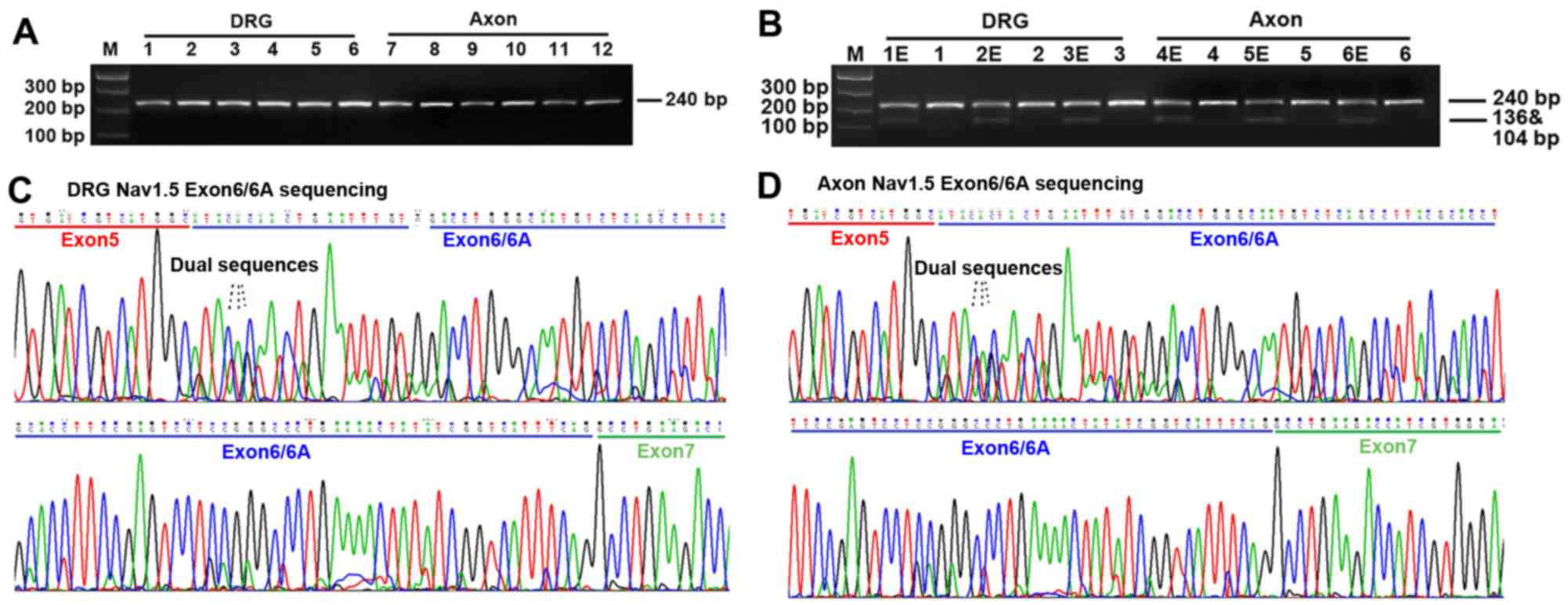
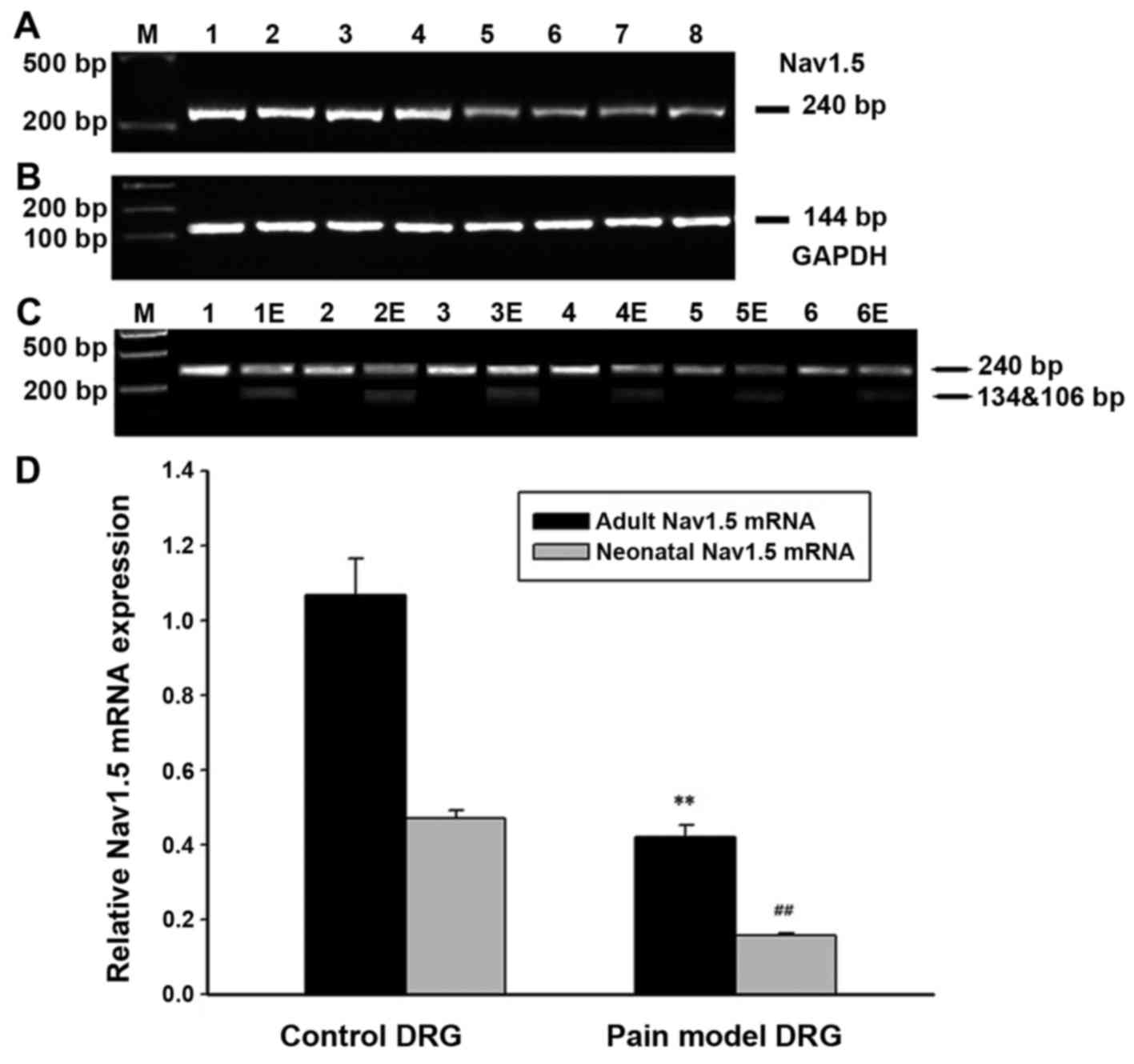
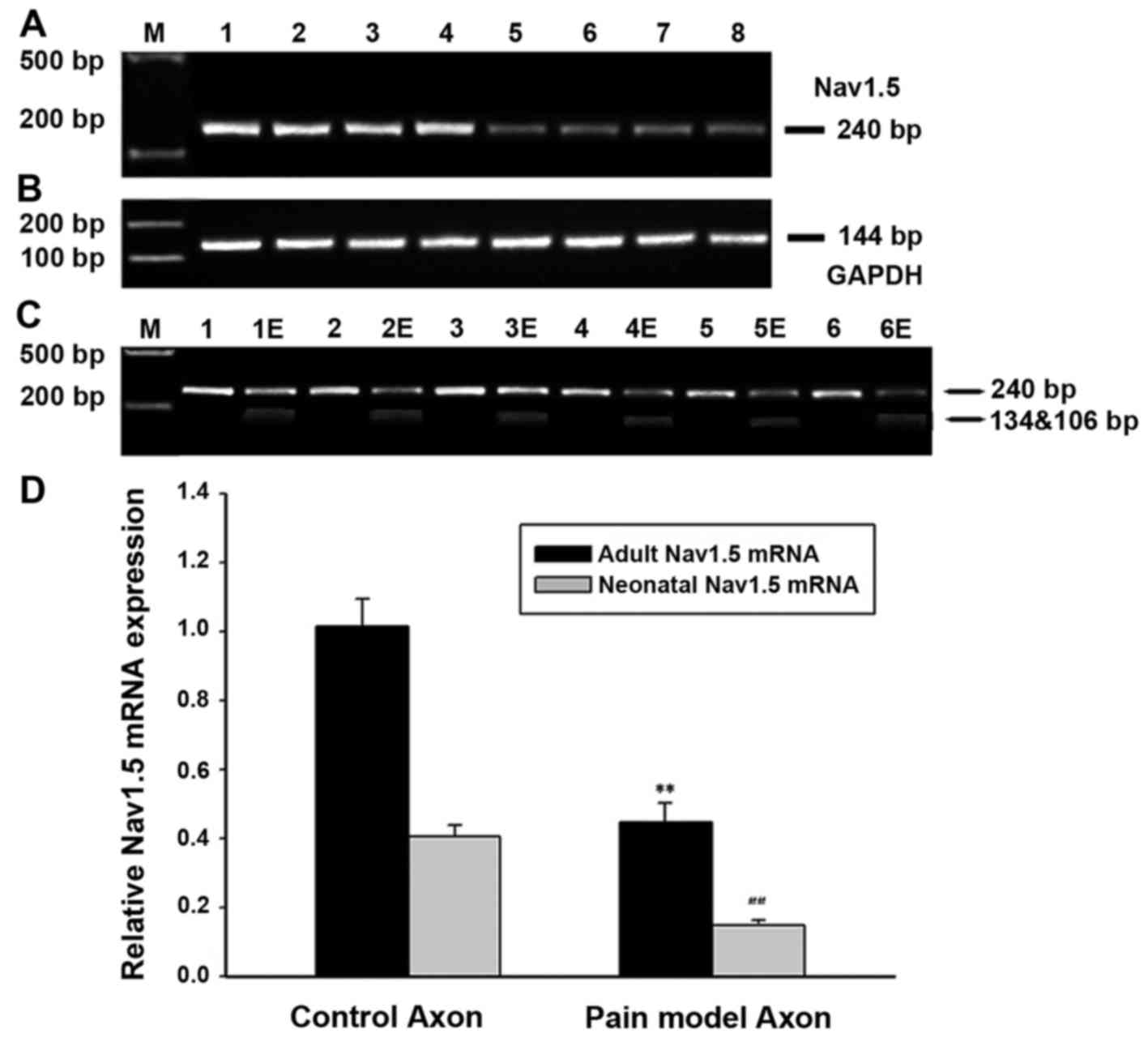
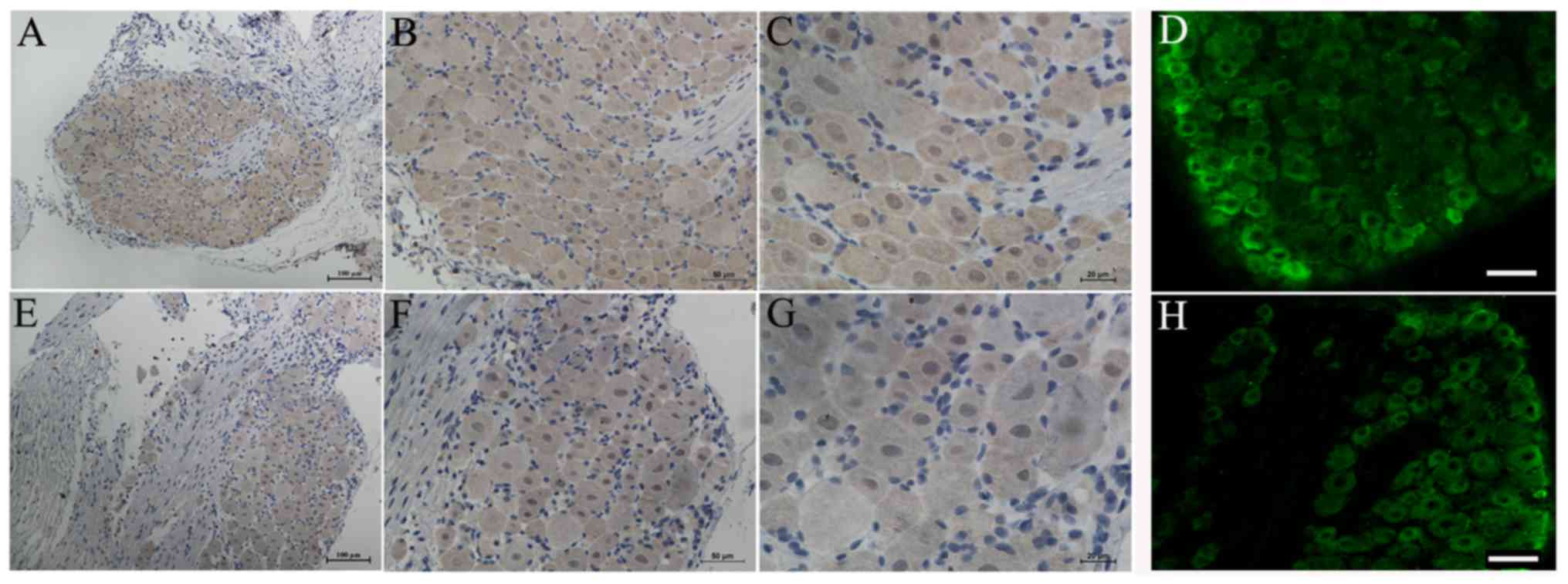
|
1
|
Liu M and Wood JN: The roles of sodium
channels in nociception: Implications for mechanisms of neuropathic
pain. Pain Med. 12(Suppl 3): S93–S99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cummins TR, Sheets PL and Waxman SG: The
roles of sodium channels in nociception: Implications for
mechanisms of pain. Pain. 131:243–1257. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Catterall WA: From ionic currents to
molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated
sodium channels. Neuron. 26:13–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu FH and Catterall WA: Overview of the
