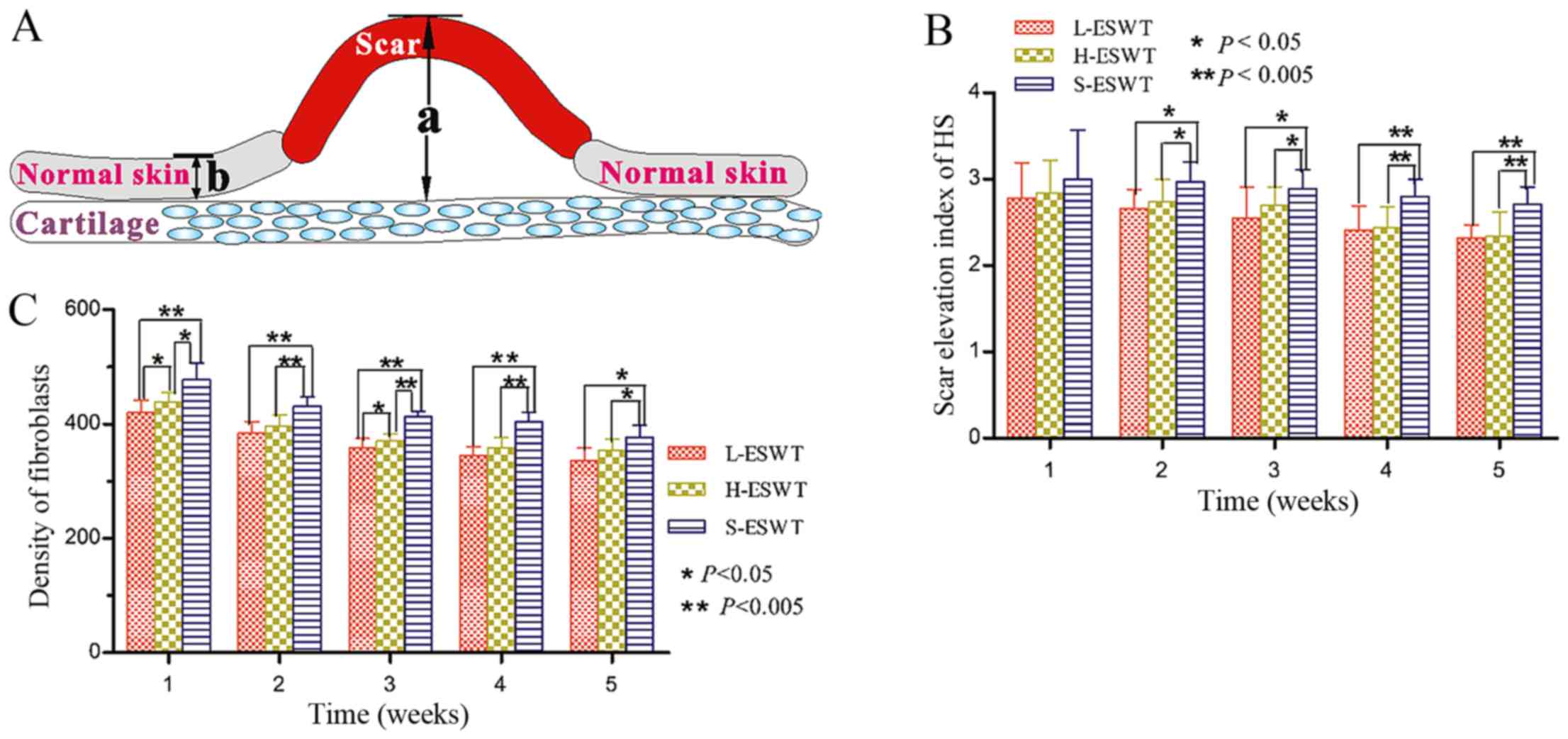
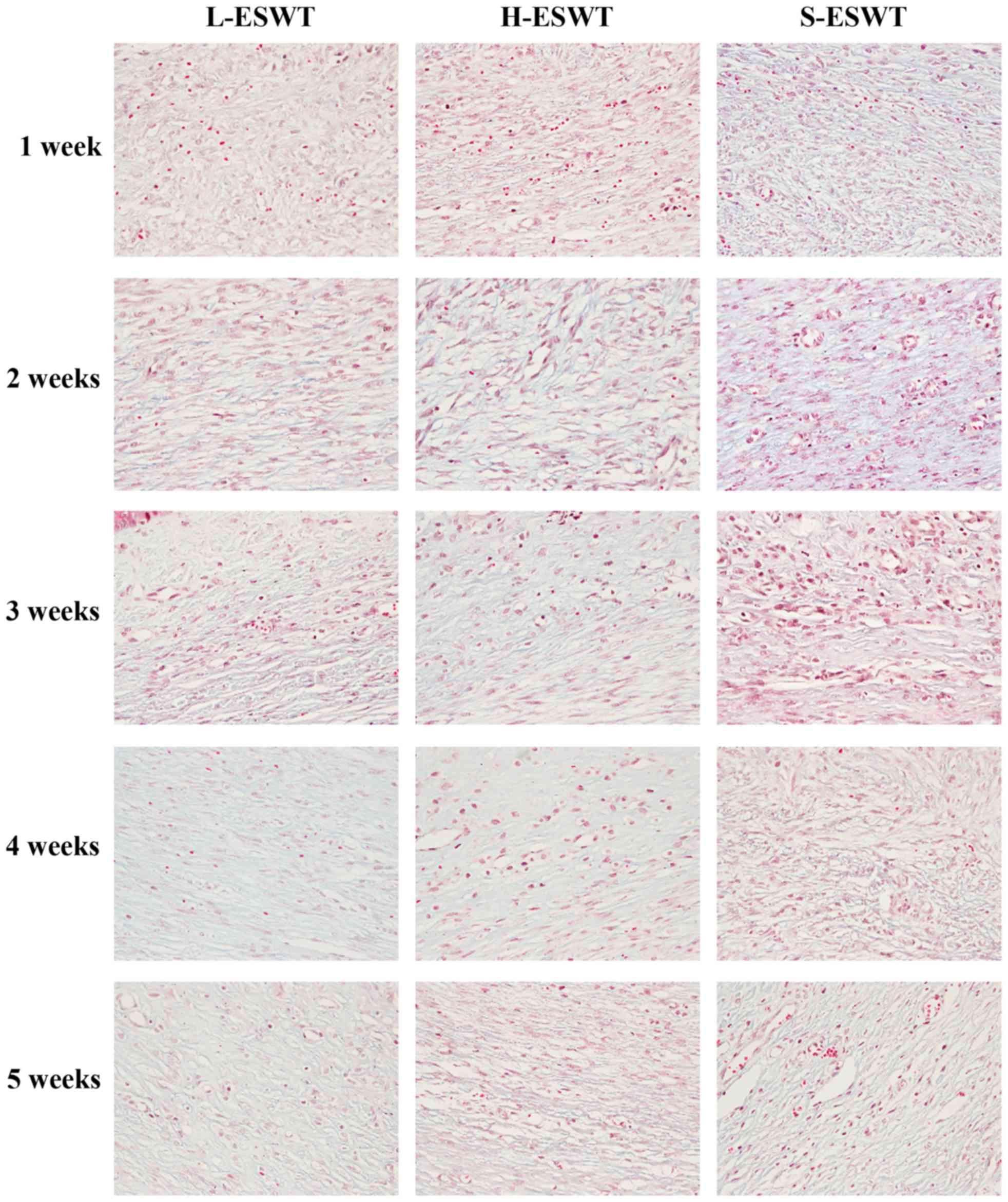
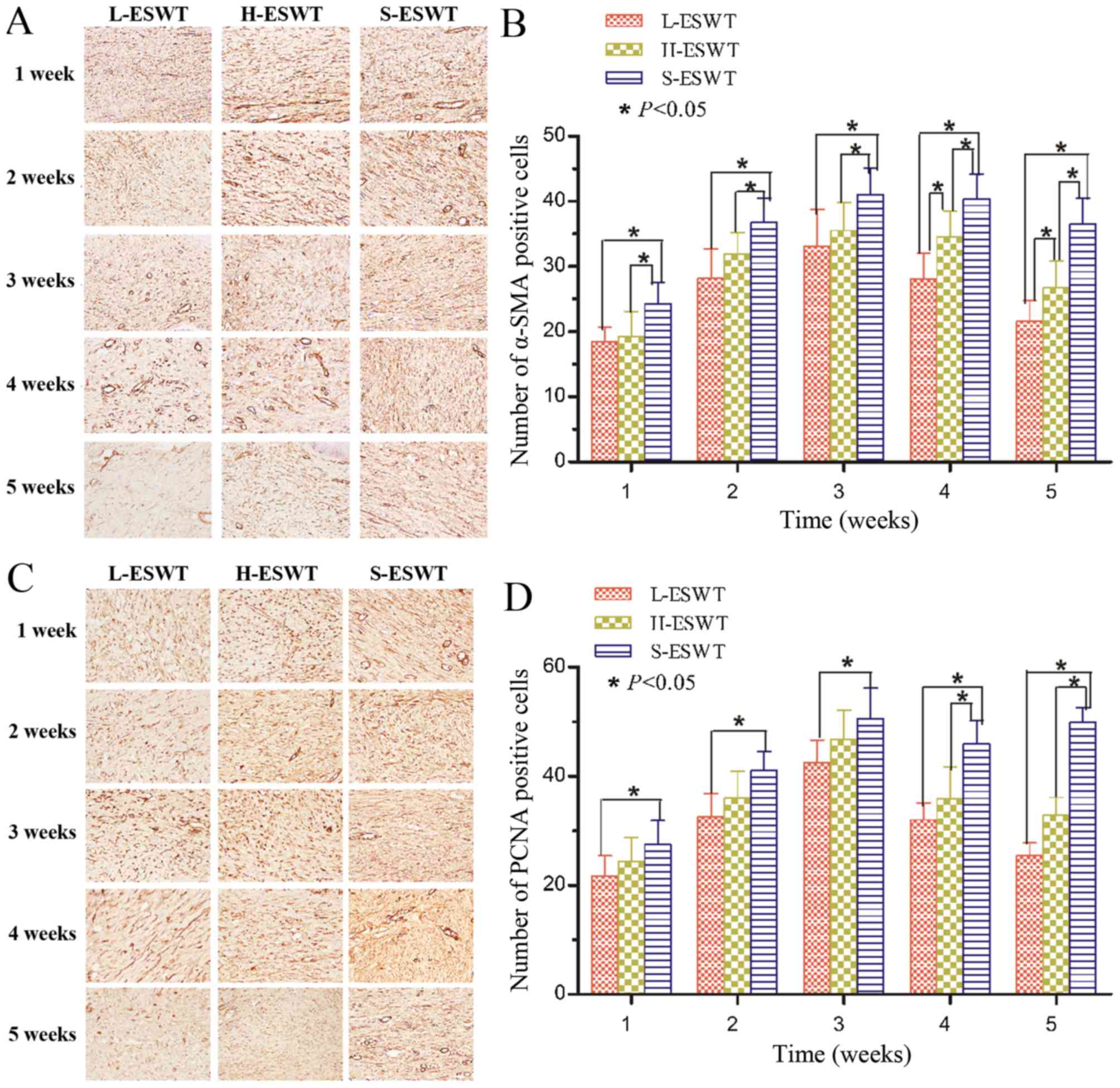
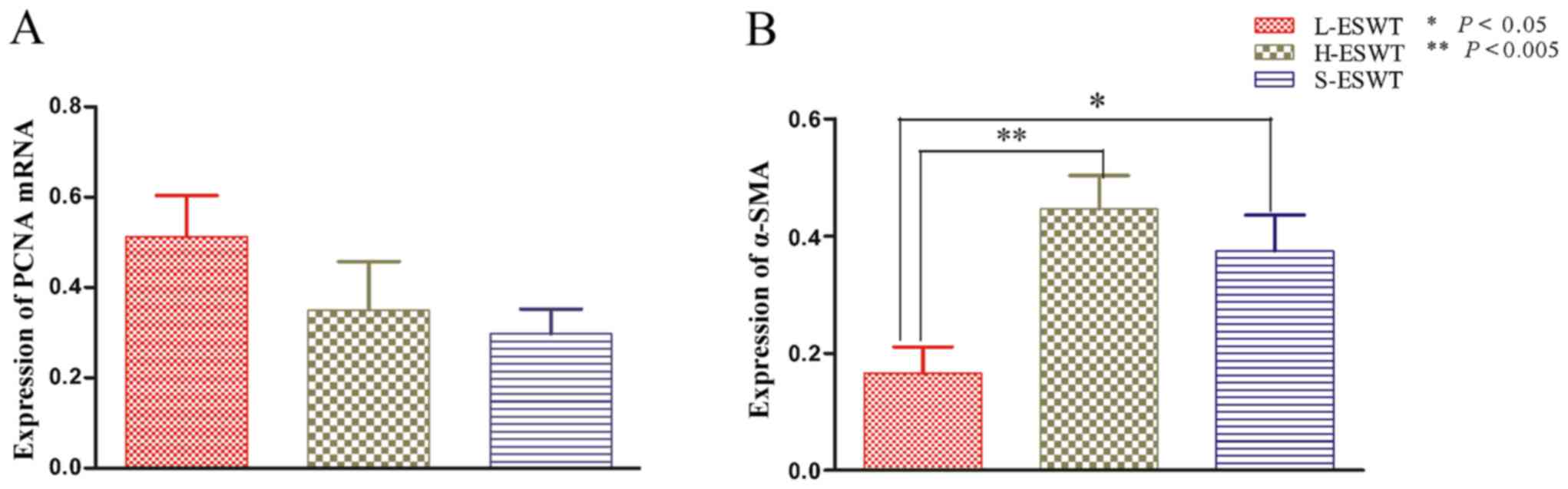
|
1
|
Stadelmann WK, Digenis AG and Tobin GR:
Physiology and healing dynamics of chronic cutaneous wounds. Am J
Surg. 176(Suppl 2A): 26S–38S. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Midwood KS, Williams LV and Schwarzbauer
JE: Tissue repair and the dynamics of the extracellular matrix. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:1031–1037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T,
Ruzicka T and Jeschke MG: Hypertrophic scarring and keloids:
pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol
Med. 17:113–125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Nedelec B, Shankowsky H, Scott PG, Ghahary
A and Tredget EE: Myofibroblasts and apoptosis in human
