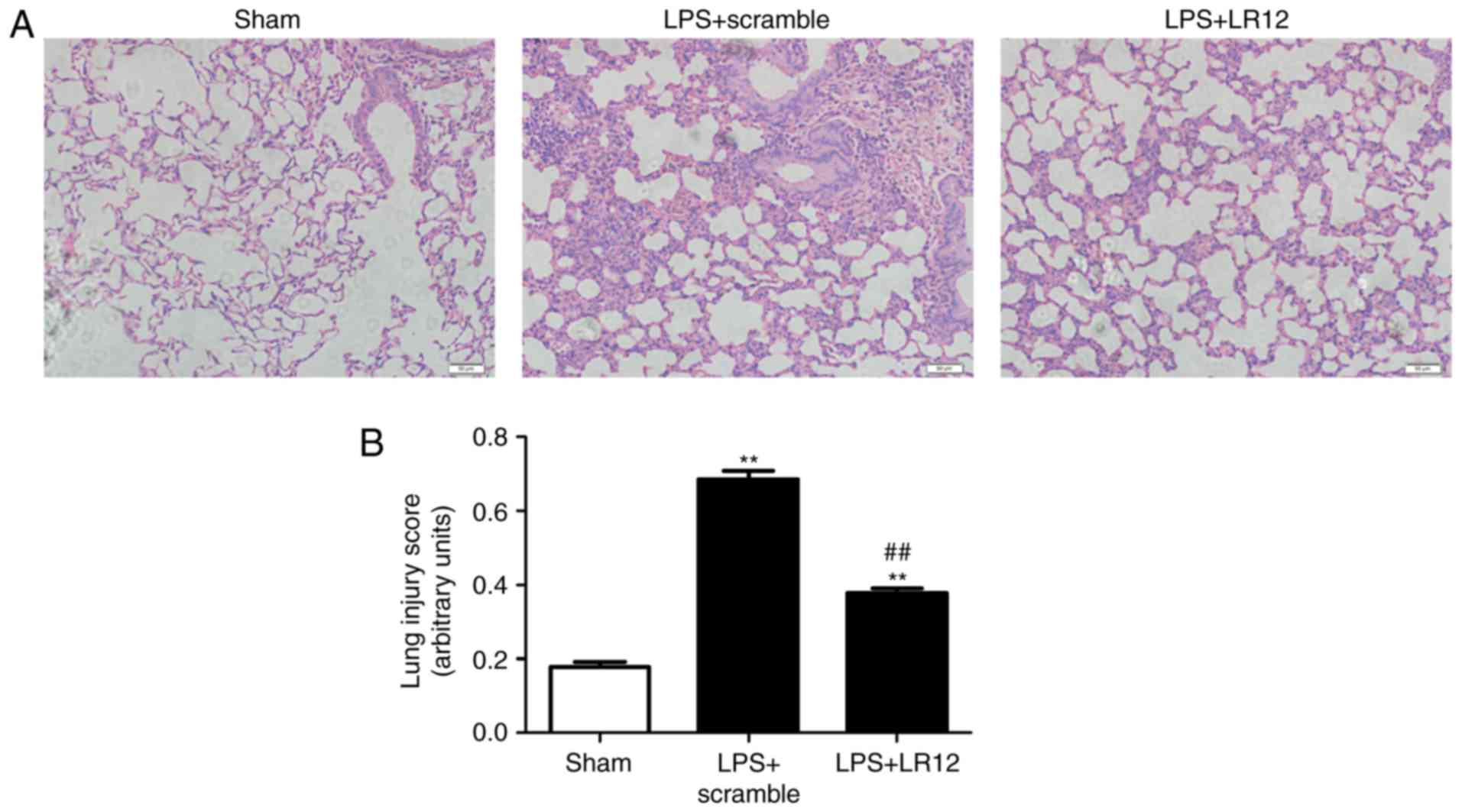
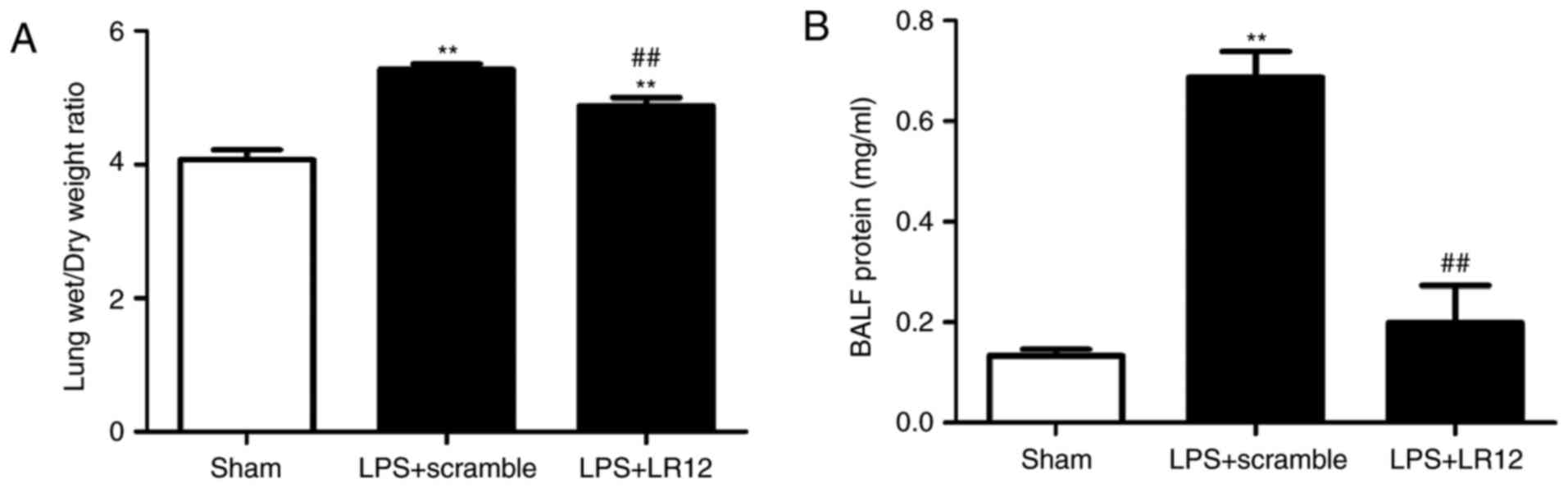
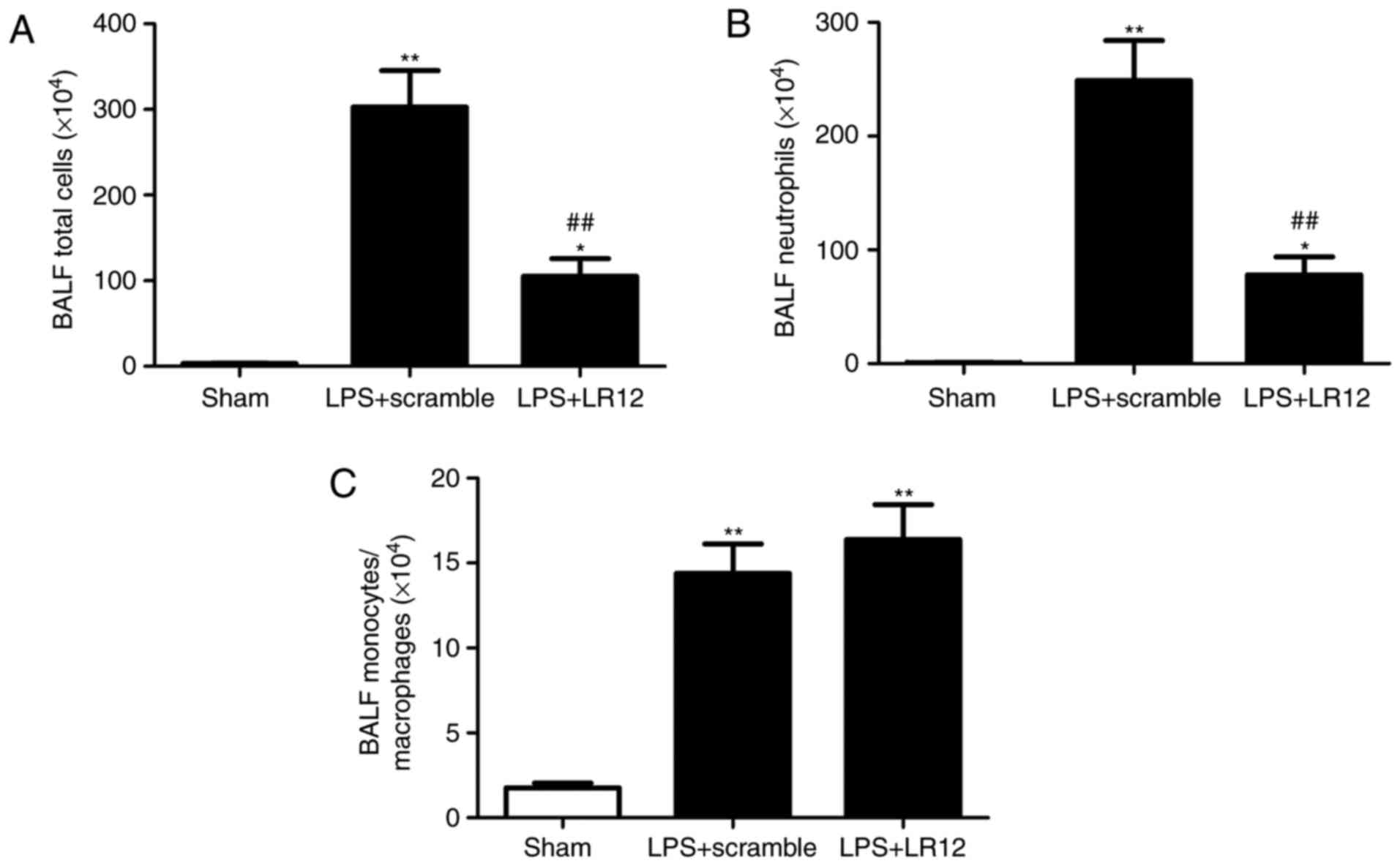
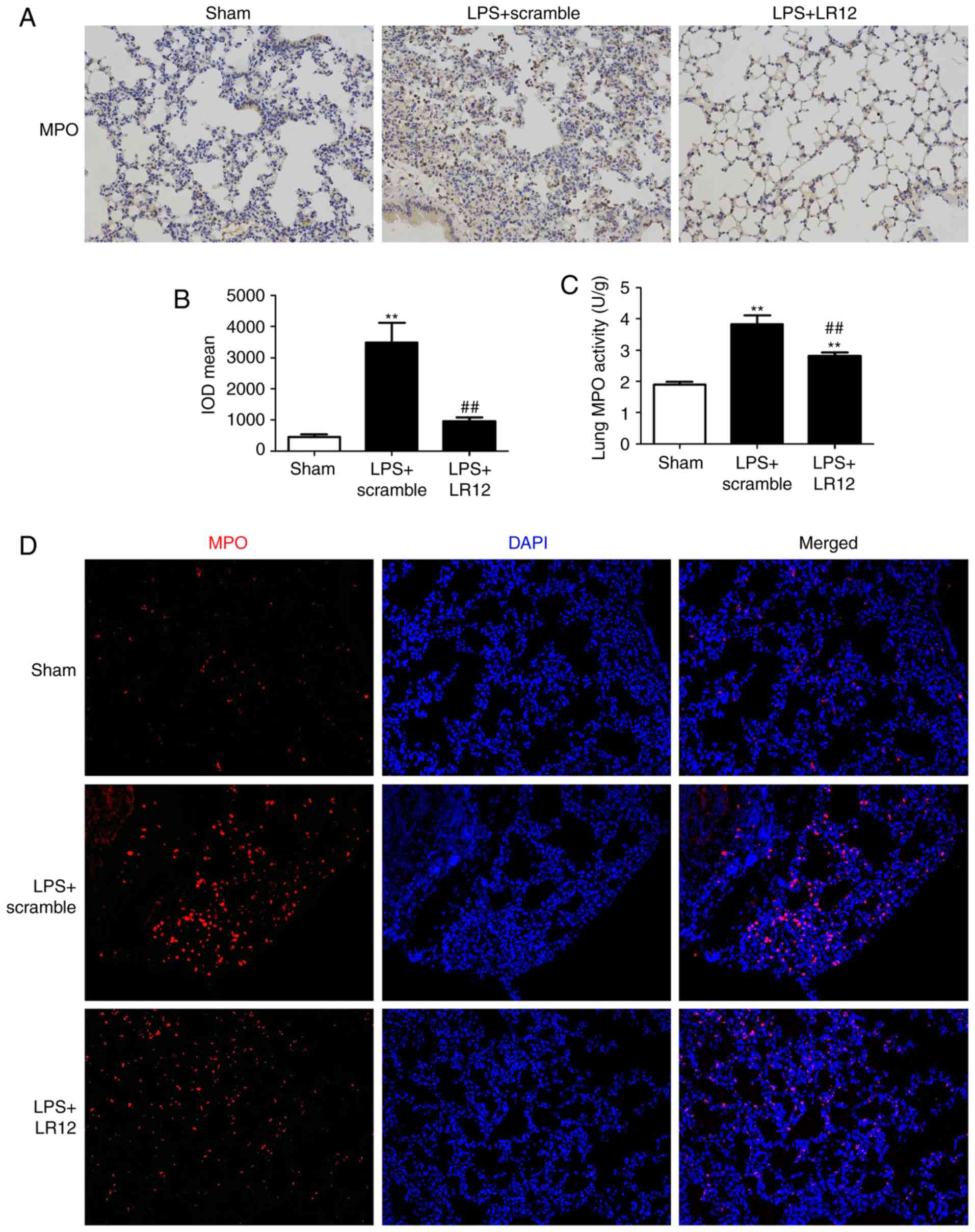
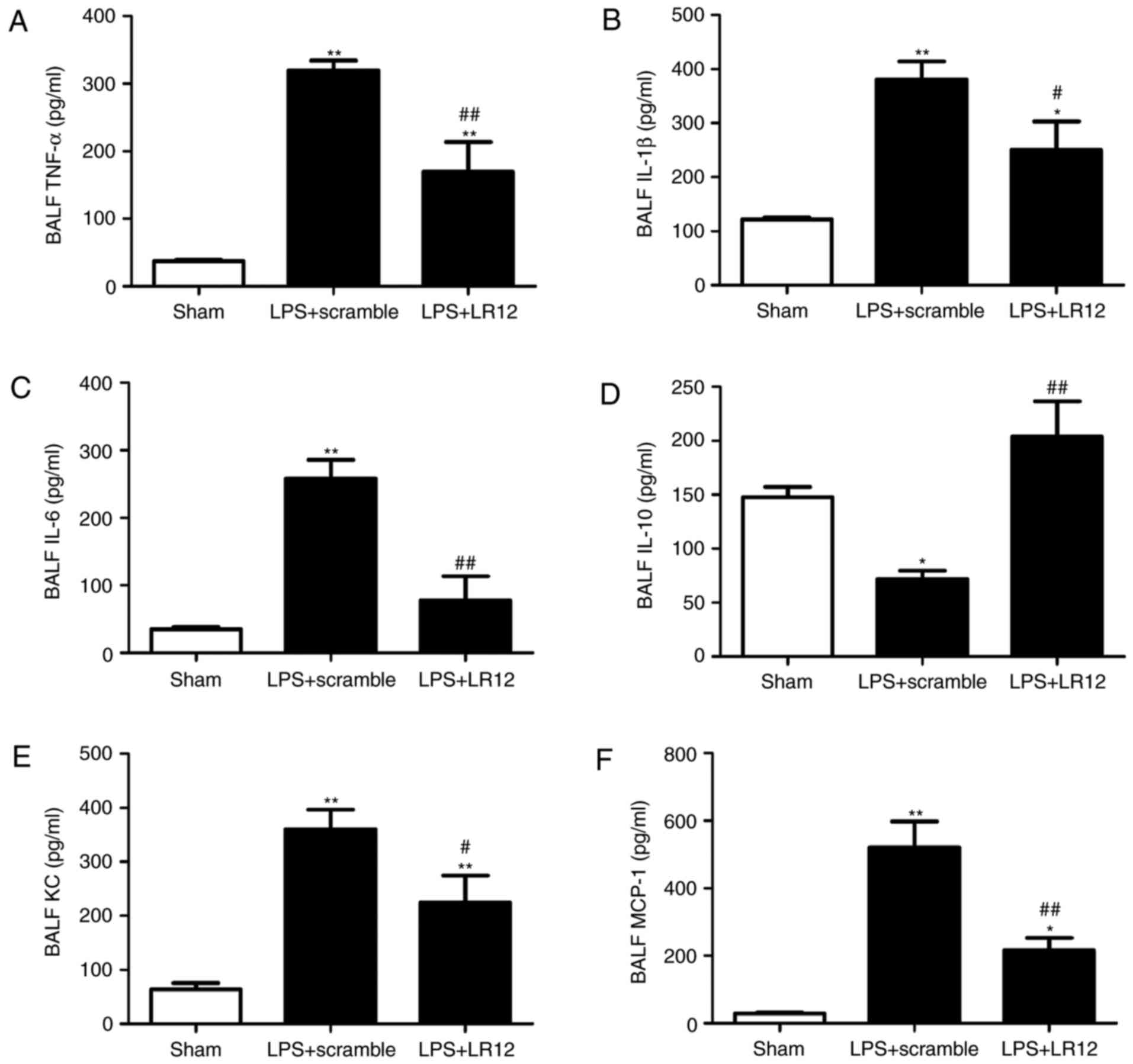
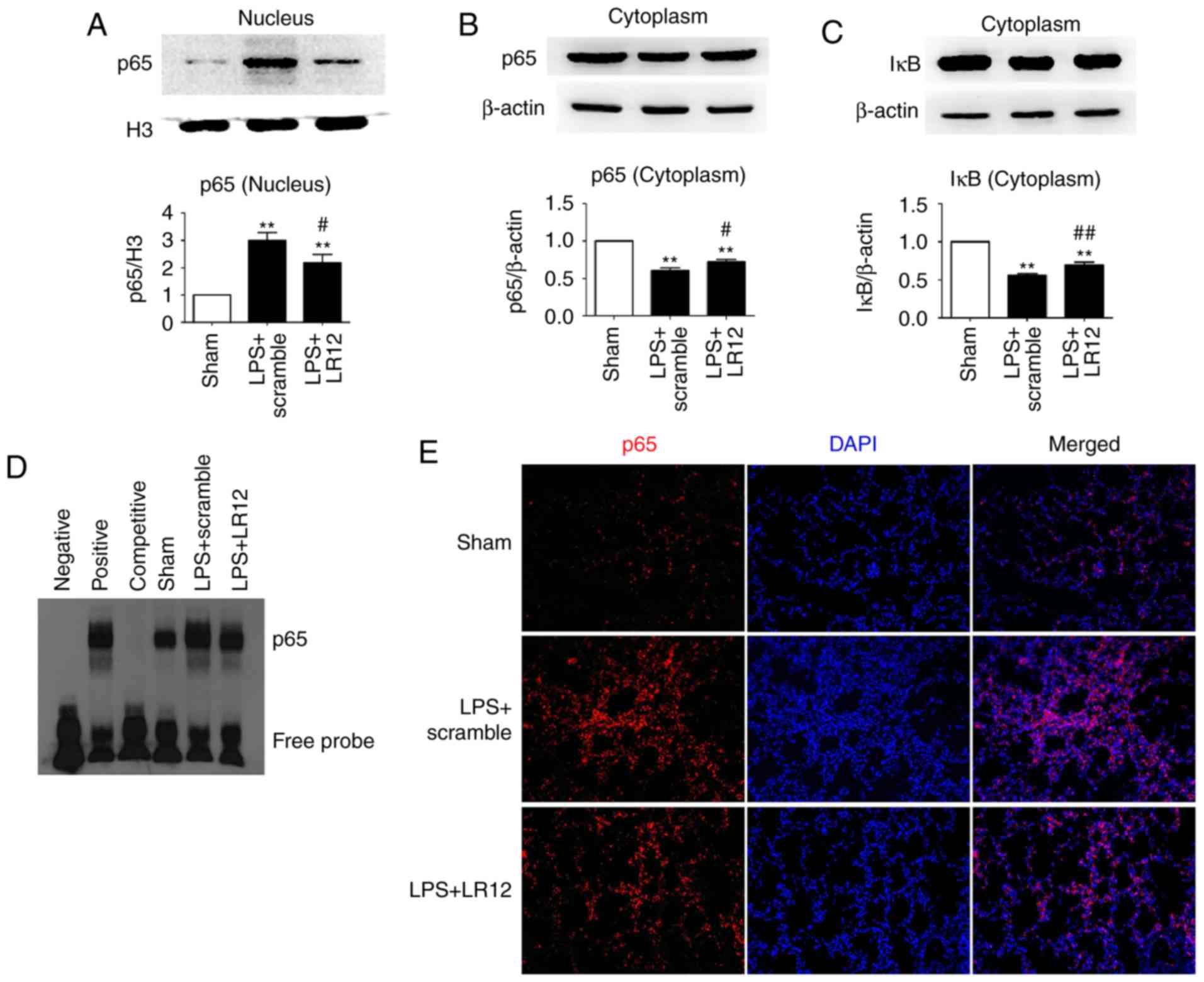
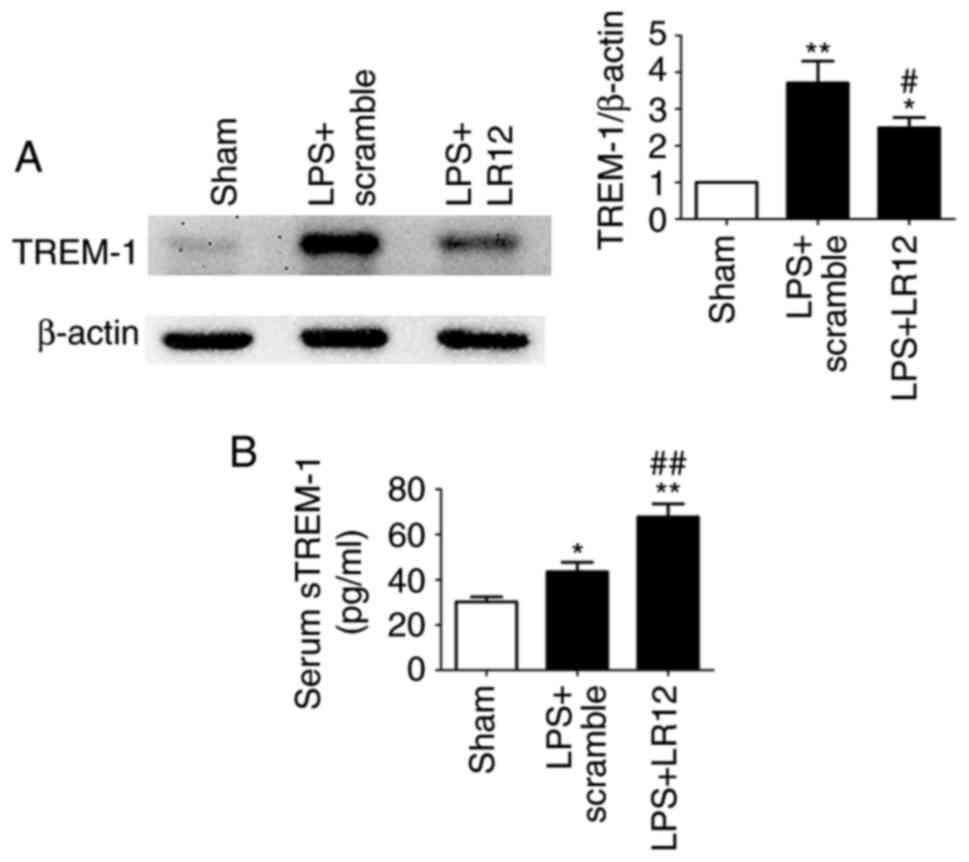
|
1
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gong J, Guo S, Li HB, Yuan SY, Shang Y and
Yao SL: BML-111, a lipoxin receptor agonist, protects haemorrhagic
shock-induced acute lung injury in rats. Resuscitation. 83:907–912.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Serhan CN: Resolution phase of
