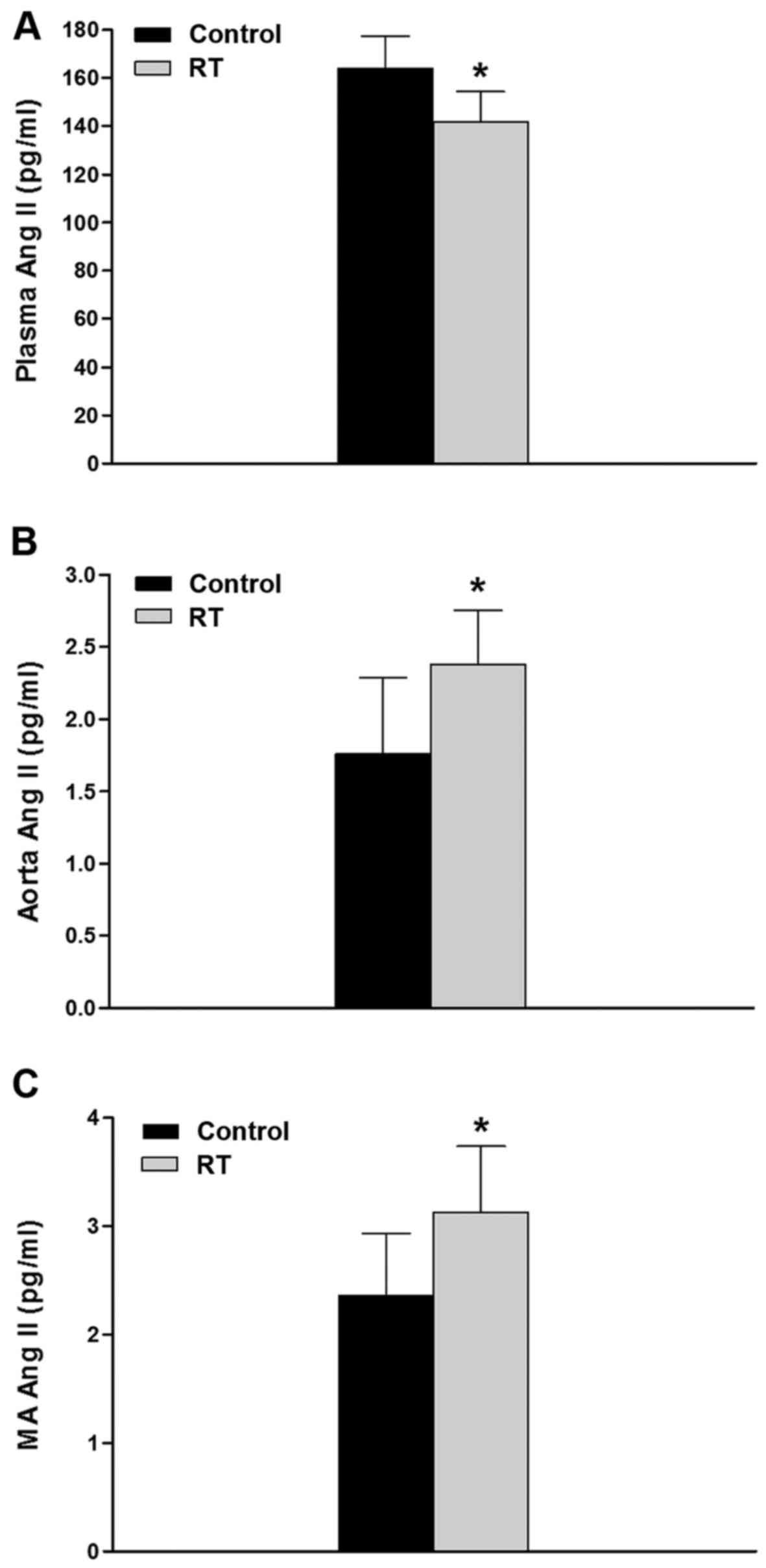
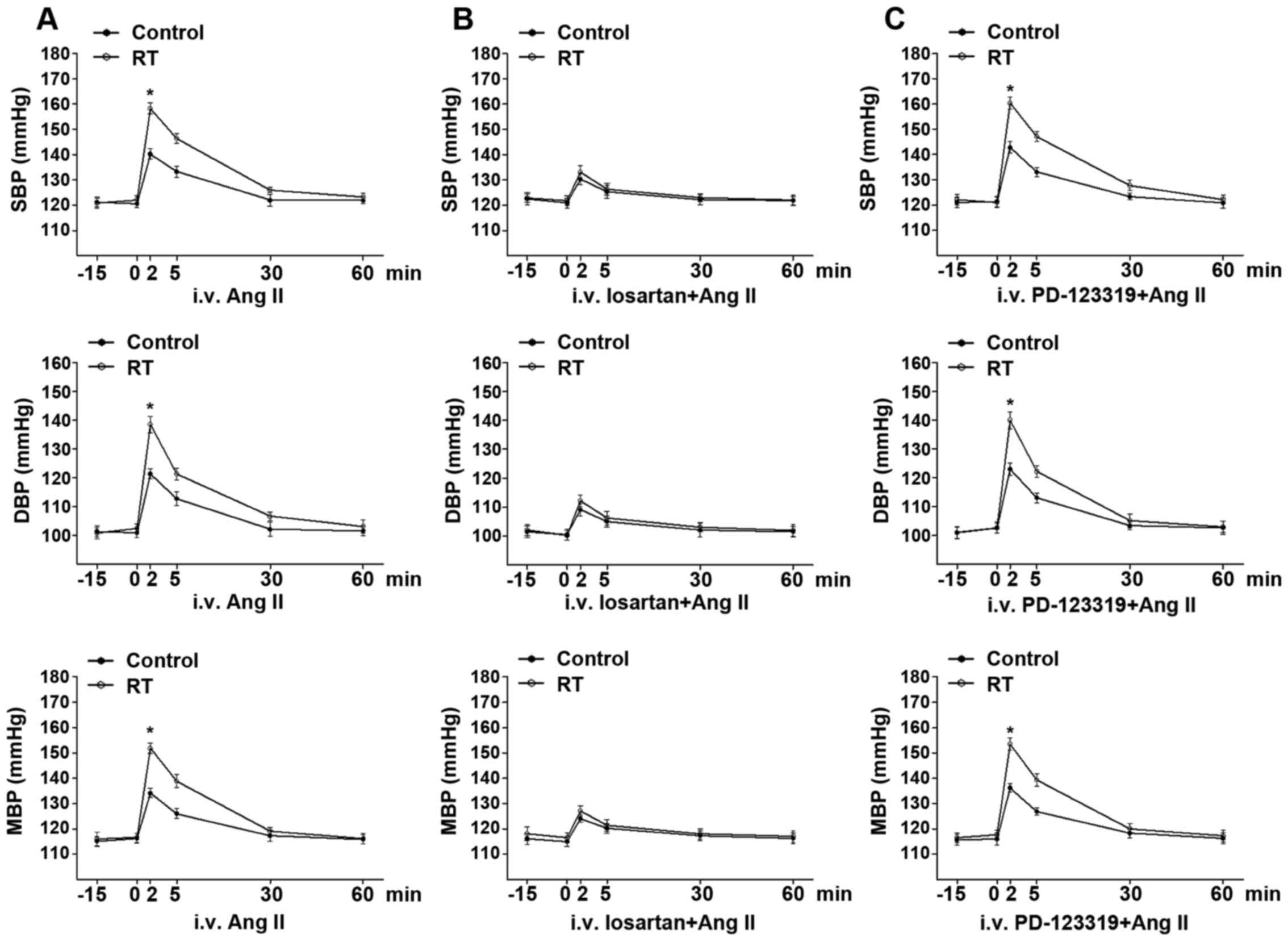
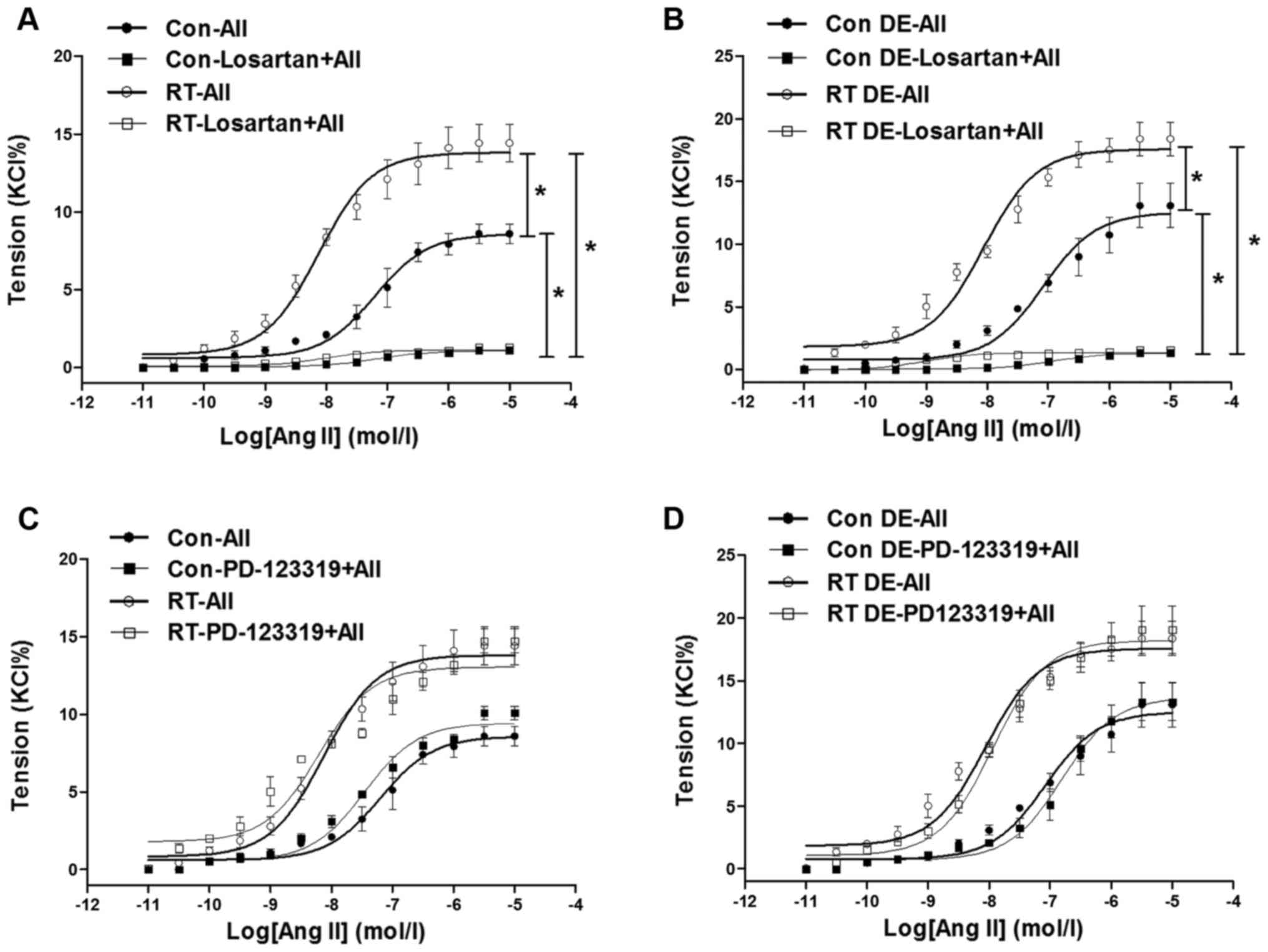
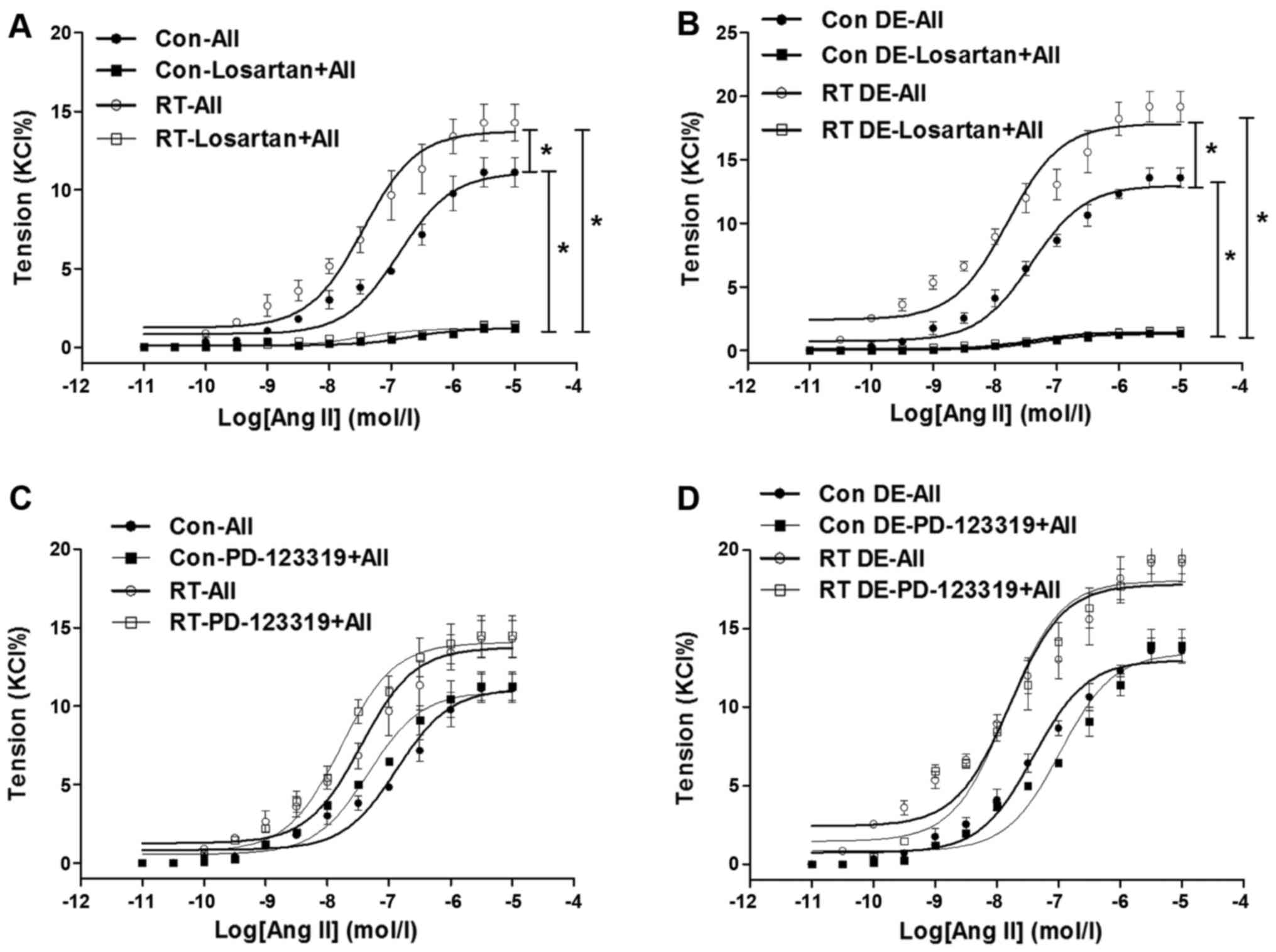
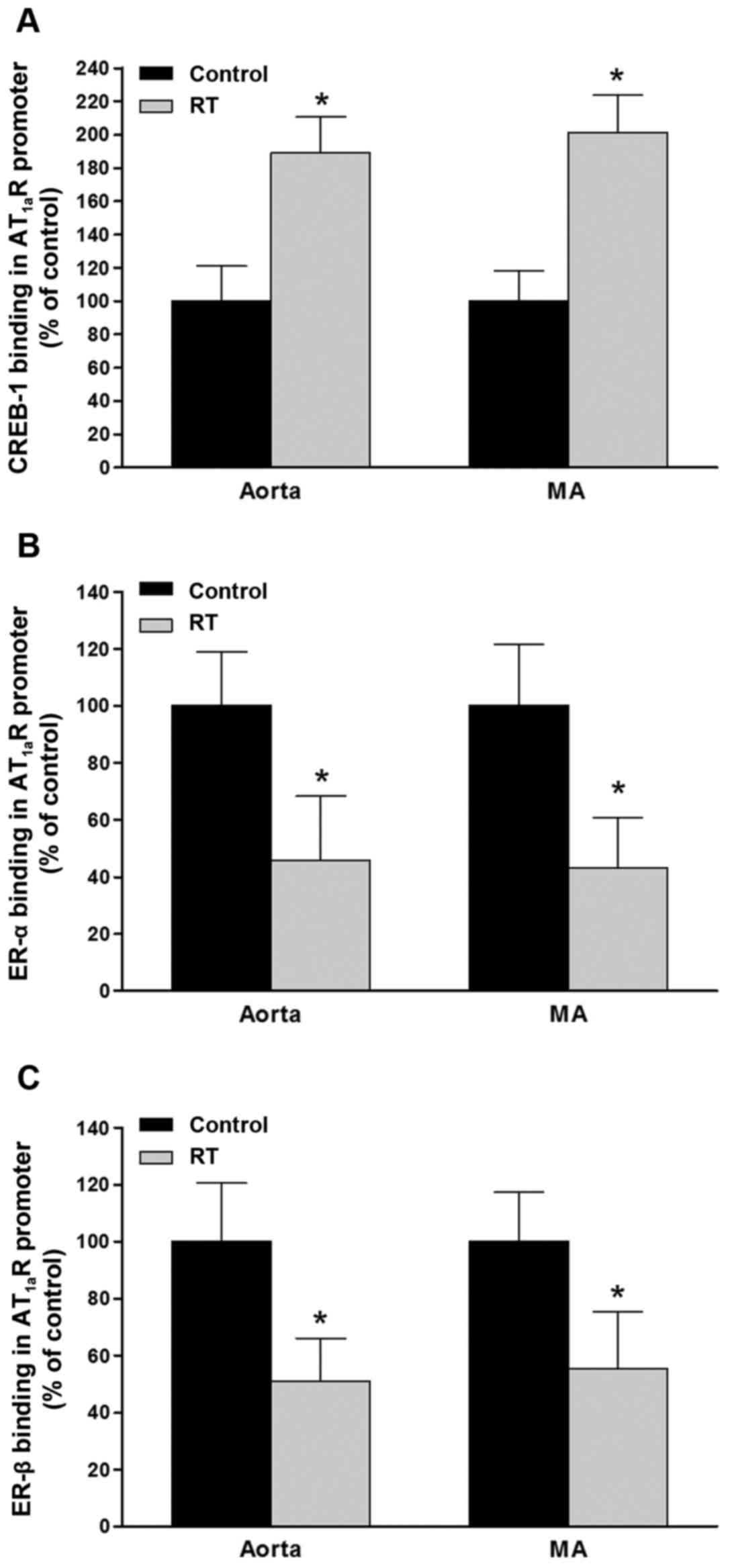
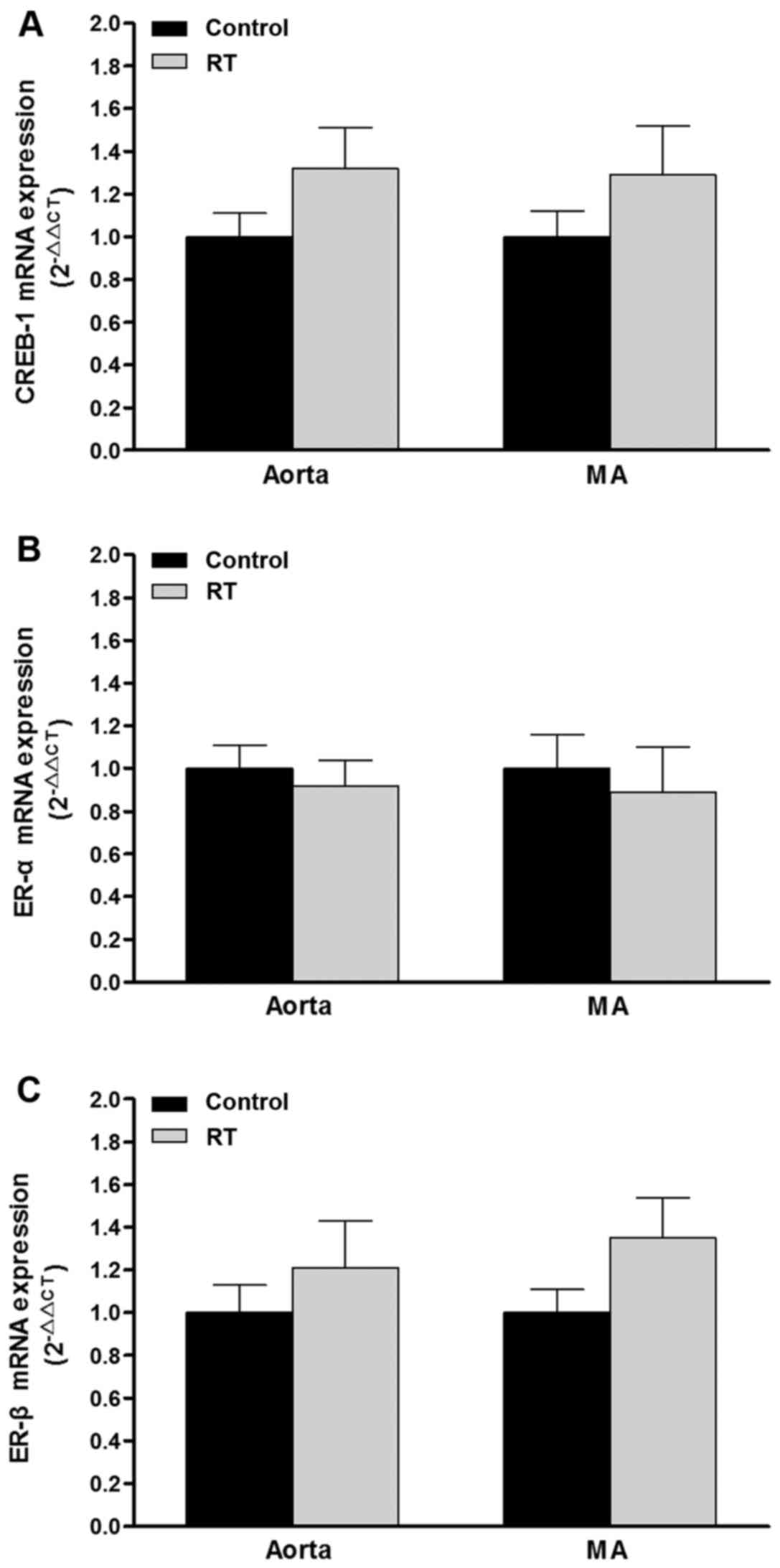
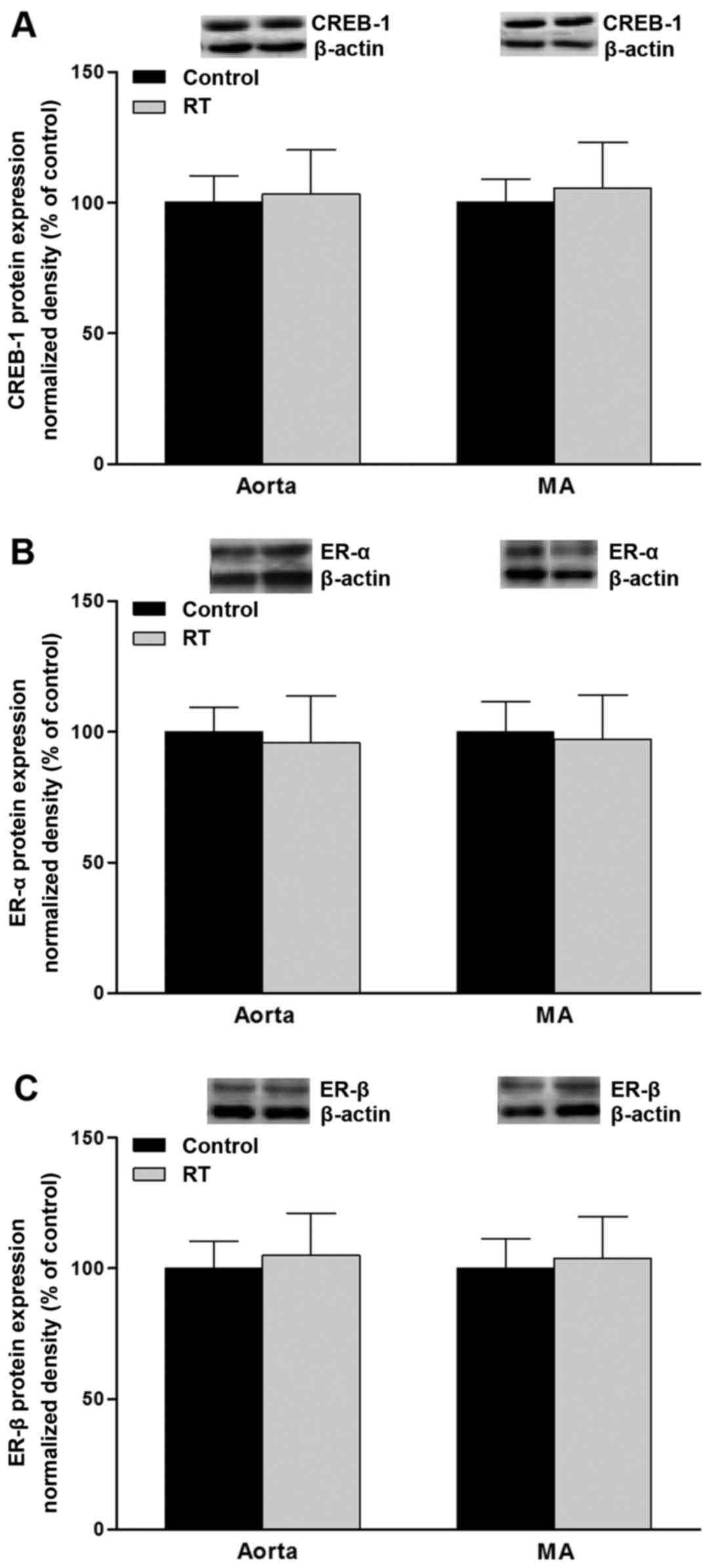
|
1
|
Chandran S and Vincenti F: Clinical
aspects: Focusing on key unique organ-specific issues of renal
transplantation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 4:42014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lyerová L, Viklický O, Nemcová D and
Teplan V: The incidence of infectious diseases after renal
transplantation: A single-centre experience. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 31(Suppl 1): S58–S62. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Saidi RF and Hejazii Kenari SK: Clinical
transplantation and tolerance: Are we there yet? Int J Organ
Transplant Med. 5:137–145. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holmberg C and Jalanko H: Long-term
effects of paediatric kidney transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:301–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mitsnefes MM, Khoury PR and McEnery PT:
Early post-transplantation hypertension and poor long-term renal
allograft survival in pediatric patients. J Pediatr. 143:98–103.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stoumpos S, Jardine AG and Mark PB:
Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality after kidney
transplantation. Transpl Int. 28:10–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Briese S, Claus M and Querfeld U: Arterial
stiffness in children after renal transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol.
