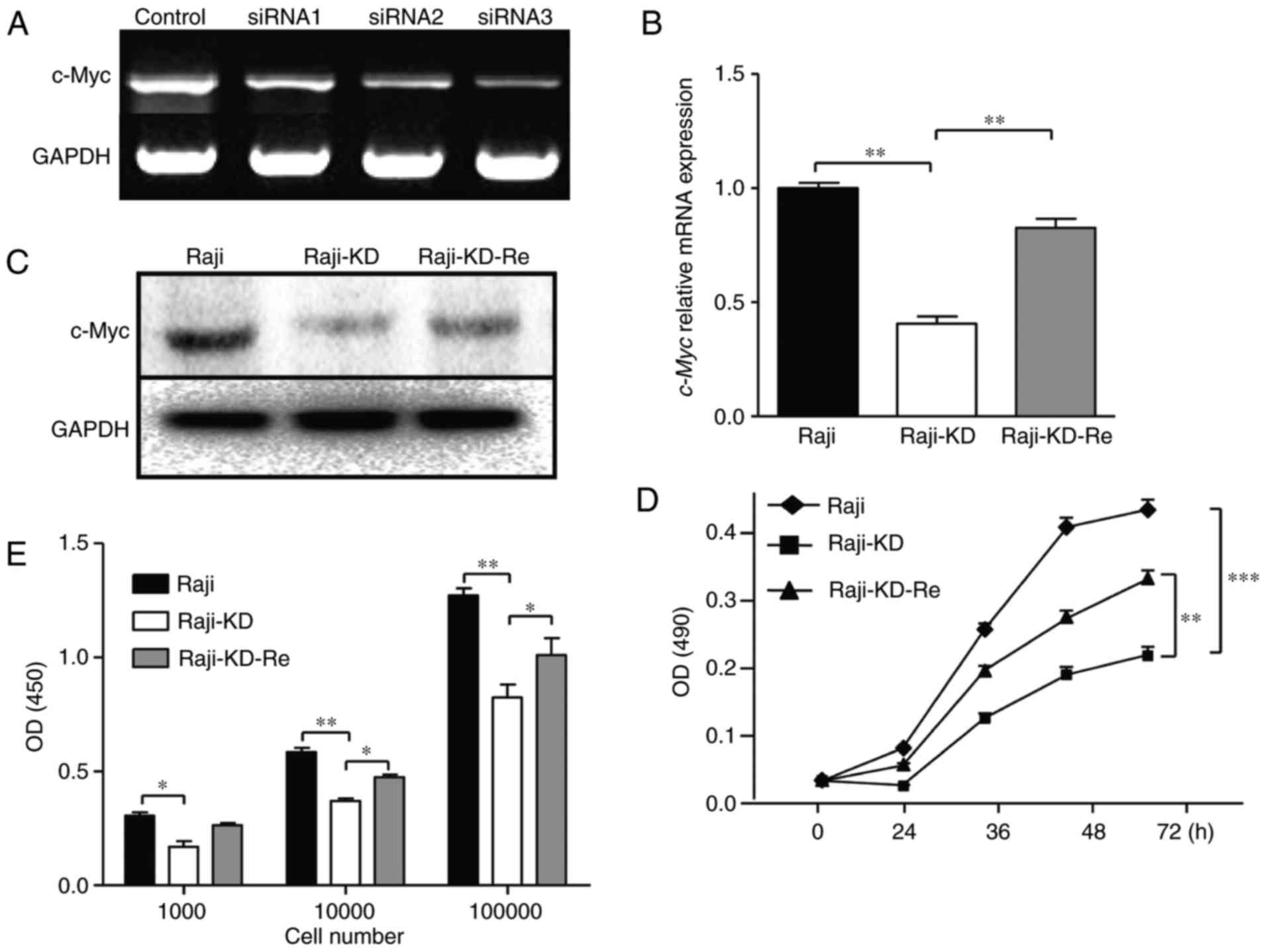
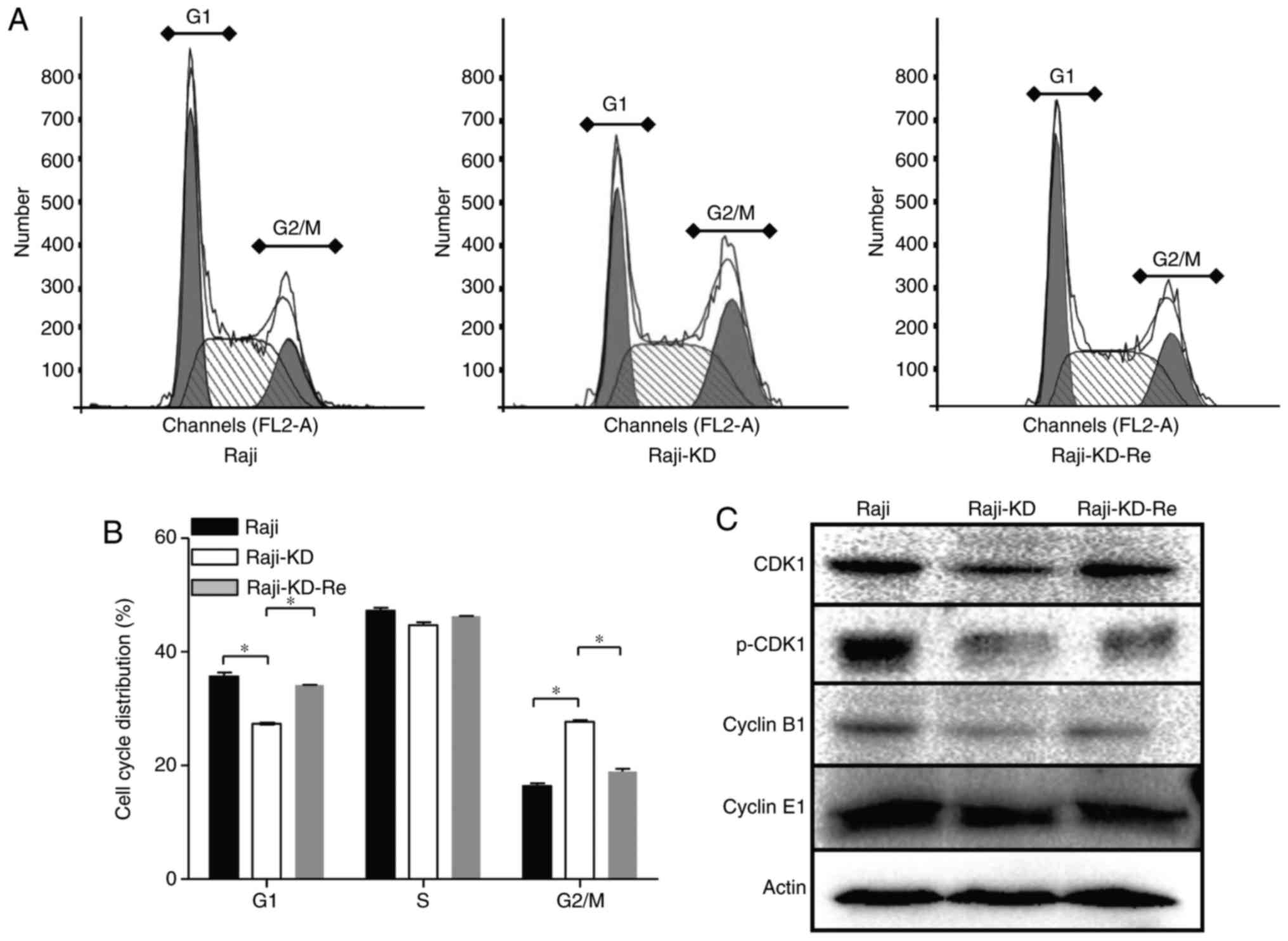
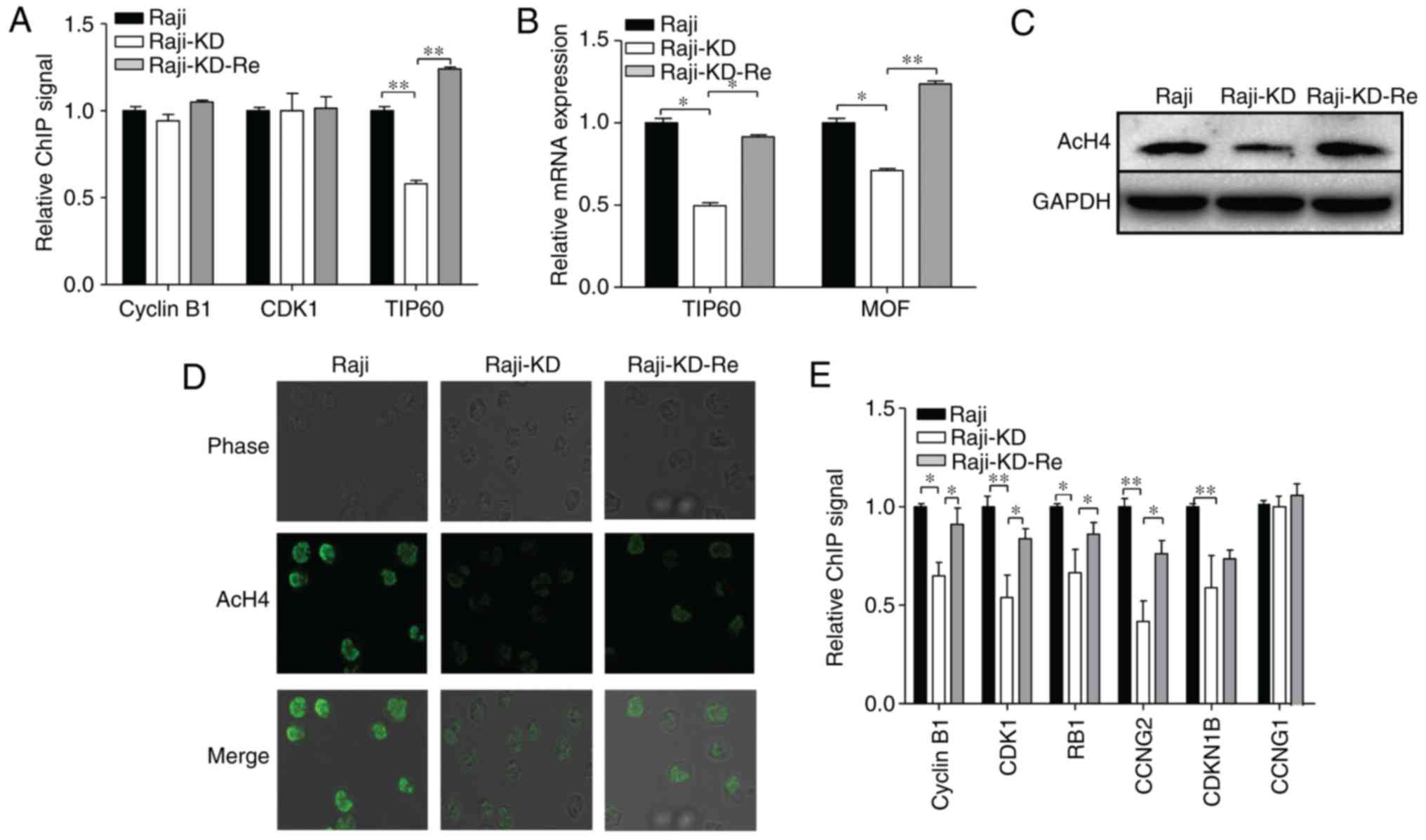
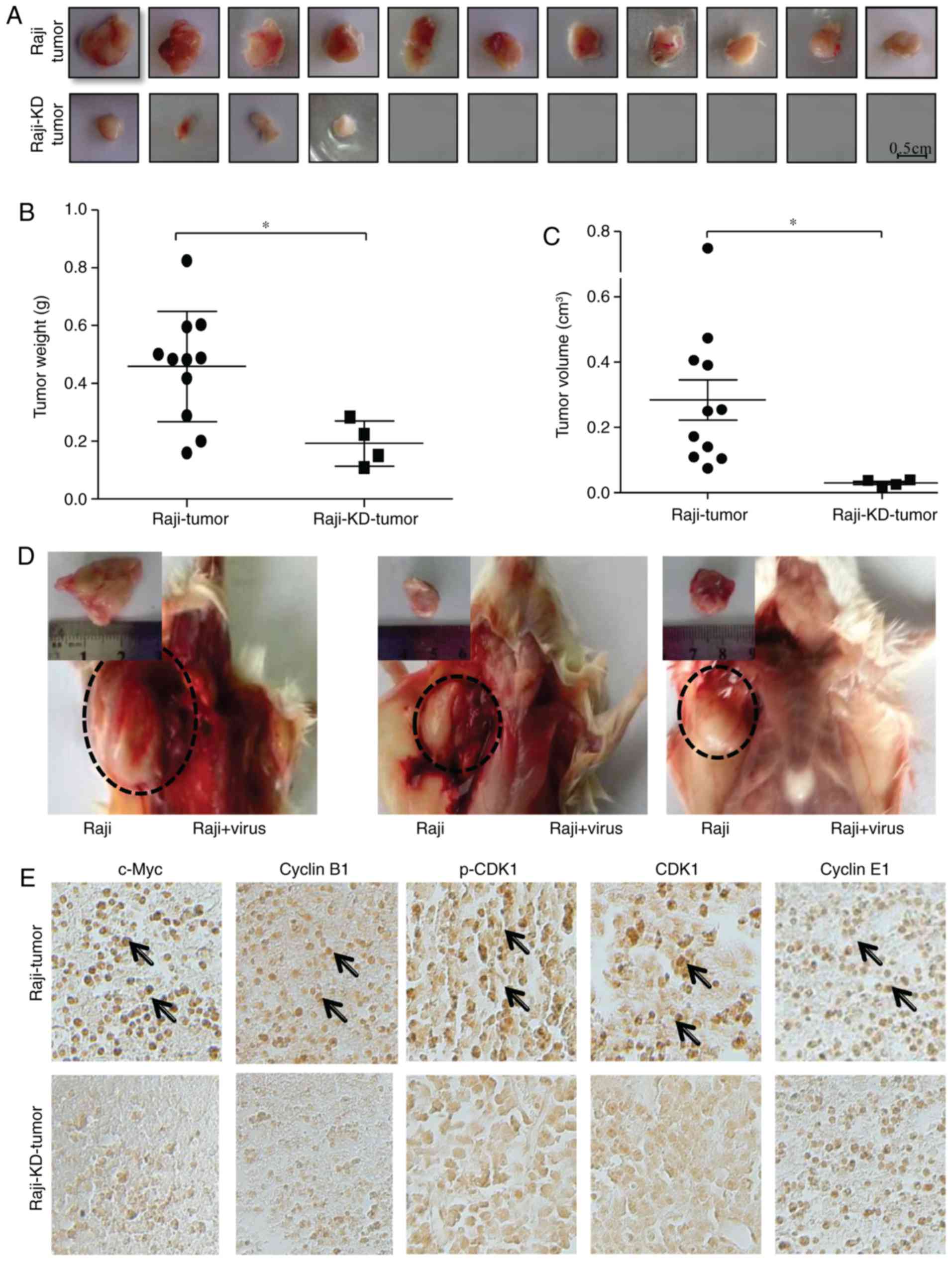
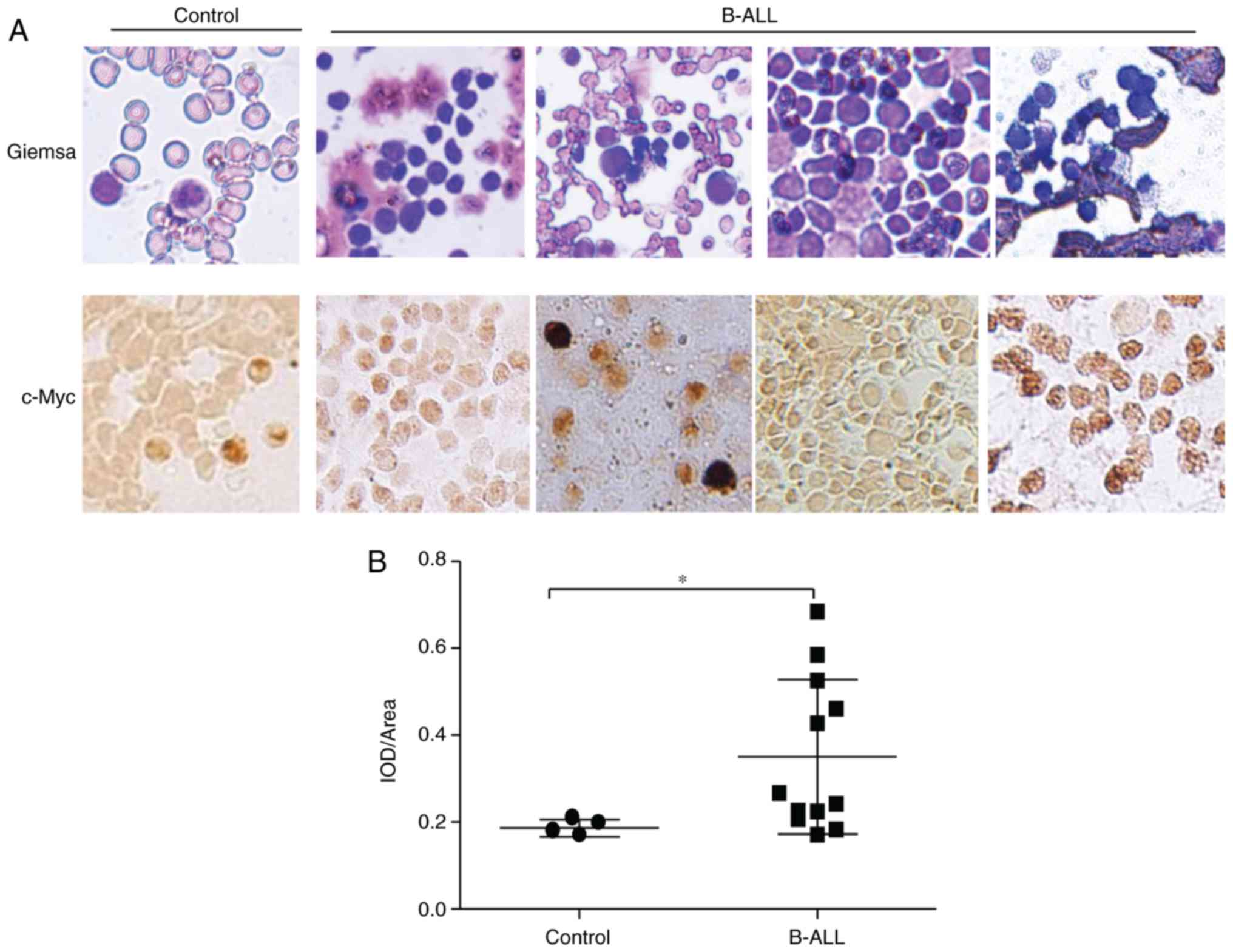
|
1
|
Villarreal-Martinez L, Jaime-Pérez JC,
Rodríguez-Martínez M, González-Llano O and Gómez-Almaguer D: Acute
lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood presenting as aplastic anemia:
Report of two cases. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 34:165–167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liew M, Rowe L, Clement PW, Miles RR and
Salama ME: Validation of break-apart and fusion MYC probes using a
digital fluorescence in situ hybridization capture and imaging
system. J Pathol Inform. 7:202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeller KI, Zhao X, Lee CW, Chiu KP, Yao F,
Yustein JT, Ooi HS, Orlov YL, Shahab A, Yong HC, et al: Global
mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17834–17839. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Teriete P, Hu A,
Raveendra-Panickar D, Pendelton K, Lazo JS, Eiseman J, Holien T,
Misund K, Oliynyk G, et al: Direct inhibition of c-Myc-Max
heterodimers by celastrol and celastrol-inspired triterpenoids.