voltage-gated sodium channel family. Genome Biol. 4:2072003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Catterall WA: Voltage-gated sodium
channels at 60: Structure, function and pathophysiology. J Physiol.
590:2577–12589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laedermann CJ, Pertin M, Suter MR and
Decosterd I: Voltage-gated sodium channel expression in mouse DRG
after SNI leads to re-evaluation of projections of injured fibers.
Mol Pain. 10:192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Devor M: Sodium channels and mechanisms of
neuropathic pain. J Pain. 7(Suppl 1): S3–S12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rook MB, Evers MM, Vos MA and Bierhuizen
MF: Biology of cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 expression. Cardiovasc
Res. 93:12–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Schroeter A, Walzik S, Blechschmidt S,
Haufe V, Benndorf K and Zimmer T: Structure and function of splice
variants of the cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.5. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:16–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Kameyama M,
Kameyama A and Zong ZH: Analysis of four novel variants of
Nav1.5/SCN5A cloned from the brain. Neurosci Res. 64:339–1347.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Zong ZH, Lin L,
Kameyama M and Kameyama A: New variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A encode
Na+ channels in the brain. J Neurogenet. 22:57–175.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xing D, Wang J, Ou S, Wang Y, Qiu B, Ding
D, Guo F and Gao Q: Expression of neonatal Nav1.5 in human brain
astrocytoma and its effect on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis
of astrocytoma cells. Oncol Rep. 31:2692–12700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Renganathan M, Dib-Hajj S and Waxman SG:
Na(v)1.5 underlies the 'third TTX-R sodium current' in rat small
DRG neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 106:70–182. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kerr NC, Holmes FE and Wynick D: Novel
isoforms of the sodium channels Nav1.8 and Nav1.5 are produced by a
conserved mechanism in mouse and rat. J Biol Chem.