inflammation: Novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving
lipid mediators and pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:101–137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tsushima K, King LS, Aggarwal NR, De
Gorordo A, D'Alessio FR and Kubo K: Acute lung injury review.
Intern Med. 48:621–630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shang Y, Jiang YX, Ding ZJ, Shen AL, Xu
SP, Yuan SY and Yao SL: Valproic acid attenuates the multiple-organ
dysfunction in a rat model of septic shock. Chin Med J (Engl).
123:2682–2687. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Maderna P and Godson C: Lipoxins:
Resolutionary road. Br J Pharmacol. 158:947–959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bouchon A, Dietrich J and Colonna M:
Cutting edge: Inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a
novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol.
164:4991–4995. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schenk M, Bouchon A, Birrer S, Colonna M
and Mueller C: Macrophages expressing triggering receptor expressed
on myeloid cells-1 are underrepresented in the human intestine. J
Immunol. 174:517–524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bouchon A, Facchetti F, Weigand MA and
Colonna M: TREM-1 amplifies inflammation and is a crucial mediator
of septic shock. Nature. 410:1103–1107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Colonna M and Facchetti F: TREM-1
(triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells): A new player in
acute inflammatory responses. J Infect Dis. 187(Suppl 2):
S397–S401. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dower K, Ellis DK, Saraf K, Jelinsky SA
and Lin LL: Innate immune responses to TREM-1 activation: Overlap,
divergence, and positive and negative cross-talk with bacterial
lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 180:3520–3534. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao W, Mindrinos MN, Seok J, Cuschieri J,
Cuenca AG, Gao H, Hayden DL, Hennessy L, Moore EE, Minei JP, et al:
A genomic storm in critically injured humans. J Exp Med.
208:2581–2590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hara H, Ishihara C, Takeuchi A, Imanishi
T, Xue L, Morris SW, Inui M, Takai T, Shibuya A, Saijo S, et al:
The adaptor protein CARD9 is essential for the activation of
myeloid cells through ITAM-associated and Toll-like receptors. Nat
Immunol. 8:619–629. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fortin CF, Lesur O and Fulop T Jr: Effects
of TREM-1 activation in human neutrophils: Activation of signaling
pathways, recruitment into lipid rafts and association with TLR4.
