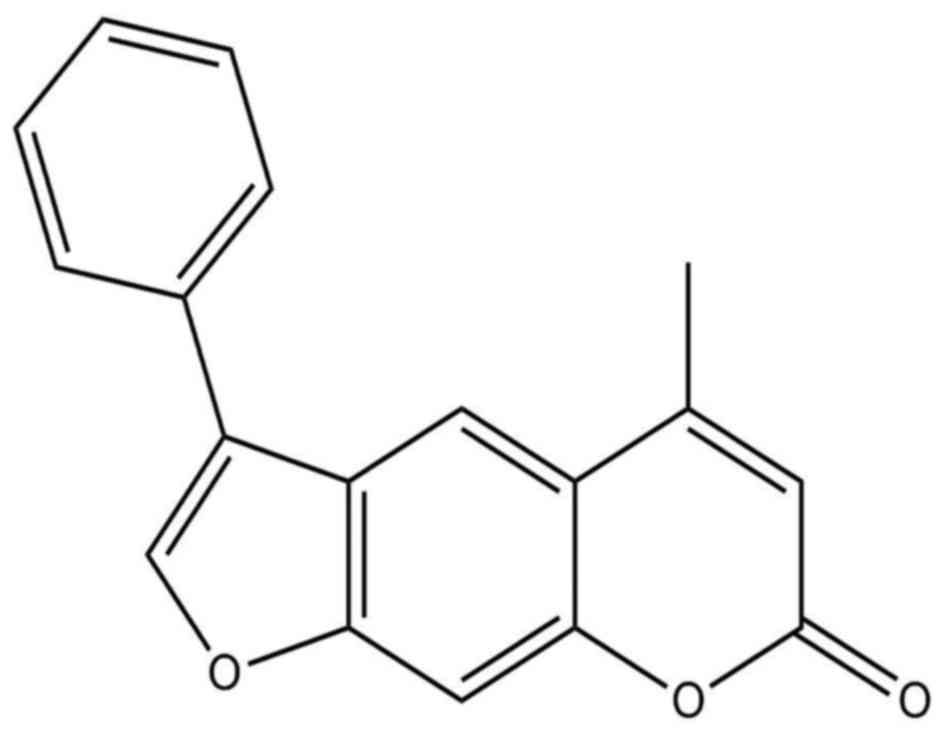
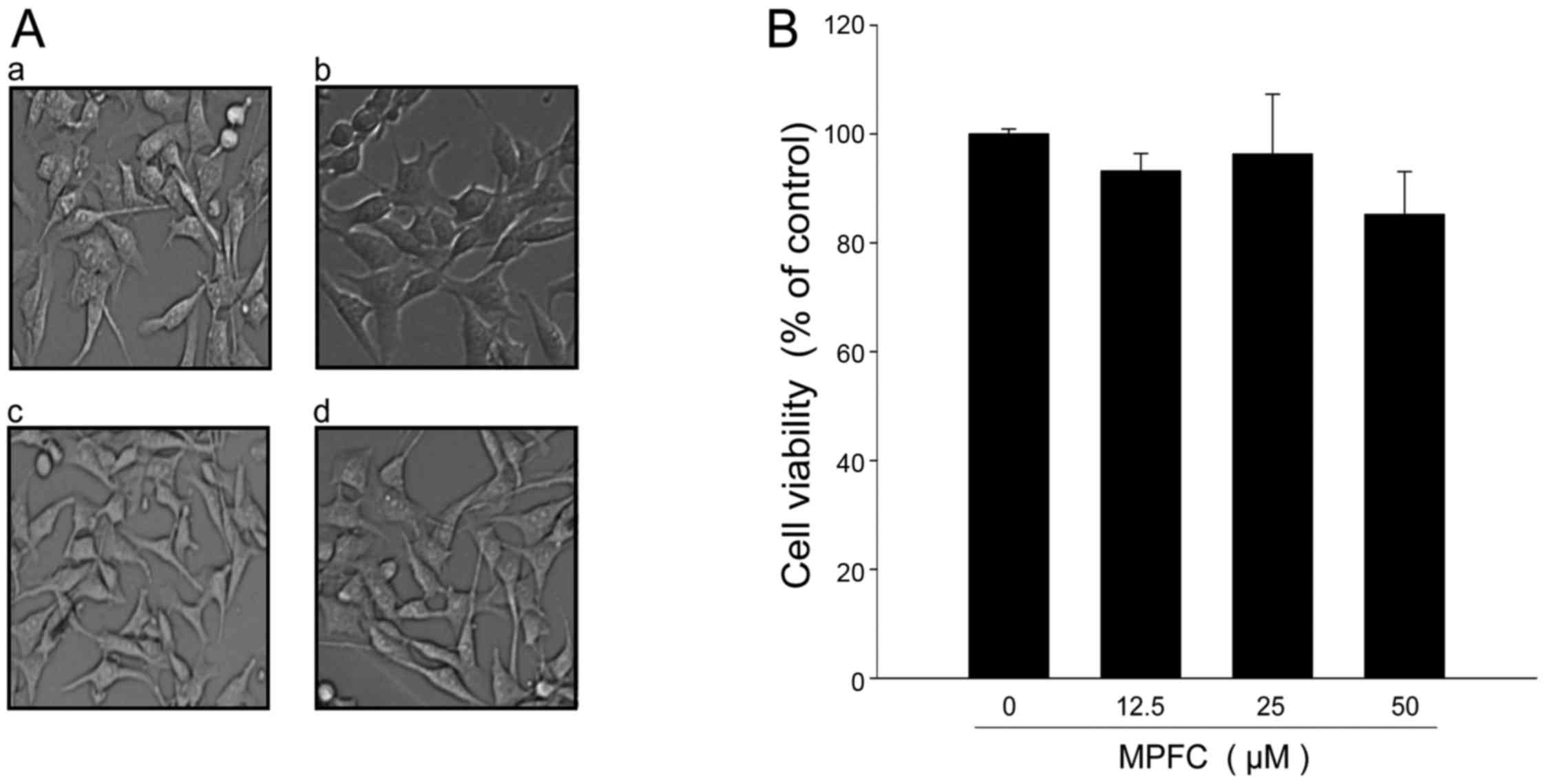
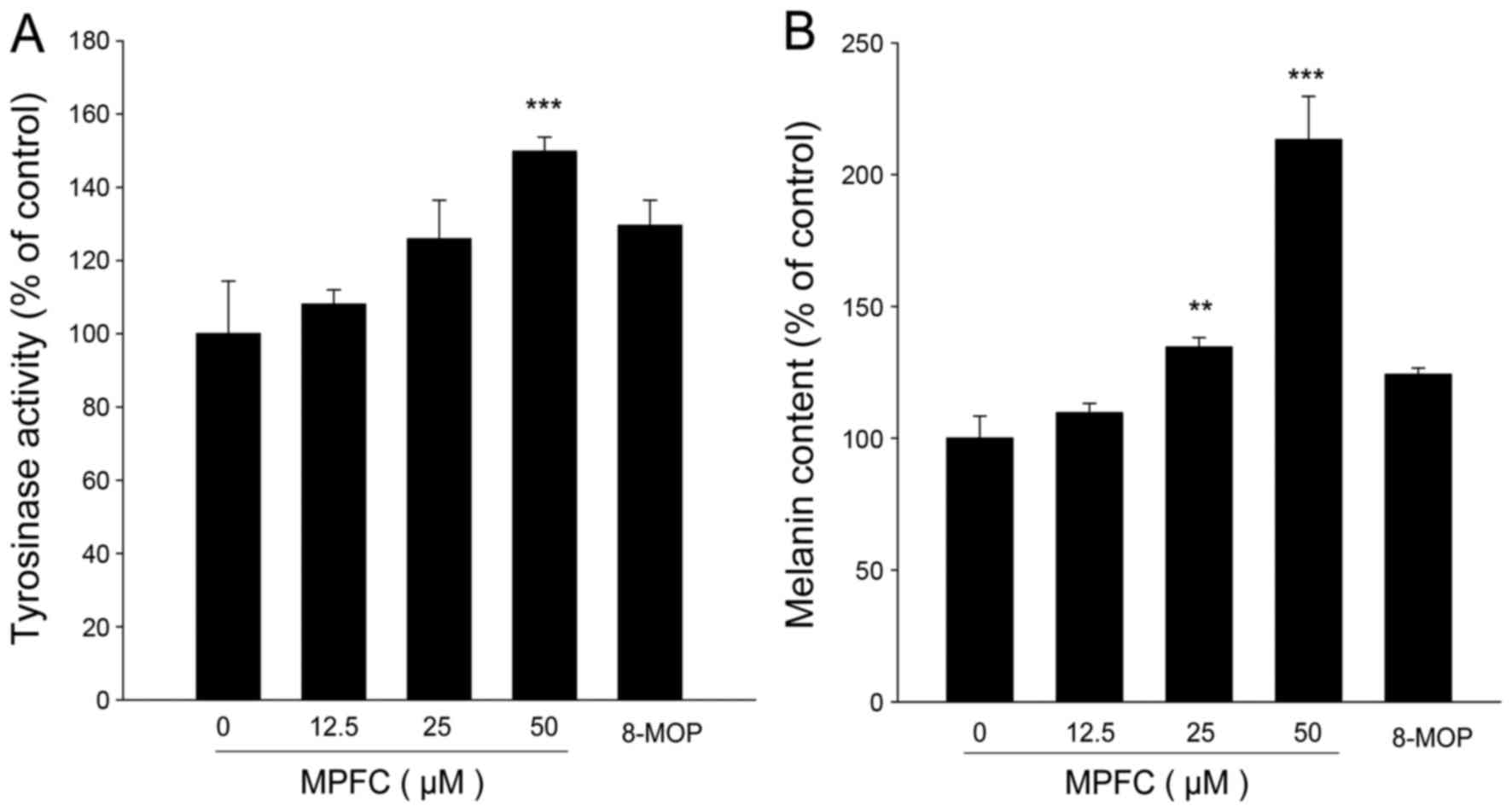
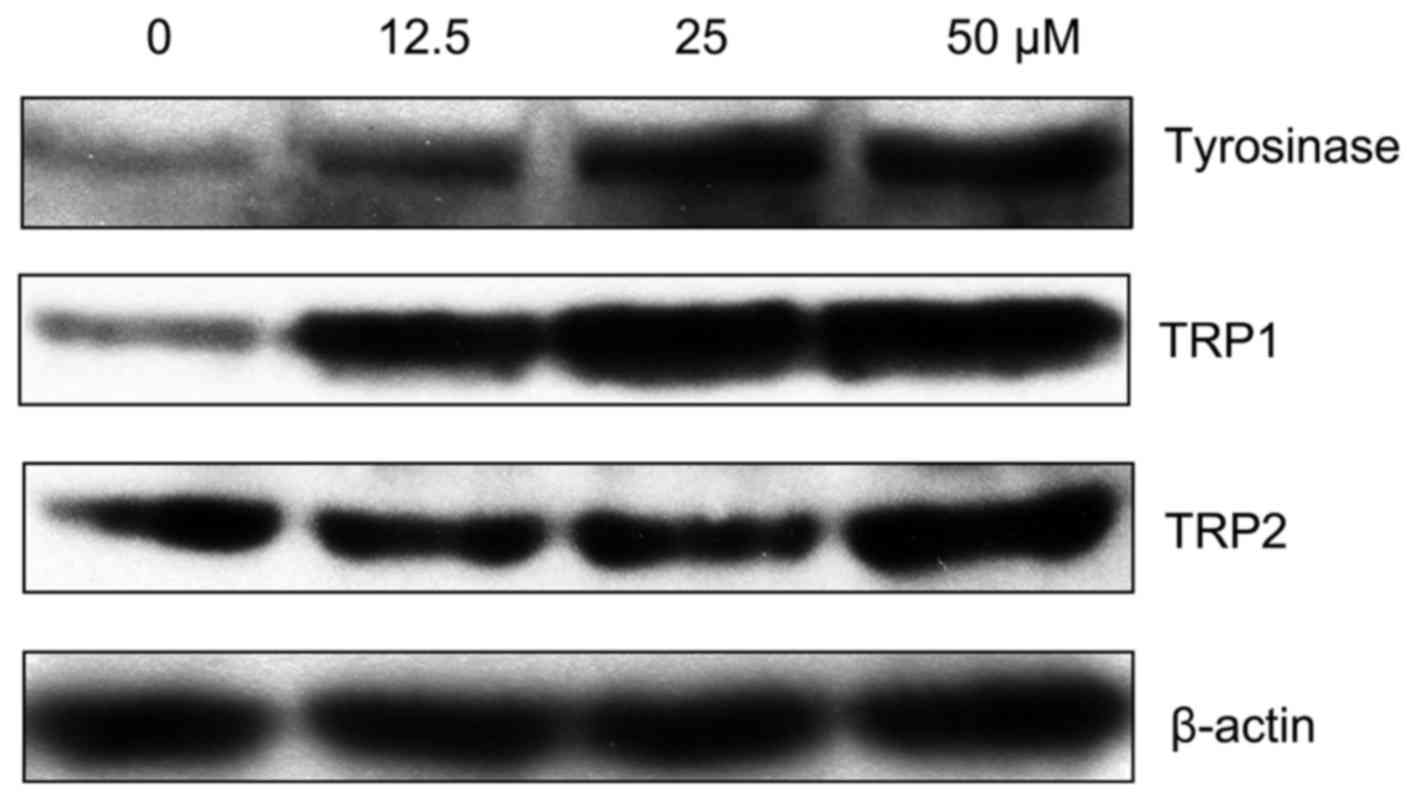
|
1
|
Donata, Kesavan M, Austin, Mohan KS,
Rajagopalan K and Kuttan R: Clinical trial of certain ayurvedic
medicines indicated in vitiligo. Anc Sci Life. 9:202–206.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lotti T, Zanardelli M and D'Erme AM:
Vitiligo: What's new in the psycho-neuro-endocrine-immune
connection and related treatments. Wien Med Wochenschr.
164:278–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M and
Petronic-Rosic V: Vitiligo: A comprehensive overview Part I.
Introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis,
differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and
work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 65:473–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Silpa-Archa Narumol, Nitayavardhana
Sunatra, Thanomkitti Kanchalit, Chularojanamontri Leena, Varothai
Supenya and Wongpraparut Chanisada: Comparison of the efficacy and
safety of 0.1% tacrolimus ointment and 0.1% mometasonefuroate cream
for adult vitiligo: A single-blinded pilot study. Dermatologica
Sinica. 34:177–179. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Park SH, Kim DS, Kim WG, Ryoo IJ, Lee DH,
Huh CH, Youn SW, Yoo ID and Park KC: Terrein: A new melanogenesis
inhibitor and its mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 61:2878–2885. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hearing VJ: Biochemical control of
melanogenesis and melanosomal organization. J Investig Dermatol
Symp Proc. 4:24–28. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Screaton RA, Conkright MD, Katoh Y, Best
JL, Canettieri G, Jeffries S, Guzman E, Niessen S, Yates JR III,
Takemori H, et al: The CREB coactivator TORC2 functions as a
calcium- and cAMP-sensitive coincidence detector. Cell. 119:61–74.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J, Shang J, Ping F and Zhao G:
Alcohol extract from Vernonia anthelmintica (L.) willd seed
enhances melanin synthesis through activation of the p38 MAPK
signaling pathway in B16F10 cells and primary melanocytes. J
Ethnopharmacol. 143:639–647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim HJ, Kim JS, Woo JT, Lee IS and Cha BY:
Hyperpigmentation mechanism of methyl 3,5-di-caffeoylquinate
through activation of p38 and MITF induction of tyrosinase. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:548–556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hemesath TJ, Price ER, Takemoto C,
Badalian T and Fisher DE: MAP kinase links the transcription factor
microphthalmia to c-Kit signalling in melanocytes. Nature.