23:2241–2245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cseprekál O, Kis E, Dégi AA, Kerti A,
Szabó AJ and Reusz GS: Bone metabolism and arterial stiffness after
renal transplantation. Kidney Blood Press Res. 39:507–515. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harrison-Bernard LM: The renal
renin-angiotensin system. Adv Physiol Educ. 33:270–274. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Paul M, Poyan Mehr A and Kreutz R:
Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol Rev.
86:747–803. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mehta PK and Griendling KK: Angiotensin II
cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the
cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C82–C97.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Karnik SS, Unal H, Kemp JR, Tirupula KC,
Eguchi S, Vanderheyden PM and Thomas WG: International Union of
Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIX Angiotensin receptors:
Interpreters of pathophysiological angiotensinergic stimuli
[corrected] Pharmacol Rev. 67:754–819. 2015.
|
|
13
|
de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright
JW and Unger T: International union of pharmacology. XXIII The
angiotensin II receptors Pharmacol Rev. 52:415–472. 2000.
|
|
14
|
van Thiel BS, van der Pluijm I, te Riet L,
Essers J and Danser AH: The renin-angiotensin system and its
involvement in vascular disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 763:3–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gabriëls G, August C, Grisk O, Steinmetz
M, Kosch M, Rahn KH and Schlatter E: Impact of renal
transplantation on small vessel reactivity. Transplantation.
75:689–697. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Formica RN Jr, Friedman AL, Lorber MI,
Smith JD, Eisen T and Bia MJ: A randomized trial comparing losartan
with amlodipine as initial therapy for hypertension in the early
post-transplant period. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:1389–1394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pilmore HL, Skeans MA, Snyder JJ, Israni
AK and Kasiske BL: Cardiovascular disease medications after renal
transplantation: Results from the patient outcomes in renal
transplantation study. Transplantation. 91:542–551. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goldberg AD, Allis CD and Bernstein E:
Epigenetics: A landscape takes shape. Cell. 128:635–638. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zoghbi HY and Beaudet AL: Epigenetics and
human disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 8:a0194972016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mas VR, Le TH and Maluf DG: Epigenetics in
kidney transplantation: Current evidence, predictions, and future
research directions. Transplantation. 100:23–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bontha SV, Maluf DG, Mueller TF and Mas
VR: Systems biology in kidney transplantation: The application of
multi-omics to a complex model. Am J Transplant. 17:11–21. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim JI, Jung KJ, Jang HS and Park KM:
Gender-specific role of HDAC11 in kidney ischemia- and
reperfusion-induced PAI-1 expression and injury. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 305:F61–F70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sui W, Lin H, Peng W, Huang Y, Chen J,
Zhang Y and Dai Y: Molecular dysfunctions in acute rejection after
renal transplantation revealed by integrated analysis of
transcription factor, microRNA and long noncoding RNA. Genomics.
102:310–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Betts G, Shankar S, Sherston S, Friend P
and Wood KJ: Examination of serum miRNA levels in kidney transplant
recipients with acute rejection. Transplantation. 97:e28–e30. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Becker-Cohen R, Nir A, Rinat C, Feinstein
S, Algur N, Farber B and Frishberg Y: Risk factors for
cardiovascular disease in children and young adults after renal
transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 1:1284–1292. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Baumann M, Chang J, Thürmel K, Roos M, von
Eynatten M, Sollinger D, Lutz J and Heemann U: Fisher-Lewis kidney
transplantation model as a tool for investigation of
transplantation-induced cardiomyopathy. Transplant Proc.
41:2612–2615. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao D, Xu Z, Huang X, Longo LD, Yang S
and Zhang L: Prenatal gender-related nicotine exposure increases
blood pressure response to angiotensin II in adult offspring.
Hypertension. 51:1239–1247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gasc JM, Shanmugam S, Sibony M and Corvol
P: Tissue-specific expression of type 1 angiotensin II receptor
subtypes. An in situ hybridization study Hypertension. 24:531–537.