279:24826–124833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kerr NC, Gao Z, Holmes FE, Hobson SA,
Hancox JC, Wynick D and James AF: The sodium channel Nav1.5a is the
predominant isoform expressed in adult mouse dorsal root ganglia
and exhibits distinct inactivation properties from the full-length
Nav1.5 channel. Mol Cell Neurosci. 35:283–1291. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ren CT, Li DM, Ou SW, Wang YJ, Lin Y, Zong
ZH, Kameyama M and Kameyama A: Cloning and expression of the two
new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A in rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem.
365:139–1148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hartmann HA, Colom LV, Sutherland ML and
Noebels JL: Selective localization of cardiac SCN5A sodium channels
in limbic regions of rat brain. Nat Neurosci. 2:593–1595. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu L, Nishiyama K, Hollyfield JG and Wang
Q: Localization of Nav1.5 sodium channel protein in the mouse
brain. Neuroreport. 13:2547–12551. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frenz CT, Hansen A, Dupuis ND, Shultz N,
Levinson SR, Finger TE and Dionne VE: NaV1.5 sodium channel window
currents contribute to spontaneous firing in olfactory sensory
neurons. J Neurophysiol. 112:1091–11104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Onkal R, Mattis JH, Fraser SP, Diss JK,
Shao D, Okuse K and Djamgoz MB: Alternative splicing of Nav1.5: An
electrophysiological comparison of 'neonatal' and 'adult' isoforms
and critical involvement of a lysine residue. J Cell Physiol.
216:716–1726. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Decosterd I and Woolf CJ: Spared nerve
injury: An animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain.
Pain. 87:149–1158. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ou SW, Kameyama A, Hao LY, Horiuchi M,
Minobe E, Wang WY, Makita N and Kameyama M: Tetrodotoxin-resistant
Na+ channels in human neuroblastoma cells are encoded by
new variants of Nav1.5/SCN5A. Eur J Neurosci. 22:793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fraser SP, Diss JK, Chioni AM, Mycielska
ME, Pan H, Yamaci RF, Pani F, Siwy Z, Krasowska M, Grzywna Z, et
al: Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of
human breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5381–15389.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang W, Gu J, Li YQ and Tao YX: Are
voltage-gated sodium channels on the dorsal root ganglion involved
in the development of neuropathic pain? Mol Pain. 7:162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moldovan M, Alvarez S, Romer Rosberg M and
Krarup C: Axonal voltage-gated ion channels as pharmacological
targets for pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 708:105–1112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Numann R, Catterall WA and Scheuer T:
Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C
phosphorylation. Science. 254:115–1118. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schreibmayer W: Isoform diversity and
modulation of sodium channels by protein kinases. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 9:187–1200. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grant AO and Wendt DJ: Block and
modulation of cardiac Na+ channels by antiarrhythmic
drugs, neurotransmitters and hormones. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
13:352–1358. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tateyama M, Kurokawa J, Terrenoire C,
Rivolta I and Kass RS: Stimulation of protein kinase C inhibits
bursting in disease-linked mutant human cardiac sodium channels.
Circulation. 107:3216–13222. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hallaq H, Wang DW, Kunic JD, George AL Jr,
Wells KS and Murray KT: Activation of protein kinase C alters the
intracellular distribution and mobility of cardiac Na+
channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H782–H789. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|