391:298–301. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Price ER, Ding HF, Badalian T,
Bhattacharya S, Takemoto C, Yao TP, Hemesath TJ and Fisher DE:
Lineage-specific signaling in melanocytes. C-kit stimulation
recruits p300/CBP to microphthalmia. J Biol Chem. 273:17983–17986.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen T, Heo SI and Wang MH: Involvement of
the p38 MAPK and ERK signaling pathway in the anti-melanogenic
effect of methyl 3,5-dicaffeoyl quinate in B16F10 mouse melanoma
cells. Chem Biol Interact. 199:106–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
El Mofty AM: Vitiligo and Psoralens.
Pergamon Press; Oxford: pp. 1147–1195. 1968
|
|
14
|
Fitzpatrick TB, Parrish JA and Pathak MA:
Phototherapy of vitiligo (idiopatic leukodermia). Sunlight and Man:
Normal and abnormal photobiologic responses. Tokyo University
Press; Tokyo: pp. 783–791. 1974
|
|
15
|
Parrish JA, Fitzpatrick TB, Shea C and
Pathak MA: Photochemotherapy of vitiligo. Use of orally
administered psoralens and a high-intensity long-wave ultraviolet
light system. Arch Dermatol. 112:1531–1534. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jois HS, Manjunath BL and Venkatarao SJ:
Chemical examination of the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. J Indian
Chem Soc. 10:411933.
|
|
17
|
Späth E and Kainrath P: Über Bergamottin
und über die Auffindung von Limettin im Bergamottöl (XXXIV.
Mitteil. über natürliche Cumarine). Ber Dtsch Chem Ges.
70:2272–2276. 1937.In German. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Felsten LM, Alikhan A and Petronic-Rosic
V: Vitiligo: a comprehensive overview Part II: treatment options
and approach to treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 65:493–514. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tippisetty S, Goudi D, Mohammed AW and
Jahan P: Repair efficiency and PUVA therapeutic response variation
in patients with vitiligo. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:438–440. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Niu C, Pang GX, Li G, Dou J, Nie LF, Himit
H, Kabas M and Aisa HA: Synthesis and biological evaluation of
furocoumarin derivatives on melanin synthesis in murine B16 cells
for the treatment of vitiligo. Bioorg Med Chem. 24:5960–5968. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Niu C, Yin L, Nie LF, Dou J, Zhao JY, Li G
and Aisa HA: Synthesis and bioactivity of novel isoxazole chalcone
derivatives on tyrosinase and melanin synthesis in murine B16 cells
for the treatment of vitiligo. Bioorg Med Chem. 24:5440–5448. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li HR, Habasi M, Xie LZ and Aisa HA:
Effect of chlorogenic acid on melanogenesis of B16 melanoma cells.
Molecules. 19:12940–12948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tuerxuntayi A, Liu YQ, Tulake A, Kabas M,
Eblimit A and Aisa HA: Kaliziri extract upregulates tyrosinase,
TRP-1, TRP-2 and MITF expression in murine B16 melanoma cells. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 14:166–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Westerhof W and d'Ischia M: Vitiligo
puzzle: The pieces fall in place. Pigment Cell Res. 20:345–359.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Spritz RA: The genetics of generalized
vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases. Pigment Cell Res.