hypertrophic scars: the effect of interferon-alpha2b. Surgery.
130:798–808. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slemp AE and Kirschner RE: Keloids and
scars: a review of keloids and scars, their pathogenesis, risk
factors, and management. Curr Opin Pediatr. 18:396–402. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang L, Scott PG, Dodd C, Medina A, Jiao
H, Shankowsky HA, Ghahary A and Tredget EE: Identification of
fibrocytes in postburn hypertrophic scar. Wound Repair Regen.
13:398–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ali SS, Hajrah NH, Ayuob NN, Moshref SS
and Abuzinadah OA: Morphological and morphometric study of cultured
fibroblast from treated and untreated abnormal scar. Saudi Med J.
31:874–881. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Williams CC and De Groote S: Clinical
inquiry: what treatment is best for hypertrophic scars and keloids.
J Fam Pract. 60:757–758. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shridharani SM, Magarakis M, Manson PN,
Singh NK, Basdag B and Rosson GD: The emerging role of
antineoplastic agents in the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic
scars: a review. Ann Plast Surg. 64:355–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dymarek R, Halski T, Ptaszkowski K,
Slupska L, Rosinczuk J and Taradaj J: Extracorporeal shock wave
therapy as an adjunct wound treatment: a systematic review of the
literature. Ostomy Wound Manage. 60:26–39. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chaussy C, Brendel W and Schmiedt E:
Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock
waves. Lancet. 2:1265–1268. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rassweiler J, Rassweiler MC, Frede T and
Alken P: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: an opinion on its
future. Indian J Urol. 30:73–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valchanou VD and Michailov P: High energy
shock waves in the treatment of delayed and nonunion of fractures.
Int Orthop. 15:181–184. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maffulli G, Hemmings S and Maffulli N:
Assessment of the effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave
therapy (ESWT) for soft tissue injuries (ASSERT): an online
database protocol. Transl Med UniSa. 10:46–51. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mittermayr R, Hartinger J, Antonic V,
Meinl A, Pfeifer S, Stojadinovic A, Schaden W and Redl H:
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) minimizes ischemic tissue
necrosis irrespective of application time and promotes tissue
revascularization by stimulating angiogenesis. Ann Surg.