Oncotarget. 6:32380–32395. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang N, Ichikawa W, Faiola F, Lo SY, Liu
X and Martinez E: MYC interacts with the human STAGA coactivator
complex via multivalent contacts with the GCN5 and TRRAP subunits.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:395–405. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dang CV: MYC, metabolism, cell growth, and
tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 3:a0142172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cao X, Bennett RL and May WS: c-Myc and
caspase-2 are involved in activating Bax during cytotoxic
drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 283:14490–14496. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang O, Yang F, Liu Y, Lv L, Ma R, Chen C,
Wang J, Tan Q, Cheng Y, Xia E, et al: C-MYC-induced upregulation of
lncRNA SNHG12 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration
in triple-negative breast cancer. Am J Transl Res. 9:533–545.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Treszl A, Adány R, Rákosy Z, Kardos L,
Bégány A, Gilde K and Balázs M: Extra copies of c-myc are more
pronounced in nodular melanomas than in superficial spreading
melanomas as revealed by fluorescence in situ hybridisation.
Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 60:37–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruiz-Pérez MV, Henley AB and
Arsenian-Henriksson M: The MYCN protein in health and disease.
Genes (Basel). 8. pp. E1132017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang Y, Yoo HM, Choi I, Pyun KH, Byun SM
and Ha H: Interleukin 4-induced proliferation in normal human
keratinocytes is associated with c-myc gene expression and
inhibited by genistein. J Invest Dermatol. 107:367–372. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nupponen NN, Kakkola L, Koivisto P and
Visakorpi T: Genetic alterations in hormone-refractory recurrent
prostate carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 153:141–148. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nupponen NN, Hyytinen ER, Kallioniemi AH
and Visakorpi T: Genetic alterations in prostate cancer cell lines
detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 101:53–57. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gugger M, Burckhardt E, Kappeler A,
Hirsiger H, Laissue JA and Mazzucchelli L: Quantitative expansion
of structural genomic alterations in the spectrum of neuroendocrine
lung carcinomas. J Pathol. 196:408–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hecht JL and Aster JC: Molecular biology
of Burkitt's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 18:3707–3721. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Neri A, Barriga F, Knowles DM, Magrath IT
and Dalla-Favera R: Different regions of the immunoglobulin
heavy-chain locus are involved in chromosomal translocations in
distinct pathogenetic forms of Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 85:2748–2752. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frank SR, Schroeder M, Fernandez P,
Taubert S and Amati B: Binding of c-Myc to chromatin mediates
mitogen-induced acetylation of histone H4 and gene activation.
Genes Dev. 15:2069–2082. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pfeifer D, Chung YM and Hu MC: Effects of
low-dose bisphenol A on DNA damage and proliferation of breast
cells: The role of c-Myc. Environ Health Perspect. 123:1271–1279.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lane AN and Fan TW: Regulation of
mammalian nucleotide metabolism and biosynthesis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 43:2466–2485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yap CS, Peterson AL, Castellani G, Sedivy
JM and Neretti N: Kinetic profiling of the c-Myc transcriptome and
bioinformatic analysis of repressed gene promoters. Cell Cycle.
10:2184–2196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seo HR, Kim J, Bae S, Soh JW and Lee YS:
Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation of c-Myc on Ser-62 is essential in
transcriptional activation of cyclin B1 by cyclin G1. J Biol Chem.