20:271–278. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guerra L, Dellambra E, Brescia S and
Raskovic D: Vitiligo: Pathogenetic hypotheses and targets for
current therapies. Curr Drug Metab. 11:451–467. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Taieb A, Alomar A, Böhm M, Dell'anna ML,
De Pase A, Eleftheriadou V, Ezzedine K, Gauthier Y, Gawkrodger DJ,
Jouary T, et al Vitiligo European Task Force (VETF); European
Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV); Union Europeenne des
Medecins Specialistes (UEMS): Guidelines for the management of
vitiligo: the European Dermatology Forum consensus. Br J Dermatol.
168:5–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Eun JS, Kim KS, Kim HN, Park SA, Ma TZ,
Lee KA, Kim DK, Kim HK, Kim IS, Jung YH, et al: Synthesis of
psoralen derivatives and their blocking effect of hKv1.5 channel.
Arch Pharm Res. 30:155–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grass JA, Hei DJ, Metchette K, Cimino GD,
Wiesehahn GP, Corash L and Lin L: Inactivation of leukocytes in
platelet concentrates by photochemical treatment with psoralen plus
UVA. Blood. 91:2180–2188. 1998.
|
|
30
|
Chakraborty DP, Roy S and Chakraborty AK:
Vitiligo, psoralen, and melanogenesis: Some observations and
understanding. Pigment Cell Res. 9:107–116. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanof NB: Melanin formation in
vitiliginous skin under the influence of external applications of
8-methoxypsoralen. J Invest Dermatol. 24:5–10. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lei TC, Virador V, Yasumoto K, Vieira WD,
Toyofuku K and Hearing VJ: Stimulation of melanoblast pigmentation
by 8-methoxypsoralen: The involvement of microphthalmia-associated
transcription factor, the protein kinase a signal pathway, and
proteasome-mediated degradation. J Invest Dermatol. 119:1341–1349.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park HY and Gilchrest BA: Signaling
pathways mediating melanogenesis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
45:919–930. 1999.
|
|
34
|
Bellei B, Maresca V, Flori E, Pitisci A,
Larue L and Picardo M: p38 regulates pigmentation via proteasomal
degradation of tyrosinase. J Biol Chem. 285:7288–7299. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ye Y, Chu JH, Wang H, xu H, Chou GX, Leung
AK, Fong WF and Yu ZL: Involvement of p38 MAPK signaling pathway in
the anti-melanogenic effect of San-bai-tang, a Chinese herbal
formula, in B16 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 132:533–535. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim DS, Jeong YM, Park IK, Hahn HG, Lee
HK, Kwon SB, Jeong JH, Yang SJ, Sohn UD and Park KC: A new
2-imino-1,3-thiazoline derivative, KHG22394, inhibits melanin
synthesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:180–183.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bu J, Ma PC, Chen ZQ, Zhou WQ, Fu YJ, Li
LJ and Li CR: Inhibition of MITF and tyrosinase by
paeonol-stimulated JNK/SAPK to reduction of phosphorylated CREB. Am
J Chin Med. 36:245–263. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oka M, Nagai H, Ando H, Fukunaga M,
Matsumura M, Araki K, Ogawa W, Miki T, Sakaue M, Tsukamoto K, et
al: Regulation of melanogenesis through phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-Akt pathway in human G361 melanoma cells. J Invest
Dermatol. 115:699–703. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Khaled M, Larribere L, Bille K, Aberdam E,
Ortonne JP, Ballotti R and Bertolotto C: Glycogen synthase kinase
3beta is activated by cAMP and plays an active role in the
regulation of melanogenesis. J Biol Chem. 277:33690–33697. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hirata N, Naruto S, Ohguchi K, Akao Y,
Nozawa Y, Iinuma M and Matsuda H: Mechanism of the melanogenesis
stimulation activity of (−)-cubebin in murine B16 melanoma cells.
Bioorg Med Chem. 15:4897–4902. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ganss R, Schütz G and Beermann F: The
mouse tyrosinase gene. Promoter modulation by positive and negative
regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 269:29808–29816. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|