1994.
|
|
30
|
Bulum B, Ozcakar ZB, Kavaz A, Tutar E,
Ekim M and Yalcinkaya F: Hypertension in children after renal
transplantation. Pediatr Int. 57:1138–1142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weir MR, Burgess ED, Cooper JE, Fenves AZ,
Goldsmith D, McKay D, Mehrotra A, Mitsnefes MM, Sica DA and Taler
SJ: Assessment and management of hypertension in transplant
patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:1248–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chatzikyrkou C, Eichler J, Karch A, Clajus
C, Scurt FG, Ramackers W, Lehner F, Menne J, Haller H, Mertens PR,
et al: Short- and long-term effects of the use of RAAS blockers
immediately after renal transplantation. Blood Press. 26:30–38.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Reudelhuber TL: The renin-angiotensin
system: Peptides and enzymes beyond angiotensin II. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 14:155–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Steckelings UM, Rompe F, Kaschina E and
Unger T: The evolving story of the RAAS in hypertension, diabetes
and CV disease: Moving from macrovascular to microvascular targets.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 23:693–703. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rizzoni D, De Ciuceis C, Salvetti M, Paini
A, Rossini C, Agabiti-Rosei C and Muiesan ML: Interactions between
macro- and micro-circulation: Are they relevant? High Blood Press
Cardiovasc Prev. 22:119–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaplan NM and Victor RG: Primary
hypertension: Pathogenesis (with a special section on renal
denervation and carotid barorecptor pacing). Kaplan's Clinical
Hypertension. 11th edition. Williams and Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA:
pp. 40–115. 2014
|
|
37
|
Triggle CR, Samuel SM, Ravishankar S,
Marei I, Arunachalam G and Ding H: The endothelium: Influencing
vascular smooth muscle in many ways. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
90:713–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kang KT: Endothelium-derived relaxing
factors of small resistance arteries in hypertension. Toxicol Res.
30:141–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Touyz RM and Schiffrin EL: Signal
transduction mechanisms mediating the physiological and
pathophysiological actions of angiotensin II in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Pharmacol Rev. 52:639–672. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Horowitz A, Menice CB, Laporte R and
Morgan KG: Mechanisms of smooth muscle contraction. Physiol Rev.
76:967–1003. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Perez-Vizcaino F, Cogolludo A and Moreno
L: Reactive oxygen species signaling in pulmonary vascular smooth
muscle. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 174:212–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hansen PB: The complex field of interplay
between vasoactive agents. Kidney Int. 76:929–931. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Beevers DG, Morton JJ, Nelson CS, Padfield
PL, Titterington M and Tree M: Angiotensin II in essential
hypertension. Br Med J. 1:4151977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Morton JJ, Garcia del Rio C and Hughes MJ:
Effect of acute vasopressin infusion on blood pressure and plasma
angiotensin II in normotensive and DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.
Clin Sci (Lond). 62:143–149. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Campbell DJ: Angiotensin II generation in
vivo: Does it involve enzymes other than renin and
angiotensin-converting enzyme? J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone
Syst. 13:314–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kakar SS, Sellers JC, Devor DC, Musgrove
LC and Neill JD: Angiotensin II type-1 receptor subtype cDNAs:
Differential tissue expression and hormonal regulation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 183:1090–1096. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Millis RM: Epigenetics and hypertension.
Curr Hypertens Rep. 13:21–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Deaton AM and Bird A: CpG islands and the
regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25:1010–1022. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xiao D, Dasgupta C, Li Y, Huang X and
Zhang L: Perinatal nicotine exposure increases angiotensin II
receptor-mediated vascular contractility in adult offspring. PLoS
One. 9:e1081612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Haack KK, Mitra AK and Zucker IH: NF-κB
and CREB are required for angiotensin II type 1 receptor
upregulation in neurons. PLoS One. 8:e786952013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Nickenig G, Strehlow K, Wassmann S, Bäumer
AT, Albory K, Sauer H and Böhm M: Differential effects of estrogen
and progesterone on AT(1) receptor gene expression in vascular
smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 102:1828–1833. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wenger NK, Speroff L and Packard B:
Cardiovascular health and disease in women. N Engl J Med.
329:247–256. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Miller VM and Duckles SP: Vascular actions
of estrogens: Functional implications. Pharmacol Rev. 60:210–241.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
El-Mas MM and Abdel-Rahman AA:
Longitudinal assessment of the effects of oestrogen on blood
pressure and cardiovascular autonomic activity in female rats. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36:1002–1009. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|