Int Immunol. 19:41–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ornatowska M, Azim AC, Wang X, Christman
JW, Xiao L, Joo M and Sadikot RT: Functional genomics of silencing
TREM-1 on TLR4 signaling in macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 293:L1377–L1384. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nathan C and Ding A: TREM-1: A new
regulator of innate immunity in sepsis syndrome. Nat Med.
7:530–532. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang F, Liu S, Wu S, Zhu Q, Ou G, Liu C,
Wang Y, Liao Y and Sun Z: Blocking TREM-1 signaling prolongs
survival of mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa induced sepsis. Cell
Immunol. 272:251–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gibot S, Kolopp-Sarda MN, Béné MC,
Bollaert PE, Lozniewski A, Mory F, Levy B and Faure GC: A soluble
form of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1
modulates the inflammatory response in murine sepsis. J Exp Med.
200:1419–1426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gibot S, Buonsanti C, Massin F, Romano M,
Kolopp-Sarda MN, Benigni F, Faure GC, Béné MC, Panina-Bordignon P,
Passini N and Lévy B: Modulation of the triggering receptor
expressed on the myeloid cell type 1 pathway in murine septic
shock. Infect Immun. 74:2823–2830. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hommes TJ, Hoogendijk AJ, Dessing MC,
Van't Veer C, Florquin S, Colonna M, de Vos AF and van der Poll T:
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (TREM-1) improves
host defence in pneumococcal pneumonia. J Pathol. 233:357–367.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Klesney-Tait J, Keck K, Li X, Gilfillan S,
Otero K, Baruah S, Meyerholz DK, Varga SM, Knudson CJ, Moninger TO,
et al: Transepithelial migration of neutrophils into the lung
requires TREM-1. J Clin Invest. 123:138–149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Gibot S, Massin F, Alauzet C, Montemont C,
Lozniewski A, Bollaert PE and Levy B: Effects of the TREM-1 pathway
modulation during mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Crit
Care Med. 36:504–510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kamei K, Yasuda T, Ueda T, Qiang F,
Takeyama Y and Shiozaki H: Role of triggering receptor expressed on
myeloid cells-1 in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 17:305–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gibot S, Massin F, Alauzet C, Derive M,
Montemont C, Collin S, Fremont S and Levy B: Effects of the TREM 1
pathway modulation during hemorrhagic shock in rats. Shock.
32:633–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schenk M, Bouchon A, Seibold F and Mueller
C: TREM-1-expressing intestinal macrophages crucially amplify
chronic inflammation in experimental colitis and inflammatory bowel
diseases. J Clin Invest. 117:3097–3106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu T, Zhou Y, Li P, Duan JX, Liu YP, Sun
JY, Wan L, Dong L, Fang X, Jiang JX and Guan CX: Blocking
triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Sci Rep. 6:394732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gattis JL, Washington AV, Chisholm MM,
Quigley L, Szyk A, McVicar DW and Lubkowski J: The structure of the
extracellular domain of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid
cells like transcript-1 and evidence for a naturally occurring
soluble fragment. J Biol Chem. 281:13396–13403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Derive M, Bouazza Y, Sennoun N, Marchionni
S, Quigley L, Washington V, Massin F, Max JP, Ford J, Alauzet C, et
al: Soluble TREM-like transcript-1 regulates leukocyte activation
and controls microbial sepsis. J Immunol. 188:5585–5592. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Derive M, Boufenzer A and Gibot S:
Attenuation of responses to endotoxin by the triggering receptor
expressed on myeloid cells-1 inhibitor LR12 in nonhuman primate.