283:15601–15610. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu YX and Manley JL: New insights into
mitotic chromosome condensation: A role for the prolyl isomerase
Pin1. Cell Cycle. 6:2896–2901. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ehedego H, Boekschoten MV, Hu W, Doler C,
Haybaeck J, Gaβler N, Müller M, Liedtke C and Trautwein C: p21
ablation in liver enhances DNA damage, cholestasis, and
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 75:1144–1155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang X, Di Liberto M, Jayabalan D, Liang
J, Ely S, Bretz J, Shaffer AL III, Louie T, Chen I, Randolph S, et
al: Prolonged early G(1) arrest by selective CDK4/CDK6 inhibition
sensitizes myeloma cells to cytotoxic killing through cell
cycle-coupled loss of IRF4. Blood. 120:1095–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ravens S, Yu C, Ye T, Stierle M and Tora
L: Tip60 complex binds to active Pol II promoters and a subset of
enhancers and co-regulates the c-Myc network in mouse embryonic
stem cells. Epigenetics Chromatin. 8:452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bretones G, Delgado MD and León J: Myc and
cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:506–516. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nussenzweig MC, Schmidt EV, Shaw AC, Sinn
E, Campos-Torres J, Mathey-Prevot B, Pattengale PK and Leder P: A
human immunoglobulin gene reduces the incidence of lymphomas in
c-Myc-bearing transgenic mice. Nature. 336:446–450. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miller DM, Thomas SD, Islam A, Muench D
and Sedoris K: c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5546–5553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davis AC, Wims M, Spotts GD, Hann SR and
Bradley A: A null c-myc mutation causes lethality before 10.5 days
of gestation in homozygotes and reduced fertility in heterozygous
female mice. Genes Dev. 7:671–682. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mateyak MK, Obaya AJ and Sedivy JM: c-Myc
regulates cyclin D-Cdk4 and -Cdk6 activity but affects cell cycle
progression at multiple independent points. Mol Cell Biol.
19:4672–4683. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song A, Ye J, Zhang K, Sun L, Zhao Y and
Yu H: Lentiviral vector-mediated siRNA knockdown of c-MYC: Cell
growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase in Jijoye
cells. Biochem Genet. 51:603–617. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schorl C and Sedivy JM: Loss of
protooncogene c-Myc function impedes G1 phase progression both
before and after the restriction point. Mol Biol Cell. 14:823–835.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Felsher DW, Zetterberg A, Zhu J, Tlsty T
and Bishop JM: Overexpression of MYC causes 53-dependent G2 arrest
of normal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:10544–10548.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Vo BT, Wolf E, Kawauchi D, Gebhardt A,
Rehg JE, Finkelstein D, Walz S, Murphy BL, Youn YH, Han YG, et al:
The interaction of Myc with Miz1 defines medulloblastoma subgroup
identity. Cancer Cell. 29:5–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wolf E, Lin CY, Eilers M and Levens DL:
Taming of the beast: Shaping Myc-dependent amplification. Trends
Cell Biol. 25:241–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Smith ER, Cayrou C, Huang R, Lane WS, Côté
J and Lucchesi JC: A human protein complex homologous to the
Drosophila MSL complex is responsible for the majority of histone
H4 acetylation at lysine 16. Mol Cell Biol. 25:9175–9188. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rozenblat S, Grossman S, Bergman M,
Gottlieb H, Cohen Y and Dovrat S: Induction of G2/M arrest and
apoptosis by sesquiterpene lactones in human melanoma cell lines.
Biochem Pharmacol. 75:369–382. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wiese KE, Haikala HM, von Eyss B, Wolf E,
Esnault C, Rosenwald A, Treisman R, Klefström J and Eilers M:
Repression of SRF target genes is critical for Myc-dependent
apoptosis of epithelial cells. EMBO J. 34:1554–1571. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hoffman B and Liebermann DA: Apoptotic
signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene. 27:6462–6472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shen T and Huang S: The role of Cdc25A in
the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:631–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shah S, Schrader KA, Waanders E, Timms AE,
Vijai J, Miething C, Wechsler J, Yang J, Hayes J, Klein RJ, et al:
A recurrent germline PAX5 mutation confers susceptibility to pre-B
cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 45:1226–1231. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shou Y, Martelli ML, Gabrea A, Qi Y,
Brents LA, Roschke A, Dewald G, Kirsch IR, Bergsagel PL and Kuehl
WM: Diverse karyotypic abnormalities of the c-myc locus associated
with c-myc dysregulation and tumor progression in multiple myeloma.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:228–233. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|