253:1024–1032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao JC, Xian CJ and Yu JA: Advancement in
the research of effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on
wound angiogenesis. Chin J Inj Repair Wound Healing. 9:80–84.
2014.
|
|
17
|
Zhao J, Xue Y, Yu J, Shi K, Xian C and
Zhou X: Advances in the research of mechanism of enhancement of
wound healing with extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Zhonghua Shao
Shang Za Zhi. 31:315–317. 2015.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Speed C: A systematic review of shockwave
therapies in soft tissue conditions: focusing on the evidence. Br J
Sports Med. 48:1538–1542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Goertz O, Lauer H, Hirsch T, Ring A,
Lehnhardt M, Langer S, Steinau HU and Hauser J: Extracorporeal
shock waves improve angiogenesis after full thickness burn. Burns.
38:1010–1018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kloeters O, Tandara A and Mustoe TA:
Hypertrophic scar model in the rabbit ear: a reproducible model for
studying scar tissue behavior with new observations on silicone gel
sheeting for scar reduction. Wound Repair Regen. 15(Suppl 1):
S40–S45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou M, Li LH, Peng H, Li R, Feng CC, Xu
WD, Leng RX, Pan HF and Ye DQ: Decreased ITGAM and FcγRIIIA mRNA
expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Med.
14:269–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang CJ, Ko JY, Chan YS, Weng LH and Hsu
SL: Extra-corporeal shockwave for chronic patellar tendinopathy. Am
J Sports Med. 35:972–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yin MC, Ye J, Yao M, Cui XJ, Xia Y, Shen
QX, Tong ZY, Wu XQ, Ma JM and Mo W: Is extracorporeal shock wave
therapy clinical efficacy for relief of chronic, recalcitrant
plantar fasciitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized placebo or active-treatment controlled trials. Arch Phys
Med Rehabil. 95:1585–1593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiele S, Thiele R and Gerdesmeyer L:
Lateral epicondylitis: this is still a main indication for
extracorporeal shockwave therapy. Int J Surg. 24(Pt B): 165–170.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang CJ, Cheng JH, Kuo YR, Schaden W and
Mittermayr R: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in diabetic foot
ulcers. Int J Surg. 24(Pt B): 207–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang CJ, Ko JY, Kuo YR and Yang YJ:
Molecular changes in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
94:105–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Waugh CM, Morrissey D, Jones E, Riley GP,
Langberg H and Screen HR: In vivo biological response to
extracorporeal shockwave therapy in human tendinopathy. Eur Cell
Mater. 29:268–280. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fioramonti P, Cigna E, Onesti MG, Fino P,
Fallico N and Scuderi N: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the
management of burn scars. Dermatol Surg. 38:778–782. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saggini R, Saggini A, Spagnoli AM, Dodaj
I, Cigna E, Maruccia M, Soda G, Bellomo RG and Scuderi N:
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: an emerging treatment modality
for retracting scars of the hands. Ultrasound Med Biol. 42:185–195.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yagmur C, Akaishi S, Ogawa R and Guneren
E: Mechanical receptor-related mechanisms in scar management: a
review and hypothesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 126:426–434. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bravo R and Macdonald-Bravo H: Existence
of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen
during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J
Cell Biol. 105:1549–1554. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moldovan GL, Pfander B and Jentsch S:
PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 129:665–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nedelec B, Ghahary A, Scott PG and Tredget
EE: Control of wound contraction. Basic and clinical features. Hand
Clin. 16:289–302. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moulin V, Larochelle S, Langlois C,
Thibault I, Lopez-Vallé CA and Roy M: Normal skin wound and
hypertrophic scar myofibroblasts have differential responses to
apoptotic inductors. J Cell Physiol. 198:350–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lim MJ, Ahn J, Yi JY, Kim MH, Son AR, Lee
SL, Lim DS, Kim SS, Kang MA, Han Y, et al: Induction of galectin-1
by TGF-β1 accelerates fibrosis through enhancing nuclear retention
of Smad2. Exp Cell Res. 326:125–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|