Anesthesiology. 120:935–942. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Boufenzer A, Lemarié J, Simon T, Derive M,
Bouazza Y, Tran N, Maskali F, Groubatch F, Bonnin P, Bastien C, et
al: TREM-1 mediates inflammatory injury and cardiac remodeling
following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 116:1772–1782. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Derive M, Boufenzer A, Bouazza Y,
Groubatch F, Alauzet C, Barraud D, Lozniewski A, Leroy P, Tran N
and Gibot S: Effects of a TREM-like transcript-1-derived peptide
during hypodynamic septic shock in pigs. Shock. 39:176–182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matute-Bello G, Downey G, Moore BB,
Groshong SD, Matthay MA, Slutsky AS and Kuebler WM; Acute
LungInjury in Animals Study Group: An official American Thoracic
Society workshop report: Features and measurements of experimental
acute lung injury in animals. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
44:725–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matthay MA and Zimmerman GA: Acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Four decades of
inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 33:319–327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA, Esmon C,
Bhattacharya J, Coller B, Doerschuk CM, Floros J, Gimbrone MA Jr,
Hoffman E, Hubmayr RD, et al: Future research directions in acute
lung injury: Summary of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 167:1027–1035. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moon C, Han JR, Park HJ, Hah JS and Kang
JL: Synthetic RGDS peptide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting integrin signaled MAP kinase
pathways. Respir Res. 10:182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang B, Gong X, Wan JY, Zhang L, Zhang Z,
Li HZ and Min S: Resolvin D1 protects mice from LPS-induced acute
lung injury. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 24:434–441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bleharski JR, Kiessler V, Buonsanti C,
Sieling PA, Stenger S, Colonna M and Modlin RL: A role for
triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in host defense
during the early-induced and adaptive phases of the immune
response. J Immunol. 170:3812–3818. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tessarz AS and Cerwenka A: The
TREM-1/DAP12 pathway. Immunol Lett. 116:111–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Klesney-Tait J, Turnbull IR and Colonna M:
The TREM receptor family and signal integration. Nat Immunol.
7:1266–1273. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang DY, Qin RY, Liu ZR, Gupta MK and
Chang Q: Expression of TREM-1 mRNA in acute pancreatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:2744–2746. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu N, Gu Q and Zheng YS: Expression of
triggering receptor-1 in myeloid cells of mice with acute lung
injury. World J Emerg Med. 1:144–148. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Baig MS, Zaichick SV, Mao M, de Abreu AL,
Bakhshi FR, Hart PC, Saqib U, Deng J, Chatterjee S, Block ML, et
al: NOS1-derived nitric oxide promotes NF-kB transcriptional
activity through inhibition of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1.
J Exp Med. 212:1725–1738. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Blackwell TS, Lancaster LH, Blackwell TR,
Venkatakrishnan A and Christman JW: Differential NF-kappaB
activation after intratracheal endotoxin. Am J Physiol.
277:L823–L830. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kang JL, Lee HW, Lee HS, Pack IS, Chong Y,
Castranova V and Koh Y: Genistein prevents nuclear factor-kappa B
activation and acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Am
J Respir Crit Care Med. 164:2206–2212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Blackwell TS and Christman JW: The role of
nuclear factor-kappaB in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 17:3–9. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang A, Wang S, Zhang J and Wu H: Genipin
alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB and
NLRP3 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 38:115–119. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yan C, Guan F, Shen Y, Tang H, Yuan D, Gao
H and Feng X: Bigelovii A protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by blocking NF-κB and
CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein δ pathways. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:92016042016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gomez-Pina V, Martinez E, Fernández-Ruiz
I, Del Fresno C, Soares-Schanoski A, Jurado T, Siliceo M, Toledano
V, Fernández-Palomares R, Garcia-Rio F, et al: Role of MMPs in
orchestrating inflammatory response in human monocytes via a
TREM-PI3K-NF-κB pathway. J Leukoc Biol. 91:933–945. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A,
Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks
BG, Fitzgerald KA, et al: Cutting Edge: NF-kappaB activating
pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3
inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol.
183:787–791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Knapp S, Gibot S, de Vos A, Versteeg HH,
Colonna M and van der Poll T: Cutting edge: Expression patterns of
surface and soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid
cells-1 in human endotoxemia. J Immunol. 173:7131–7134. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mahdy AM, Lowes DA, Galley HF, Bruce JE
and Webster NR: Production of soluble triggering receptor expressed
on myeloid cells by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human neutrophils
involves de novo protein synthesis. Clin Vaccine Immunol.
13:492–495. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gomez-Piña V, Soares-Schanoski A,
Rodriguez-Rojas A, Del Fresno C, Garcia F, Vallejo-Cremades MT,
Fernández-Ruiz I, Arnalich F, Fuentes-Prior P and López-Collazo E:
Metalloproteinases shed TREM-1 ectodomain from
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol.
179:4065–4073. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Palazzo SJ, Simpson T and Schnapp LM:
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells type 1 as a
potential therapeutic target in sepsis. Dimens Crit Care Nurs.
31:1–6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Zakynthinos S,
Baziaka F, Papadomichelakis E, Virtzili S, Koutoukas P, Armaganidis
A, Giamarellou H and Roussos C: Soluble triggering receptor
expressed on myeloid cells 1 as an anti-inflammatory mediator in
sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 32:237–243. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|